When a decorative rat has small cubs, it causes a lot of positive emotions. Especially if your beloved pet brings a litter for the first time. And despite the fact that the female takes care of the brood on her own, in some cases she may need help.
This means that the owner must know how to care for little rat pups from birth, when to pick them up, how to raise them to be tame, and when to hand them over to new owners.
Rats - popular Lariskas
Looking at photos of decorative rats, you understand that there is no single standard for determining the “breed”.
The ranking of the most popular of these decorative rodents includes:
- standard - large, smooth-haired animals with a tail equal to the size of the body. Reach up to half a kilogram of weight;
- satin - differ from their counterparts in soft long fur with a good shine;
- Dambo - round large ears and a sharp muzzle, a pear-shaped not very long body and an elongated tail;
- Sphynx - hairless individuals, may be born with age spots, but as adults the skin becomes pink;
- tailless - appeared in 1983 as a result of an unplanned mutation. Their body is shaped like a pear.
Differences in appearance
Rodents are nocturnal, hiding from the sun and people. But under certain circumstances they can be seen. How to distinguish rats from mice - you need to evaluate parameters, weight, body features.
- Body length. A mouse is a small rodent that can crawl into any crevice in the house. The body size of most species of mice does not exceed 12 cm, and their thin tail is almost the same. Even the most well-fed individual does not grow larger than the average size. The rat is a large rodent. Some specimens reach sizes of 40 cm, on average it is an animal with dimensions of about 30 cm.
- Head shape. Mice and rats differ in skull shape. The first representatives of the genus have a triangular-shaped muzzle, flattened, with small round eyes clearly visible. The rat has an elongated muzzle, and its nose is conspicuous.
- Tail. Mice and rats have equally long tails, corresponding to their body parameters. However, their structure is somewhat different. In rats, the tail is thick at the base, the length is approximately equal to the body dimensions. Only the base is covered with wool, then there is bare skin with a scaly covering. Mice have a thin tail covered with hair. The coloring is practically no different from the color of the body. At the tip is a small brush with long hairs.
- Ears, nose, eyes. If you manage to see the animal at a distance of up to 2 m, you can see the differences in the structure of mice and rats. Mice's ears are wide at the base and round. Always alert, standing firmly on the sides of the skull. The eyes are large, relative to the proportions of the muzzle. The nose is flattened. Rats have small, elongated ears, pressed to the head. The eyes are round and small. The nose is elongated; attention is most focused on it.
- Weight. The difference in weight between rodents is significant. The largest rat reaches a mass of no more than 50 g. A rat can grow up to 900 g, but on average - 500 g.
On a note!
The smell of a rat is also different from that of a mouse. Rats leave behind a smell of honey and musk. Mice smell like dirty socks.
Photos of rats and mice are presented below. Using it, you can clearly evaluate the appearance of rodents and compare them with each other.
How else can you tell the difference between a female and a male? Indirect signs
In addition to differences in reproductive organs, male and female rats typically differ in body size and type, behavior, smell, and other factors.
In general, males are larger, wider and heavier, with thicker tails and coarser coats. They have broad heads and shoulders that have a “brick” shape.
Adult males usually weigh from 300 to 800 g, and females from 250 to 500 g.
However, some pet rats can weigh even more than this.
Male rats often become more accustomed to human affection than female rats, who tend to do so later in life.
Most female rats prefer to move around a lot rather than sit still, but not all male rats share this trait.
Male rats can certainly be calm and relaxed, but that doesn't make them lazy. Almost all rats, given a lot of attention from birth, will enjoy time with their people and the touch we often want to share with them.
Women's hormonal cycles can sometimes affect their behavior, making them more restless and even irritable. However, many females show almost no signs of estrus and yet remain alert.
Female rats reach sexual maturity at the age of 34 to 38 days, and males slightly later - from 39 to 47 days.
Menopause in females occurs between 15 and 18 months, although some females remain fertile into old age. Males are capable of constantly reproducing offspring until old age. They do not have a reproductive cycle, but their testosterone levels fluctuate greatly.
Male rats have a musky odor, while female rats smell like grapes.
Sex hormones are also associated with the slightly musky odor that many males have (not heavy or unpleasant). People often describe their female rats as smelling like grapes, perfume, or even popcorn. This is the smell of the rats themselves, not their cage - most likely it is the smell of urine or feces.
We humans are individuals too, and we all look for different traits and characteristics in the animals we choose as pets. So, regardless of gender, your rats can be active, interesting and affectionate companions.
How to care for baby rats
The total growth period for a rat is one year. During this time, the animal reaches the size of an adult: males weigh up to 600 g, and females - about 300 g. However, the foundation for full development is laid at a very early age. The cage with the female and newborn rats should be placed in the quietest and warmest room, where no one will disturb the family.
