It is generally accepted that only river fish can be infected with parasites, and sea fish cannot. Then where do the red and orange worms in pollock come from? “VredStop.ru” figured out the issue. The fact is that pollock belongs to the so-called cod fish species. They are highly susceptible to helminthiasis. Moreover, the most dangerous parasites cannot be seen without a microscope. They are about a millimeter in size and are found not only in the belly, but also in the meat, gills, eyes, and also on the scales of the fish.
Orange and red worms rarely cause illness in humans. These are acanthocephalans that attach to the intestinal walls of pollock. By themselves, they are light yellow, but after drinking blood, they acquire a brighter color. If the fish has been shock-frozen, clean the acanthocephalan thoroughly and heat the meat for 20 minutes.
A little history: why were only pollock backs sold in the USSR?
Historically, people have always treated pollock as a cheap food product. In the USSR, fish was sold everywhere in canteens. But the production of food products was greatly hampered by a speculative campaign that began in Europe in the early 70s. Thanks to television, pollock gained the reputation of being a fish heavily affected by nematodes (worms). There was a serious stir of rejection not only of pollock, but also of cod.
Very soon, studies carried out in European countries showed that the fish is absolutely harmless to human health, even if affected by worms. When frozen, nematodes die within 24 hours. In Europe, opposition to pollock has been reduced to zero. But in the USSR, people for a long time avoided buying products made from it. This forced producers to introduce into circulation the “back” of pollock, devoid of belly and intestines. Only 40% of the whole fish was left, and the rest was sent to waste.
Are worms in pollock dangerous for humans or not?
In most cases, worms in pollock are not dangerous to human health. The fish undergoes shock freezing, which is akin to its disinfection from helminths. Parasites die at critically low temperatures and cannot reproduce in the human body.
Cold processing of fish occurs on fishing vessels, where it is stored in refrigerators at a temperature of -25 degrees. After this, the fish is kept in refrigerated cars with a temperature of -18-25 degrees. According to clause 4.7.1 of SanPin 3.2.1333-03 “Prevention of parasitic diseases on the territory of the Russian Federation”, if these conditions are met, pollock is considered disinfected.
Moreover, according to the law, worms found in the digestive tract or in the gills are not taken into account, according to clause 5.2.8 of SanPin 2.3.4.050-96 “Production and sale of fish products.” Paragraph 5.2.7 states that to determine the food and feed suitability of marine fish, only parasites that are found in muscle tissue are important.
Most producers provide trial lots of fish to check for compliance with standards. Of course, no one deliberately looks at her for helminths. It is unrealistic to check every fish.
Pyloric appendages
Great Soviet Encyclopedia. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia. 1969—1978.
See what “Pyloric appendages” are in other dictionaries:
PYLORICAL APPENDICES - blindly ending intestinal outgrowths that serve many people. fish and some insects to increase digestion. surface and neutralize food during its transition from the acidic environment of the stomach to the alkaline intestine. In fish, P. p. usually extend from the beginning of the middle ... ... Biological encyclopedic dictionary
Stomach - I The stomach is an expanded section of the digestive tract, in which chemical and mechanical processing of food is carried out. The structure of the stomach of animals. There are glandular, or digestive, glands, the walls of which contain... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
What do worms look like in pollock, and how do they differ from intestines?
The intestines in not completely gutted pollock look like large worms or helminth larvae. This is what they look like in the photo:
The picture is frightening, but in fact it is part of fish anatomy - the intestines and blind finger-like processes of the stomach. The latter increase the area of the digestive surface.
The worms in pollock look completely different. Usually they are smaller in size, thinner, located chaotically, and do not stretch along the ridge. Worms can look different. The bulk of worms are transparent or whitish in color. They are often rolled into spirals and resemble threads in appearance. Photo:
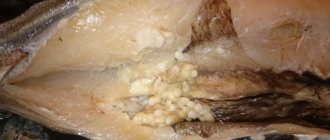
The worms are red or deep orange in color and usually belong to the acanthocephalan species. This is what they look like in the photo:
Description and photo of acanthocephala
Acanthocephalans are parasites from the family of spiny-headed worms. Another name for them is acanthocephala. They are quite large and clearly visible on the surface of the fish’s body due to their bright color. The color of the worms ranges from dull orange to orange-red. The body has a characteristic ringing and appears segmented. But in reality, the acanthocephalan is a complete parasite. At the anterior end you can see a proboscis framed with hooks, adapted for fastening in the intestine. If necessary, the proboscis is retracted into the body. Photo:
There are about 500 species of acanthocephalus. Some can reach a length of 70 cm, while others look quite small compared to them.
