Home / Pests and diseases
Back
Published: 06/23/2019
0
5/5 — (1 vote)
Among potato pests, the Colorado potato beetle, which is distinguished by its endurance and gluttony, is usually put in first place. But another enemy is no less dangerous - the potato nematode, which is difficult, and most often impossible, to get rid of. Crop losses can be up to 50-80%, so the main thing is to prevent the appearance of the pest on the site.
- 1 Description of the pest
- 2 Varieties
- 3 Signs of potato damage
- 4 Control methods 4.1 Chemicals
- 4.2 Folk remedies
- 4.3 Agrotechnical methods
Description of the pest
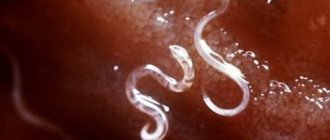
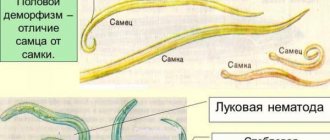
Nematodes are one of the most dangerous potato pests. This is a microscopic roundworm 0.6-1 mm long. It can live on the roots, tubers and stems of the plant. The female's body is round in shape and smaller in size than that of the male. In summer it is white, by autumn it acquires a golden-brown or brown tint.
Photo of potato nematode. Taken from wikimedia.com
The male lives for 1.5 weeks and dies after fertilization of the female. Females accumulate up to 800 eggs in their bodies. In the fall they die and turn into cysts in which eggs are stored. Under favorable conditions, egg capsules can be stored for up to 10 years.
Cultivation of nematode-resistant varieties
Over the course of many years of growing potatoes, domestic gardeners have noticed that not all varieties of this crop are equally affected by the nematode. Among potato varieties, there are some that show some resistance to these roundworms. Here is their list:
- Krinitsa;
- Sante;
- Atlant;
- Red Scarlet;
- Stonefly;
- Rosara;
- Breeze;
- Uladar;
- Lily;
- Veras;
- Lapis lazuli;
- Yanka;
- Rodrigue;
- Crane.
Although they say that the occurrence of a nematode on a site can be compared to a natural disaster, one should not give up. If you don’t fight it at all, you may end up without a harvest at all. Therefore, it is necessary to correctly carry out all agrotechnical measures, and if symptoms are present, spray the bushes with nematicides.
Types of nematodes
There are several types of pests, the most common in our country is the golden nematode.
Potato golden nematode
This type of nematode damages the roots of the plant, which become too branched.
Nutrients do not circulate well, and as a result, the lower leaves of the bush begin to dry out. The tubers are small or not formed at all.
Stem nematode
The pest attacks potato stems and tubers.
Dark spots appear on the skin of the tubers. The pulp becomes loose or turns into dust.
Root-knot nematode
This type of nematode destroys the roots and tubers of the plant.
Growths or galls up to 3 cm thick form on the roots. Potato tubers become lumpy. The pest also affects pumpkin crops.
Pallid nematode
On plantations affected by the nematode, rare, painful stems are formed.
There are no more than three of them, they turn yellow prematurely. The tubers are formed very small or not formed at all.
Signs of a parasite
Infection of vegetables is not accompanied by specific signs - this does not allow it to be detected in a timely manner. Symptoms are most often mistaken for a bacterial disease or nutritional deficiency.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
A gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert. See also: Mustard and vinegar against the Colorado potato beetle: proportions and processing rules
Ask a Question
Important! For the first few years, the pest is practically invisible and losses from it are insignificant. However, after 3-5 years, a farmer can lose up to 80% of the entire harvest!
The main signs of infection are:
- plant growth retardation;
- early yellowing leaves;
- weakened stem, sometimes turning yellow early;
- the lower leaves quickly fall off;
- delayed flowering;
- excessive bushiness of the vegetable;
- branched root system.
Suppression of infected bushes begins immediately after the first shoots - there are few leaves, weak stems, and insignificant flowering. Affected individuals die off long before the harvest begins.
