Fleas are small blood-sucking insects that are probably familiar to those who have pets. The name translated from Greek means “wingless pump”. There are approximately 2,000 species of fleas worldwide. Some of them are typical for our area. Since ancient times, these insects have been under close attention, since they often annoy animals and carry terrible infections. What are fleas and where do they come from?
About 20 such creatures can appear in a person’s house. Varieties of domestic fleas are closely related to warm-blooded animals and birds, since each species prefers its own feeders. Only in case of rapid reproduction or out of despair do they settle on another animal or in a person’s house.
The most famous insects
The types of fleas considered are mainly those that are frequently encountered. Or are characteristic of a given territory. There is no point for an ordinary person to study a tropical insect in detail if we don’t have one.
cat flea
The insect often annoys cats, especially in the warm season. A cat can pick them up from other animals, or simply by walking down the street. Small insects make their way into the fur and begin to suck blood. With a large amount, the cat loses calm, does not eat, sleeps poorly, and becomes absent-minded. In addition to changes in behavior, fleas also change the appearance of your pet. The fur becomes crumpled and dull as the animal constantly itches. Near the roots, tiny grains of dandruff—flea eggs—are visible on the fur. Swelling, blisters, redness and scratches appear on the skin. This condition threatens infection and allergies.
Dog flea
Prefers dogs. The routes of infection are the same - from other animals or on the street. Even those pets that sit at home and walk on the balcony or in the arms of their owners run the risk of picking up fleas. Because small insects can enter the house through clothing. Signs of infection in dogs are similar to those in cats. The animal is constantly itching, trying to lick or pull out pests with its teeth. She whines in her sleep, loses her appetite, and becomes irritable. In addition to the fact that parasites can reward you with worms and other nasty things, dermatitis develops, which is difficult to get rid of.
Rat flea in the photo
The most unpleasant variety, since it chooses for its nutrition the blood of rodents, namely rats and mice. Animals are not known for their cleanliness and do not even disdain dead meat. Hence the risk of spreading infections and serious diseases. Insects appear in the house along with rodents.
What species are transmitted from animals
Rat, cat and dog fleas prefer to feed on the blood of animals whose skin is thin and hair is thick, which allows the parasites to move comfortably and find the most suitable places to bite.
In addition, wool makes it easier to lay eggs. However, these types of insects, if there is no suitable animal nearby, will readily attack humans. At the same time, they do not live in public permanently.
After the parasite drinks blood, it jumps to the floor, where it is less likely to be caught than on exposed skin.
Human flea
This species is often confused with lice and bed mites. There is something similar. They feed on blood and hide closer to the place where a person sleeps. They annoy you with strong frequent bites. They do not disdain pets. They live in the fur of pigs.
Chicken or poultry
Affects birds in the wild and in the chicken coop. Free birds can reward domestic chickens. Pests get deep under the feather cover. The behavior of the birds changes, and irritations and bite marks appear on the skin. A person can pick up an insect while being close to birds. However, fleas do not drink human blood for long. They don’t stay in the house, although they bite painfully and unpleasantly.
Ground (or sand) fleas
Wound from earth flea larvae escaping from
earth fleas
These pests are also called basement pests because they settle in dark, damp places and appear in the house even if there are no animals. The lower floors of multi-storey buildings and private buildings suffer especially from the invasion. They appear to be darker in color and slightly shorter in length.
Methods of control and prevention
People living in apartments on lower floors, keeping pets, having summer houses and garden plots, as well as storing things in basements, must first of all prevent the appearance of fleas.
During the winter heating season, a favorable environment is created in the basements of houses for the development and vital activity of synanthropic flea species. This is the optimal temperature and humidity required for ectoparasites.
In this regard, it is necessary:
- First of all, limit or completely eliminate the access of cats and dogs to basements by sealing holes and windows.
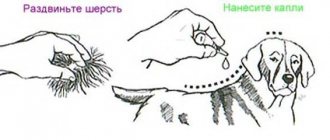
- When keeping pets, use hygiene products (shampoos, soaps) based on insecticides, flea collars, etc.
- After deratization (destruction of rodents), immediately carry out disinfestation (extermination of insects).
- All flea-infested premises in one building are treated simultaneously (on the same day) or for 2-4 days in a row.
Do you have fleas? Contact us! Our specialists will not only correctly identify the type of fleas and develop a strategy for a set of measures, but will also carry out effective disinfestation of your premises with suitable preparations.
Anatomical structure of an insect
People are often interested in the question: “Does a flea fly?” not really. Thanks to activity and high jumps, this impression is created. In appearance, the varieties differ little. Mainly in size and color.
