In 1785, South Africa was seriously affected by voracious insects that covered an area of 5,200 km². In a short period, almost all vegetation was destroyed, so the question of how to deal with locusts still remains relevant. Scientists have noticed that lonely individuals coexist completely harmlessly with people. However, swarms of insects resemble a fearless army consisting of many chariots. They quickly destroy fields ready for harvest, causing irreparable harm to farmers. Let's get to know the merciless enemy better and learn how to protect yourself from locusts mechanically and chemically.
How to recognize locusts
Inexperienced people may confuse a locust with a large grasshopper, but they differ in both appearance and feeding principle. The grasshopper eats small insects, and the locust eats exclusively plants.
Appearance
The body size of an adult varies from 5 to 20 cm. The hind legs of the insect are bent over the body; they are significantly longer than the hind and forelimbs. The transparent wings are practically invisible, as they are reliably protected by hard elytra. When opened, various patterns become visible on them.
If we look at the external differences, the grasshopper’s mustache is very long, while the locust’s is short.
The locust has short antennae, a large head and large eyes. Sounds during flight are produced through the friction of the elytra on the upper part of the hind legs. When insects fly across a field, a chirping sound of intense pitch can be heard over a long distance.
Locusts feed exclusively on plant foods: fields, gardens and forests suffer from the invasion.
Depending on the climatic conditions and environment, locusts have different colors. Several individuals produced in one offspring differ when growing up in different regions. The developmental stage of the insect also influences the shade. Single individuals are colored bright green, yellow or gray and have distinctive sexual characteristics, but when they join in flocks, these indicators are smoothed out. In flight, locusts are distinguished by speed and endurance. Sometimes she covers a distance of 120 km at a time in attempts to find food.
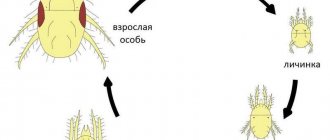
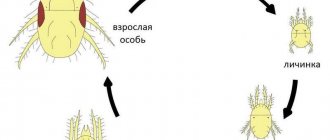
Development and characteristics of reproduction
The larvae resemble fully formed adult insects, but they cannot move with the help of wings. Instead of a developed apparatus, they have rudiments. After the maturation stage, the integument changes several times, then the pest takes wings and turns into an adult insect. The larvae cause great damage to plant roots; they are able to eat more than an adult insect.
Swarms have different characteristics depending on the temperature regime of the ground from where the locusts begin to fly away. The composition of the air also influences the formation of a colony. With a small temperature gap between the soil and wind, the flock descends low. When the temperature difference is large, the locusts can be seen from afar as a cloud, as they rise high. Small cumulus colonies, containing 1 to 10 million individuals, are less than 1 km across.
Why are locusts dangerous?
The insect is one of the most terrible among all pests of fruit-bearing crops. For crops, the breeding season is considered the most dangerous. The larvae of the pest are highly voracious, but remain solitary. It is difficult to recognize them, but in just a few weeks they form into adults and begin to move to other places. This leads to the death of most agricultural plants. At this stage, colonies already appear, which are easy to detect. But other difficulties arise - with their destruction.
The flight presents a formidable spectacle - flocks of several tens of square kilometers are obscured by the Sun.
The insect is not harmful to humans and their health. But the appearance of pests causes a storm of unpleasant sensations. Children may be afraid of locusts. If the territory is occupied by insects, then they interfere with working and staying there. They produce an irritating rattling noise, and pets also react restlessly to these creatures. With the growth of locusts in the garden, a real threat arises not only in relation to cereal crops.
Melon crops - watermelons, pumpkins, cabbage - may be affected. The plants don't stand a chance. It eats everything from roots to leaf tips. After the departure of the colony, the field remains deserted.
Under natural conditions, with temperature changes and a lack of cereal crops, the number of individuals in the colony decreases. The pest also becomes extinct due to disease. Typically, the restoration of locust numbers occurs within about 10 years, after which their massive invasions occur.
Reproduction and development stages
At the very beginning of the reproduction process, the males of these insects secrete and distribute a certain hormonal substance that has specific characteristics, which attracts females.
After this, the male connects with the female using the genitals and deposits a spermatophore at the base of the ovipositor. The mating process can last from two to twelve hours.
In the process of laying them out, it releases a foam-like sticky substance, which contributes to the normal development of the future generation of locusts. Small locusts begin to appear after 12-14 days.
