Flies are very annoying insects. And most people obviously don't like them. In addition to the constant buzzing, they are carriers of various diseases, spreading them on their paws. Let's answer the question that worries many people: “How many legs does a fly have?”
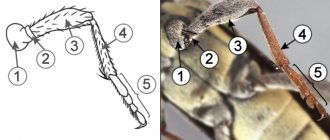
You can find information on this issue in many encyclopedias - there are exactly 6 of them. There cannot be more legs. But it is possible to encounter a fly with a smaller number, because the legs of a fly are very small and it is easy to lose them at any moment, for example, when flying away from an angry person.
Probably everyone has seen how flies land on the surface and begin to rub their legs. Why is this being done?
After research by scientists, it was found that there are small claws on each leg of the fly. Between these claws there are small hairs or even bristles. Each of them has a round micro-suction cup. It secretes fat, which ensures that the hairs adhere tightly to the surface. This surface can be anything, even smooth glass. By rubbing its limbs, the fly cleans these hairs and makes them stickier.
It is logical that fat-free paws will not be able to stick to slippery surfaces.
Interesting facts about flies
1. There are about 30,000 species of flies, inhabiting all continents except Antarctica and the Arctic.
2. On average, a fly lives about a month.
3. The offspring of one female fly is about one hundred eggs per day.
4. A fly's wings beat about 200 times per second.
5. The structure of the fly's eye is very complex; it consists of many hexagonal lenses. With their help, flies see colors and even ultraviolet light.
6. Flies transmit many diseases, including typhoid, leprosy, and anthrax.
7. Flies sense odors at long distances, up to 750 meters.
Epidemiological significance
Most flies are carriers of dangerous bacteria and infections. Insect larvae can parasitize any animal, as well as humans.
Flies can become carriers of pathogens:
- epidemic conjunctivitis;
- intestinal infections;
- other serious illnesses.
Important: Some types of flies can be deadly.
Anatomy of a fly - external structure
The general plan of the structure of dipterans, the skeleton of a fly is the same as that of other insects - head, chest, abdomen. The head contains the mouthparts, antennae, and eyes. The chest consists of three segments, with a pair of transparent wings, and three pairs of legs. The space in the chest is filled with powerful muscles. The abdomen includes most of the digestive organs and the reproductive system.
On a note!
Flies have pronounced sexual dimorphism, when the appearance and structure of the female differs from the male.
Fly head
Includes the organs of vision, nutrition, and hearing.
- Oral apparatus. Regardless of the differences in nutrition of many species of flies, their oral apparatus is represented by a proboscis of a sucking, licking type. A pair of extended blades of the upper and lower lips come into contact with food. The fly's jaws are powerful. Numerous tubules converge in the fly's proboscis, at its central point. The mouthparts of a fly that feeds on blood are additionally equipped with hard, sharp scales that serve as teeth and help pierce the skin of animals and humans. The liquid is drawn into the head using a pharyngeal pump.
- The eyes occupy most of the head. They form a complex system, which was taken as the basis for the development of a modern photo camera. They consist of many simple eyes that look like a faceted mesh from the outside. The insect receives a comprehensive but mosaic image of objects. Each eye includes several hundred or thousands of facets. The housefly has about 4 thousand of them. Many species have 3 simple eyes located on the crown of the head. This structure allows you to instantly capture movement, but does not provide a complete picture of the image.
- Mustache. A kind of antenna serves as a landmark. They help to catch odors and determine the direction of movement. In the process of evolution they changed, there are differences in males and females.
Interesting!
Males always have larger eyes than females. This allows them to react faster to movement and better assess their surroundings. Females have a more developed olfactory system, with the help of which they find a favorable environment for laying eggs.
The structure of a fly's head
Breast
Consists of three segments - prothorax, midthorax, metathorax. The bones of the fly and the main part of the muscles provide flight, so the middle part is the most developed. How many legs does a fly have? 3 pairs. Each consists of 5 parts and has its own powerful muscles. The structure of the fly's paws ends with claws and suction cups, which allow the insect to stay on a vertical, horizontal surface and even upside down. When walking, the soft pads compress and secrete a sticky secretion. This feature helps flies to hang on and move freely on window glass and smooth surfaces.
On a note!
The paws are one of the main sense organs - smell. Using its legs, the insect determines the taste of food and analyzes the quality. After a few seconds of analysis, it begins to feed or flies away.
Wings of a fly
The upper ones are well developed, transparent, membranous. The posterior pair is deformed into appendages - halteres. They maintain balance in flight, allow them to hover in the air, and also make a buzzing sound. Thin wings are reinforced with cylindrical veins.
Interesting!
During the flight, an insect can turn off one or the other wing, abruptly change its trajectory, perform complex maneuvers, and take off without preliminary acceleration. The structure and abilities of the insect were taken as the basis for many flying structures in airplanes and helicopters.
Abdomen
It has a cylindrical shape, elongated, consists of 10 segments, includes the organs of the fly responsible for reproduction, respiration, nutrition and other important functions. The elastic chitinous cover expands as food arrives during pregnancy. Therefore, the weight of the fly varies depending on these conditions.
Interesting!
An ordinary housefly or housefly weighs 12 mg; during pregnancy, the weight increases to 15 mg. Your weight can increase to the same level after a meal. The male is smaller, weighing about 12 mg. One gram contains about 80 of these insects.
