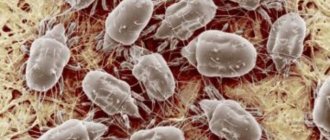
Powdery mildew is one of the most common diseases in the garden. It affects absolutely everything that the fungal spores land on. But it is caused by various types of fungus that infect certain plants. For example, the pathogen Oidium tuckeri settles on grapes. Having a negative effect on shoots, leaves, flowers and berries, the fungus significantly reduces the development of the plant and can even lead to its rotting.
Another name for powdery mildew on grapes is oidium or ashtray. Fungal spores tolerate frost well, as they hide under the scales of the eyes, in the soil, under fallen leaves. In late spring, when the temperature reaches +18 °C ... +25 °C, spores wake up and begin to develop on the surface of the leaf. With increased air humidity, development occurs faster. Therefore, as a rule, growth activation occurs after rain.
Description of grape oidium or powdery mildew
The first symptoms of powdery mildew appear on the shoots of grapevines already in early spring, when the leaves begin to bloom on the plants
. Some of the stems begin to lag in growth, the foliage on them grows curly, and a dirty white coating is clearly visible on the leaf blades.
It may cover the leaves partially or completely. By the first ten days of June, if no measures have been taken to combat the disease, the ashtray coating spreads to the entire foliage, on both sides.
Photo of grape oidium
The tops of the lashes, flowers and the resulting brushes seem to be covered with a coating of flour or ash. Over time, all parts of the grape vines affected by oidium dry out and die. Ripening berries begin to burst, and in hot weather they begin to dry out.
Powdery mildew can “deal with” almost the entire crop if the fight against it is not started in a timely manner.
Important!
Today, among the European grape varieties, almost none of them have high resistance to oidium!
Grape oidium - control methods and prevention - video
From the moment the grapevines are infected with oidium until the active development of the mycelium takes from one to two weeks. The best temperature for the active growth of oidium mycelium is 23-30 degrees Celsius, but this fungus can develop at lower temperatures.
Dense grape bushes with poor ventilation and an abundance of foliage are affected by powdery mildew more quickly.
Main signs of damage
Visual diagnosis is carried out according to the characteristic signs of oidium.
The first signs are that the leaves on top are sprinkled with a white powdery fungal coating, which darkens over time. Heavily affected leaves turn yellow but do not fall, reducing the assimilation surface area and weakening the plant.
Escape. Dark shapeless spots merge with each other. Sometimes green twigs are completely covered with plaque. From severe damage, the shoots turn black and die - uneven lignification occurs, which subsequently suffers most from frost. In spring, such shoots grow slowly and the leaves curl.
Inflorescences and berries. Symptoms vary depending on the degree of ripeness. Young fruits, with a sugar content of up to 8%, become covered with plaque and dry out. When the berry has reached ripe size, and only then infection occurs, it will continue to ripen. But the fungus also lives and will damage the integrity of the epidermis, because of this the berries will crack and become deformed. If the bones protrude outward, this is a characteristic symptom of the lesion. Often the spoilage of berries is enhanced by the pathogen of gray rot (Botrytis cinerea) or wet rot (Penicillium expansum). If dark spots appear on the berries under the shell, although the integrity is preserved, the skin hardens and becomes colored, a mesh pattern on the surface is also powdery mildew of grapes.
How to deal with powdery mildew on grapes
To combat grape oidium, it is necessary to simultaneously carry out a set of measures, including yourself:
- correct agricultural technology;
- a set of preventive measures;
- treatment with chemicals;
- use of traditional methods.
Experts recommend, simultaneously with the fight against oidium, to carry out a set of measures to destroy the mildew pathogen.
Prevention of these diseases consists of carrying out the same measures, and modern fungicidal preparations usually include sulfur, which has a negative effect on oidium, and copper, which destroys downy mildew.
Prevention in spring, summer and winter
It is impossible to completely protect a plant from diseases and pests, but you can reduce the risk of powdery mildew if you follow the following preventive recommendations:
- during the growing season, grapes can be sprayed with one percent Bordeaux mixture;
- at the first signs of oidium, it is necessary to stop feeding, since the components included in it only contribute to the development of the fungus (with the exception of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers);
- the vineyard must be regularly cleaned of dry, diseased and dead plants, as these are the main sources of the spread of harmful microorganisms.
In the complex fight against powdery mildew, caution should be exercised if it is decided to use several chemical agents at once. Sometimes this combination leads to burns of leaves and vines, so if there is a need for such treatment, the concentration of the original product in each solution should be reduced by as many times as the drugs are used in total. For example, if two substances are used, their concentration should be 50% of that recommended in the instructions.
3.7/5 — (4 votes)
Treatment of vineyards against oidium
If the vineyard was affected by this fungal disease last season, then next year they begin to fight it in early spring.