After the female finishes laying eggs, she leaves her offspring forever. Born locusts make their way through the soil layer with great difficulty, going through 5 immediate stages of development. Over the entire life cycle, a female locust is capable of laying eggs 6 to 12 times.
The stage of formation and growth of the locust embryo goes through an indirect development cycle (when the larva differs in external characteristics from adults). The indirect development cycle of insects is divided into two types:
- Complete metamorphosis. This type of insect development is also called complete transformation. With this form of development, the larva that hatches from the egg grows and develops for a certain period of time, and then turns into a pupa. During the pupal period, the insect is in a stage of complete rest. At this time, all vital organs in the young individual’s body completely change their structure. After some time, a fully formed adult insect emerges from the pupa.
- Incomplete metamorphosis. This type of development is precisely characteristic of locusts. Incomplete metamorphosis implies the absence of the pupal stage and the transformation of the insect from a larva directly into an adult insect. At the same time, locusts go through several biologically simple lines of development.
Often, the first laying of locust eggs occurs in early May, when the temperature becomes more or less warm.
If the number of young individuals per unit area reaches maximum values, the locust begins to develop in a different direction. It acquires larger body and wing sizes. This is how huge herds are formed, which are subsequently capable of infecting various garden crops.
A few words about migratory “Asians”
Separately, it is necessary to say about. This type of insect is capable of daily absorbing an amount of food equal to the volume of feed for two sheep
. It is incredibly difficult to fight the “Asian” - before raiding the fields, it forms complex nests in hard-to-reach thickets in swampy areas. You can defeat Asian guests only in the following ways:
- chemistry;
- burning;
- digging.
Locusts are sometimes called the jaws of the wind, and this completely reflects their essence. In regions where locust outbreaks are a frequent event, this phenomenon is described as a black cloud rapidly approaching, leaving only bare ground after disappearing.
Therefore, learning to effectively combat this natural scourge is so important.
The appearance of locusts in a summer cottage threatens to destroy the entire crop, so fighting locusts will be the most reliable way to preserve your plants. To eliminate multiplying individuals, active chemicals are used, and folk recipes can be used as prevention.
How to recognize locusts?
The name “locust” is given to several species of orthopteran insects, the main feature of which is the ability to migrate long distances. In appearance, locusts are similar to grasshoppers, but adult individuals have bright wings that crack loudly.
The breeding period is considered the most dangerous, since insect larvae are particularly voracious. During the developmental stage, individuals stay apart, so it is very difficult to find and destroy the larvae; they do not accumulate in one place. Within a few weeks, the larvae turn into adult pests and begin to move to neighboring territories, which leads to the destruction of a large volume of agricultural crops. At this time, insects are already gathering in massive colonies, so it is very easy to find them, but now it is even more difficult to destroy them.
Why are locusts dangerous?
Locusts do not cause any harm to human health, but the appearance of a large number of insects in a garden plot is in itself unpleasant. Flying and jumping pests make it difficult to stay in the occupied territory; they irritate with their noise and bring a lot of trouble to pets. As a result, the hunting of jumping insects by pets leads to additional damage to agricultural land and crops growing there.
Gigantic, leisurely
The largest locusts on the planet live in the humid tropics. The size of females reaches 18 cm, weight - more than 10 g , males are usually slightly smaller. The diet of these insects consists not of cereal crops, traditional for the family, but of herbaceous shrubs and tree branches. The habitat of the insects is northern South America.
The color of males is brighter than that of females; the upper part of their bodies is bright pink, with a general green-brown color of the bodies . But the attractive appearance is deceptive - in a field, a swarm of such giants can eat several thousand tons of crops.
Interesting! This locust is leisurely, it jumps little and practically does not fly, slowly crawling from branch to branch.
Giant locust photo below:
Is your garden really being attacked by locusts?
First of all, you should determine whether locusts have actually inhabited your garden, because they could be simple green grasshoppers. Although they have some similarities in appearance, their lifestyles are fundamentally different from each other.
Locust in a man's hand
If we look at the external differences, the grasshopper’s mustache is very long, while the locust’s is short. They also differ in the nature of their diet: grasshoppers are predators; they feed on small insects and larvae, while locusts feed exclusively on plant foods.
Moreover, the list of what locusts feed on is quite extensive: reeds, reeds, vineyards; Fields, gardens and forests suffer from pest invasions. Therefore, we can say about it that this insect is best adapted to environmental changes.