Don't worry about cleaning the nest - the mother rat will do it herself. You only need to periodically place new dry wipes in the cage, and the rat itself will throw dirty bedding into the corner. Only when the baby is 8–10 days old can you intervene in the cleaning process, carefully removing the waste material. This is only permissible if the female does not worry too much. Otherwise, cleaning should be postponed.
What do little rats eat?
The growth and development of cubs is largely influenced by the quality of nutrition. While staying near the mother for the first month, the basis of the diet is her milk. In order for it to be as beneficial as possible for babies, it is important to organize a balanced diet for the mother: in addition to the main food, the daily diet must include fruits, herbs, and animal food. Be sure to make sure that the female has enough water to drink - wash the drinking bowl and change the water daily.
Sometimes it happens that the female dies during childbirth, and if you cannot find her replacement (another nursing mother of a rat or mouse), you will have to do this yourself. Feeding newborn rat pups is not easy. For this purpose, dry infant soy formula, which is diluted with goat's milk, is best suited. Alternatively, you can use a pet milk replacer. Food is given to babies through a syringe. For convenience, you can equip it with a fabric pacifier.
Important! Little rats should not be given tomatoes, cucumbers and champignons, as well as any sweets.
In the first week you need to prepare the mixture as liquid as possible. Feedings are carried out every 2 hours during the day and a couple more times at night. In the second week, you can add ground grain feed to the mixture. Feeding periods are shortened - food is served every 4 hours. At week 3, the grain feed is simply mixed into the mixture and poured into a bowl. The cubs are already quite capable of eating it on their own.
By the end of the first month, a sufficient amount of protein should be present in the diet of rat pups, since a lack of this substance often leads to illness and mortality. The most useful additives: cottage cheese, boiled fish, apples, boiled chicken wings, egg yolks. Young rodents eat a lot: on average, their daily portion of grain is 80–100% of the weight of the animal itself.
Younger age
Starting from the fourth day, the development of little rat pups occurs at a rapid pace.
- 4th day the ears open, the pups begin to distinguish sounds and hear rustling sounds;
- 6th body is covered with soft dark fluff;
- On the 8th, teeth emerge, except for the main incisors.
After 10 days of life, the pups become active. They crawl well and master the terrain. If these are pets, they should be handled more often so that the animals grow up tame. However, during the game they should not be left unattended, since coordination of movements is not yet developed, the kids can fall to the floor from a table, any height.
When to transplant young animals
The development of baby rats occurs rapidly. At the age of 25 days, it is already possible to place the male rats separately from the girls. This recommendation applies more to males, as they can mate with sisters or their mother. After about a month, it is advisable to seat the males, otherwise they will start fighting with each other.
The young animals are provided with fully equipped cages, the same as those for adult rats. Each animal should have its own resting house. To increase physical activity, a running wheel, ladders and tunnels are placed inside.
The diet of the younger generation must include fresh greens, wheat sprouts, as well as animal foods, which contain a lot of protein. 1-2 times a week, rat pups are given fish oil.
At 5-6 weeks, the rats can be given to new owners. You shouldn’t delay this, because the younger the pet, the easier it will tolerate a change of environment.
Location
Where the black rat lives is a very interesting question. The favorite habitat for the rodent is sea vessels. Rats live side by side with humans and eat identical food. They spread around the globe thanks to water transport.
The black rat is less inventive than its relative the Pasyuk. Content with little. Settles near reservoirs and rivers. But it is less attached to water than the gray one. Does not build nests in the ground, avoids water, but if necessary, swims quite a long distance. It does not dive because fish, fry, and amphibians are of little interest to it.
Willingly settles in the forest, fields, and edges. The lifestyle is more reminiscent of voles. In urban areas, it prefers sewers, abandoned buildings, garages, garbage cans, and entrances. Can live in a person’s house, occupying the upper floors or attic.
Prevention
When a rat has no problems and is not sick, its eyes, nose and mucous membranes are absolutely clean. When there is porphyrin in your pet's nose (for no reason), your pet requires the attention of a specialist. At the veterinary clinic, they will take tests and examine the animal, as a result of which it will be possible to understand whether everything is normal or whether there is a disease. In the latter case, the doctor will prescribe treatment at home or prescribe procedures at a veterinary institution.
To prevent the animal from developing bad symptoms, the owner must follow the following rules:
- the cage with the pet should be located in a quiet, calm place - the animal needs comfort;
- The animal should not be stressed, make noise, shout or wake it up abruptly - this will scare it;
- the rat must be fed healthy and wholesome food;
- You constantly need to monitor your pet, its condition, skin and mucous membranes.