The most common acanthocephalans found in pollock are:
- Echinorhynchus gadi. Worms, 4-8 cm long.
- Corynosoma strumosum. They have a body length of up to 1.5 cm.
- Bolbosoma. Worm 1-2 cm in size.
Acanthocephalans parasitize the intestines of vertebrates: sea and river fish, birds, pigs, seals, and very rarely in humans. There are only a few confirmed cases of human infection with acanthocephalans. One of them was registered in Brazil in 1921. In a study of 1236 scatological samples, eggs of the giant acanthocephalan were identified in 2 of them, which parasitizes in the intestines of pigs and uses cockchafers as intermediate hosts.
Pyloric appendages;
Three-row (carp)
In the oral and pharyngeal cavities of fish there are glands, the mucus of which does not contain digestive enzymes, but facilitates the swallowing of food. The pharynx passes into a short esophagus. In representatives of the order Pufferfish, the esophagus forms an air sac, which serves to inflate the body.
Rice. 5. Structure of the intestines of fish
A – ramp; B – salmon; B – perch; G – carp; 1 – spiral valve;
In most fish, the esophagus goes into the stomach. The structure and size of the stomach are related to the nature of nutrition. Thus, pike has a stomach in the form of a tube, perch has a blind outgrowth, some fish have a curved stomach in the shape of the letter V (sharks, rays, salmon, etc.), which consists of two sections: 1) cardiac (anterior); 2) pyloric (posterior)
Rice. 6. Pyloric outgrowths of the stomach.
In cyclostomes, the esophagus passes into the intestine. Some fish do not have a stomach (cyprinids, lungfishes, wholeheads, gurnards, many gobies, monkfish). Food from their esophagus enters the intestine, which is divided into three sections: anterior, middle and posterior. The ducts of the liver and pancreas empty into the anterior part of the intestine.
To increase the absorption surface, the fish intestine has a number of features:
1) folded inner surface;
2) spiral valve - an outgrowth of the intestinal wall (in cyclostomes, cartilaginous fish, cartilaginous and bony ganoids, lungfishes, lobe-finned fishes, salmonids);
3) pyloric appendages (herring, salmon, mackerel, mullet); appendages extend from the anterior intestine, gerbils have one appendage, river perch have three, mackerel have about 200; in sturgeons, the pyloric appendages have fused and formed the pyloric gland, which opens into the intestine; the number of pyloric appendages in some species is a systematic feature (salmon, mullet) (Fig. 6);
4) increase in intestinal length; length is related to the calorie content of food; Predatory fish have a short intestine; silver carp, which feeds on phytoplankton, have an intestinal length 16 times longer than the body.
The intestine ends with the anus, which is usually located in the back of the body in front of the genital and urinary openings. In cartilaginous and lungfishes, the cloaca is preserved.
Fig.7. Digestive system of a shark.
Rice. 8. Internal structure of bony fish (river perch).
Digestive glands. The ducts of two digestive glands flow into the anterior intestine: the liver and pancreas.
Cartilaginous fish have a large three-lobed liver (10–20% of body weight). In bony fish, the liver may consist of one, two or three lobes. The liver produces bile, which emulsifies fats and enhances intestinal motility. The bile ducts carry bile to the gallbladder. Bile, due to its alkaline reaction, neutralizes the acidic reaction of gastric juice. Bile activates lipase, a pancreatic enzyme.
From the digestive tract, all blood flows slowly through the liver. In the liver cells, in addition to the formation of bile, the neutralization of foreign proteins and poisons ingested with food occurs, glycogen is deposited, and in sharks and cod (cod, burbot, etc.) fat and vitamins are deposited. After passing through the liver, the blood travels through the hepatic vein to the heart.