If you are still sure that your plants have been attacked by locusts, you should immediately take protective actions.
Pest extermination
When insects take wing and form multimillion-dollar flocks, an individual gardener will not be able to cope with them. But it’s not difficult to get rid of the isolated migrants who appear on the garden plot every year.
Folk methods of struggle
Adult insects, larvae and clutches are destroyed by mechanical methods. At the end of summer, the soil is dug up to reveal egg pods. In the steppe zone, in early September, areas are burned, freeing the land from stubble, and at the same time from pests. After burning, only deep-lying egg pods remain alive. Digging in late autumn allows you to bring them to the surface and destroy them.
Insecticides
Insecticides begin to be applied early in the spring. Before sowing, the soil is sprayed with any preparation from the group of pyrethroids:
- "Fastacom";
- "Tsunami";
- "Alpha cypi";
- "Karate Zeon";
- "Fury";
- "Arrivo".
Later treatments at the end of May are attacks on larvae hatching from the soil. They are carried out with organophosphorus preparations:
- "Fufanon";
- "Karbofos";
- "Sumition".
In mid-summer, when the pest population is large, plants are sprayed with preparations containing imidalocprid or fipronil:
- "Adonis";
- "Tanrecom".
The adult insect acquires a durable shell and becomes insensitive to poisons. At this time, locusts can only be treated with the latest generation of biological products containing spores of fungi or bacteria that are harmful to insects.
Microbiological means of locust control recommended for private farms
| Tradename | Active substance | Time and method of application | Dosage |
| "Metarizin" | Mushroom metarhizium anisopliae p-72. | In autumn or spring, apply to the soil in any available way. If there is a threat of insects, spray the plants with a freshly prepared solution. | 10 g/area |
| "Dimilin" | Diflubenzuron | Spraying during the period of mass hatching of larvae | 0.05 l/ha |
| Spraying during the larval phase of pest development | 0.14 l/ha |
The post-Soviet space is home to about 400 species of insects from the order Orthoptera, the closest relatives of the locust. The most dangerous types are:
- Siberian filly - destroys meadows, pastures, grains, common in Siberia, northern Russia and Kazakhstan;
- migratory Asian locust - a large grayish insect (up to 6 cm long), natural foci are located in the lower reaches of the Volga, Ural, Don, Terek rivers;
- Prus Italiana - lives in the Middle Volga region, Western Siberia and southern Russia, severely harms industrial crops in areas of irrigated agriculture.
The fight against locusts has been going on for decades. During this time, the pest managed to acquire resistance to almost all pesticides. Insect resistance to insecticides is passed on from generation to generation. Modern drugs belong to the “bio” class. They cause outbreaks of diseases among insects.
At the beginning of the 20th century, B.P. Uvarov, a Russian entomologist and geographer who studied locusts in the Stavropol province and Tiflis, and then led the activities of the international center for the study of locusts in Great Britain, published the theory of phases. It was developed by a scientist based on studies of Asian locusts and Danish locusts. Uvarov proved that both species are identical and vary depending on the density of the pest. The more pests per square meter, the higher their tendency to spread.
In other words, at a low population density, sedentary locusts are born, and at a high population density, migratory locusts appear, which means that the process of pest emergence can be controlled by reducing the number of locusts per unit area. This is done by plowing the land on which the species lays eggs. By reducing the infestation of the outbreak, it is possible to prevent the transformation of harmless fillies into a dangerous polyphagous pest.
What you need to know about this enemy to defeat him
Locusts are born from eggs around May. Up to hundreds of insects emerge from one clutch (pod). They grow for some time in clump colonies, eating all the greenery around them. In the middle of summer, when there is little food left, the colonies “take wing” and migrate in huge masses to the north and west, with an average speed of up to two tens of kilometers per hour. Their flight is a rather menacing spectacle - flocks of several tens of square kilometers are able to obscure the Sun. In August, the hunger for pests increases many times over – insects begin to lay eggs. The insect digs a groove in the ground and squeezes eggs into it in a foamy shell. The shell hardens, turning into a capsule that saves the eggs from winter frosts. The top of the container is covered with earth for greater safety. And the process repeats again.
