Photo of a parasite
The development of civilization served as an impetus for the rapid evolution of parasitic insects. The appearance of the head louse as a separate type of parasite, and then its morphotype - a linen variety called body louse, is due to the behavioral line of humanity.
According to the theory of evolution, body lice are considered a late type of evolution, since clothing, as a substrate for habitation, appeared much later than hair in mammals.
Two representatives of the same form interbreed well with each other, giving new generations of individuals best adapted to modern living conditions. The result of evolution can be considered the reluctance of the linen parasite to settle in the folds of woolen clothing, since a person does not wear woolen products, putting them directly on the naked body.
Externally, the body louse is very similar to parasites that lead their way of life under the scalp. The slightly elongated light gray-yellow body of the linen parasite barely reaches three millimeters in length. Laying eggs in the seams of clothes and on the lint of linen, the blood-sucking insect feeds on human blood, temporarily crawling onto the skin from the folds of clothing.
Unlike the head louse, the structure of the jointed legs of the linen parasite is not adapted to life on the surface of the human body, hair, and the fur of domestic animals.
Like the head form of the parasite, body lice lay eggs, or nits, firmly attaching them with a specific secretion. Thanks to this substance, removing nits from a woven surface is quite problematic - they are firmly glued to the fabric. The linen parasite prefers linen and cotton fabrics, avoiding settling in the folds of smooth and slippery silk clothing.
The appearance of the larva of the laundry parasite is no different from the adult, but is much smaller in size. Just like adult parasites, larvae feed on the blood of the host. A well-fed insect has striking differences from a hungry individual. Its dark abdomen makes it look like a flea, but unlike a flea, a louse does not have the ability to jump.
What does a body louse look like and how is it different from a head louse?
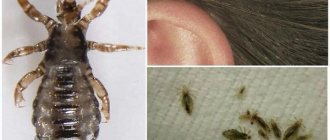
Body louse - or as it is also called, body louse, linen louse - differs from the head and pubic louse in the size and structure of the paws. This is the largest parasite, its size is 3–4 mm. It is similar in shape to hair. The body is oval, elongated. The shell is translucent, the insides are visible through it. Color – gray-yellow, pale. When saturated it turns purple.
The body louse has antennae, thanks to which it easily finds a food source and communicates with relatives. The mouthparts are the same as those of the head parasite.
The lice also have three pairs of legs, but their structure is such that they cannot move along hair with a round or triangular cross-section, like hair and pubic hair, respectively.
Like the head louse, the body louse feeds on human blood. This is a species-specific parasite, that is, it does not infect other species and does not live on animals and birds.
Lifestyle
The body louse does not live on the human body. These parasites live in the folds of clothing, underwear, bedding and accessories. They move onto the human body to get food, and after satiation they leave. You can see the parasite on the body only during feeding. An adult needs to receive food every 3 to 4 hours, so it goes hunting several times a day.
Body lice eggs are also found in clothes and underwear. They do not deposit nits in human hair or skin. Layers can also be located on the surface of clothing, but more often - in folds, seams, in the thickness of pillows, blankets and mattresses.
Life activity
Bed lice need human blood to thrive. To do this, 3-4 times a day they crawl onto the body, pierce the skin, sucking out up to 5 µl at a time. When a linen louse bites, it secretes saliva containing enzymes that prevent blood clotting. These enzymes cause specific reactions on the skin: pain, irritation, allergies.
The lifespan of one individual is on average 38 days. Every day, a linen louse lays 12-15 eggs (nits), which amounts to several hundred over the entire period. The embryo turns into an adult sexually mature louse in 5-7 days. If apartment types of bedbugs are active at night, then the linen louse also bites during daylight hours.
They actively reproduce in warm conditions (+31…+32ºC), withstand temperature fluctuations from 0º to +40ºC. At moderate temperatures (+10...+20º C), linen louse survives without food for up to 1.5 weeks, nits - much longer. They die when heated above +44ºC.
Body louse development cycle.