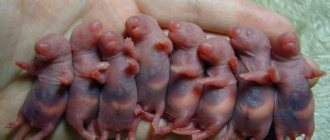
What do newborn rat pups look like?
The decorative rat bears its cubs for 20-26 days, the period depends on the size of the litter. There are from 2 to 9 babies in one litter.
Newborn rat pups look completely helpless. They are born naked, blind and deaf, with underdeveloped limbs and a very short tail.
Rats can only move their paws and open their mouths. Despite their helplessness, babies are able to find the only available source of nutrition, the mother's nipple, by smell.
At birth, a small rat weighs 4-6 g. If the litter is large, then it contains cubs weighing 3 g. The body length of a newly born rodent depends on the sex and is 5-9 cm. Boys are usually larger than girls.
Newborn rodents have pink, thin skin. Blood vessels and internal organs are visible through it.
How to feed baby rats
During the first 14-16 days, rat cubs feed only on mother's milk. Then they begin to become more active, crawling around the nest and even trying the food that their mother brings. 3 weeks after birth, the pups eat vegetables, grain mixtures, lean meat, eggs, cottage cheese, and fresh herbs.
There are often situations when small rats are left without maternal care. This happens for various reasons:
- Mom doesn't have enough milk;
- the female died after giving birth;
- someone touched the little rat with their hands, and the mother abandoned him.
In each case, the babies will have to be artificially fed, otherwise they will die.
Orphaned cubs must be kept warm. A lot of paper napkins are placed in the nest. They are replaced as they become dirty. To warm little rats, you can use a rubber heating pad or a plastic bottle with warm water.
To feed the litter, a cat or dog milk substitute, which is sold at a veterinary pharmacy, is suitable. If you can't find it, you can use baby formula. To increase the nutritional value, add a little condensed milk with a fat content of about 12% or glucose, as well as a little calcium gluconate.
It is convenient to feed small rats from an insulin syringe without a needle. The animal is carefully taken vertically in the left hand, and the head is held with the thumb and forefinger. The tip of the syringe is inserted into the mouth. The piston is moved very slowly so that the little rat does not choke.
Attention! If milk flows from the spout during feeding, it must be removed with a napkin. To clear the nasal passages of liquid, you should pinch the little rat's butt. When it beeps, the milk will completely leave the respiratory tract.
In the first week of life, rat pups are fed every 1.5 hours, then every 2.5-3 hours. At this age, they eat no more than 0.3 ml of formula at a time. It is quite simple to determine that the baby is full - his stomach is clearly visible through the thin skin on his stomach. It looks like a white transverse stripe. If its length is two-thirds the width of the body, then the stomach is full. Week-old rat pups eat about 0.5 ml of milk at a time, and at the age of 10-12 days - 1 ml.
Attention! Before each feeding, the baby rats receive a abdominal massage. This is necessary to improve intestinal motility. Gently move the fingertip clockwise for about a minute. Usually, after such stroking, the animals empty their bowels.
Interesting facts about rats
- During the Middle Ages, when a rat invasion was comparable to a natural disaster, in German cities rat catchers who presented 5 thousand rat tails were awarded special privileges.
- On the islands of Oceania, the small rat is bred as a pet for food.
- Karni Mata is an Indian temple where rats are welcomed, revered, fed, watered and protected in every possible way. A visitor who accidentally kills a sacred animal is required to bring to the temple a golden figurine in the form of a rodent.
- The gray rat consumes about 12 kg of food per year, but spoils much more. According to experts, the entire harvest of every 6 farmers goes to feed rats.
- In the US state of Illinois, it is illegal to “hit a rat with a baseball bat.” Violators face a fine of $1,000.
- In countries such as China, Vietnam, Thailand, India, Cameroon, Laos, Myanmar, Cambodia, Mozambique, Ghana, Nigeria, and in some areas of the Philippines and Indonesia, rats are eaten. They make soup from the rodents, dry them, and also cook the rats on the grill, first singeing the animal’s thick fur, which, when ignited, spreads an unpleasant odor. At the same time, people distinguish the taste of different types of rats and consider rat meat a delicacy, which, by the way, in some African countries is cheaper than beef or fish.
Reproduction
The Siamese color gene is recessive. This means the following: cubs with this color will be obtained only if both partners have this color.
The process of breeding Siamese rats at home is simple. To get healthy, beautiful offspring, you must adhere to the following rules.
- For mating, rats older than 3 months must be selected. The selected pair must be placed in a cage for several days.
- Pregnancy lasts a maximum of 24 days. The expectant mother should eat well; protein foods must be included in the diet.
- Bloody discharge and the animal's desire for privacy may indicate that labor is approaching.