The face of a fly can be easily seen under a microscope, but even when carefully examined with the naked eye, one can see an elongated mouthparts and large eyes of green, red, yellow, brown, and blue. The ears of a fly are located on different parts of the body and help to detect air vibrations and ultrasound.
Structure of a fly
general information
A fly is an insect of the order Diptera, a type of arthropod. Some of them are eaten by other animals (birds, frogs, predatory insects). Others are predators themselves and regulate the numbers of numerous insects.
And also among them there are parasites (bloodsuckers) of animals or humans.
They can hover in the air, fly backwards, or fly upside down. Their reaction is 10 times greater than that of humans. Some species have viviparity, although most individuals are characterized by oviparity.
The size of an adult housefly reaches 0.6-0.8 cm. The weight of flies ranges from 0.12 g to 32 g (African fly). They live on all continents, except in Antarctica.
Life cycle of a fly
Many people wonder how long a fly lives; does it really fly only for one season? And where does it disappear then? In fact, the average lifespan of a fly is between 1 and 2.5 months. How long flies live in an apartment depends on the degree of favorable conditions for their existence, temperature conditions, humidity levels and other factors. Typically, the temperature in the room is about 25 degrees, which is optimal for an insect such as a housefly. The homeland of this representative is the central part of Asia, but following people they have spread everywhere. Of particular interest is the memory of an ordinary fly.
You enter the room and see a bed. On the bed there are two dogs, four cats, a giraffe, five cows and a duck. There are also three chickens flying over the bed. The answer is not six, it's four. The question is how many feet are on the floor. Because the bed has only one leg and has four legs to support the bed, and the person who entered the room was on their feet when they entered, not on their feet.
How are flies born?
He asks how many feet are there on the floor? You do not walk on your feet, but on your feet, so that your feet are not on the floor. So the answer is 4 from the bed. The person touches the floor with his feet so it's not right, it's 4 off the bed and that's it. The bed could actually just be a mattress, in which case there are no feet on the floor. The bed could have a frame with two legs, in which case there would be Or maybe 4 legs from the bed. Their feet do not lie on the floor, their feet lie on the floor.
Peculiarities of fly reproduction
We have looked at how long a fly lives; it remains to consider the reproductive characteristics of these individuals. A female can lay about 100 white eggs at a time, having a length of only 1.2 mm. During the life cycle, females lay eggs 6 times on average. If conditions are favorable, reproduction occurs in winter. It takes up to 50 hours for an egg to develop. The larvae reach a length of 13 mm and are white in color. They live in fecal matter. After three molts, the flies turn into pupae. 36 hours after emerging from the pupal state, individuals are considered adults and can reproduce. The cycle of life is short.
Anatomically speaking, we stand on our feet. Beds do not have legs, but posts or even legs. If we focus on the organics of the matter, we are denying the fact that a bed can only have a wooden frame such as the "Platform" style. The mystery was not well constructed and left the path open to too many plot holes.
You can't count when your feet are on the floor and not your feet. Since beds can have different numbers of legs depending on design and size, you must use the most logical theory to get one answer, so a bed should not have legs to get one answer.
Wintering flies
Many people are interested in the question of where flies spend the winter. It turns out that over a one-year period, a room can change from 9 generations of insects, and pupae and adults go into hibernation for the winter, and fertilized females can also overwinter. During cold times - winter - flies are in cold rooms and are inactive. It turns out that they have to die for a while in order to live out their cycle for the next year when the warmth arrives. The insect can be revived only during warming. It is necessary that the outside air warms up to 10 degrees.
There is nothing to indicate that you are the only observer, or that you entered the room through the floor rather than a raised platform. There's nothing that says "you have" legs at all - even double amputees can walk, although not necessarily on their legs. There's nothing that says you're in the same room as the bed - so what floor, including others in adjacent rooms? It's hard to define "legs" - of course, beds and other pieces of furniture can have legs. Needless to say, some animals do not have one or more legs hanging from the bed onto the floor.
What to do if you are bitten by a scolopendra
But if you do get bitten by a scolopendra, be prepared for the following consequences (we’ll warn you right away, not fatal). The bites can be very painful and go away slowly over 1-2 days. The main symptoms that you may experience: at the very moment of the bite there will be a sharp and prolonged pain; the severity of the pain can vary (from slight to “10” on a 10-point pain scale); body temperature may increase; you may feel severe weakness; Most likely, the sensitivity of the skin in the bite area will significantly increase, swelling and redness will appear, and loss of sensitivity and a feeling of numbness may also occur.
Scolopendras are somewhat similar to wasps, which do not leave a sting in the wound and can sting a person several times in a row. Often, at the moment of detection by a person, this creature continues to inflict multiple punctures, introducing even more poison. Centipedes usually bite when a person is resting in bed, but they can also crawl into clothes and bite the moment you start getting dressed.
But there is good news: scolopendra bites are not fatal! For a person to die from its poison, he must be bitten by several thousand individuals at the same time!
Helpful advice: if you are bitten by a scolopendra, find a heating pad at home, fill it with moderately hot water (up to 45 degrees C) and apply it to the bite site - this simple measure should bring relief. Scientists have not yet found an explanation for this phenomenon, but they suspect that this is possible due to the fact that some components of scolopendra venom are unstable to heat. The second remedy is ice and analgesics.