Life cycle
A nit is a capsule, an egg in which an insect larva develops. Its dimensions are no more than 1.5 mm; it can be difficult to discern nits; their accumulation looks like sand. The egg is translucent, attached to the surface with the help of a sticky secretion secreted by the female. Within 7–10 days, a larva, a nymph, emerges from the nit. In 7–10 days, it goes through several molts and becomes an adult, ready for reproduction. Females live up to 45 days, males - up to 30 days. An adult female lays 4 – 5 eggs per day.
Reader Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is there an organization for the extermination of body lice and what is its name?
The state organization for treating premises against parasites is the SES. There are also private companies that, if they have a license, can also conduct similar events.
How quickly do linen lice reproduce?
The fertilized female lays eggs, which after a few days transform into larvae. The full cycle of transformation into a sexually mature individual takes about 2 weeks.
Do lice live in feather pillows?
Lice can live in pillows, including feather pillows.
How long does a body louse live without a person?
A body louse can live without its owner for 4 days; if the air temperature reaches 30 degrees or higher, then it will live only 1 day. But at temperatures below 9 degrees Celsius, the parasite goes into hibernation and can live without food for up to 2 weeks.
Why are body lice dangerous?
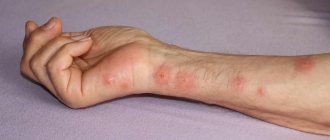
Body lice bites when they puncture the skin and suck out blood are painless. When these insects pierce the epidermis, they inject a substance into the wound that prevents the blood from clotting and at the same time relieves pain. After this effect wears off, when the louse becomes saturated and moves away from the bite site, the wound begins to itch unbearably.
Even one louse leaves several new bites on the body per day, and if their population grows, there will be many wounds on the skin. Body lice bites are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- redness;
- swelling;
- swelling;
- dried traces of blood on the wound.
With a large number of bites, areas of the skin acquire a blue tint.
The parasite can bite through the skin on any part of the body, but most often bites appear:
- on the neck;
- behind the ears;
- on shoulders;
- on the upper back;
- on the chest.
Lice bite both adults and children, but it is easier for them to pierce children's skin, so children are the most desirable victim for them.
Why are lice bites dangerous?
- severe itching;
- when scratched, the bite sites do not heal for a long time;
- wounds become infected;
- parasites are carriers of typhoid fever and other diseases;
- a person becomes nervous and restless from constant itching;
- allergic reactions, which are expressed by severe swelling, increased body temperature, inflammation of the lymph nodes and other signs.
Body lice infestation is called body lice. This is a disease that needs to be treated.
Help with bites
Having discovered bed lice bites on a person, the following tips will help alleviate the victim’s condition.
- The first thing that means treating linen lice bites is maintaining hygiene. It is necessary to take a hot shower, thoroughly washing off any parasites that have entered the body. In some cases, pediculicidal drugs with antiparasitic properties are used, which are used according to the instructions. Wash off the composition from the skin using a detergent.
- Hydrogen peroxide, Zvezdochka balm, tar soap or Rescuer will help reduce itching and relieve inflammation of damaged areas.
- If allergies occur, it is necessary to take antihistamines and gels that relieve the allergic process.
- Symptomatic therapy is necessary for skin complications and the development of pustular lesions.
How can you get body lice?
Contrary to popular belief, body lice are not limited to people who lead an asocial lifestyle. Of course, due to the fact that such people do not have access to washing and heat treatment of clothes and linen, it is difficult for them to get rid of body lice. But you can catch body lice not only from them.
You can become infected with body lice:
- using personal belongings of infected people;
- in crowded places;
- in direct contact with patients;
- in shops and markets when trying on clothes;
- on long-distance trains;
- in social institutions - hospitals, kindergartens, health camps, etc.
Unfortunately, treating public areas with a large flow of people does not always provide protection from insects.
Body lice do not have wings, they cannot fly, but they move quite quickly. They can cover a distance of 50 cm in just a minute, so they do not need very close or prolonged contact with a carrier of the parasites to become infected.
How to get rid of lice
These parasites are often confused with fleas or bedbugs. The type of bites and other symptoms are similar, and besides, they all do not live on humans.