- From 8 to 18 rat pups can be born. Females are good mothers; they surround their offspring with love and care.
- While the female feeds and cares for her cubs, they cannot be handled. Otherwise, she may refuse them.
- The cage should always be kept clean and practically sterile.
Watch the video below for all about caring for pet rats.
Caring for Baby Rat
Shortly before the baby rats are born, you need to find a suitable place for the cage. It is placed in a quiet room so as not to disturb the new mother and her offspring. If there are other pets living in the house - a cat or a dog, you should limit their access to the rodents' home.
The cage must be protected from direct sunlight and drafts. The suitable temperature for keeping small rat pups ranges from +22…+26 degrees.
When the female gives birth, it is advisable not to disturb her. During the first week, it is generally not recommended to disturb her, to clean the cage, and, especially, to reach into the nest with your hands to see what the little rats look like.
Of course, it is necessary to find out how many cubs were born, and also to make sure that they are all alive and healthy. It is better to carry out the first inspection of the nest in the absence of the female, when she goes out to eat. You need to carefully remove the roof of the house and look inside. Little rat pups should not be touched with your hands until they are 2 weeks old.
If cubs are found in the nest that show no signs of life, you should wear gloves and carefully remove them.
This is interesting! Rats usually eat stillborn babies. For people this is wild, but for rodents it is absolutely normal. In this way, the female replenishes protein reserves in the body in order to feed healthy offspring, and protects little rat pups from contracting dangerous infections.
The mother rat will take care of her babies herself. She feeds them and warms them, licks their bellies so that the little rats can defecate. The only thing required of the animal owner is to provide the female with good living conditions and adequate nutrition. Her diet should contain a lot of protein and vegetables. Little rats get protein from their mother's milk. Due to this, they are actively growing.
In the second week of life, the owner must examine the cubs, assess their fatness and general condition - it may happen that some of the little rats are retarded in growth and development. This can only be detected by visual inspection.
If weak babies are found in the nest and clearly do not have enough mother's milk, the well-fed pups will have to be separated from the female for several hours every day. At this time, weakened animals will be able to eat in order to catch up with the rest in development.
When the little rats' eyes have opened, they can be picked up without gloves. At two weeks of age, animals no longer need maternal care as much as newborns. Even if the female refuses them, the babies will not die.
Structure and appearance
In the wild, black rats hunt at night. Therefore, the body structure and appearance of animals are maximally subordinated to the main goal - to survive in any conditions. Rodents have incredibly strong, resilient bodies. They can adapt to changes in their environment.
Domesticated rodents quickly adapt to new conditions and adjust their biorhythms to the regime of their owners. There are several varieties of black rats.
Breed names often duplicate feline or canine species. Domestic animals can differ not only in fur color, but also in body type, eye color, weight, and life expectancy.
The size of dark-colored domestic rodents is much smaller than their gray counterparts. A distinctive feature of black rats is that the tail length (29–30 cm) exceeds the body dimensions (20–22 cm). The weight of large dark-colored individuals sometimes reaches 300 g.
The large black rat's round ears give it the appearance of a large mouse. These smart and curious animals with elongated muzzles have a good memory and cannot be offended.
Pets' eyes can be multi-colored, but most often they are dark. A barely visible tassel at the tip of the tail is the only decoration of these beautiful animals.
Black rodents are reliably protected from temperature fluctuations by a warm coat, which consists of top pile and undercoat. The color intensity of the fur depends on the habitat of the animal. Among southerners, the dark color is significantly diluted with gray shades, while northerners have black fur with a greenish tint.
How does mating happen?
Males are ready to breed at any time, but they become especially interested in mating during the female's estrus. At home, mice of different sexes are kept separately. A female is placed with a male only for mating. When rodents live together permanently, the mouse gives birth to one litter after another. This will negatively affect her health.
A female can only give birth to cubs if she meets a male during estrus. During this short period of time, her behavior changes. In the presence of a male, she raises the back of her body and freezes in this position for several seconds.
The acquaintance of opposite-sex individuals does not last long. The male then approaches from behind and performs sexual intercourse. Coitus alone is not enough to conceive babies. It is advisable to leave the couple together for a day to allow several mating attempts to occur. Then the probability of the mouse having babies will increase significantly. In the intervals between mating games, rodents eat, drink water and wash their fur.
Attention! The female should be placed in a separate cage the day after her meeting with the male. She needs rest while bearing her cubs.
In the wild, rodents breed only in the warm season. House mice breed all year round. The animal owner must control this process. Rodentologists recommend mating a female with a male 4-5 times a year. Due to frequent pregnancies and childbirths, immunity decreases and the risk of stillbirth or non-viable babies increases.
