Description and appearance
The cabbage butterfly is a butterfly from the white butterfly family and belongs to the class of insects, a type of arthropod. The insect received the specific name “cabbage plant” due to the fact that cabbage is one of the main food plants for caterpillars. This is a fairly large representative of the Lepidoptera order; its wingspan can reach 60 mm.
The description of the cabbage butterfly should begin with its distinctive feature, namely its wings. The cabbage white butterfly has four wings, which are powdery white on the upper side. The corners of the front wings are black; in females, the pattern is supplemented with black spots. The underside of the wings of females is greenish, while that of males is closer to yellow. This is an excellent disguise. When the cabbage butterfly folds its wings, it is difficult to see it against the background of the grass.
Appearance
The body of the white butterfly is dark and covered with hairs. On the head there are large eyes and rather long antennae. Six legs with sharp claws, thanks to which the insect is held on to plants. The legs themselves are weak, so the butterfly practically does not crawl.
Generations
In the hot season and in the southern regions, as a rule, three generations develop, in the north - two. The first comes out in the southern regions by the end of April-early May, in the northern regions - by the end of May-beginning of June. The more numerous second generation appears in July-August. Butterflies fly until the very end of September. The third generation in the southern regions may mix with the second. However, as a rule, individuals of the third instar spread throughout the plant and live further apart from the rest and may linger until October.
Lifestyle and habitat
Cabbage whites are found in Europe, Africa, Australia, Japan and Asia. In Russia, this butterfly can be found in almost all regions, with the exception of the Far North.
Cabbage butterflies are daytime butterflies. They can be seen in parks and gardens, in meadows and forest clearings, in vegetable gardens and roadsides. Cabbage white caterpillars reach a length of 2.5 - 3.5 cm, but due to their green body with dark spots they are not easy to notice in dense foliage. However, the presence of caterpillars on cabbage very soon becomes noticeable, as they gnaw the leaf from the edges to the veins.
Butterflies love open spaces, but do not fly far from a food source. They are mainly active in sunny weather, and when it is cloudy, they sit on low bushes or grass with half-opened wings. The most comfortable temperature for cabbage is from 20 to 25⁰С.
The harmfulness of cabbage whites
Cabbage whiteweed is a widespread pest of cruciferous crops. Caterpillars are harmful. Young larvae scrape off the top layer of the leaf - the parenchyma, and adults roughly eat the edges of the leaves. The EPV (economic threshold of harmfulness) is determined during the leaf whorl phase and is 3-5 caterpillars on one plant; if the EPV is exceeded, it is advisable to apply chemical treatment. The damage is most intense in the second half of summer. They cause great harm to white cabbage and cauliflower, and also harm rutabaga, radishes, turnips, rapeseed, mustard, etc.
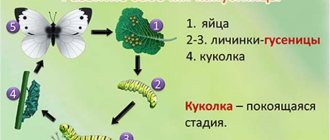
Reproduction and life cycle
The development cycle of the cabbage butterfly includes 4 stages:
- egg;
- larva (caterpillar);
- chrysalis;
- adult insect.
After mating, the female lays eggs on the underside of leaves of plants from the cruciferous family. During its life, a butterfly can lay 200 to 300 eggs. Cabbage eggs are light yellow and shaped like a cone. After about 10–20 days, cabbage white larvae hatch from the eggs.
Life cycle
At first the caterpillar is yellow-green, but gradually its color changes to gray-green with dark spots and streaks. The larval stage can last from 14 to 25 days, during which time the caterpillar molts four times. Then the caterpillar crawls from the plant to a stone, fence, tree, attaches itself to it with a silk thread and pupates. The cabbage pupa is angular, greenish-yellow with dark dots. This stage of development of the cabbage white butterfly lasts from 10 to 15 days, depending on weather conditions.
It often happens that the pupa hibernates, overwinters, and the butterfly appears the very next year after the onset of warm weather.
Prevention measures
Prevention of the appearance of Cabbage White is the timely destruction of pupae and oviposition. To prevent the spread of the pest, you must do the following:
- periodically inspect the underside of the leaves of cruciferous plants and destroy the eggs found;
- inspect dry branches, tree trunks, barn walls and other places where pupae may overwinter;
- Regularly carry out spring whitewashing of tree trunks and main branches.
What does cabbage eat?