Are centipedes dangerous for your home?
And you don’t have to worry about clothes, paper documents, furniture and other items. A centipede is not a moth or a silverfish. She is not at all interested in your things. Another thing is that some centipedes can spoil the air in the house due to the fact that they secrete a bad-smelling secretion - but this is unlikely - there must be too many of these arthropods in your house for you to smell it. In addition, since centipedes are plant scavengers, they may become interested in rotting wood. We advise you to check attics and basements more often for moisture and for such “yummy things.”
We hope we didn't intimidate you. Therefore, at the end, in order to “whiten up” our heroes a little, let’s tell you how centipedes are useful. They are very active in destroying pests. Their diet includes bedbugs, flies, cockroaches, termites and even spiders. So sometimes centipedes turn into real “guardians of housing” from even more harmful creatures. Therefore, if you are not afraid of such many-legged neighbors, then live with them “in peace and harmony.”
Classification of flies
There are 40 thousand species of flies in the world, which can be divided into three large groups:
- settlement: live in close proximity to humans, are not able to survive in the wild; house flies;
- semi-settlement (facultative-settlement): can live both near humans and in the wild; blow flies;
- grazing: live in livestock droppings on pastures, fly into populated areas; dung flies;
Gray blowflies are corpse lovers
Flies are also divided into those that feed:
- fruits and berries: melon and garden;
- vegetables: lily, cabbage, garlic, cucumber, sprouts;
- flowers: peony;
- blood of animals and people: black (April), tsetse fly;
- rot and carrion: green, domestic, dung, gray meat;
- other insect pests: hoverflies, blackbirds;
Garden flies damage the harvest of fruits and berries
Flies live next to us, but can everyone tell how many legs they have?
How many legs does a housefly have? Can everyone immediately answer such a simple question? For most people, all small, buzzing, flying or crawling creatures are disdainful. Where can one be observant and count the number of legs? And that's the best case scenario. And at worst, they drive you into panic . On the other hand, what kind of panic can there be at the sight of such an object as familiar to us all as a fly? Yes, it can seriously ruin your mood on vacation, especially in August. Yes, she can interrupt her Sunday morning nap. But it's just an insect.
What types of flies are most common?
The world of flies is diverse, which, in addition to the structure of the body and life cycle, have one common property - intrusiveness. Whatever the insect is: dangerous or relatively harmless to humans, it will be very difficult to get rid of it. What attracts flies to us? These creatures have a well-developed sense of smell, they are attracted to various sweet and not so sweet aromas (but the most pleasant smell for most of them is the aroma of rot), to which they fly. We prepare a lot of dishes with all sorts of tastes and smells - these are the things that attract these insects so much that they force them to travel quite large distances compared to their size and fly into our homes.
The alluring aroma overrides everything for flies, sometimes even the instinct of self-preservation, so many people, when asked “How many species of flies do you think there are?” They answer: “one is annoying.”
house fly
The housefly (or housefly) lives exclusively in close proximity to a person’s home, where there is a lot of food and quickly rotting household waste. It is impossible for this type of insect to exist away from people, so in the warm season they are nearby all the time: they live in our kitchens, where food and waste are stored, they fly in through open windows to stay for several hours, and it is quite difficult to drive them out.
House flies are considered the most annoying
House flies do not have a piercing-sucking mouthpart, so they cannot bite a person, but this does not make them completely harmless. These insects have three pairs of limbs, each with small suction tentacles, to which various bacteria and microorganisms stick, and then they are transferred by flies to food. Creatures of this species are completely unremarkable: they have a gray-brown body with nondescript wings, but very bright red eyes. They occupy almost the entire head, the lower part of which is yellowish and the upper part is sand-colored. The head has antennae and an oral cavity.
House flies have huge red eyes
Flies have two pairs of wings: the first is used for flight, the second (called halteres) is used to maintain balance. It is the halteres that make the sound that we call buzzing.
House flies are diurnal insects that fall asleep after dark and wake up when the sun has already risen. They are active only in the warm season; in the fall, with the onset of the first cold weather, they hibernate.
On average, houseflies live 3–4 months. First, the adult female lays eggs (about a hundred in one clutch), from which a larva emerges after 8–50 hours (depending on the climate). This is a small worm up to 13 mm long that lives in animal feces and household waste. The larva moults approximately once a week; after the third, the outer shell of the worm hardens, falls off, and the creature turns into a pupa. After 3 days, an adult is born, which becomes sexually mature after 36 hours. Over its relatively long life, one fly can lay up to 10 thousand eggs.
The fly larva looks like a small chopped off worm
These insects eat the same food as humans, but prefer liquid or semi-liquid food because they are unable to bite. To eat solid foods, flies secrete saliva, which is capable of dissolving substances of varying hardness.
The housefly can be found throughout Russia, but the closer to the south, the milder and warmer the climate and the more abundant this insect is. It is very difficult to fight him, but it is possible. The most effective are ordinary insect nets, which can be placed in window and door openings, and sticky tapes, which have a certain kind of smell that attracts flies - they sit on the tape, stick and cannot fly away. It is not recommended to use fumigators and various chemical baits, especially if there are pregnant women, children or pets in the house, since these products release harmful substances into the air.