Development of baby rats by day
Newborn rodents grow very quickly, a defenseless blind lump becomes an adult after 4 weeks, males reach sexual maturity at 5, and females at 6 weeks. The development of rat pups day by day is as follows:
1st day
Immediately after birth, the pups are naked, pink, blind and deaf babies with underdeveloped limbs and a small tail, who can only squeak, suck and sleep.
5-6th day
The bodies of newborns begin to be covered with the first soft hair, the skin has become flesh-colored with dark spots, the presence of which determines the color of rodents.
8-10th day
The baby rats are erupting their first teeth, the babies are already covered with short velor fur, the cubs are becoming very nimble, they start fights over the mother’s nipple, their movements are not yet fully coordinated.
12-13th day
The babies' eyes open, the pups explore the territory, actively try to get out of the nest, but the rat diligently returns the children to their original place.
Growth and development of babies
Little rats grow very quickly. In the first week of life, they gain 3 g of weight every day. Babies actively suck mother's milk, which has high nutritional value. It contains almost 9% protein, the same amount of fat and 4% lactose.
In the first days of their lives, rat pups are constantly near their mother. She moves them from place to place to warm everyone with her body. Small animals do nothing but eat and sleep. On the second day, hungry babies may begin to make a barely audible squeak. Approximately 4 days after birth, the ears of rat pups rise. Now they can hear.
Already on the 4-5th day of life, you can determine what color the little rat pups will have. In light-colored rat pups, the skin remains pink, while in dark-colored pups, it acquires a grayish tint. During this period, the first soft fluff appears on the body.
At the age of one week, baby rats' incisors begin to emerge. The molars will appear no earlier than in 3 weeks. In some individuals they grow only on the 35-40th day of life.
The rate of tooth growth depends on the individual characteristics of the animal and diet.
One of the most significant periods in the life of little rats is the time when their eyes open. This occurs 14-17 days after birth. At first a small gap appears between the eyelids, but after a couple of days the babies begin to see.
From this moment on, the little rats become more active and begin to crawl out of the nest. They look around with great curiosity, go around every corner of the cage, learn to wash themselves and clean their fur. By the way, by this time it has already completely grown back. Between the 15th and 20th days of life, females develop nipples.
At 3 weeks of age, the pups look like their adult counterparts. Their body length reaches 14-15 cm, but the tail is still short. At 25 days the animals become completely independent. Females are already capable of becoming pregnant, but this is undesirable, since the body is not yet fully formed and strengthened. The development of rat pups continues until they are one year old.
Rats are omnipresent
Their settlements were found in freezers, where they built nests inside frozen carcasses, using animal tendons as building material. They raised offspring in such nests, eating frozen meat. black rat photo Rats are classified as pest mammals. Having existed in close proximity to humans for many centuries, they have adapted to a hidden way of life. Their activity is expressed in colossal harm to everything that man creates. Rats destroy crops, damage building structures, and chew through electrical wires. In addition, it is noted that they are carriers of infections that cause the outbreak of diseases that are deadly to humans, such as plague. Typhus, brucellosis, pseudotuberculosis. Fighting rat colonies with the help of chemical and natural poisons does not bring the desired effect. Rodents are capable of developing immune resistance to poisons used to exterminate them.
Why are rats dangerous?
Rats are a disaster for all humanity. They gnaw through walls in the basements of houses, sewer pipes, damage electrical mains, and damage crops.
Rats are carriers of more than 20 infectious diseases, such as leptospirosis, plague, salmonellosis, pseudotuberculosis and others. Many are dangerously fatal to human life.
It is difficult to exterminate rats using chemicals because the animal’s body quickly adapts to the poison and develops protective immunity to toxins.
Preventive measures
To prevent mice from wanting to settle in a house or apartment, it is necessary to deprive them of the opportunity to find food and modest corners. All products must be hidden and garbage must be taken out. Place cotton pads with a few drops of essential oil of mint, wild rosemary, and wormwood in the corners.
Things need to be shaken up, neatly folded and closet doors closed tightly. Arrange wild rosemary and wormwood branches.
It is necessary to clear pantries and other places of trash and unnecessary things. Keep books on closed shelves. Fix all water leaks.
Regularly wipe the floors with vinegar or turpentine. Throw out the trash and wash the bin to remove odors.
Little gray mice look very cute. But…!!! They are a source of infection and very often are carriers of many diseases that can be dangerous for humans and often incompatible with life. High fever, severe headache, shortness of breath, lethargy or confusion, a rapidly spreading rash, sharp pain in the lumbar and kidney areas are obvious symptoms of mouse fever in adults.
According to analytical information from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, a number of infectious diseases are transmitted to people from rodents (field mice, rats, squirrels). Adults suffer the course of the disease much more severely than children. Their body is characterized by the appearance of extensive symptoms and the development of various complications, while sometimes it can only occur like a cold. Men aged 16-50 years are most susceptible to infection.