Control of potato nematode
Pest control is complicated by the fact that it is difficult to immediately notice it on potatoes. Gardeners use different means.
Chemicals against nematodes
Chemicals are used when absolutely necessary because they are toxic.
The most commonly used means of contact action are:
- Lindan,
- Karbofos,
- Phosphamide.
It must be remembered that for greater effect, chemicals are combined with biological and agrotechnical means.
Folk remedies
Before planting potatoes, spray the infusion of sprouts from the tubers. This will lure the larvae out of the cyst, and they will die from lack of food.
Along the perimeter of the potato plot, plant plants that repel parasites:
- marigold,
- beans,
- calendula.
Biological products
Biological preparations have a narrowly targeted effect and act directly on the pest. These include: Basamil, Metarizin.
Agrotechnical methods
When planting potatoes, add the following to each hole:
- manure,
- chicken droppings,
- ash.
You can use mineral fertilizers containing:
- nitrogen,
- potassium,
- copper,
- phosphorus,
- cobalt
- and manganese.
Enriching the soil with minerals will prevent the development of nematodes.
Agrotechnical methods of getting rid of nematodes
Other preventive measures and means of combating nematodes without the use of chemicals are also conditionally effective. This:
- Maintaining crop rotation.
- Selection of varieties and hybrids that are relatively resistant to nematode damage (for example, for tomatoes - Nagano F1, Evpator F1, Malika F1; for garden strawberries - Festivalnaya, Zhemchuzhnitsa, Dessertnaya, Saxonka, Raketa; for potatoes - Scarlet, Fresco, Picasso, Diamant) .
- Careful selection of healthy seed.
- Warming the tuber bulbs and corms before planting for 15 minutes at a temperature of about 45-50°C or 3-5 minutes at a temperature of 55-60°C.
- Pre-plant disinfection of the soil with hot water, removal of the top layer, digging and mandatory mulching.
- Regular care of plantings - weeding and thinning.
- Careful watering - drops of water should not remain on the stems and leaves for a long time, because... this promotes the development of nematodes.
- Planting phytoncidal plants between rows that help repel pests, for example, marigolds or calendula.
- If an infection is detected during the growing season, promptly remove affected and weakened plants.
- After harvesting, remove all plant debris from the site and remove (burn) all remaining contaminated plant material along with the surrounding soil.
- To increase fertility and partially destroy the nematode, the area freed up after harvesting in August - early September is well sown with grain (preferably winter) crops. First, the area is cleared of weeds and plant residues, the soil is loosened and only then grains are sown “randomly” to a depth of 2-3 cm. When persistent frosts occur, the soil along with the winter crops is dug up, making a full rotation of the layer. In this way, it is enriched with organic matter and freed from the most dangerous pest - the nematode, which in such unfavorable conditions for it simply freezes out.
Preventive measures
Potato nematode does not respond well to various drugs; preventive measures are more effective:
- Competent crop rotation. Potatoes cannot be planted in the same area every year. Do this once every 3-4 years.
- Sow mustard, rye, legumes, marigolds, and calendula on the affected area. Excretion from their roots is destructive for the pest, but for the soil it is an excellent means of replenishing lost elements. Useful information: Green manure what is it Mustard as green manure Spring vetch - fertilizer for the garden
- Use urea. In autumn and spring, add the drug to the soil; the nematode does not tolerate this product. Learn how to use urea as fertilizer.
- Use healthy tubers. Before planting in the ground, they need to be treated with potassium permanganate.
- Increase soil fertility. There will be more earthworms, and they are the enemies of the nematode.
- Use nematode-resistant potato varieties. But after 3-4 years they need to be replaced with regular ones, as the pest quickly adapts.
- Burn the tops of diseased plants.