Body length from 2 to 8 mm. On average 3-4 mm. The body is flattened from the sides and extended upward. Divided into 3 parts: head, chest, abdomen. 3 pairs of legs are located in the chest area. The last pair is much longer and more springy, allowing you to jump long distances and high up. The presence of a sensory organ helps to detect air vibrations, the presence of carbon dioxide, various odors and temperature. In this way, the insect finds food. There are no wings. Body color ranges from light brown to dark, almost black.
They feed exclusively on blood. They prefer their own type of animal. Dogs don't stay long on cats, cats don't stay on rats, and so on. Man is also a temporary phenomenon. After a good meal, the insect can starve for months. Hence the great vitality and adaptability to life.
Biological portrait
Pet owners know well what fleas are, as they often encounter this problem with their pets. If you look at the insect close up, you can see a lot of detail. Scientists, studying the flea under a microscope, noted the general similarity of all species:
- All parasites have a narrow body, laterally compressed, but smooth and covered with bristles and spines, which help them to hold well and move in fur, feathers, between the folds of linen and clothing.
- Despite the fact that there are only three pairs of legs and a complete absence of wings, the flea has good jumping ability and great speed of movement. It is almost impossible to catch it with your hands and crush it.
- The size of the flea varies from 1 to 5 mm. In some species, females can reach 10 mm in length. Behind the eyes are antennas that are used as a navigation device, determining location in space, obstacles, and picking up sounds and smells.
- Only fleas have some structural features: in the back of the abdomen there is a sensory organ that is capable of detecting the slightest vibrations in the air.
- The color of the young bloodsucker is black; brown or yellow fleas are found only in adulthood.
- The mouthparts are designed to pierce the skin and suck out blood. Unlike other blood-sucking insects, the flea's proboscis does not have a second channel for injecting an anesthetic enzyme, so bites are very painful.
Flea
The flea's wings have lost their function and turned out to be vestiges due to the insect's transition to a parasitic lifestyle. But the flea has a well-developed and strong second, and especially third, pair of legs, which helps it jump up to half a meter in height and up to one and a half meters in length, staying on the surface at any angle.
Interesting!
While jumping, the insect constantly changes direction. The jump itself gives the flea an acceleration that is 50 times greater than the acceleration of a spaceship.
The flea weighs on average 0.03 grams, reproduction occurs at a rapid pace, laying approximately 1,500 eggs during its life. The transition stage between eggs and larvae lasts about two weeks. The larvae are worm-like, move quickly, feed on decaying debris, do not like light, and try to hide in cracks, carpets and other dark places.
Life cycle
The insect goes through 4 stages of development:
- Egg;
- Larva;
- Pupa;
- Adult.
Already on the 2nd day after fertilization, the female lays eggs. Moreover, he doesn’t do it in an organized manner, but throws it out wherever he can. He doesn’t choose a special place. This usually happens on the animal and the eggs fall down. Can produce up to 50 eggs per day. Laying is done in portions of 5-15 pieces. This number is 400 per month. Over his entire life, about 2 years can save 1000.
The flea remains in this state for approximately 14 days. Then a larva - a worm - is born. Worms crawl into dark, damp places. They feed on undigested feces of adults or organic food. During its existence, the larva molts 3 times. Gradually turns into a pupa. The entire life cycle of the larva is 15 days. Under unsuitable conditions, the pupa can remain dormant for about 1.5 years.
Unusual facts about fleas
Interesting facts about fleas are collected in the 6-volume edition of the Catalog of the Rothschild Collection of Fleas in the British Museum. The structure of the flea was studied by M.L. Rodschild, daughter of the famous Charles Rothschild, who collected the largest collection of these insects. It was she who first began to study the mechanism of flea jumping and fully described what they are.
Interesting!
The color of the “vampire” coat depends on the color of the fur of the animal on which the insect parasitizes. There are red, black, and brown fleas. Insects of different ages also differ in color - the darker the color, the younger the imago. The brown digestive tract is visible through the white or yellowish coat of the larvae, as they feed on coagulated blood from the excrement of adult insects.
The weight of blood that a bloodsucker drinks is 6 times greater than that of a flea. Blood helps her not only survive, but also reproduce. A hungry “vampire” falls into a lethargic state. But as soon as you feel the approach of food, the insect “comes to life” and jumps onto the victim.
Flea eggs
Females mate once in their lives, but produce 500-800 eggs. A well-fed female throws out eggs with force, scattering them around. Household fleas lay eggs in carpets, animal bedding, and their fur.