Incorrect or late diagnosis, incorrectly selected treatment or lack thereof can lead to death. Although there is no cure for the virus itself, supportive therapy makes it easier to cope with the disease.
Mouse fever
– a natural focal rare infectious disease with an acute course (hemorrhagic fever, accompanied by renal, pulmonary or cardiac syndrome), where the reservoir of the pathogen is an animal (rodent class).
The causative agent of the disease
: Hantavirus, having different strains.
Affected areas
: small vessels, renal apparatus, lungs, heart.
Geography
: A variant of the virus is common in Eurasia that causes renal syndrome, i.e. affects the kidneys. In this case, the disease has a medical name (HFRS), leading to mortality in 10% of cases. Epidemic nephropathy (EN), which is one of the types of HFRS, occurs mainly in Scandinavian countries, but its mortality rate is several times lower.
An infected rodent carries the infection for two years. And it is assumed that only certain types of virus can kill them too. In other cases, the virus does not pose a serious danger to the rodent.
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is a rarer type of mouse fever, which occurs mainly in America. But, according to statistics, it leads to death approximately 7 times more often (76%).
Demography:
Anyone can get sick, but men aged 16-50 are at greater risk.
Incubation period
on average it lasts 12-15 days, but the individual tolerance of an adult, as well as the state of the immune system and predisposition to resistance, can increase the incubation period from up to 8 weeks.
Severity of the disease:
varies depending on the virus causing the disease. Infections caused by the Hantaan and Dobrava viruses tend to cause severe symptoms, while the Saaremaa and Puumala viruses are more easily tolerated. Full recovery may take several weeks or months.
Since we usually have murine fever, accompanied by renal syndrome, the article will focus mainly on it.
Determining the sex of baby rats
In baby rats, the sex can be determined no earlier than five days of age. The only thing that can indicate in small rats which individual is in front of you, female or male, is the presence of nipples in females. During this period, the animals still lack hair, and in girls you can find barely noticeable nipples. In boys they are completely absent, and in place of the genitals you can see small dark spots, which over time will secrete into the testicles.
Video: how to determine the sex of little rats
The sex of rats can be determined as early as five days of life. First of all, a male can be determined from a female by the presence of primary sexual characteristics
If you don’t want to pick up a rodent, then you can observe the behavior of the animal and pay attention to its dimensions, but these will be indirect signs
How long after birth can you pick up
Seeing small newborn lumps swarming around an adult female, you just want to pick them up or at least touch them. Under no circumstances should this be done. Firstly, their body is still very fragile and the slightest wrong movement or compression can lead to injury to the baby. Secondly, after you hold the baby in your hand, its coat will acquire a specific human smell. Mother rats often abandon such babies: they stop taking care of them, don’t feed them, and don’t keep them warm. The result is inevitable death. Despite all the caring behavior of females towards their offspring, they can kill a baby that emits an alien odor.
You will be interested to know what to do if decorative rats fight among themselves.
By three weeks, babies already look strong enough and can eat “adult” food. Even if the female does not want to accept a cub that smells like a human, it will be able to live and feed on its own. Experienced rat breeders recommend not delaying the taming of decorative rats. When the animal is a month old, it needs to be taken as often as possible, then the baby will be more obedient and affectionate.
Features of behavior
The character of these animals cannot be called simple. Siamese are characterized by alertness. If the animal has a bad upbringing, then it may attempt to bite its owner. This behavior needs to be stopped and try to find a common language with your pet as quickly as possible. To do this, you can use the following tips:
- from childhood, an animal needs to be picked up, talked to, called by name, so to speak, tamed and established contact;
- aggressive behavior of a rat can be stopped by light blows on the face, shouting or clicking on the nose;
- from the first minutes of communication you need to show that you are in charge.
What is porphyrin
Porphyrin also has a red-brown color, similar to blood. Such secretions are produced by the Harderian gland, which is located in the corners of the eyes, during stress, illness or pain. Porphyrin has the ability to bind metals. It performs certain functions in the rat’s body. First of all, it protects the eyes from light by lubricating the nictitating membranes. In bright light, this consistency is produced more actively. The Harderian glands are sensitive to ultraviolet rays and, under their influence, produce more porphyrin. This substance also signals the pet’s health status.
You should know that with age, the production of this consistency in this rodent increases. One-year-old specimens produce more porphyrin, even at the age of 3–4 months. But after 2 years, the amount of this consistency decreases, so when determining the normal volume of production of this substance, you need to take into account the age of the pet. Excess indicates problems in the animal’s body. In this case, it is better to take the rat to a veterinarian for examination.
