Springtime brings with it a charge of positive emotions; nature awakens in all its diversity, including the world of insects. Not all of them are friendly to humans, and some are quite dangerous. Some of them are not easy to get rid of. For example, you need to know exactly how to remove a tick and not harm your health or the well-being of a loved one who has become the target of the parasite’s aggression. There are several proven methods for removing the pest. It is better not to touch it with your fingers, but to use special devices for removing them, which can easily fit in a pocket or small compartment of a backpack.
If you need quick and effective treatment of an area against ticks, we recommend contacting EcoSept!
Causes of tick bites in humans
Ticks are bloodsuckers, so they are just waiting to crawl onto someone and have a good meal.
And let him eat for himself, but bad luck - ticks carry dangerous diseases. If you are bitten by a sick bloodsucker, it can pass the disease on to you. Experienced tourists know where danger lurks, and we will try to remember too.
A tick bite can be earned in several ways:
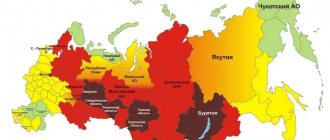
- if you visit regions endemic for ticks, forests and parks (the most infectious ticks are in Siberia, the Volga region and the Urals);
- if you walk around in such regions in open clothes. The tick will easily crawl into a secluded place on your body and attach itself for several hours;
- if you communicate closely with animals (dogs, cats), who often carry ticks, or people: they can bring a bloodsucker on clothes, in a bouquet of flowers or on branches.
Let's say you are going to the forests in the Urals. Be sure to dress with as much skin coverage as possible, such as tucking pants into socks and sleeves into gloves. This will make it difficult for the tick to get on the skin. These bloodsuckers usually sit in the grass and cling to their legs.
Once on a person, ticks look for places with thin skin, so they are often found in the groin, on the lower back, in the armpits, behind the ears and on the neck, as well as in the hair on the head.
Features of behavior
Evolution has helped ticks acquire qualities that have helped them exist successfully for many hundreds of years. They can sit quietly for a long time on tall grass or bushes. When the opportunity arises, they jump on animals or humans. This is basically how ixodid ticks behave - they are carriers of dangerous diseases. They don't bite right away. First, the parasite crawls along clothing from bottom to top, trying to find a suitable place.
If the tick has burrowed under the skin, it means it has been found. Typically, it bites where blood vessels are close to the surface of the body. It can take him up to 3 hours to find such a place. During this time you can easily get rid of it. After the location is found, the tick bites and gradually immerses its head into the skin to get to the blood. His abdomen remains outside.
It is easy to detect a tick under the skin, although this is a rather rare occurrence. It looks like a small tumor, but when you touch it you can feel a hard lump. The behavior of bloodsuckers depends on their species. Some, having drunk blood, fall off on their own after about 3 hours. These are mostly males. Females penetrate deeper into the subcutaneous tissue.
What does a tick bite look like on a person?
After going outdoors, examine your skin, and where you can’t, let your friends check. Finding a tick bite is especially easy if the tick bite is still in place. As it becomes saturated, it gets fatter, so it is difficult to view it. And if he has already eaten and fallen off, what other signs are there of a tick bite in a person?
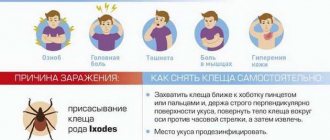
- You can tell that you have been bitten by a tick by a red round spot on the surface of the skin. Rarely is the shape oval or with uneven edges, explains therapist Olga Fedorenko , who runs the Instagram channel doc.fedorenko. — Additional signs of a tick bite in a person may include swelling, rash and itching. In this case, there is usually no pain.
Itching and other signs of a tick bite in humans occur in response to the bloodsucker’s saliva getting into the wound. Often such symptoms are observed in allergy sufferers, children, the elderly and those whose immunity is weakened. In this case, the allergic reaction to the bite can be quite severe, but its symptoms can be relieved with the help of antihistamines.