However, treating vines with preparations containing sulfur should begin when the air temperature is at least 20 degrees Celsius - at lower temperatures, solid sulfur does not turn into vapor in order to effectively fight fungi on the foliage and shoots of grapes.
Advice!
It must be remembered that treatment with such preparations in the heat can cause burns on the leaf blades, so spraying grapes against oidium should be carried out in the early morning or in the evening.
To cope with oidium, at least 3 such treatments must be carried out with an interval of 1.5-3 weeks
. The maximum number of treatments of a vineyard with fungicidal preparations containing sulfur is no more than 6. During the treatment process, this preparation must completely cover the foliage. If the sulfur is soaked, then there will be no effect from treatment with such a preparation.
Treatment of grapes from oidium - video
For preventive spraying of grapevines against oidium, the following drugs are usually used:
- Talendo;
- Karatan;
- Switch.
THE BEST VARIETIES OF GRAPES!
Grapes Libya Grapes Transfiguration Grapes Codryanka
To fight oidium, which has already affected the vineyard, you need to use:
- colloidal sulfur;
- Thiovit Jet;
- Speed;
- Horus.
It is impossible to cope with oidium without the use of chemicals, but it is possible to minimize the negative impact of such agents on the vineyard and its fruits. To do this, regular preventive treatment of the bush should be carried out.
Preventive actions
To prevent the spread of oidium, you need to follow simple rules. They cannot completely eliminate the likelihood of the fungus spreading, but they can reduce this likelihood to a minimum.
Basic preventive actions:
- timely garter, chasing of vines;
- preventing crowded plantings;
- pruning stepsons as they grow;
- removing weeds and loosening the soil in the root circle;
- preventive spraying of bushes throughout the season;
- burning fallen leaves in autumn;
- collect dried grapes in a timely manner;
- Fertilize regularly to increase the immunity of the bushes.
The use of fungicides in the fight against oidium on grapes
Below are a number of fungicidal preparations that are most effective against oidium on grapevines.
One of the new generation fungicidal drugs is Azofos
, which effectively fights fungal diseases and is environmentally friendly for plants and warm-blooded organisms.
Iron sulfate
You can treat the vineyard for preventive purposes, and also use it in the fight against oidium. Effective against most fungal infections, but incompatible with phosphorus agents.
Copper sulfate
– the most famous and effective drug against oidium on grapes, containing copper and having an effective effect on fungi.
Karatan
It is a contact fungicidal agent with a narrow effect and can effectively suppress the development of oidium.
Colloidal sulfur
is the oldest drug, used in a vapor state to treat most diseases of grape bushes, and also suppresses the development of spider mites. Compatible with almost all other fungicidal preparations.
Ordan
– a systemic and contact fungicidal drug, specially created to combat fungi.
Ridomil Gold
– a contact-systemic fungicidal drug intended to combat fungal diseases.
One of the most effective systemic fungicides with long-term effects on the fungus is Skor
. It can be used to combat and prevent scab, oidium, leaf curl, late blight and a number of other diseases.
Tiovit Jet
is an insecticidal and fungicidal drug that can have a protective effect on grapevines against spider mites and oidium.
One of the best systemic fungicidal agents for the treatment of fungal infections is Topaz
. Works great against oidium on grapevines.
Horus is a local systemic fungicide.
. It is actively used in the fight against fungal diseases.
Systemic contact agent Switch
gardeners actively use it to combat fungal diseases that have appeared on grapes, and also as a preventative drug.
Talendo
- one of the newest drugs, developed specifically as a prophylactic agent to prevent the appearance of fungi on grapevines.
Ecosil
is a drug that is used as a growth regulator and enhances the immunity of the vineyard. Has fungicidal properties.
Important!
The last treatment of grapes against oidium with fungicidal agents should be carried out a couple of months before harvest.
What to do if treatment does not help?
A novice gardener is not always able to recognize oidium at an early stage of damage. Therefore, further treatment may be ineffective. In this case, you need to act quickly. For destruction, you can use chemicals, doubling their concentration. You should also add Ecosil to the tank mixture, which will enhance the fungicidal effect.
The bushes should be treated 2-3 times every 3 days, alternating the product each time. Before wintering, it is necessary to treat the vine and the soil near the bush with a 5% solution of iron sulfate.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
Note! If the oidium has infected all the leaves, then it is not necessary to remove the growing stepsons so that the plant has the opportunity to accumulate nutrients for the winter due to them.
Folk recipes for combating grape oidium
Many gardeners who prefer not to use any chemicals in their garden plot try to fight oidium with folk remedies.