If there is a suspicion of infection, it is necessary to inspect the bed and frequently worn clothing, paying attention to folds and gathers. This is where parasites can hide. Traces of vital activity - excrement, dead insects, empty nits - are also found in textiles.
If even small traces are found, it is necessary to begin a comprehensive fight. First, you need to wash all your linen and clothes. Before washing, you can soak items in a pediculicide solution. Insects die at temperatures above 40 degrees, so to be safe, it is advisable to wash items at 60 degrees or more for at least 30 minutes. You also need to iron the items, paying attention to the seams and folds so that there are no nits left in them. When unfavorable conditions occur, they can fall into a kind of hibernation and then continue their life cycle.
In summer, when it’s hot, you can take out linens, pillows, blankets in the sun. Lice are afraid of direct sunlight and high temperatures.
Temperature treatment also works in the opposite direction, that is, lice can be frozen out. In winter, you can dry things after washing in the cold.
You can use a steamer to treat mattresses, pillows, blankets, sofas and other upholstered furniture where pests may also be present. You can take things to the dry cleaner. This is especially effective for carpets, bedspreads and other heavy textiles.
Cabinet furniture, for example, cabinets for storing clothes and bed linen, must be treated with insecticides. A vinegar solution is suitable for these purposes. You can also use professional products - pediculicides, for example, Medilis-Super or Medilis-Malathion. They are suitable for treating any surface, that is, they can be used to treat cabinets, other furniture, and wash floors, window sills and other places where pests may be found. The treatment must be comprehensive, since with selective etching, lice can simply move to another place. Without shelter in underwear and without food, a louse can live up to a day, and then continue to parasitize and reproduce. To prevent this, you need to treat all possible places where the pest can hide.
Treatment of the body when infested with body lice involves the use of pediculicides. They come in the form of a spray, lotion or soap. You need to wash your entire body, including your head, diluted in the required proportion or ready-made. Since lice do not live in hair, one such treatment will be enough to wash away all the pests. Skin damage, scratches, and ulcers in their place are treated with conventional antiseptics and wound-healing drugs.
When dealing with lice, it is necessary to take appropriate safety measures. For example, chemicals should not be used in the presence of pregnant or nursing women or children under 5 years of age. When using special medications, you must be careful and strictly follow the instructions. It is forbidden for the products to come into contact with the mucous membrane. Do not inhale them, as they are toxic in high concentrations.
In general, fighting body lice is easier and faster than fighting head lice. The main thing is not to leave untreated clothes, linen or places where they are stored. If body lice appear on one family member, then you need to treat the belongings of all household members.
Prevention of head lice
Prevention of lice is not an absolute guarantee of protection against them, but it does help prevent their rapid development and spread. If you notice pests in time, fighting them will be quick and will not require too much effort.
It is believed that lice do not like strong odors, so bedding and clothing storage areas can be scented. Essential oils or bunches of dried plants are suitable for this. The strongest aromas:
- tea tree;
- geranium;
- mint;
- tansy, etc.
It is worth saying that tansy is a traditional means of combating lice of all types. It's quite effective. Therefore, if there is a possibility of infection, for example, if not very clean people live in the neighborhood, then you can hang bunches of tansy in your apartment or put them in closets. Tansy solution can be used to treat things or wash a person. You can even bathe children in it (in a small concentration and avoid ingestion or getting into the nose).
If you have been to a place where you could become infected with body lice, or have been in contact with a carrier of lice, upon arriving home you should treat your clothes - wash and iron them. You can also wash yourself with dust or tar soap. There is no such thing as too much caution.
Causes and routes of infection of parasites
Not only lice, but also other insects appear in the house in unsanitary conditions. Their appearance is especially important if in the house:
- lack of personal hygiene;
- lack of order;
- dirty things;
- improper storage of laundry;
- general use of personal hygiene items and things;
- use of a shared bed for sleeping.
If there are soft toys nearby, then parasites can also live in them. The favorite materials of lice are cotton, wool, and natural fabrics with an uneven surface.