Ticks in Moscow
If the head of the parasite remains in the body
What to do if the tick ruptures and the head of the parasite remains in the human body? In this case, you can resort to the following methods:
- Using thread . If a small part of the parasite remains on the surface, then you can use the method described above with a loop.
- Removal with a needle . You will need a regular sewing needle. It is pre-disinfected or heated over a fire. Then the remaining head of the parasite is carefully pryed with the tip (based on the principle of removing a splinter) and pulled out of the wound.
Sometimes you can come across a recommendation to leave the head in the body. This fragment will rot over time and will be rejected by the human body. Whether to listen to this recommendation or not is up to everyone to decide for themselves. But it should be remembered that the head of the tick also contains particles of infection, which all this time (albeit in small quantities) continue to poison the body.
First aid after a tick bite
If you find a tick attached to your body, the first thing to do is remove it. It is best to entrust this matter to specialists: go to the emergency room at the clinic. If this is not possible, we pull out the tick ourselves, the main thing is not to let its head come off and remain in the wound. This is not so easy, because the tick holds on very tightly. Under no circumstances should you crush it - the danger of contracting some disease will only increase.
Before removing the tick, use alcohol or chlorhexidine to treat the tick bite site on a person. It would be nice if you have special medical tweezers on hand to remove the arachnid, but a self-made loop or a “vacuum” syringe will do.
What happens to a tick when it drinks blood?
The tick sucks blood for several reasons - to continue development, replenish reserves, lay eggs. The larvae live in the soil where they developed into eggs. They wait for the victim to drink blood. Most often these are rodents, reptiles, and amphibians. At the end of the meal, it falls to the ground, molts, and turns into a nymph. To move to the next stage of development, blood is again needed.
Tick drunk on blood
A fertilized female will not be able to lay eggs until a sufficient amount of blood enters her body. During the feeding process, her body inflates, increasing to 1-2 cm. The female becomes clumsy and vulnerable. The main goal of a fed female is to get to the ground and lay eggs.
Does the tick die after it drinks blood - the male yes, the female not immediately - as soon as she completes her mission of laying eggs. The adult does not bite again.
How to pull it out
The signs of a tick bite on a person have been sorted out, the bite itself has been found, now the bloodsucker needs to be pulled out.
- We treat hands, tweezers and the bite site with alcohol or chlorhexidine.
- We grab the insect with tweezers as close as possible to its head and to your skin, respectively.
- Slowly turn the tick approximately 180 degrees, perpendicular to the skin, making unscrewing movements. To remove the bloodsucker, more turns may be required, the main thing is not to rush or jerk.
- When the tick is removed, treat the bite site with alcohol or any other analogue again.
- Place the removed tick in a small glass container and close tightly.
- Take the tick to a laboratory to find out if it carried any diseases.
“If you don’t have tweezers, use a woolen thread or a lasso handle,” advises therapist Olga Fedorenko . “You can also cut off the top of the syringe, apply it to the bite site and pull out the tick under pressure.
How to get rid of a tick
Signs of demodicosis
Infection occurs when a tick gets under the skin. What to do in this case? How to determine the onset of the disease? The first sign of the presence of this parasite is a general persistent redness of the facial skin. Further symptoms:
- The appearance of acne with ulcers on the face.
- Inflammation, irritation and hardening of the skin around the eyes, increased tearing, dryness, the appearance of stye that does not respond to conventional treatment. As the disease progresses, the cornea becomes damaged and vision decreases.
- Dilated blood vessels.
- Purulent rashes on other areas of the skin.
Direct sunlight helps reduce the area of inflammation.
What to process
First of all, remember that you should not lubricate the tick with oil or cream in the hope that it will come out on its own. Rely on yourself better.
You can treat a tick bite on a person with soap and water, and then it would be a good idea to walk over it with an antiseptic. You can use alcohol or chlorhexidine, which is sold at any pharmacy. Alternatively, 5% iodine, cologne, or any disinfectant that is at hand will do.
If the tick's proboscis breaks and remains in the skin, do not try to pick it out; it will come out on its own after some time.
