Spiders amaze with their persistence and hard work. They can be found in almost every corner of the planet. Spiders may not look very attractive, but they are an important part of the ecosystem. Most arachnids are predators, but they can also become prey for other animals. Experienced summer residents know the importance of arachnids in nature and human life, because these creatures help fight pests.
Useful properties of arachnids
Representatives of the class have a number of useful properties:
- being predators, they destroy insects that can harm agriculture;
- These animals themselves are also a link in the food chain. Spiders, ticks and other orders are prey for small mammals, toads, birds, lizards and other vertebrates;
- mites that live in soil participate in soil formation processes;
- Tick venom is used in medicines;
Pharmacists use the venom of arachnids to make sleeping pills and sedatives.
- people weave fabrics from the webs of some spiders;
Fig.1.
Golden silk from spider webs People have learned to use spider web threads in weaving. In Fig. 1 you can see golden silk from the web of Madagascar spiders.
- scorpions and spiders are used to prepare various dishes in Asian countries and China;
Fig.2. Dishes made from arachnids
- spiders catch their victims on the web, thereby regulating the number of insects;
Fig.3. Web Hunt
- By feeding on plant remains, earth mites fertilize the soil.
general characteristics
The second name for the class of arachnids is arachnids . Their origin is connected with ancient Greek mythology. The experienced weaver Arachne dared to challenge Athena herself. The goddess could not bear such impudence and turned the woman into a spider.
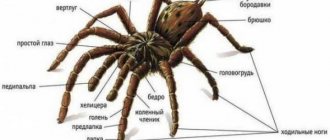
The body of arachnids has a pronounced division into 2 sections - cephalothorax and abdomen . Arachnids have 4 pairs of limbs that are used for movement. Another 2 pairs are modified into chelicerae and pedipalps. They are located in the front of the cephalothorax near the mouth opening.
The body length of arachnids ranges from 0.08 mm (some types of mites) to 21 cm (black scorpion). Since the body of arachnids is covered with a dense chitinous shell, their soft tissues cannot grow evenly.
As a result, as animals grow older, they molt several times.
Arachnids inhabit almost the entire planet. They are not found only in the Far North and Antarctica. Most species are land animals, although there are also aquatic ones. Most often, arachnids are predators. They hunt insects and crustaceans. However, many of them cannot digest food inside their body. The animals inject saliva into the victim, which can dissolve soft tissue and turn it into a mushy mass, which is then sucked up.
Dangerous properties of arachnids
Despite the large number of beneficial properties, we should not forget that many arachnids are dangerous to human life and health.
For example, the karakurt spider, which lives in southern Europe and Asian countries, is dangerous for animals (deadly for horses and camels). It poses the same danger to humans, especially to children’s bodies.
Scorpion venom causes swelling, redness of the bite site, nausea and convulsions.
TOP 1 article
who are reading along with this
The meaning of arthropods
It should also be remembered that most ticks are carriers of dangerous diseases. For example:
- Taiga and dog ticks can infect encephalitis or tularemia as they are carriers of these diseases;
- Scabies parasitizes human skin and is the causative agent of scabies, causing itching and redness of the skin;
- Bed mites feed on exfoliated skin particles and cause allergic reactions;
- A number of mites parasitize the skin of domestic animals and can easily get on human skin;
- Flour mites live in flour, thereby making it unfit for consumption;
- Cheese mites spoil cheese;
- Spider mites cause serious damage to the harvest of fruit trees and shrubs.
Many species of arachnids are listed in the Red Book. Among them are the common salpuga, as well as some species of scorpions and spiders.
Spiders: what's the use of them?
As you know, a spider's web is of great benefit; for example, to catch up to four hundred insects, one spider will need only a day. Incredible, right? This means that all cobwebs on garden trees or fences, as well as shrubs, vegetable gardens, and vineyards are of great benefit for clearing harmful insects. Since predatory animals appear in small numbers in spring, this is the best time for spiders to reproduce. Spiders can withstand cold weather quite well, so their work can last continuously all year round.
For a person, harm from a spider occurs when it weaves its webs around home walls; of course, this does not look at all attractive. And the spiders themselves are not very beautiful, and some people are so scared that they develop a phobia. You need to be afraid of spiders if you live in an area where they are poisonous.
The spider's catch is usually flies, so if you are overwhelmed by these annoying flying insects, then under no circumstances drive out all the spiders, leave at least one. In a day, a spider can eat approximately as much as it weighs.