Why are insects dangerous?
What diseases do fleas transmit? During an epidemic, these are the first carriers of infection. They carry pathogens of 25 diseases. Sometimes such infection is fraught with serious consequences and threatens death.
- Plague;
- Mycobacterium;
- Tularemia;
- Brucella;
- Typhus;
- Hepatitis.
This alone is enough to begin an intensive fight against parasites. The bites themselves also have a negative impact on the skin. Because they cause irritation, redness, swelling and severe allergies. If there are animals in the house, you need to start pest control with them. It’s better to constantly monitor your pets: bathe them with a special shampoo, put on bracelets and drop drops on the withers. The house can be destroyed with folk remedies or professional insecticidal preparations. In any case, there is no point in delaying the procedures. Since 25 females can multiply by a quarter of a million in a month.
Parasite behavior
Appearance of a flea
Not everyone knows what fleas look like. People who do not have animals in their homes usually have very general ideas about these insects. A person may not know whether fleas have wings. He, unlike a zoologist, is not interested in the question of the number of legs a flea has. But this does not mean that he will never encounter this phenomenon in his life. Parasites can be accidentally brought home from stray dogs and cats from the street. Infection is possible while relaxing in the forest or on the beach.
Fleas are found in all seasons of the year. Both males and females feed on blood. They live in the nests of birds, squirrels, in the burrows of gophers, hamsters, jerboas and other small animals, and are distributed throughout the world. The main hosts are mammals. Representatives of fleas have been found even in Antarctica. But against the general background, the colony of insects that bite humans is not so numerous.
The feeding process can last from one minute, if the parasite is disturbed, to several hours. Some species require multiple meals, others are rarely saturated, but in excess, without even having time to digest the incoming blood. There are insects that leave the owner after their meal, but there are also those that remain in the animal’s fur until the next attack of hunger.
Features of character and lifestyle
Photo: Flea insect
Some fleas (such as rabbit fleas) are very host specific, while other species parasitize a variety of mammals. The cat flea infects not only the domestic cat, but also dogs, foxes, mongooses, possums, leopards and other mammals, including humans, if its normal hosts are not available.
Related mammals tend to parasitize fleas, which are themselves related. Thus, peak rabbits (Ochotona) living in the rocky mountains are infested with two distinctive genera of fleas that are also found on peaks in the mountains of Asia, indicating a close phylogenetic relationship between these geographically separated hosts. Bird fleas have relatively recently adapted to their hosts. They share several similarities, one of the most obvious of which is the increase in the number of ridges on the upper surface of the thorax, which serve to anchor them within the feathers.
Interesting fact: Monkeys do not eat fleas, nor do horses and most ungulates. The most parasitic group of mammals are rodents. Their habit of building nests in burrows promotes the development of flea larvae. Animals without permanent residence tend to carry fewer fleas.
Although both flea sexes feed voraciously and repeatedly on blood, they survive for varying periods of time, regardless of the host. For example, a rabbit flea can survive nine months at temperatures near freezing without feeding.
Classification
The flea order includes more than 2000 species of insects. They are united into 15 families, which, in turn, consist of 200 genera. They all have almost the same body structure and lifestyle. Parasites are classified mainly according to one characteristic - the type of animal on which they feed. Although insects do not have strict specialization, they still prefer a certain type of blood. Currently, the most common types of fleas are:
- feline
- canine
- chicken
- human
- rat
- goat
- elk
- rabbit
- mouse
The list can go on for a long time. There is, perhaps, not a single creature on Earth that does not have its own blood-sucking “parasite”. At the same time, parasites are not particularly picky when choosing food. In the absence of “their” animal, they easily switch to feeding on the blood of another species. For example, a cat flea can be found on a dog, and a rat flea can easily feast on human blood. Such illegibility often leads to confusion when trying to classify a population of insects, especially since the species differ little from each other in their structure and way of life.
Interesting fact! Fleas are extremely tenacious. It is a known fact that an insect, frozen for a year, woke up from hibernation and, as if nothing had happened, continued to live.
How to get rid of it?
Parasites must be combated; modern drugs will help even in advanced cases. First you need to determine where the insects in the house come from. So, if fleas were brought by pets, they need to be treated. If parasites are coming from the basement or from neighbors, seal the existing cracks. To get rid of fleas at home, we recommend using modern insecticidal preparations that do not have a pungent odor and do not harm people and pets.
Chemicals
Since a flea cannot eat the bait, insecticidal preparations are produced in the form of a spray, powder, or aerosol. All means affect the nervous system of the parasite and paralyze it.