The adhesive tape needs to be changed every 2-3 months or as it becomes full of flies.
Hoverfly
Hoverflies (or syrphids) are very similar in appearance to wasps. Even the behavior of these insects is identical: syrphids can freeze in place during flight, continuing to flap their wings, but they are completely harmless to humans - they do not bite like wasps.
Hover flies get their name from the sound that is produced when their wings work - it is very similar to the murmur of water.
Hoverflies are found mainly in fields, orchards and vegetable gardens, where there are many umbelliferous and compound-flowering plants. Like all insects, they are most active during the daytime during warm seasons, and hibernate in the winter.
Hoverflies are harmless creatures
Hover flies have a small body covered with alternating black and yellow stripes. They have only one pair of transparent wings and huge brown eyes. Hoverflies have a long proboscis, which they use to obtain nectar; They do not bite either people or animals.
The wasp's body is more segmented
Syrphids feed mainly on plant nectar, but they can also feast on aphids, eggs of various insects and spider mites. They are not attracted to human food at all.
Wasp flies lay 150–200 eggs at a time; The laying is done mainly in the habitats of aphids, which are very convenient for the larvae to hunt. They appear 2–4 days after the eggs are laid and look like small worms chopped off at the back. The larvae feed on their own, becoming more and more voracious every day; Thus, in 2–3 weeks of their life they are able to eat more than 2 thousand aphids. Then the larvae turn into pupae, from which an adult emerges after 7–10 days.
Hoverfly larvae are very lazy, but their hunt for aphids looks quite interesting: as soon as the victim is noticed, the worm rises, begins to sway from side to side and after a few moments very quickly pounces on the prey, instantly devouring it. To get more food, you need to move. To do this, the larva “rolls” the mass of its body from one end to the other, thus moving in space.
Aphids parasitize plants
Hoverflies do not live long: on average, 1–1.5 months, but even in such a short life they bring a lot of benefits to the garden, eating a variety of insects. Many summer residents create favorable conditions for the life of hoverflies so that they settle on their territory and save them from pests. There is no need to get rid of syrphids.
Green fly
The green (or carrion) fly is rightfully considered one of the most beautiful insects: it has a neat glossy body of emerald color, large brown eyes that go well with a pair of smoky wings. All its legs have tentacles to which bacteria and microorganisms stick, which this fly carries over long distances.
The green fly has an incredibly beautiful color
It is a pity that such a beautiful creature feeds on carrion and rot, so it must be driven away and even destroyed, and not admired as one would like. The carrion fly lives on animal carcasses, in household waste and in feces, but is sometimes found on flowers with a very strong sweet smell.
Green flies are also found on flowers with a pronounced sweet aroma
Green flies lay up to 180 eggs in the same place where they feed - in rotten food and bodies. Females try to hide their eggs as deep as possible so that when the larva is born (and this happens after 6–48 hours), it has a lot of food. Flies remain at the larval stage for 3 to 9 days, after which they crawl into the soil, where they turn into pupae. After another 10–17 days, an adult fly appears and climbs to the surface.
Green flies live 2–2.5 months (if you count from laying eggs); during the winter they hibernate in the foliage and bark of trees.
You should not allow carrion flies to appear in your home, as they will carry on their paws a huge amount of bacteria from corpses and feces, which will at a minimum cause poisoning and intestinal diseases. The most effective means against these flies are insect nets and ordinary adhesive tapes, which have a pleasant smell for flies. If you don't have pets at home, you can buy a flytrap plant.
The flycatcher is a very beautiful plant that feeds on the blood of insects
Beetle fly
Honeybee moths belong to the hoverfly family, but they look like bees rather than wasps. They have a rather large body - on average, 1.5 cm in length, the abdomen is quite “plump”, which is why these flies resemble bees. The body is brown in color with large reddish-yellow spots on the sides. Unlike other flies, the flies are covered with very small hairs - even the eyes and limbs have hair.
Another name for the bee-bearing silage is the tenacious silice.
Beekeepers live near plants with strong-smelling flowers, the nectar of which they feed on. Adults are absolutely harmless to both people and insects, so there is no point in specially breeding them, and there is also no reason to destroy them.
Illices lay their eggs in various sewage, so the entry of eggs or larvae into the human body (for example, from unwashed hands or food) can lead to infection with intestinal diseases (for example, enteritis).
The larva is born 18–48 hours after laying eggs, the length of its body reaches two centimeters, but the special breathing tube with which the worm breathes can stretch as much as 10 cm. This is due to the fact that the larvae live in sewage, and You should breathe only clean air.
The flies are most active from July to October; in cold weather, these flies hibernate.
The bee has a hairier and more segmented body
Since only eggs and larvae of bee flies can cause harm to humans, wash your hands thoroughly after coming from the street, rinse food and make sure that rotting household waste does not accumulate at home, where the bee fly could lay its eggs.
Ktyr
Ktyri are large predatory flies that destroy other insects: mosquitoes, midges, beetles and even bees. They feed exclusively on flying organisms and do not harm either humans or their crops, so they should not be scared away or even destroyed - although they are ugly to look at, they are good helpers in the fight against pests and blood-sucking insects.