Therapy for demodicosis
The main method of control is complex treatment, which consists of the external use of special ointments, creams, solutions, as well as strengthening the immune system.
It should be borne in mind that only by eliminating the causes of the disease can good results be achieved and relapses avoided.
Doctors recommend regularly cleansing your facial skin with special cosmetics and doing mild peeling. Patients may be prescribed Permethrin and Metronidazole ointments. The full course of treatment for mites under the skin usually lasts just over a month.
Where to contact
If the goal is to remove the bloodsucker, you can go to the nearest emergency room. Specialists will carefully remove the tick, and all you have to do is show the “pet” to the laboratory workers. To remove the mite, place it in a clean container; test tubes, jars, and vials will do. It is better if this container is humid. To create comfortable conditions for the tick, place there, for example, a napkin moistened with water. In this form, the tick must be delivered to the laboratory within two days.
Each region has its own organizations responsible for research of this kind. Addresses of laboratories can be found in Rospotrebnadzor. Typically, research is carried out by specialists from regional “Centers for Hygiene and Epidemiology”. They will check your tick and give you the results - sick/not sick and what it is sick with. This usually takes one or two days.
If you don't want to or can't test a tick for a particular disease, you can test yourself. Most often, ticks transmit encephalitis and borreliosis. You can get tested for these diseases in infectious diseases hospitals, virology and commercial laboratories.
It will be more convenient for you if the chosen clinic tests for both diseases at once.
Symptoms of borreliosis
If a tick carrier of borreliosis is bitten, the bite site takes on the appearance of specific erythema, which gradually increases to 10-20 cm, and sometimes up to 60 cm in diameter. The erythema patch may be round, oval, or irregular in shape. The victim may experience burning, itching and pain at the site of the bite, but more often the first signs are limited to erythema alone.
After some time, a border of rich red color forms along the contour of the spot, while the border itself looks slightly swollen. In the center, the erythema becomes pale white or bluish. After a few days, a crust and scar forms in the area of the bite, which disappear without a trace after about 2 weeks.
The incubation period before the first symptoms appear ranges from several days to 2 weeks. Then comes the first stage of the disease, which lasts from 3 to 30 days. During this period, the patient experiences muscle aches, headache, weakness, fatigue, sore throat, runny nose, stiff neck muscles, and nausea. Then, for some time, the disease can go into a latent form for up to several months, during which the heart and joints are affected.
Unfortunately, erythema is often mistaken for a local allergic reaction, without giving it much significance. And malaise during the first stage of the disease is attributed to a cold or overwork at work. The disease passes into a latent form, and openly declares itself after a few months, when serious damage to the body has already been done.
Popular questions and answers
In which regions is there a high risk of contracting encephalitis or borreliosis from a tick?
The majority of bites from infected ticks are recorded in the Urals, Siberia, the Far East and the regions of the Northwestern Federal District. When hiking in these regions, you need to be extremely careful, and even better, get vaccinated in advance. You need to understand that infected ticks can also be found in other parts of Russia; residents of all regions of the country seek medical help because of their bites every year.
Is it true that ticks live on trees?
In fact, ticks are usually located in tall grass, about 30 cm from the ground. This makes it easier for them to cling to the legs of those walking by. For the same reason, ticks especially like to be located near paths; they sense where people and animals most often walk. Sometimes ticks climb onto bushes and lower branches of trees.
Where do ticks usually bite?
A tick bite on a person is usually located in places where the skin is thin; it is easier for the tick to bite through it. They stick in the groin, on the stomach and lower back, in the armpits, on the chest, behind the ears, on the neck and on the scalp. A tick bite on a person looks like a red round spot, and the tick itself, as a rule, is located on it, plunging its proboscis under the skin.
Is it possible to fill a tick with oil or alcohol?
A common misconception is that if you pour oil, gasoline, alcohol, or grease onto a tick, it will suffocate and fall off on its own. Nothing of the kind, with your manipulations you can only spur the tick to stick tighter. It is better to treat the tick bite with antiseptics, for example, alcohol or vodka, just water and soap will do, and then pull it out with tweezers.