The cabbage white butterfly, like most butterflies, feeds on flower nectar. They choose a flower, descend on it and suck out the life-giving moisture with the help of their proboscis. Of the many flowering plants, butterflies prefer:
- cornflower;
- dandelion;
- alfalfa;
- thistle;
- meadow greenweed;
- marjoram.
But cabbage caterpillars are much more harmful to crops than adult butterflies, since they feed on plant leaves. It is the larvae that are the reason why cabbage grass is considered a dangerous pest. Green caterpillars most often occupy the leaves of plants from the cruciferous family, namely:
- different varieties of cabbage (white cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, kohlrabi);
- radish;
- radish;
- rape;
- turnip;
- rutabaga;
- mustard.
Cabbage caterpillars eat other plants, for example:
- capers;
- mignonette;
- nasturtium.
The caterpillars stick together, quickly eating the leaves, of which very soon only veins remain. Having finished with one plant, insects crawl to neighboring ones, thus causing serious damage to the plantings.
Nutrition
The second and third generations of insects become a real disaster for summer residents and gardeners. The first month of summer is the most favorable for breeding offspring of the cabbage butterfly.
The insect’s favorite food crops appear in the garden:
- cabbage;
- radish;
- turnip;
- horseradish;
- turnip;
- radish;
- garlic;
- capers.
The pest most often leaves egg masses on the underside of the leaves of these vegetable crops. The emerging caterpillars begin to actively feed on juicy young leaves. First they eat the outer side, then move to the central part. By damaging the leaves of vegetable crops, the caterpillars disrupt the processes of photosynthesis in the plant, thereby causing irreparable damage to the future harvest. When the larvae eat the cabbage leaves down to the base, they move on to the inner leaves of the cabbage head. This leads to the destruction of the entire plant. An adult white moth does not damage vegetation.
Cabbage butterflies eat nectar and pollen of wildflowers:
- dandelion;
- chamomile;
- alfalfa;
- coltsfoot;
- meadow greenweed.
Damage caused by the cabbage butterfly
As already noted, the real pest is not the imago, but the caterpillar of the cabbage butterfly. It is at this stage of development that the insect poses a real danger to fields and vegetable gardens. Butterflies are quite prolific, and the larvae are very voracious. An infestation of caterpillars can cause the destruction of a significant portion of the crop.
Caterpillars
But it’s not just plants that can suffer from caterpillars. The fact is that the larvae secrete a poisonous toxin, which can cause the death of the bird after it eats the caterpillar. If a toxic substance comes into contact with human skin, it may cause irritation.
Doll
What does a cabbage butterfly look like in the pupal stage? The color is almost the same as that of the butterfly - yellowish-green with black splashes. When transitioning to the pupal stage, the larva is wrapped in threads somewhat reminiscent of silk, and with them it clings to plants. If the folding into a chrysalis did not occur too late, then a butterfly will soon be born. If the atmospheric temperature does not allow the transformation to occur, then the insect enters the diapause stage and overwinters. With the onset of spring, such insects begin their first generation.
For information, diapause is the process of inhibition of physiological processes in an insect with a transition to the stage of suspended animation. The insect remains in this stage for several weeks. During this period, the pupa molts several times, and this process is called complete metamorphosis.
How to get rid of it?
Pest control mainly consists of destroying the larvae that pose a threat to crop plants. Both chemicals and folk recipes help get rid of caterpillars on cabbage and other crops. In addition, gardeners use herbal decoctions, biological preparations, traps and natural enemies of whitefish.
Insecticides
Insecticidal preparations are the most effective method of pest control. Before using them, you must carefully study the instructions, and then act, observing the dosage and remembering the precautions.
The most popular insecticides for cabbage include:
- Kinmiks;
- Spark;
- Fufanon;
- Karate.
Due to their high toxicity, such products are recommended to be used to get rid of caterpillars on cabbage in case of severe infestation. If the situation has not gone too far, you should try to use safer means, for example, biological products.
Biological products
The composition of biological products allows you to treat cabbage and other plants throughout the entire growing season. The only time when processing is not recommended is immediately before harvesting. The most effective products from this category:
- Fitoverm;
- Actofid;
- Vermicide;
- Lepidocide.
Biological methods show good results only in the case of not too extensive damage by caterpillars.