Reproduction and lifespan of rats
Rats do not have a mating season; they can breed year-round. But the peak of sexual activity comes in spring and summer. The female mates with different males, pregnancy in rats lasts up to 24 days, and the lactating female carries the cubs for up to 34 days.
Rats prepare nests in advance and cover the bottom with soft grass, cloth, and paper for the birth of offspring. The cubs emerge naked and blind. When dead rat pups are born, the mother devours them; the number at birth can be up to 20.
- The male can eat all the offspring if there are non-viable rat pups; he does not take part in caring for them. The female, on the contrary, provides meticulous care, feeds milk, licks the babies and removes debris from the nest.
After 17 days, the little rats open their eyes, and a month later they lead a full-fledged life on their own. Puberty begins after 3-4 months, and they can reproduce 6 months after birth. Life expectancy is up to two years.
Gray rats breed up to 8 times a year, but black rats breed only in the warm season. Today, experts estimate that there are 2 rats per person in the world.
Rat bites and their dangers
Rats are also dangerous because they often bite people. Let us remember that with such bites there is a risk of infection with sodoku and tetanus, but even without that, the rodent bite itself is very painful and is often accompanied by bleeding. This is no wonder: with its jaws a rat can develop a pressure of up to 500 kg/cm2, which allows it to gnaw copper and lead.
Biting a human finger down to the bone is no problem for an adult rat. The bites themselves can fester when infected with a third-party bacterial infection, and without treatment, ulcers often develop at the site of the abscesses.
However, rats bite until they draw blood mainly for self-defense when they are caught or driven into a hopeless dead end. Very rare, but documented cases of these animals biting through the skin of sleeping people.
Rats often bite when they are very hungry. In this case, they tend to gnaw off the strong skin on the heels of humans; they also bite the feet of large animals; they can gnaw off the heels of elephants so that they cannot walk.
The famous animal trader Carl Hagenbeck had three elephants die in one night from rats gnawing on their feet. Small animals - rodents, lizards and frogs, birds in nests - are easily killed and eaten by rats. If this happens in a chicken coop or rabbitry, the damage from rats can be very serious.
Coat type
In addition to the standard gray rats with short shiny fur, there are unusual species of decorative rodents:
- Rex. These animals' fur is quite rough to the touch, curly and sticks out in different directions. Their distinctive feature is also their curled mustache and bushy tail.
- Velveteen. This type of rat has fairly soft fur, which lies in waves, but often looks disheveled.
- Fuzz. The body of these rodents is covered with white-gray down, which becomes longer and thicker on the face and stomach. Guard hairs are absent.
- Sphinx. The pink folded skin of the rat is devoid of fur. Individual fine hairs may be found on the abdomen and head.
- Double Rex. These rodents have hairless areas alternating with areas covered with hair.
There are also quite a lot of varieties of decorative rats that are not recognized by the international classification. But it is fair to note that this does not make them any less beloved by their owners.
I like it I don't like it
How are close relatives different?
It would seem that these species are similar, but they have the biggest difference at the genetic level. Rats have 22 sets of chromosomes, mice have 20. Hence the differences in intelligence, lifestyle and behavior.
Rats are cautious animals. They are cunning, easy to train, and dexterous. Their training takes place at the dog level. One of the trained rats, Magwa, a Gambian hamster breed, received merit and a medal.
Rats have a good sense of smell and can evaluate the quality of food, temperature and humidity. In a pack of rats there is a hierarchy and responsibilities. They protect the young, care for the sick, and avoid predators.
Mice are less intelligent and do not learn or act cooperatively. Small rodents are less organized. In case of danger, they do not defend themselves, but rush about, so they become victims of predators much more often.
Both types of animals can eat plant foods, but will not give up meat. But larger rodents, rats, are more likely to attack and attack others, even mice.
Coat color
There is a wide variety of colors and coat tones for decorative types of rats. Based on this criterion, they are divided into groups.
Homogeneous
With uniform coat color in decorative rats, all hairs should look the same and be the same color.
The following colors are available:
- black;
- white (albinos);
- Russian blue and smoky blue, which differ only in the intensity of the tone;
- brown-gray;
- platinum;
- beige;
- champagne
There are several types of light gray color:
- with a blue tint (Russian silver);
- with a pink tint (dav);
- with a chestnut tint (lilac);
The name of the color is also determined by the color of the eyes. For example, rats with champagne coat colors should have pink eyes. And in white decorative rodents they are red and black.
Ticked
Each fur of such a rat is colored in several colors:
- Agouti. The basis of the classic color is soft brown hairs with black tips. A silver-gray tone predominates on the belly. Blue agouti is characterized by a combination of brown with silver or cool blue color. The platinum agouti has light gray and beige hairs that are effectively complemented by a blue tint.
