Many owners are faced with unplanned rat offspring as rats become sexually mature at 5 weeks of age. This is why it is so important to separate all females from males when growing up. However, many owners breed rats.
In this article, we will look at how to properly breed rats and care for females. We will also learn about important factors affecting the health and future of rat droppings.
Making the decision to breed rats
Before mating two rats, it is important to know the genetic background of both parents and siblings. You also need to make sure they are in good health. Therefore, it is important to find a responsible and reliable veterinarian who will treat your animal if the need arises. Breeding pet store rats is not a good idea because you don't know the genetic history.
You should also have funds available to see a veterinarian if complications arise during the birth. For example, for an emergency caesarean section if the mother dies during childbirth or the babies get stuck in the birth canal. Money will also be needed for future medical complications, food and cages for 20 baby rats, and for your current rats.
If you take your rats to a pet store, be aware that they may sell your rats in exchange for snake food rather than pets. You can try advertising in online rat communities.
Are you thinking about breeding rats to make money? Then you should consider that the cost of care, housing, feeding and medical bills for your rats is more expensive than the money you will make from selling them.
A good breeder knows the pedigree and genetics of their rats and does not breed rats with health problems, mycoplasma disease, or a history of tumors in their pedigrees.
How many pups are born in a litter?
The usual number of litters for the first time is up to 12 pups - according to the number of nipples of their mother. However, anomalies also occur when a female can give birth to from 1 to 22 babies. At the same time, cubs can be born as all viable or partially dead offspring. There is a high probability of death of rat pups due to lack of nutrition (lack of free nipples).
If the number of newborns is more than 12, the female is able to feed them, but in this case it is necessary to provide her with high-calorie nutrition and create conditions for rest between feedings. You also need to pay attention to the nest - enlarge it, insulate it. In good conditions, the rat will feed the babies in two “shifts”, then there will be no need to cull them.
What you need to know before breeding
Anyone can be a breeder, but not everyone can be a good breeder!
When breeding for the greatest variety of patterns and colors of the babies, breed two rats of different colors and markings. For example, if you cross Dumbo with Dumbo, you will likely get all the children with Dumbo ears. Or if you cross Siamese with Siamese, you will most likely get all Siamese.
Breeding should be done with caution, as mating with sick rats or rats with a history of disease can have devastating consequences for parents and children.
Some health problems are not noticed until the rat reaches an advanced age. So just because a rat is young and looks healthy doesn't necessarily mean they don't have tumors or respiratory problems.
- Don't breed rats with pneumonia.
The disease can be transmitted to infants. This includes both men and women. It is most often transmitted by an infected rat sneezing near a healthy rat. If a rat is infected with pneumonia as an infant, symptoms usually do not appear until they are 3 months old. - Do not mate temperamental or high-biting rats.
These traits can be passed on to babies. Temperament is not always genetic. It can be caused by poor handling or care of the animal at an earlier age. But it is best to avoid breeding rats with temperament problems. - Do not breed females under 4 months old.
Their bodies are too small and birth can cause internal complications that can be life-threatening. They may also be too young to care for baby rats. - It is best not to breed females older than one year, especially females older than two years.
Caring for babies is stressful for a young and healthy mother, but for an older rat it can be very tiring for them and can ultimately shorten their lifespan or prevent the mother from caring for the babies.
Young mothers sometimes tend to have no maternal instincts and do not breastfeed or care for their babies. Sometimes they do not care for the babies for the first few hours or even days, but then they return and take on their motherly duties.
Breed only strong, well-nourished and healthy females of the breed.
Nutrition
Breeding rats presupposes a proper diet for rodents. After selecting individuals, it is necessary to adjust their diet in order to remove excess weight and make them more active.
To increase the endurance of a pregnant female, it is necessary to include wheat germ, eggs, fish and poultry in her diet. In this case, you need to exclude strawberries, vegetable oils, bell peppers and boiled liver from your diet.
Clean and fresh water in the drinking bowl is a vital element in the diet of ornamental rats, especially during the mating period. In addition, it is recommended to place the animals in a separate spacious cage for free movement.