Various methods have been tested in the fight against locusts. Scientists have long tried to find a natural predator to destroy these insects. For example, in 1762, the mynah bird was imported to the island of Mauritius from India, and after 8 years the locust population dropped sharply. But this was not a universal solution. Moreover, it is extremely dangerous. Just remember how much trouble the Australians’ experiments in integrating rabbits and aha toads into the local ecosystem brought. By the way, at the same end of 2010, locusts in Australia captured an area of half a million square kilometers. There were other famous cases of “class struggle” against nature. 70s, China. There was a shortage of grain in the country, and it was believed that it was the fault of the birds. In particular, sparrows. The Chinese army began to fight them, shooting flocks of birds with shotguns and rifles. Dead birds were transported by the thousands of trucks. When the birds became scarce, the initiative again passed to the ubiquitous locusts, which were left without a natural predator. All of this is a reminder of how fragile the balance of the ecosystem is.
New method of fighting locusts (video)
But the struggle still did not stop. The main target was insect clutches - as the most vulnerable objects. Fields and floodplains, meadows and arable lands were plowed so that the egg capsules froze. In some cases, even shelling of territories with military artillery, burning of discovered swarms, and ultrasonic repellers were used. In affected areas, special trap ditches with shields were dug in order to disrupt the direction of locust spread. Chemical achievements were also used: dusting contaminated areas with HCH powder, a weak solution of arsenic, calcium arsenic acid or sodium. The latter compound was often supplemented with water, bran and molasses, turning into a poisonous bait.
Since 1921, V.P. Uvarov first published an amazing “phase theory” carried out on Asian locusts and Danish locusts. Its essence is that these types of locusts are the same original species, and their behavior is largely determined by the density of the insects. The higher the density, the higher the tendency of the bands to move, and vice versa. Moreover, low population density leads to the birth of sedentary locusts, and increased density leads to the birth of winged locusts. That is, the type and nature of behavior of an adult insect is determined at the stage of its maturation, and, therefore, this process can be regulated. In fact, the plowing of contaminated lands is a means of reducing the density of the locust population.
Despite significant theoretical and practical advances, pest control remains very challenging. The reason for this is a lack of resources: equipment, poison, qualified specialists. The difficulty lies in the fact that the breeding grounds for pests are vast uninhabited areas of the steppes, inaccessible areas. Thus, most often in practice one has to deal with already adult winged armadas of insects, and the success of the fight depends on the efficiency of “intelligence”, the speed of decisions made and the available “combat” resources.
Chemical method of combating migratory locusts
Treatment of large areas is carried out using aviation 20-30 minutes before sunrise, if the wind speed does not exceed 3 m/s. With evening pollination, less efficiency is observed.
To combat a single phase of locusts, poisoned baits are used. To prepare them, you need horse or sheep manure as bait, 12% hexachlorane dust at a rate of 200-400 g and 5-10 liters of water per 10 kg of manure. Baits can be introduced by aircraft, machines or manually.
Chemicals can be used to control the pest regardless of the time of year (from spring to autumn), but it is most effective to treat with insecticides in the spring, before sowing crops. The procedure is repeated a second time in case of a massive pest invasion.
Insecticides of the synthetic pyrethroid group are effective in the fight against migratory locusts: Fastak, Karate Zeon, Tsunami, Arrivo, Gladiator, Taran and others. When protecting against locusts, as a rule, take the maximum dosages allowed by the instructions of the drugs.
If there are older larvae, it is recommended to add organophosphorus insecticides (Fufanon, in an amount of 50% of the maximum dosage) to the solution.
During a locust invasion, the most effective drugs are imidacloprid-based - Confidor, Tanker, Image. They protect crops from pests for several weeks.
Dimilin (active ingredient Diflubenzuron 250 g/kg, wettable powder).
The uniqueness of this insecticide lies in its special mechanism of action: it inhibits the growth of insects - it stops the process of formation of chitin in the body of the larvae, as a result of which the molting process is disrupted and the death of the pest occurs.
The advantages of this drug are: low toxicity to humans, warm-blooded animals and beneficial insect fauna; rapid decomposition in water and soil; long aftereffect period (up to 40 days).
To protect against locusts, insecticide is applied when the pest is in the larval stage of development. The application rate of the drug is 0.14 kg/ha. Used in pastures, areas with wild vegetation, gardens and forest belts.
Locust video
The appearance of locusts in a summer cottage threatens to destroy the entire crop, so fighting locusts will be the most reliable way to preserve your plants. To eliminate multiplying individuals, active chemicals are used, and folk recipes can be used as prevention.
How to recognize locusts?
The name “locust” is given to several species of orthopteran insects, the main feature of which is the ability to migrate long distances. In appearance, locusts are similar to grasshoppers, but adult individuals have bright wings that crack loudly.