- Aerosols will help when treating a large affected area. Be sure to evacuate all residents, after the procedure, ventilate the room and do wet cleaning.
- Powders are distributed in habitats and have a long-lasting effect.
- Liquid microcapsules are not washed out after cleaning.
The most popular and effective are:
- Raptor spray, marked “against crawling insects”, has a pleasant smell;
- Combat - spray, analogue of Raptor;
- Sinuzan is a professional product with a rather unpleasant odor;
- Chlorpirimark is suitable not only for removing fleas, but also the Colorado potato beetle;
- Biorin is a professional product that destroys all existing insects;
- Dust is especially effective against parasite larvae;
- Delcid is an emulsion intended for pets;
- Pyrethrum - powder scattered in corners, poisons parasites.
After killing the insects, you need to do a wet cleaning by adding ammonia or eucalyptus essential oil to the water. It is advisable to place branches of wormwood and lavender under the bed.
How do fleas bite humans?
The flea pierces the skin when it bites, causing stabbing pain and unbearable itching. At the same time, it does not secrete an anesthetic substance, but introduces enzymes that prevent blood clotting. Since the parasite does not have a proboscis like mosquitoes, it has to penetrate the layer of skin to reach a blood vessel. The bite site swells as if from a cigarette burn. After the fleas are saturated, the wounds converge, which prevents blood from escaping.
Each person reacts to a bite differently. For some, the itching goes away quickly, while for others, signs of inflammation persist for several days. With pulicosis, the skin swells, ulcers appear on the oral mucosa, and the central nervous system is affected. An allergic reaction to human bites causes fever, chills, and indigestion.
Systematics and characteristics of the order “fleas”
Representatives of this order with complete transformation are secondarily wingless. They completely lost the ability to fly during adaptation to ectoparasitism at the adult stage. These bloodsuckers are carriers of pathogens of various diseases in humans and animals. They have a highly specialized oral apparatus designed to pierce the skin of the victim and suck out blood.
Information about the taxonomy of representatives of the order “fleas”:
| Categories | Category names | |
| Basic | Kingdom | Animals |
| Chapter | Bilaterally symmetrical, bilateral | |
| Type | Arthropods | |
| Class | Insects | |
| Squad | Fleas | |
| Intermediate | Sub-kingdom | Eumetazoans, or true multicellular organisms |
| Subsection | Protostomes | |
| Supertype | Shedding | |
| Subtype | Tracheal, or tracheal-breathing (parous) | |
| Superclass | Hexapods | |
| Suborder | Ceratophyllomorpha | |
| Hystrichopsyllomorpha | ||
| Pulicomorpha | ||
| Pygiopsyllomorpha | ||
What diseases do fleas carry?
These insects are dangerous because they can be carriers of pathogens of a number of diseases, some of which can cause the death of the sick person. By themselves, they cause 2 diseases in the bitten person: pulicosis and sarcopsillosis, or tungiasis. The infections they carry depend on the species of parasite. Flea saliva that enters a person’s bloodstream through a bite can become a source of the following diseases:
- plague;
- tularemia;
- typhus;
- salmonellosis;
- brucellosis;
- listeriosis;
- rickettsiosis;
- hepatitis B and C;
- encephalitis;
- trypanosomiasis, etc.
Most bloodsuckers can transmit infections. The total number of diseases transmitted by them includes more than 25 names. Also, these ectoparasites can act as intermediate hosts of some parasitic worms, such as common nematodes.
Signs of appearance in the apartment
Since these insects are small in size, detecting their presence can be difficult. One way is to spread a white sheet on the floor, on which the parasites will be visible after some time. The presence of small red spots on exposed parts of the body, most often on the legs, may be a reason for suspicion. Elements of the rash in this case appear in the morning and are accompanied by severe itching.
Even if the owner of a four-legged friend has no idea what fleas look like on dogs, he should be alerted to changes in the pet’s behavior. For example, a dog becomes restless, irritable, constantly itches and gnaws something out of its fur, then an allergic reaction occurs at the site of the bites, and the hair falls out. When the described symptoms appear, feces of fleas and small dark insects can be found on the dog’s skin, which quickly disappear from view when examined.
Cat fleas behave in a similar way. In addition, the appearance of fleas in a cat can be signaled by helminths, which are detected when examining the feces in the animal’s tray. Also, when bathing, you can notice insects trying to actively move to dry parts of the pet’s body, dark crumbs of feces in the water.
Sometimes fleas are confused with other blood-sucking parasites. Without knowing what bed fleas look like, when examining a place to sleep, they can be confused with lice or bedbugs.