Folk methods of struggle
Folk remedies for caterpillars on cabbage have been known for a long time and have proven their effectiveness more than once. Such methods are absolutely safe for humans and plants and at the same time cope well with pests. The following folk recipes are most often used:
- pollination of affected leaves with dry tobacco dust;
- sprinkle baking soda on affected plants;
- spraying with herbal infusions.
Spraying
The easiest option is to collect caterpillars by hand, but it will require a lot of time, effort and patience, so it is only applicable at the initial stage of infection.
Traps
Many gardeners act comprehensively and fight both caterpillars on cabbage and butterflies to prevent the laying of eggs and the appearance of new pests. Traps are used to catch butterflies. These can be adhesive tapes hung next to the beds, or traps with sweet bait in the form of jam or syrup with the addition of brewer's yeast, placed between the rows. When deciding to use traps, you need to take into account that not only pests, but also beneficial insects can get into them.
Recipes for infusions for spraying plants
One of the most common methods of combating caterpillars is the use of a variety of herbal infusions for spraying or watering. Several popular and effective recipes:
- pine decoction (200 g of pine needles or cones per 1 liter of boiling water, leave for a week, dilute with a bucket of water);
- mustard decoction (100 g of mustard powder per bucket of hot water, leave for 2-3 days);
- Pour 1 kg of fresh potato tops with a bucket of boiling water, leave for 4 hours, strain, add a little crushed laundry soap;
- Mix 0.5 kg of wood ash with 10 liters of water, leave for 3-4 hours, add 2-3 tbsp. l. liquid soap;
- Boil 1 kg of dried wormwood in 1.5 - 2 liters of water for 15 - 20 minutes, when it cools down, pour the decoction into a bucket of water;
- per bucket of water 50 ml of ammonia;
- Fill a bucket one-third full with crushed burdock leaves, add water, leave for 4 days, strain and water the affected plants;
- 1 bottle of pharmaceutical valerian per 3 liters of water, apply immediately after mixing.
For spraying, you can use salt water (2 full tablespoons of salt per bucket of water).
Chemical methods of control
When growing cabbage in small areas, it is recommended to use bacterial compounds that have minimal impact on the heads and leaves. Biological products that repel and destroy butterflies can be used throughout the growing season. Treatments should be stopped immediately before harvesting. The most popular products are “Bitoxibacillin”, “Fitoverm” and Lepidocid.
If there is a strong spread of cabbage whites over a large area of the garden, toxic insecticides should be used. Chemicals are only allowed to be used during the period when leaves are forming. When using insecticides at a later stage, toxic substances may accumulate in the plant.
The spraying procedure must be carried out in the morning, in the absence of wind and precipitation. It is important to thoroughly treat the leaves on the underside, where pests can hide and oviposition is located. Effective drugs include Karate, Karbofos, Kinmiks and Actellik.
How to protect your garden from cabbage weeds?
The following recommendations will help protect your garden and future harvest from the white-winged pest:
- already at the beginning of summer it is necessary to remove cruciferous weeds from the beds;
- beds with crops that attract cabbageweed should be located at a distance from each other;
- between beds with cabbage and other cruciferous vegetables, carrots, dill, and parsley are planted, which attract natural enemies of pests;
- to protect cabbage from the caterpillars of the white butterfly, tomatoes are planted next to it (the pest also cannot stand the smell of lemon balm, marigold, valerian);
- at the end of the season in the fall, it is necessary to dig up the area so that pests cannot overwinter in the ground;
- It is advisable to plant cruciferous vegetables in different places each season.
In addition, you need to regularly inspect the leaves of plants in order to notice eggs and larvae in time and take action.
Preventive measures
For preventive purposes, mechanical means are used, as well as methods in which certain drugs are used:
- Immediately after the butterflies begin to fly, all wild cruciferous plants must be removed from the area. The first generation of caterpillars does not cause much harm to cultivated plants. However, it should be remembered that it is they who form the second, most dangerous generation;
- mulching the beds where plants of the cabbage family are grown with green grass disorients the whites with a specific smell;
- using birch tar to spray cabbage plantings. This remedy can also repel another malicious pest of cruciferous crops - the flea beetle;
- The undersides of cabbage leaves should be regularly inspected for egg-laying eggs.
Cabbage whites are pests that can cause enormous damage to the crop. The fight against them must begin immediately after their discovery, using complementary chemical and folk remedies. You can protect your area from pest attacks by keeping the area clean and following simple recommendations from experts.