Life cycle
The life cycle of individuals of different species is somewhat different, but has common features. Breathing is carried out using spiracles located on the lower part of the abdomen. From them, air enters the trachea and pulmonary sacs. Some representatives have a primitive respiratory system; air enters the body through holes located on the entire surface of the body.
The digestive system of individuals is designed to consume semi-liquid food. Consists of the esophagus, stomach, posterior lid, usually ending in the cloaca. In front of the cloaca there are excretory glands. Additionally, the secretion of waste products is carried out with the help of coxal glands.
Almost all spiders are predators. Small individuals feed on small insects and arthropods. Large representatives eat snakes, lizards, and frogs. In most cases, the predator stings the prey and injects poison inside through the wound. After 40-60 minutes, the insides of the prey turn into liquid pulp and the spider sucks it up.
All arachnids are heterosexual. Sexual dermographism is very pronounced. Males usually have a smaller body size and a dull color, unlike females.
Reproduction occurs in several stages:
- The male shows the female his readiness to mate. Methods differ between species. Some touch the web, others make a special sound.
- If the female is ready, she allows the male to approach. Using special bulbs located on the pedipalps, the male introduces seminal fluid into the female’s genitals.
- After mating, the female often eats the male if he does not have time to escape.
- After 60-75 days, the female lays eggs, and after 35 days the spiderlings appear. They stay close to their mother for some time, then scatter.
Sexual maturity in different species occurs at the age of 3-5 years. The lifespan of individuals differs. Males of most varieties live no longer than 3-6 years. Females can live up to 15 years. Some species of tarantulas live up to 25 years.
Reasons for appearing in the apartment
The main reason for the appearance of arthropods in a human home is the availability of food. Suitable living conditions are also important:
Many predators can be seen in the house in the autumn. They are attracted by the favorable temperature, because the apartment is warmer than outside.- Depending on the type of arthropod, it can be seen both in dry and wet places. The level of air humidity also affects the choice of habitat - heat-loving spiders settle in the kitchen and bedroom, while lovers of cold and dampness prefer to live in the basement or bathroom.
- Insects most often appear in rooms where cleaning is rarely carried out. It is in such rooms that arthropods actively breed and feed.
Predators enter a house from the street and stay there if living conditions are favorable. If there is no food, the spider leaves the home and goes in search of a new one. The most likely places for arthropods to enter an apartment:
- furniture stored outdoors for a long time;
- garden or wild flowers, herbs brought into the house;
- Street clothes;
- open windows, doors and cracks in the floors and walls.
What is a web
The predominant number of arachnids are capable of building trapping nets from a special substance found in special warts. They produce threads that can be compared even to steel wire in their strength. The web pattern is characteristic of each species. There are drops of sticky liquid on the spirally twisted threads. If an insect gets caught in it, it has little chance of getting out. In addition to the trapping net, dwellings and cocoons are made from this substance. The importance of arachnids in nature and human life is also determined by the way they feed.
Lacquer bug
Relatives of cochineal scalebugs are varnish scalebugs. They produce shellac resin, which is used in the paint and varnish industry. Also, this connection does not conduct electricity, therefore it is used in electrical engineering as an insulating material. However, contrary to the name, real shellac is not currently used to cover nails.
Read also: Rounding numbers to tenths
Shellac in products is designated as food additive E-904
In addition, the substance is edible; it can be used to coat tablets and candies.
Insects are part of nature; without them, the Earth's ecosystem could not exist. But even on a smaller scale, some of these creatures bring benefits to humans, and quite tangible ones.
Internal structure
There is no complete circulatory system. Blood too. It is replaced by lymph. There are 3-4 holes in the heart, called ostia. Through the ostia, lymph from the animal's body enters the heart, and from there, through the arteries, the heart drives lymph into the spaces between the internal organs. From the spaces, lymph enters the pericardial region of the body and returns again to the heart. Lymph has a mechanism that additionally supplies the spider with oxygen.
Spider structure
The respiratory system has a peculiar appearance. The lung sacs have plates and look like books. The breathing holes that open the lungs are equipped with protective covers. There are also long tracheal tubes that transport oxygen from the openings to the organs of the spider's body.
Being a predator, the spider has a well-developed central nervous system and a significant brain volume. In the cephalothorax of the arthropod there are 2 nerve ganglia, from which many nerves diverge, leading to the organs of the spider. These nodes are the brain of the animal.