Helpful advice
If there is no nematode on the site, this does not mean that it will never appear there. Therefore, it is better to play it safe. How exactly? Experts recommend deep plowing (digging) in the fall, thoroughly washing planting material of unknown origin, periodically disinfecting equipment and not forgetting about plants that the pest is afraid of. In addition to marigolds, legumes, calendula, and mustard have a negative effect on the nematode. If you are not lazy in the fall and sow rye on your plot, it will destroy up to 90% of the harmful larvae, and in the spring it will be embedded in the soil and serve as an excellent fertilizer.
Prevention
The potato nematode is very dangerous: the pest is widespread and can lead to the loss of a significant part of the crop. In addition, cysts persist in the soil for decades. Therefore, it is very important to follow certain preventive measures, including the following actions:
- Select seed material carefully.
- Disinfect potato tubers before planting, for example, keep them for 30 minutes in hot water or in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate.
- Water the soil with boiling water the day before sowing to destroy the larvae and adults of the potato nematode.
- Marigolds or calendula can be planted between rows of potatoes.
- Periodically inspect the plants and immediately dig up bushes affected by potato nematode. At the same time, you cannot shake off the cysts from the roots - the plant must be taken away and destroyed. Carefully treat the remaining plantings with the described preparations.
What to remember
- It is impossible to notice the nematode , and the first signs appear already at a severe stage of infection. That is why it is so important to take all measures to prevent the appearance of the pest.
- Carry out prevention . This will reduce the likelihood of nematodes appearing and help save the crop.
- Use special preparations to kill worms . The most effective of them are nematicides.
- In the fall, carefully prepare the site for the next season: dig up, remove plant debris.
- Properly care for plants . It is especially important to monitor watering, since moist soil and high temperatures are the best conditions for this pest.
- Choose resistant potato varieties . Red Scarlet, Victoria, Volare are suitable. Before planting, it is important to disinfect the soil and seed material.
Nematode-resistant potato varieties
In 2022, the following nematode-resistant potato varieties are included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements approved for use on the territory of the Russian Federation:
- 7 For 7
- Aurora, Ivory Russet, Isle of Jura, Axenia, Aksona, Diamond, Almera, Alova, Alouette, Albatross, Alvara, Aramis, Argos, Arizona, Arctic, Arosa, Arrow, Arsenal, Artemis, Archidea, Aspia, Asterix, Atlas
- Baltic Rose, Batya, Bafana, Bellaprima, Bellarosa, Belmonda, Bernina, Bettina, Bonnie, Bonus, Bravo, Brook, Burnovsky
- Valise, Inspiration, Vega, Vektar Belorussky, Wendy, Verdi, Vershininsky, Vesnyanka, Vetraz, Victoria, Vilow, Vineta, Virage, Volare, Volat, BP 808, Vympel, Valor
- Gala, Gloria, Dove, Granada, Grand, Gulliver, Hussar
- Damaris, Danae, Debut, Daisy, Delicate, Dolphin, Dolphine, Right Hand, Jelly, Gioconda, Dido, Dina, Ditta, Donata, Dubrava
- Eurasia, Eurostarch, Elena, Zhivitsa, Zhukovsky Early, Zhuravinka
- Fun, Zekura, Zyryanets, Impala, Inara, Indigo, Irbitsky
- Canberra, Capri, Caprice, Captiva, Karatop, Carlena, Carmen, Caruso, Kemerovo, Ketsky, Keya, Kibits, Colette, Colomba, Kolyma, Queen Anna, Corolle, Courtney, Beauty, Beauty, Strong, Krinitsa, Crisper, Crispsforol, Christel , Body, Kumach, Courage
- Labadia, Labella, Lad, Ladoga, Lapis Lazuli, Laperla, Latona, Lady Anna, Lady Claire, Lady Rosetta, Lady Sarah, Leoni, League, Lilly, Lisana, Lukyanovsky, Lyudmila, Lux, Lucinda