The breeding period is considered the most dangerous, since insect larvae are particularly voracious. During the developmental stage, individuals stay apart, so it is very difficult to find and destroy the larvae; they do not accumulate in one place. Within a few weeks, the larvae turn into adult pests and begin to move to neighboring territories, which leads to the destruction of a large volume of agricultural crops. At this time, insects are already gathering in massive colonies, so it is very easy to find them, but now it is even more difficult to destroy them.
Why are locusts dangerous?
Locusts do not cause any harm to human health, but the appearance of a large number of insects in a garden plot is in itself unpleasant. Flying and jumping pests make it difficult to stay in the occupied territory; they irritate with their noise and bring a lot of trouble to pets. As a result, the hunting of jumping insects by pets leads to additional damage to agricultural land and crops growing there.
Features of the parasite
Locust is a parasitic insect. It belongs to the true locusts. These are large grasshoppers with protective colors. Leads a herd or solitary lifestyle.
The color of the first type of locust is black with orange spots. This species has long wings. This allows insects to quickly cover vast distances.
Nutrition
Locusts are amazingly voracious.
It can destroy:
- Cane;
- Reed;
- Cereals;
- Garden vegetables;
- Hemp;
- Buckwheat;
- Fruits;
- Grape.
Winged locusts attack in swarms. She is able to instantly eat the crops in the fields.
How the locusts sing
How does a pest chirp? Its trills can easily be confused with the chirping of grasshoppers or cicadas. Their sound apparatus is quite simple. It consists of an impressive row of bumps on the thighs of the hind legs and a thickened vein on the front wing.
When the parasite moves its leg along the wing, abrupt chirping sounds are heard.
At noon, insects sing loudly. At dawn and dusk they chirp quite quietly.
How does the parasite live and reproduce?
Reproduction is considered the most dangerous period. The larvae of this pest are the most voracious. While developing, locusts try to stay apart. Therefore, detecting and destroying it is quite difficult.
Within a few weeks, the larvae transform into adults, quite large individuals. In search of food, they move to neighboring territories. This contributes to the destruction of huge volumes of agricultural crops. Finding adult individuals is easy, but poisoning them to protect the crop is difficult.
How to deal with a pest
How to get rid of locusts?
If traces of its activity are visible to the naked eye, you must resort to:
- mechanical cleaning;
- digging;
- burning the remains of cereals;
- chemical treatment.
Features of mechanical cleaning
Using this control method, you can get rid of several adult insects. If the crops are attacked by a whole flock, it is impossible to save them in this way.
Note! This method is best suited for eliminating insect larvae living in the ground at shallow depths.
This is best done in August. Particular attention should be paid to areas located near lowlands and natural bodies of water.
Features of digging
How to protect crops? It is recommended to find the larvae in advance and destroy them. This can be done by digging. This control measure does not always help.
During invasions there are no results at all. Many larvae have grown by this time. This technique will be more beneficial if you add special preparations to the loosened soil. This is best done during preparation.
Burning (not a humane method of locust control)
If ovipositions are found located near the ground surface, disposal by burning is recommended. This is possible when the depth of detection of clutches is no more than 5 centimeters. Otherwise, this will not be enough to protect crops.
More heat can be achieved by sprinkling problem areas with straw and peat. This helps to increase the depth of heating.
This method is suitable for field protection. It can be used for prevention when the parasite is found in neighboring areas.
After completing the procedure, the soil needs to be dug up. In winter, the cold will help destroy those pests that are hidden in the depths.
Chemical treatment
Chemicals (insecticides) can be used to control locusts. They protect greenhouses at any time of the year. But it is advisable to do this before sowing.
Important! It is recommended to carry out this procedure in the spring. The second time manipulation is carried out after the invasion - for prevention.
Treatment is carried out using synthetic pyrethroids and imidacloprids.
Among the most powerful chemicals are:
Areas where adult larvae are located are best treated with Fufanon. During the period of invasion, it is advisable to treat all zones with such poison as Image, Confidor, Taran.
To achieve the best effect, it is best to take the maximum dosage of poison.
Application of Fastak
The main component is alphacypermethrin. It has a powerful effect and affects the locust body with lightning speed.
It can be used as a means to combat not only adult insects, but also larvae.
The product is resistant to precipitation and is used in small doses. The drug has a repellent effect. Therefore, it is safe for bees. It is advisable to use it in the garden. Only freshly prepared solution is used.