Ktyr can fight even a hornet
These flies really don’t look very attractive: a small dark brown body completely covered with hairs, huge brown eyes, a sting with poison that they inject into their prey. The limbs, incredibly long compared to the body, are also covered with hairs. It is with them that the ktyrs catch their prey in the air. Long, powerful dark brown wings with small light stripes help keep themselves and their prey in flight.
Chtyrs lay their eggs in various rotting matter: wood, soil, and so on. As soon as the larvae emerge from the eggs, they immediately begin to destroy small insects that are nearby. Often one larva becomes a victim of another (and the adult can eat its own kind).
Ktyrs, like all flies, live 2–2.5 months and are active in the warm season. They are found in cities, in gardens, and far from people.
Tsetse fly
The tsetse fly is the most dangerous fly on the entire planet Earth, which, fortunately, lives in Africa. She is a carrier of the so-called sleeping sickness, from which you can die if timely medical care is not provided. This fly feeds exclusively on the blood of animals and people.
Bernhard Grzimek (zoologist and conservationist) in his book “No Place for Wild Animals” said that it was thanks to the tsetse fly that the habitats of large wild animals, practically untouched by humans, were preserved in equatorial Africa.
The female gives birth to larvae, which immediately become pupae, in a dark place, closer to the soil. This is where the pupae will develop over several days until they develop into adults.
The tsetse fly is very beautiful, although the color of its back is unremarkable - gray
Tsetse flies are unusually beautiful: the insect's chest is reddish-gray, covered with longitudinal dark brown stripes, a yellow-gray abdomen, a gray back with a black-milky pattern, a long branched proboscis, transparent powerful wings, which the insect folds one on top of the other and on which is clearly visible coffee-colored drawing. But do not be fascinated by this creature - they are dangerous for humans.
The wings of the tsetse fly have an unusual hatchet pattern.
If you travel to Africa, be sure to get vaccinated against sleeping sickness.
We are surrounded by countless different insects: some of them harm humans, some, on the contrary, help with various pests and save the harvest. You need to be able to distinguish friends among all insects and not kill them, but create favorable conditions for their life. Chemicals, of course, are better at destroying various insects, including aphids, but they are not as safe for humans as, for example, hoverflies. Use the helpers that nature itself gives you
How to fight: effective methods
How to get rid of flies in an apartment? The main thing is to remove factors that attract harmful insects. Most owners themselves provoke the entry of flies into the apartment, attracting them with an abundance of freely available food and unsanitary conditions. Basic home protection measures in the form of a mosquito net sharply reduce the number of annoying “neighbors.”
Five steps for successful fly control:
- keep the kitchen and other rooms clean, put food in the refrigerator;
- take out the trash can on time;
- block entry routes: windows, ventilation grilles;
- bring indoor humidity to normal levels;
- get rid of junk, wash windows, provide access to sunlight.
After eliminating the reasons that allow buzzing pests to freely rule the apartment, it’s time to think about effective methods for killing flies. The best option is an integrated approach.
Sticky traps
Adhesive tape with a special composition is a simple, effective means for catching flies and mosquitoes. Hang sticky traps in the kitchen, in areas where insects are most concentrated. The appearance of ribbons dotted with flies is unattractive, but ready-made traps work flawlessly: the insects stick tightly to the surface, the owners can only remove and throw away the tape along with the pests.
Insecticides
Treating areas where flies accumulate with insecticides gives excellent results. After disinfestation, collect dead pests and think about how to prevent the reappearance of unnecessary “neighbors.”
Effective drugs:
- aerosols. Raptor, Dichlorvos Neo, Clean House, Raid, ARGUS, Off, MOSQUITAL;
- granules and powders. Clean house dust, Bayt Mukha, Baygon;
- crayons. Cockroach crayons, for example Mashenka, are effective against winged pests.
Important! When disinfesting premises, safety measures are required: a respirator, old thick overalls, medical gloves, plastic goggles to protect the eyes. It is forbidden to smoke, drink, or eat during treatment with insecticides.
After spraying the aerosols and working solution, close the apartment and leave for a certain time. Upon return, ventilate the room and wash surfaces with soap.
Homemade baits
How to make:
- method number 1. Combine sugar (100 g) and any sweet syrup - a quarter cup. Cut strips of thick paper, make a hole, secure with a strong thread. Grease the cardboard with thick sugar and wait until the trap dries. Use as prepared adhesive tape;
- method No. 2. Pour 250 ml of apple cider vinegar into a 0.5 liter jar, stretch the film on top, make several small holes so that insects can get inside. Instead of film, a plastic or tin lid is suitable. Harmful insects are attracted to the smell of vinegar and will certainly get inside. Place a trap jar in the kitchen.
Bright aromas
Pungent odors that repel harmful insects will help drive annoying “neighbors” out of your home. A safe method without the use of toxic drugs is suitable if there are children and pets at home, but flies have settled in the apartment. How to effectively combat buzzing pests using aromatic ingredients?