- Madeira, Madeline, Manitou, Manifesto, Margarita, Masai, Maestro, Lighthouse, Melody, Memphis, Merlot, Meteor, Mia, Miranda, Bear, Molly, Mondeo, Mont Blanc, Mozart, Music, Mustang, Madison
- Navan, Nandina, Natasha, Naiad, Nida, Newton
- Oceania, Oxania, Oleva, Omega, Onega, Opal, Orchestra, Charm
- Padarunak, In Memory of Kulakov, Panther, Passwords, Picasso, Picolo
- Star
- Saw, Pyrol, Platinum, Blame, Prime, Pushkinets
- Ragneda, Radonezhsky, Ramos, Ranomi, Real, Red Anna, Red Lady, Red Scarlett, Red Sonya, Red Fantasy, Riviera, Ricarda, Rikea, Rodrigue, Rozhdestvensky, Rosanna, Rosara, Roko, Romantse, Russian woman, Royal, Rumba, Brook , Rowanushka
- Sagitta, Saxon, Salin, Sandrine, Sanibel, Santana, Sante, Sarovsky, Saturna, Safia, Sappho, Northern Lights, Northern, Silvana, Symphony, Sifra, Scarb, Slavyanka, Smolyanochka, Sprint, Stemluk, Madam
- Tanay, Toucan, Turbo
- Uladar
- Fabula, Favorite, Pheasant, Felox, Fidelia, Fioretta, Folva, Fresco
- Hostess, Huzar
- Cerata Kvs
- Sheri
- Evolution, Excellence, El Mundo, Estrella
- Hero of the day, Yuna
- Yanka.
- How to grow Red Scarlet potatoes correctly?
- Storing apples: store them for the winter at home
- Raspberry pests: how to deal with them on private farms
- Raspberry diseases: description and treatment
- Gymnosperm pumpkin: description and varieties
Affected plants should be dug up and burned.
Signs of the pest, description and treatment:
| Signs of appearance Description:
| |
| Chemicals Description:
| |
| Biological drugs Description:
| |
| Folk methods of struggle Description:
| |
| Prevention Description:
|
How to get rid of it in the soil?
How to get rid of nematodes in the soil? Root worms, which cause yellowish or brown galls on plant rhizomes, can also be controlled with preventive methods. When planting plants (especially succulents and shade-loving plants), use only disinfected gardening tools .
Do not plant plants in random gatherings ; it is better to allocate a pot to each bush for a short quarantine.
Warm up or treat the soil with hot steam for at least 40 minutes.
Each plant should be checked for any diseases or abnormalities .
The rhizomes of a newly purchased flower must be washed and left for 15 minutes in a special solution .
You can use a 0.5% solution of fosdrin or a 0.5% solution of the insecticide parathion . At the end of the procedure, wash the roots again, let them dry and replant the plant in new soil.
The most common plants susceptible to attack by roundworms are aloe, cacti and greenhouse inhabitants . They are the ones who need careful care and regular preventive measures to protect against nematodes.
Signs of potato damage
A plant affected by a nematode begins to turn yellow, and the process occurs from bottom to top. Leaf blades curl and turn yellow for no apparent reason. The development of flowers stops, the buds are small and deformed. Besides:
- A sign of stem nematode are thickenings and deformations on the stem and stolons.
- The gall can be found on the roots, where it forms galls (round or irregularly shaped swellings) in which females with larvae are located.
- If a bush is infected with golden potato nematode, cysts are visible on the root system - numerous brown balls into which fertilized females turn after death. One cyst contains 600-800 eggs.
Reviews from gardeners
Vlad K
Basically, this small parasite appears on depleted soils without the use of crop rotation. Sow the plot with green manure in the fall; when planting, add 2-3 cups of manure, 1 cup of ash and a spoonful of bird droppings into the hole. It is good to sow marigolds; the worm cannot tolerate them.
Source: farmerforum.ru
geniusik
To prevent potato nematode disease, you need to ensure that all planting material is healthy and use resistant varieties. But if the disease does appear, all affected plants should be dug up and burned.
Source: chudo-ogorod.ru