Figure 9. General topography of the internal organs of the sterlet:
1
- heart;
2
– abdominal cavity;
3
– liver
; 4
– gallbladder;
5
– cardiac section of the stomach;
6
– pyloric section of the stomach;
7
– pyloric gland;
8
– duodenum;
9
– spiral valve;
10
– rectum;
11
– anus;
12
– pancreas
; 13
– swim bladder;
14
– spleen;
15
– testes;
1
6 – genital duct;
17
– genital opening.
4) stomach;
The barrier function of the liver (cleansing the blood of harmful substances) determines its most important role not only in digestion, but also in blood circulation.
What other parasites are found in pollock?
Pollock fish are affected by about 90 types of worms. The degree of infection by helminths is 35% of the population. This means that certain worms are found in every third carcass. Sources of infection are diseased fish, shellfish and the water itself. Worms develop from larvae that penetrate the gills, intestines, under the skin or into the muscles. The most common types of parasites found in pollock (excluding acanthocephalans):
- Anisakids. Rolled into a spiral and protected by a transparent capsule. If it is opened, the length of the worm will be 1.5-2.5 cm. Anisakides affect the intestines, internal organs, and muscle tissue of pollock. Depending on the subspecies, they can be of different colors: white and yellowish (Anisakis simplex), grayish (Contracaecum aduncum), orange-red (Pseudoterranova decipiens). The largest species of anisakid is the cod worm Pseudoterranova decipiens. Its length can reach 4 mm and thickness 1 mm. The color of the worms ranges from whitish to red-brown. Photos of parasites:
- Broad tapeworm (diphyllobothria). The average size of an adult is 10 m with a width of 1.5 cm. Its larvae, 0.6-1 cm in size, parasitize fish. They are mainly found inside organs and in muscle tissue. The color of the larvae is white or gray. Diphyllobothria is considered dangerous to humans. Parasites can live in the small intestine for up to 29 years and reach a size of 15 m. However, the symptoms of the disease are not expressed. Minor abdominal pain, diarrhea, asthenia and weight loss may occur. What do worm larvae in fish and an adult look like:
Traditional treatment
In the fight against fish tapeworm, it is recommended to supplement the effect of traditional drugs with folk remedies.
Pumpkin seeds and castor oil
In the morning on an empty stomach, eat 50 g of raw pumpkin seeds. After half an hour, you need to drink 15 ml of castor oil. This method allows you to thoroughly cleanse the body of dead or paralyzed helminths.
Pumpkin seeds will remove dead parasites from the body
Find out more about the beneficial properties of pumpkin seeds for worms in our article.
Onion infusion
In the evening, chop 1 large onion and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave the liquid to infuse in a cool place for 8–10 hours. In the morning, strain the infusion and drink 250 ml half an hour before meals. Repeat the procedure at lunchtime and in the evening. Treatment lasts 5–7 days.
Onion infusion will quickly cure you of worms
Milk with salt and garlic
Dilute 1 tsp in a glass of hot milk. salt and chopped garlic clove. Drink in the evening for 3-5 days.
Folk remedies help get rid of helminthiasis if they are used as an adjuvant in complex drug therapy.
The tapeworm, or wide tapeworm, is a rather dangerous parasite for the human body. The helminth usually lives in representatives of freshwater bodies of water. You can become infected with it through infected river and sometimes sea fish.
The tapeworm can reach large sizes, which can cause serious complications in the functioning of internal organs. It is important to go to the hospital at the first unpleasant symptoms in order to detect and eliminate the disease in time.
What to do with pollock affected by worms?
Non-living acanthocephalans and worm larvae are safe for human health. Final destruction occurs during heat treatment. When producing canned food, fish are not even gutted. Therefore, it is not uncommon for dead worms to be found in preserved food.
Pollock affected by worms can be eaten. This must be done after heat treatment at a temperature of at least 60 degrees for 20 minutes.
The fish should be well cooked or fried right down to the bones. If pollock needs to be cooked by cold smoking or salted, and the carcass was purchased chilled, you can disinfect it by freezing. Worms die:
- at a temperature of -18 degrees for 2 weeks;
- at -20 for 5 days;
- at -30 for 10 minutes.
Advice. Worms in pollock often cause disgust. In this case, it is recommended to purchase gutted carcasses, free of intestines and worms.