Application of Caesar
This drug affects the nervous system of pests. The permeability of cell membranes is disrupted, and sodium channels are blocked. This helps the parasite die quickly.
The impact is immediate. Protection is provided for 2-3 weeks. It is advisable to use this product during the growing season. One or two sprays per season are enough. The last processing time is 1 month.
Tsunami
To prevent locusts from destroying crops, the drug Tsunami is used. It affects the nervous system of parasites. After paralysis of all limbs and organs, death occurs.
The tsunami stops egg laying. The process of feeding the larvae is slowed down. One of the main advantages is the instant impact on contact.
Has a high toxic effect. You can use the drug even in bad weather.
Karate Zeon
Karate Zeon successfully fights locusts. The product affects the nervous system of the pest. Feeding activity stops after a few minutes. Afterwards paralysis occurs, and then the death of the insect.
Note! The drug can be used both during planned treatment and in case of force majeure. The drug is compatible with many adjuvants and pesticides.
Application of Fury
The drug affects the nervous system of insects. The effect occurs within 20-30 minutes. To a greater extent, it helps with the appearance of parasites.
It is advisable to spray plants during the growing season. The solution must be freshly prepared. The procedure is carried out in dry, windless weather. It is advisable to do this in the morning. Leaves should be dipped evenly.
Arrivo
The drug affects the nervous system of pests. They die almost instantly. The main advantage is effectiveness in a small dosage.
Has a long lasting effect. This allows the number of treatments to be reduced. Does not have phytotoxicity. Safe for humans. But it is better not to let pets into the treated area for a while.
Application of Ram
Quickly destroys insects by acting on the receptor points of their nervous system. Stops the manifestation of resistance in parasites.
The period of protective action varies from 2 weeks to 1 month. Used in small doses. It is used in favorable weather conditions, but is resistant to rain and sunlight.
Damage from locusts in a garden plot
Larvae and adult locusts are safe for humans. They do not bite or attack people or animals. However, a large number of insects accumulated on the site is unpleasant in itself. The disturbed insect takes off, loudly cracking its wings, scaring children and pets. Dogs chase it around the entire site and damage the plantings in an attempt to catch the insect. Even a few jumping, crackling larvae on the site create the impression that the dacha is occupied by locusts.
The pest also causes direct damage - it eats plants, including roots. He especially loves cereals, pumpkins, and legumes, eating peas, beans, and even bluegrass without leaving a trace. The beds become empty, bald spots appear on the lawn - this is the result of the activity of the polyphagous pest.
The imago is superior to the larvae in harmfulness and completely destroys the plants, like a fire. They don't even disdain the thatched roofs of their houses. Having multiplied greatly, adult locusts are capable of leaving behind a lifeless space, since each individual must eat about 300 grams of vegetation during its life.
Measures to combat voracious insects
There are three main methods for controlling locusts: mechanical, agrotechnical and chemical.
Mechanical
Mechanical measures to combat these insects are ineffective, but in some specific cases they should be used.
Using mechanical measures it will not be possible to get rid of sexually mature fillies, but eggs laid in the ground can be destroyed.
The most dangerous breeding period for locusts falls in the middle - end of August, it is at this time that many agricultural crops are at their peak of growth.
Females lay eggs in the ground, so mechanical destruction is aimed at getting rid of eggs and preventing pests from multiplying.
If the field has already been harvested by the end of August, then soil is needed.
In some cases, it is advisable to use stubble burning, but in this way it will not be possible to get rid of all the eggs, since they are located at a depth of 5-7 cm, and a small fire will not be able to disperse a sufficiently high temperature to such a layer of soil.
Agrotechnical
Agrotechnical methods of controlling the future generation of fillies are used in large fields. To do this, using special equipment, the soil is harrowed and cultivated.
After such machinations, almost all of the laid eggs are thrown onto the surface of the earth and die after some time.
Control using agrotechnical methods is carried out in early or mid-autumn, thus it is possible to reduce the number of offspring of fillies for the next season.
Over the long history of agriculture, man has learned to cope with almost all insect pests. What is used: ingenious traps, various herbal decoctions and infusions, and a wide arsenal of chemicals. But, despite this, there are still pests today, the battle with which often ends not in favor of humans. One of them is the all-consuming locust, the attack of which can be compared to a full-fledged natural disaster. Today we will talk about the peculiarities of the life of locusts and the main methods of combating them.