It's simple:
- first way. Dry the peels removed from oranges, tangerines or lemons and place them on the table or in kitchen cabinets. The smell of citrus fruits repels not only flies, but also moths;
- second way. Cut a lemon or orange in half, insert clove buds (spice), and place the aromatic composition on the kitchen table. After a while, the buzzing will stop and the insects will leave the room;
- third way. Place bouquets of aromatic herbs in the kitchen and other rooms where flies live. Many insects cannot tolerate the smell of wormwood, lavender, mint, bay leaf, and thyme. Richly scented basil and eucalyptus also repel winged pests. Every two to three months, new bouquets should appear in place of the old ones, then the bright smell of plant components will be most effective;
- fourth way. Onion juice is good at repelling insects. A product that brings tears to the owners is suitable as a last resort if other aromas do not work. Grind several onions with a blender, squeeze out the juice, pour into saucers, place containers in areas where houseflies crawl. A sharp, unpleasant smell quickly drives insects out of the apartment, provided that the factors that attract pests are eliminated;
- fifth way. Pour 2 liters of warm water into a bowl, add 10 drops of lavender essential oil, wipe the windows, kitchen table, cabinet doors, and other surfaces in the kitchen with the solution. The aroma of lavender repels various flying and crawling insects.
Respiratory and digestive organs
The structure of the respiratory system is very different from the human one. You can explain how a fly breathes as follows. The fly has no blood. She inhales air through holes located on the sides between the head and the rear end of the body. Each “nostril” turns into a tube that forms a network of air inside the body. Such air vessels supply oxygen to all other organs, i.e., the heart of a fly is the same thin tube that periodically contracts and pushes air inside.
The digestive system of these insects is even more interesting. Their main diet consists of human food remains and organic matter. The fly's mouth secretes saliva, which contains specific enzymes that can dissolve tissues and solids. First, with the help of a proboscis, the fly injects saliva into the food it finds and waits for its action. After the food turns into liquid, the insect begins to lick it with its mouth. After saturation, the insect begins to defecate frequently - almost every 5-15 minutes. She regurgitates the digested contents of the stomach, leaving small black discharge on various objects, dishes and food.
Nutrition
Adults feed on a variety of solid and liquid substances of plant and animal origin. The housefly's mouthparts lick and suck; flies cannot bite skin or drink blood, unlike the similar autumn flies (Stomoxys calcitrans). Flies can only consume liquid food; To consume solid food, they first dissolve it in saliva. The housefly is a polyphagous species. For the eggs to mature, the female needs protein food. Flies have chemoreceptors on their leg limbs, which the insects can use to identify food, such as sugar, as it passes through them. Housefly larvae have an excellent appetite, especially for meat. Tirelessly and devastatingly, they eat both the larvae of harmful insects and the carrion they encounter.
Reproductive system
The genital organs are located in the abdomen. In males they are represented by testes, in females - by eggs, accessory glands and ducts. The structure of males is distinguished by the presence of special “grabs”. To raise offspring, each female lays from 70 to 150 eggs. Some species are viviparous (meat and cadaverous).
Interesting!
The penises of male flies were studied by Charles Darwin, who was amazed at their complex structure and the presence of growths and hooks. Modern scientists have found that their genitals have the ability to twist up to 180°, and some types of flies can rotate it up to 360°. This is necessary for ease of mating, so as not to turn upside down.
Reproduction
There are several species that reproduce by viviparous fruits. But most of them are those that lay larvae. Flies eggs can be laid 2-3 days after mating.
And in one clutch you can count about 150 eggs. Over the course of its entire life, this number per fly can reach up to 3 thousand.
In a day, worms will appear, then within a week their number will increase 800 times. And a new life is ready.
Flies are dangerous because they themselves are carriers of dangerous diseases.
The role of the limbs
It should be noted that a fly needs legs not only to rest between flights or to walk. Amazing fact: each limb of this insect is equipped with taste buds! As soon as a fly lands on a particular object, it immediately determines the degree of its edibility.
Attention! In addition to taste, flies also have tactile receptors on their legs. The limbs perform several important functions at once, so flies carefully monitor their cleanliness.
How do flies wash themselves?
Flies do not wash themselves in the usual sense of the word. They clean their legs and wings frequently and thoroughly. Despite the fact that flies are carriers of many diseases and are considered one of the “dirtiest” creatures, they strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Why do flies rub their legs?
Anyone who has ever observed the behavior of flies has noticed how often and diligently they rub their legs against each other. The fact is that while walking, the surface of the bristles becomes dirty. Small dust particles and other debris prevent full contact of the paws with the surface.
When a fly rubs its legs, it not only cleans them, but also stimulates the secretion of a sticky secretion. Thus, this simple action provides the insect with freedom of movement.
Carriers of infections
However, it is a carrier of many infectious and far from harmless diseases. And if she, a fly, lands on the ceiling, there is no harm. But if it's food that you didn't wash after the visit of an uninvited guest, that's a completely different story.
- Firstly, if you swallow its eggs, you can become infected with entomosis, a disease caused by fly larvae.
- Secondly, it spreads the causative agents of many diseases by carrying them on its paws.
Article on the topic: How to care for a water newt
How many are there? Each individual has as many as 3 pairs, that is, 6 pieces, on each of which, with the help of a magnifying glass, you can see small claws, and between them, in turn, there are small hairs or even rather bristles. Thus, there is scope for microorganisms to “choose” a temporary shelter , which will serve as a convenient transport for settling in our space. An insect, flying from place to place, will leave a trail of its “passengers”.
Why don't they fall from the ceiling?
As for the fly itself, on each leg it has round micro-suction cups that secrete an adhesive substance, which actually ensures that the bristle hairs stick to any surface, even smooth glass, not to mention the ceiling. A significant role here is played by the ability of the claws to cling to uneven surfaces.