What to do if it is not possible to take a tick for analysis?
Observe the condition of the injured person. If the inflammation at the site of the tick bite disappears within 1-2 days, the likelihood of developing any disease is considered minimal. If the swelling remains or worsens, go to the doctor. It will not be superfluous to constantly change the temperature of the victim. If it increases within 10 days of the bite, there is a serious risk of developing an infection, so do not delay visiting a doctor.
What if after a bite you start taking antibiotics just in case?
Such a safety net is pointless and dangerous. Firstly, not every tick is infected, secondly, not every sick tick will transmit this or that ailment to you, thirdly, it is no coincidence that antibiotics are given according to prescriptions; without the proper knowledge you will not select the optimal drug and dosage. But the worst thing is that delay due to antibiotics can lead to serious problems.
Prevention
It is well known that disease is easier to prevent than to treat. As already mentioned, one of the main causes of demodicosis is a weakened immune system. Therefore, proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle are one of the main conditions that help to avoid the disease.
To prevent ticks from parasitizing under the skin of a person, you should follow the rules of personal hygiene, constantly wash your hands, and do not use common household items.
It is also necessary to take a shower and visit the bathhouse at least once a week. During this procedure, the pores and sebaceous ducts are cleaned.
It's hard to believe, but scabies mite infection is not related to hygiene. This parasite feels great on both clean and dirty bodies. It can remain on the surface for no more than 30 minutes. During this time, the tick gnaws through the passage and hides under the skin. A preventative measure that will help avoid infection with this parasite is to minimize physical contact with strangers.
Compliance with all these measures will protect you not only from diseases caused by subcutaneous mites, but also other dangerous ailments.
What can be the consequences after a tick bite?
Just because a tick was not a carrier of any infection does not mean that its bite is harmless.
— If you do not seek medical help in time, you may encounter various consequences of such a bite. Firstly, suppuration may occur at the site of the tick bite. Secondly, allergies of various kinds and edema (Quincke's edema) are possible. The consequences can be very serious, including paralysis, respiratory arrest, cessation of brain activity and death, explains general practitioner Olga Fedorenko.
Repellents
Repellents include the following:
- "Biban" and "Biban-gel";
- "DEFI-Taiga";
- “Off! Extreme" and "Off for Children";
- "Reftamide maximum."
They are applied to clothing, as well as to unprotected areas of the body in a circular motion from the shins to the chest. The tick will not want to inhale the repellent and will crawl in a different direction, which means it will return back to the grass. The treated fabric retains its anti-tick properties for a period of five to seven days.
How dangerous is a tick bite?
In itself, a tick bite on a person does not pose a serious danger; the main risk is the infections that the arachnid can reward its victim. Most of these infections respond well to treatment, but only in the early stages. That's why it's so important to diagnose them as soon as possible. It’s good if you still have the same tick, because if it is infected, the doctor will be able to take preventive measures. It will be possible to find out whether you are infected only two weeks after the bite; only then will antibodies to viruses appear in the blood, and they serve as a marker of the disease.
— The tick is examined by PCR for six infectious diseases. If an infection is found in it, emergency prevention is carried out. For encephalitis - the introduction of immunoglobulin, for borreliosis - a course of antibiotics, explains general practitioner Olga Fedorenko . - You also need to donate blood for tests: for encephalitis and borreliosis - no earlier than 10 days after the bite.
If you catch the disease at an early stage, there is every chance of a successful recovery, but if you miss the moment, you can expect serious complications, the worst of which is death.
Acaricidal agents
These agents have nerve paralytic properties and paralyze ticks. If ticks come into contact with clothing treated with this composition, complete paralysis of the limbs occurs and they fall dead from the fabric.
These include:
- "Reftamid taiga";
- “Picnic-Anticlesh”;
- "Tornado-anti-mite";
- "Gardex anti-mite."
These products should not be sprayed onto clothing worn directly by people. It is first processed, and only then put on the body. Such clothing can retain its protective function for 10-12 days.