FOLK METHODS OF COMBATING OIDIA - video
The most effective folk remedies for grape oidium:
- mow the grass on the site, wait until it becomes moldy, then put it in a container, filling it halfway, add water, mix, filter and process the vines. Such treatments can be carried out throughout the season;
- 5 kg of ash is poured with water in an amount of 7 liters, left for 24 hours, filtered and enough water is added so that the volume of the working fluid doubles. Green soap is added to the resulting solution as an adhesive, and grape vines are regularly treated with this liquid. You can not infuse the ash, but boil it for 1/3 hour;
- straw dust is poured with water in a ratio of 1:3, infused for at least 3 days, then the resulting infusion should be filtered and diluted with water in a ratio of 1:3;
- 3 kg of pure manure is diluted in a bucket of water, left for 3 days, filtered, and 1 tsp is added. urea. A similar liquid is used to treat grape foliage as a preventive measure against oidium on both sides;
- 5 g of potassium permanganate is dissolved in a bucket of water and the grape bushes are sprayed;
- A liter of whey or milk is diluted in a bucket of water, stirred and sprayed on grape foliage;
- 1.5 tbsp. l. soda ash and the same amount of dishwashing liquid are dissolved in a bucket of water. This working solution is used to treat grapevines.
Introduction
Oidium is a fungal disease that develops on grapes under conditions of a combination of heat and high humidity. The particular insidiousness of this fungus is that the main symptoms of reproduction appear in mid-summer, when the fruits have already formed on the vine and strong fungicides cannot be used.
To save the crop, the gardener needs to know how the disease manifests itself at an early stage and master methods for preventing infection.
Grapes resistant to oidium or powdery mildew
Currently, there are no grapes that are not affected by powdery mildew, but there are some varieties that can still resist most fungal diseases under the right conditions. We must also remember that European varieties of grapes may be susceptible to oidium before others.
The most oidium-resistant grape varieties:
- Delight;
- Mascot;
- Gift to Zaporozhye;
- Muscat velvet;
- Anniversary of Platonov;
- Matryoshka;
- Lark;
- Caucasus and a number of other grape varieties.
Causes
Powdery mildew is common in all regions of temperate climates, it appears on both grapes and other plants. Even if correct agricultural practices are followed, its occurrence cannot be completely eliminated. It is worth remembering that several reasons can provoke the development of a pest:
- dry summer with stable daytime temperatures above +25 °C;
- prolonged heat (from +30) - in this case, powdery mildew will develop even without rain;
- warm, mild winters (at -30°C spores die);
- too high planting density;
- absence or irregular pruning of grapes - excessively thickened crown;
- regular violation of watering norms, excess moisture.
Hot weather promotes infection development
Let's sum it up
Not a single grape variety is immune from infection with oidium. The disease can affect the vine, even with careful care and following all growing recommendations. Therefore, the gardener’s task is to carry out preventive treatments and take a set of measures to treat plantings when the first signs of fungus penetration into the area appear.
Previous
Useful tips Freeze grapes for the winter the smart way!
Next
Growing and caring 7 life hacks for properly minting grapes
Biological drugs
The causative agent of powdery mildew is very sensitive to the effects of Bacillus subtilis and some strains of bacteria, which is used to suppress the growth and reproduction of pathogenic fungi. Colonies of microorganisms are released in the form of a dry powder (the bacteria are in a vegetative state).
To activate microorganisms, an active solution is first prepared, which is used to spray the affected plantings up to 4 times per season.
Reviews from winegrowers about some varieties
Breeders position these varieties as resistant to fungus. The vineyards respond positively to some of them:
Vasily Krasnov
Moscow region
Last year was struck by some kind of crazy epidemic of mildew and oidium. Denal, Jubilee Platov and Sashenka, who had never squirted in their entire lives, became bald by the end of July and had to throw away the berries. But Delight, Lark and Timur held out well. I now decided to go through the forums and find only problem-free varieties. They say that dense hybrids like Kuderka, Bako, and Save Villar can withstand extreme weather conditions. I'll try to buy seedlings.rnrn
Vladimir Lozhkin
Ryazan Oblast
A couple of years ago I thought I had planted disease-resistant varieties. I grew up with Delight, White Miracle and Pink Timur. This year, mildew has not yet become as rampant as oidium. Without treatment, the neighbors' Lydia went to waste. But I had to treat my resistant ones with lethal chemicals, so they didn’t dare to eat the grapes. IMHO, the variety would be immune to all diseases at once and would not crack, and phylloxera would not settle on it!!! Even Villar Blanc will become bored with such requests. Still, you need to spray the systemic ones at least a couple of times, you’ll never guess in the spring what kind of trouble will come out. Well, there are semi-organic methods of protection closer to harvesting - Thiovit jet, Potassium Monophosphate. So don’t rely on luck, spray on time and wisely.
Ksenia Vasina
Chelyabinsk
In our harsh climate, it is almost impossible to grow grapes. All the sores stick. But through trial and error, we finally found indestructible varieties. Delight - I'm delighted with it. Sorry for the pun. It needs to be treated in spring and autumn against infection and the same amount against insect eaters. That's all! It grows, matures, and endures winters of minus 30 without problems. I also liked Palanga. Tolerates minus 30 under light shelters, does not get sick from anything!rnrn