How many legs are involved in locomotion? Almost everything. This is, in fact, why it does not fall either from a vertically located window glass or from the ceiling. All thanks to the unique 6 legs, each consisting of five joints. Moreover, the hind legs are larger than the rest.
How do flies wash themselves?
Observant and, importantly, calm people (that is, those who are not driven into panic or irritation by flies) have probably noticed that very often flies rub their paws against each other for a long time , and also “rub” their eyes with them.
Why are they doing this? By rubbing their legs together, the fly cleans out its sticky suckers, which collect dust and dirt when the insect walks on the ceiling, on your food and other surfaces, or even bits of skin when it crawls over a person. Therefore, you need to clean them all the time so as not to disturb the possibility of strong adhesion to the surface and to be able to move on any surface in any plane of space. It is also very important to remove everything in sight.
Article on the topic: How long does a pregnant elephant walk and how does pregnancy occur?
What other role do the paws play in the life of an insect?
We have already counted how many paws our “tenants” have. And they even understood their significance. But that is not all. Insect legs are also an opportunity to taste. Yes, yes, they first feel the taste of food with the help of their legs, and only then with their proboscis and lobes of the oral apparatus.
Analyzing how tasty certain foods are is hundreds of times better than a person can do using the tongue. At the end of the legs there are special bristles, which act as taste buds, as well as organs of touch.
The body of flies is also covered with small hairs. It contains sections such as the abdomen, chest and head. On the insect's head there are small antennae that replace their sense of smell. As organs of touch, like other insects, they are not used in flies. The ability to identify food by smell allows flies to quickly find places where it accumulates. This explains why flies are so fast. In addition to moving with the help of their legs , as is known, flies are also capable of flying very well and quickly, reaching speeds of more than 20 km/h.
Those who are frightened by information about flies as carriers of infections should know that various preventive and exterminatory measures will help protect the premises from uninvited guests from the world of hexapods:
- it is necessary to promptly remove all impurities that serve as food for flies;
- use insecticides to prevent their proliferation,
- In the arsenal of fighting unwanted insects, including flies, there are various Velcro and tapes.
“Why not exterminate all flies once and for all?” - the especially irritable and impressionable will ask. Such people need to understand that there are no unnecessary links in the natural food chain. Fly larvae, eating all sorts of things, including carrion and waste, clean the environment. And how many insectivorous animals and birds, as well as other insects, can serve as food themselves. So these small annoying creatures only bring colossal harm to humans, but in general they are a necessary link in nature. Is this why there is such diversity - more than 30,000 species of these insects, inhabiting all continents, except Antarctica and the Arctic.
Article on the topic: What do hippopotamuses eat in nature, what does a hippopotamus eat?
The average lifespan of a fly is about two months. The offspring of one female reaches about a hundred eggs per day. Approximately 40 hours after hatching from the pupal state, individuals are considered adults (imago) and can reproduce. So it turns out that in a year in a room, if sanitary standards are not observed, up to 10 generations of these insects can change.
Brain structure
When thinking about the brain, many people see a picture of a round substance with convolutions pop up before their eyes. With a fly things are different. The Diptera brain consists of 3 sections, namely:
- tritocerebrum;
- protocerebrum;
- deutocerebrum.
Despite its fairly simple structure, the brain is responsible for the functioning of the entire body. At the same time, the fly is not able to think. She acts instinctively.
Important: in the body there are nerve nodes called ganglia, which connect to the “brain”.
Protocerebrum
This is the largest part of the brain, responsible for coordinating any life process of an insect. This part of the “control center” contains a huge number of neurons. They are responsible for analyzing and processing the information received.
Due to the arrangement of cells in the outer layer and the fibers leading to them, the fly’s brain can be compared to the control organ of a human or animal.
Inside the protocerebrum there are additional sections. Which are divided into:
- central body;
- intercerebral part;
- protocerebral lobes;
- protocerebral pons;
- ventral bodies;
- optic lobes;
- stalked bodies.
Deutocerebrum
The section is located in front of the tritocerebrum. Responsible for the nerve endings going to the antennae. "Antennae", the only fibers extending from the secondary brain. In most cases, they begin with roots:
- sensory;
- motor.
In some species of flies these roots are not observed.
Deutocerebrum differs from protocerebrum in its simplicity. The structure diagram corresponds to a normal ganglion. This can only be explained by the fact that this section is the nerve center of only one segment - the mustache.
Harm to animals
The danger of moose fly for animals
Hunters counted up to 300 individuals on the body of one deer. The pest is able to stick tightly to the fur and cannot be torn off even with teeth.
- The bite of an elk fly causes pain, discomfort, and after a while inflammation of the affected area, swelling, and itching.
- Animals react painfully to the attack of parasites, sleep poorly, and lose strength.
- In domestic cows, the amount of milk decreases, and beef breeds of cattle lose weight.
- The tick-like fly is especially dangerous for young animals. If the infection is severe, calves become ill, are delayed in development, and even die.
- The wool comes in clumps and takes on a sloppy appearance. The wounds often become infected and begin to fester.
- During the day, the female feeds about 20 times and drinks about 1.5 ml of blood in one procedure. With severe infection, young animals die from anemia, adults become weak and sickly.