Proper processing of fish products before consumption
It is important to remember that when eating raw fish products, you need to use them for
These are the species that were grown in artificial reservoirs on an industrial scale. There, during the growing process, future products are constantly monitored and if a danger of infection with helminthic infestations is detected, appropriate measures are immediately taken. Fish caught at sea must also be deep-frozen. Regarding the inhabitants of wild rivers and lakes, it is better to choose finished products that have undergone heavy smoking or long-term salting. Fish dishes can be completely prepared so that they are not dangerous for consumption by boiling or frying, which last for at least 20 - 30 minutes.
Reviews of red and orange worms in pollock
You can find hundreds of posts on the Internet about finding red and orange worms in pollock. Sometimes fish intestines are mistaken for them, but more often they are helminths. Those who encounter them for the first time are usually very worried about their health. But people who often cook fish treat the worms in it calmly and even with a bit of irony. Here's what they say in the reviews:
Anastasia:
“Like fish are proteins, and worms are proteins. I, of course, try to clean everything thoroughly, but I wouldn’t be surprised that fried worms may turn out to be tastier than the pollock itself.”
Natalia:
“For the first time I came across red worms in pollock, and worms in fish in general. That's horrible! I took it back to the store. The seller said it was harmless, but accepted it back. I can't imagine how you can eat wormy fish. Moreover, they told me that there are no guarantees against parasites in fish. Neither the brand nor the reputation of the store or seller plays a role. I don't know how to buy it anymore. I don’t feel like it at all yet.”
Sveta:
“Orange worms in pollock are common. I have loved fried pollock since childhood. You can only miss these ribbons if you don’t look closely. They look unpleasant to me too, but I don’t get hung up on them. I cleaned the fish well, washed it, and it looks completely healthy and appetizing. The worms are all frozen or frozen; we don’t sell fresh pollock. Plus fry for 20 minutes. Here all living creatures will surely die. And those who are very worried can take antiparasitic drugs for prevention.”
How does worm infection manifest?
The most common signs of human infection with worms are:
- Acute abdomen syndrome. It manifests itself as bloating and painful sensations, cramps in the stomach and intestines. Additionally, nausea and vomiting may occur.
- Intestinal obstruction. Occurs when there is severe helminth infestation.
- Allergic rash. The presence of parasites in the body greatly increases the risk of allergic reactions. Reddish scaly spots appear throughout the body and do not have a specific location.
Important! Symptoms of parasitic infection in most cases are detected 7-21 days after infection.
If unpleasant sensations occur immediately after eating fish, this usually indicates poisoning.
Microsporidia
Pollock can be infected with microsporidia. The genus of parasites Microsporidia is a collection of protozoan intracellular microorganisms.
Microsporidiosis in most cases occurs hidden, causing complications such as:
- indigestion;
- malfunctions of the liver and kidneys;
- conjunctivitis;
- breathing problems;
- chronic diarrhea.
Prevention of helminthiases
You can protect yourself from the unpleasant consequences of eating fish with worms by following preventive measures. Necessary:
- Avoid eating raw fish.
- Eat cold smoked and lightly marinated fish with caution.
- When preparing fish dishes, monitor the quality of heat treatment. The time for frying, boiling and baking pollock should be 20 minutes or more at a temperature of 60 degrees.
- The minimum cooking time for fresh fish pie is 60 minutes.
- When salting fish, you must use at least 150 grams of salt per 1 kg of product. The minimum holding time is 3 days.
- When cooking, large fish must be cut along the ridge into layers.
- After cutting fish, cutting boards and knives should be washed with detergent and scalded with boiling water. It is strictly prohibited to use them for cutting vegetables, bread and other products that are eaten without heat treatment.
- Regular consumption of raw pumpkin seeds, onions and garlic reduces the risk of helminth infection.
- People who often eat fish, especially smoked, marinated fish, rolls and sushi, are recommended to be tested annually for helminths.
No worse than carp!
Photographer and sailor from Murmansk Roman Fedortsov works on a fishing boat and regularly posts footage of underwater creatures on social networks. He recently tweeted a photo of his new catch: a fish with human lips and teeth, reminiscent of the mermaid from In a Blue Sea, in White Foam.