- Amber. An ivory band is visible on the orange and fiery yellow hairs. The undercoat is a delicate cream color, the eyes are pink.
- Cinnamon. On the back, red-brown hairs with a bright golden edging predominate, and on the belly, gray and silver hairs predominate.
- Faun. The predominance of coffee-golden color, the silvery tint to which is given by guard hairs. The fur in the belly area is silver-cream in color. Fauns have dark ruby eyes.
- Topaz. Light coffee hairs are combined with silver ones. In color, these rats resemble fauns, but have a lighter shade of undercoat, due to which the entire color of the coat appears less saturated. Most often, they can only be distinguished by specialists who know what color these two types of rats are.
- Pearl. The color contains beige, golden and gray shades. The belly is sandy, with a grayish tint.
Silver
A peculiarity of this type of rat is the combination of hairs colored silver and other colors in equal proportions. The fur of such rodents must shine and sparkle.
A silver tint can set off a black, blue or brown tone.
Combined
This type includes rats whose color contains 2 or more shades:
- Siamese. The rodent's fur is beige in color, which becomes more saturated in the back of the body. The tail is uniformly dark. Brown spots are located on the face, ears and the bottom of the paws.
- Himalayan. The uniform snow-white coat has dark brown spots. A special feature is the red eyes. Black-eyed Himalayan rats have cream-colored spots.
- Burmese. The main coat color on the body can vary from sandy to brown, with darker spots on it. The tummy of rodents is distinguished by a gray-white color.
- Sable. The coffee color is combined with dark brown spots on the limbs.
Rats that combine white and colored parts of their fur in a certain order are called marked. The marking may take the form of a cloak, hood or train.
Difference between rats and mice
Rats and mice are representatives of the same suborder, but they differ significantly in appearance and behavior.
The body of a mouse is small, up to 20 cm, weighing up to 50 grams, rats are twice as large, they are dense and muscular, weighing up to 900 grams.
Pronounced distinctive shapes of the head and eyes, in mice it is triangular and slightly flattened with large eyes, in rats the muzzle is elongated with small eyes.
A strong body and powerful toes allow rats to jump high up to 1 meter; mice cannot do such tricks.
Mice are cowardly animals and are afraid to appear in front of people, but this does not bother rats; they can defend themselves. There are many cases where they attacked a person.
Rats are omnivores, eating meat and plant foods. On the contrary, mice have a greater preference for cereals and seeds.
Dimensions
Size is the main difference by which these rodents can be distinguished. The average body length of a baby rat is 7–10 cm, the same as an adult mouse. And rats grow up to 25 cm.
The weight of rodents also differs significantly. Rats are larger and therefore heavier than mice. An adult weighs on average 220–250 g. Moreover, males are much larger than females. Their weight with proper nutrition can reach 450 g. An adult mouse weighs only 45–85 g.
Important! In rare cases, rats can grow to gigantic sizes. In nature, there were individuals whose weight exceeded 1 kg. The length of such a rodent can reach 40–50 cm.
Head and ears
Mice differ from rats in the shape of their heads. In rats, the muzzle is strongly extended forward. And in mice it is slightly shorter and has a triangular shape. Rats have much smaller eyes.
Outwardly, they resemble black beads. Mice have large and mobile eyes. Rodents also rotate their heads differently. To do this, rats need to move their torso, and mice can twirl it without the participation of the body.
Mouse
Rats and mice differ from each other in the shape of their ears. In large rodents they are small, triangular and covered with sparse villi. In some subspecies their ends are blunted.
A mouse differs from a rat in having larger, movable ears that it can move. Rats can't do that. Mice have round ears and no hair on them.
Paws and tail
Due to their size, rats move primarily in horizontal places. To find food and escape from predators, they need to run fast and jump high. Therefore, their paws are powerful and muscular, and between the toes there are rough outgrowths of skin visible - these are rudimentary membranes.
Due to their light weight, mice can easily climb vertical surfaces. They are helped in this by small and flexible paws with tenacious claws.
Mouse
Rats have a short tail. It is thick and bristly, there is no hair on it. Its size is approximately half the length of the individual’s body. Mice have a thin tail. Its length is at least ¾ of the body size.
Rat
Wool
Rats have dark gray, dirty-colored fur. The hairs are thick and coarse, and the skin underneath is easily visible.
Important! Decorative individuals have softer wool. Its color depends on the species. Pet stores sell white, red, gray and black rodents. There are also individuals with a hood of a different color.
Decorative rats
The fur of mice is softer and silkier. These rodents have a smoky, grayish color. The hairs grow denser, so the skin is not visible through them.
Mice