Generation or life cycle
Now let's talk about the development of the fly from a scientific point of view. The life cycle of a fly follows the path of complete transformation of insects.
Attention! The complete development cycle of insects includes four stages: egg, larva, pupa and adult!
Flies are capable of laying up to one hundred and fifty eggs at a time. During her short life, the female is capable of laying more than six eggs. It is also interesting how flies lay eggs. They are able to place them in any food that has begun to spoil, which is why it is so important to monitor the accumulation of garbage and remove it from the apartment in a timely manner.
Fly eggs are very difficult to see, as they are less than one millimeter in size.
Larvae
The eggs are incubated very quickly, and literally the next day small larvae - maggots - appear. They emerge from the egg very tiny, but during development they are capable of growing more than eight hundred times.
The entire development process of maggots lasts a little more than a week under favorable conditions: an optimal temperature of 20-25 degrees Celsius and high humidity of the air and substrate in which they develop.
Maggots are in great demand among fishing enthusiasts, but for a housefly they are small and are not suitable for baiting a hook. Usually the bait is supplied by other types of flies, the so-called meat flies.
Pupae
The next stage of fly development is the pupa. The larva stops feeding and increasing body weight and size and gradually pupates. Anglers call pupating maggots caster and are also used for bait.
The caster is similar to the larva, only it has a harder shell and a brownish body color. The fly also spends about one week in this stage of development.
Our help! At low temperatures, the fly larva is not able to pupate. Therefore, fishing maggots can be stored in the refrigerator for six months or more.
Imago
A week after pupation, the last stage of flies appears. As stated earlier, adult individuals live on average for about twenty-four days, and they are able to lay eggs almost every two or three days. So these same 75 tons per year come out!
Tritocerebrum
The department is usually called the tertiary brain. His position is clear. The tritocerebrum is located between the other sections. However, the brain does not have a specific shape. The only thing we can say with certainty is that it is divided into;
- right;
- left.
There is a small jumper between the two halves. It passes under the intestines.
The main function of the tritocerebrum is to control the mouth and upper lip. The second may be absent in some types of flies.
Important: Tritocerebrum is associated with the sympathetic nervous system.
Enemies
The housefly has many enemies - birds, reptiles, amphibians, various insects and spiders. Eggs, larvae and pupae contain many types of parasites and parasitoids. Among the most important are the parasitic wasps Muscidifurax uniraptor and Spalangia cameroni; they lay eggs in the tissues of housefly larvae, and their offspring complete their development before the adult flies emerge from their pupae. Toads (Histeridae) feed on larvae in dung piles, and the predatory mite Macrocheles muscaedomesticae eats eggs. The tick eats 20 house fly eggs per day.
The pathogenic fungus Entomophthora muscae causes a fatal disease in house flies. Once infected, the fungal hyphae grow throughout the body, killing the fly in about five days. The housefly also acts as an alternative host for the parasitic nematode Habronema muscae, which parasitizes the stomach of horses. Salivary gland hypertrophy virus (SGHV), which causes swollen salivary glands, spreads among house flies through food contact and infected female house flies become infertile.
Human interaction
Houseflies are a real nuisance to humans, especially on hot days. They are carriers of diseases, especially pathogens of intestinal infections, worm eggs, eye diseases and tuberculosis. Larvae can cause tissue and intestinal myiases
To protect against flies, preventive measures are taken (storage of sewage, which serves as both food for flies and their larvae and a source of pathogenic microorganisms, out of the reach of flies) and various exterminatory measures (use of insecticides in places where larvae develop, poisoned baits, sticky tape traps and fly swatters in those places where adult insects are abundant). Using nets and other devices, flies are prevented from entering living spaces.
Maggots are used by humans as a popular fishing bait that attracts many species of fish. Often maggots are specially bred and “cleaned” by placing them in a container with sawdust, and only then sold. Fishermen store purchased maggots in the refrigerator to slow down pupation.
Sources
- https://vseonauke.com/1120405511397706563/skolko-nog-u-muhi/
- https://apest.ru/muhi/o-muhah/stroenie-muhi/
- https://PokemonGoy.ru/muhi/skolko-lapok-u.html
- https://bioros.net/vsyo-obo-vsyom/skol-ko-nog-u-muhi.html
- https://notklop.ru/muhi/2-fakty/23-stroenie-muhi/
- https://WikiParazit.ru/babochki-i-moshki/unikalnost-lapok-muhi.html
- https://zelenplaneta.ru/muhi/est-li-u-muh-i-drugih-nasekomyh-mozg.html
- https://rci76.ru/muhi-i-moshki/kakogo-cveta-krov-u-muhi.html
[collapse]
How to get into housing
A fly can appear in an apartment in only two ways:
- got pregnant;
- multiplied indoors.
More often than not, the buzzing insect still flies in from the street.
Wintering of insects.
There are other places where parasites appear - ventilation, cracks and balconies. There is a direct relationship: the more insects there are on the street, the more of them there are in a person’s home. If there is a garbage dump or market near the house, then flies will appear in the apartment often. Moreover, the premises will be attacked en masse.
Also, the general condition of the house plays an important role. When the basement is damp and dirty, insects will actively develop and fly around the apartments. If the garbage chute is faulty, the residents of the house will undoubtedly have a problem with how to get rid of flies, and other parasites as well.