Are locusts dangerous?
A representative of the Orthoptera family, the locust is very similar in appearance to an ordinary grasshopper, differing from it in its larger size (from 3.5 to 6.5 cm) and the presence of wings in adult individuals. The larvae hatch from eggs in May, and about one hundred individuals emerge from one clutch (egg capsule). The larva is distinguished from an adult insect by underdeveloped wings and the absence of genitals. Young locusts eat the surrounding greenery, and when it runs out, they grow wings and begin to migrate. At the same time, it gathers in huge flocks that can reach several kilometers in length. Moving in search of food, swarms of locusts almost in a matter of minutes destroy not only young shoots, but also mature trees and shrubs.
How to deal with locusts in the country?
Although for many residents of Russia and Ukraine the locust is a rather rare visitor, significant climate warming leads to the fact that its distribution area is significantly expanding. Most often, single individuals are found in summer cottages, which can simply be collected by hand. In regions where locust invasions are not at all uncommon, the following folk methods of combating it are used:
The fight against locusts cannot be done without chemical weapons. The preparations “Caesar”, “Fastak”, “Gladiator”, “Karate Zeon”, “Arrivo”, “Taran” are recommended for use during spring digging of the earth. In the midst of an attack, you can fight trouble with the help of “Condifor”, “Tanker” or “Image”.
Class:
Insects –
Insecta
Order:
Orthoptera –
Orthoptera
Family:
True locusts –
Acrididae
Genus:
–
Locusta
Creation of a dangerous “group”
In the past, farmers did not understand why the humble, solitary insects gathered in large swarms. This transformation of locusts into a dangerous pest seemed an incomprehensible phenomenon and even “God’s punishment.” Over time, scientists have discovered several reasons. One of them is a lack of amino acids and organic substances in the body. This occurs during dry periods when there is a lack of food. Females lay as many eggs as possible, and they develop an acute gluttony. Hot weather also influences particular activity and aggression.
Insects mercilessly devour grain crops:
- wheat;
- rye;
- oats;
- barley.
They do not pass by corn, sunflower, buckwheat, rice, soybeans, flax and hops. Swarms of locusts attack clover, alfalfa, and vegetable crops. They cope with fruit trees and berry bushes. First, the “army” marches “on foot.” But over time, the individuals, spreading their wings, move through the air. The movement speed reaches 15 km/h. In a day, the “flock” is capable of covering about 120 km, destroying all the greenery on its way. The procession continues until the individuals accumulate a sufficient amount of protein. After this, they regain the status of peaceful insects.
Measures to combat voracious insects
There are three main methods for controlling locusts: mechanical, agrotechnical and chemical.
Mechanical
Mechanical measures to combat these insects are ineffective, but in some specific cases they should be used.
Using mechanical measures it will not be possible to get rid of sexually mature fillies, but eggs laid in the ground can be destroyed.
Females lay eggs in the ground, so mechanical destruction is aimed at getting rid of eggs and preventing pests from multiplying. If the field has already been harvested by the end of August, then the soil needs to be dug up.
In some cases, it is advisable to use stubble burning, but in this way it will not be possible to get rid of all the eggs, since they are located at a depth of 5-7 cm, and a small fire will not be able to disperse a sufficiently high temperature to such a layer of soil.
Agrotechnical
Agrotechnical methods of controlling the future generation of fillies are used in large fields. To do this, using special equipment, the soil is harrowed and cultivated.
Extreme weather conditions have contributed to the developing crisis.
The reasons for the current locust outbreak lie in the cyclones and heavy rains of 2018-19.
Desert locusts typically live in dry areas of about 30 countries from West Africa to India, covering an area of about 16 million square kilometers.
But wet, favorable conditions in the southern Arabian Peninsula two years ago allowed the locusts to multiply rapidly over three generations, the UN says.
The surge has been developing since 2022
By early 2022, the first swarms of locusts headed to Yemen, Saudi Arabia and Iran. There they continued to reproduce and spread to East Africa.
By the end of 2022, new swarms had formed in Eritrea, Djibouti and Kenya.
Locust swarms are also forming along both sides of the Red Sea, affecting Egypt, Sudan, Saudi Arabia and Yemen, as well as along the border between India and Pakistan. The UN described the situation as extremely alarming.
Locust infestations are very difficult to control due to the huge areas they cover. Keith Cressman, however, believes that in this particular case the insects could have been controlled more effectively.