How to breed rats
Place the selected female and the selected male in the same cage. Watch them carefully to make sure they get along with each other and won't fight.
If they are friendly, observe and see if they mate. If you witness mating, simply wait 21-28 days for the babies to appear.
You can place a male and female in a cage together for a few weeks if they get along. Separate them in the last week of pregnancy unless you want more children. Or you can just combine them once for a few hours, it depends on what you want to do.
The female may become pregnant again immediately after giving birth, which can be a difficult ordeal for her. Therefore, if you do not want a second litter, separate the male and female in the last week of pregnancy.
If after 21-28 days there are no babies and you realize that the female is not pregnant after all, you can collect the selected pair and try again.
House
Caring for a rat at home begins with arranging a home for the pet. The larger and more spacious the house, the better the rat will feel in it. The minimum cage size for one decorative individual is 60 by 40 cm. If the bars of the cage are made of metal, the optimal size of the openings is 1.5 by 1.5 cm. Even if the pet decides to stick its head into the cage, it will not get hurt. To live comfortably in a cage, rats must have:
- feeder;
- litter;
- drinking bowl for water.
Since rodents are active animals, it would be good to organize a play area for them. There may be labyrinths, slides, stairs and other toys. The most favorite pastime of rats is swinging in a hammock. You can buy it at any pet store or make it from available materials.
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is not a good idea. Mating relatives can cause genetic problems.
Some breeders do inbreeding, which they call line breeding, to produce a rat of a certain color. Usually in this case, rat relatives are mated.
Some studies show that inbreeding in wild rats leads to a shorter lifespan for the rats. Therefore, it is suspected that inbreeding in domestic rats will lead to the same result.
There is a lot of inbreeding going on in the rat business as they have huge cages where a huge number of rats live and breed without any concerns about relatives. Or they don't keep track of diseases or legacies.
Mass-bred rats tend to have a much shorter lifespan than rats bred by responsible breeders.
Factors affecting reproduction
Despite the fact that rats breed a lot and often, there are a number of factors that have a serious impact on the reproductive functions of the rodent body.
Environment
The environment plays a huge role in the life of any living creature. A person is able to cope with this by building warm homes, creating clothes and other things to protect himself from the influence of the environment. Rats can't do that, so they've learned to adapt.
These rodents adapt perfectly to any climate, but the climate itself changes the rodents so that they do not die. So, if the population happens to live in frosty areas, the number of cubs that the female will give birth to will sharply decrease. The quality of the offspring will also suffer, as many pups will be stillborn.
Nutrition
Poor nutrition affects adult rats. Pet rodents always have access to healthy and tasty food, so they are full of energy and always healthy. Wild rats eat what they find under their feet, and this is not always food that is healthy for their body. Quite often, a rat can eat some kind of poison, but not die and suffer poisoning, but serious harm will already be done to its body . Read more about rat poisons in this article.
Living conditions
A hostile environment is often the main factor that disrupts the reproduction process. In a stressful state, when there are either traps set up or predators everywhere, female rats have a hard time with pregnancy, miscarriages often occur and dead rat pups are born. Just as mentioned above, due to the constant danger, rats may eat live young ones to protect them from predators. By carrying live rat pups from place to place, the female often exposes them to danger. Naked babies simply freeze while their mother carries them in her teeth.
What you need to know about rat pregnancy
Pregnancy in rats ranges from 21 to 23 days. Reproduction, fertilization and pregnancy always depend on the female cycle. Not everyone has the same cycle and it can vary by a couple of days.
Be careful when handling a pregnant female. Don't lift her by pressing on her belly, you may hurt her or the babies inside. During pregnancy, females are advised to limit climbing. They cannot jump as well as they used to and may fall, causing injury or complications.
You can let the mother play during pregnancy. But keep an eye on her so that she doesn't get injured or give birth in a place where you can't reach her.
You can also allow mom to play after giving birth, but make sure she doesn't leave the house for more than an hour for at least the first 2 weeks. Babies may become cold and hungry. If you allow mom to play after giving birth, make sure the crate door is closed. Otherwise, she may grab the babies one by one and take them to another place.
Estrus and heat
During estrus, the female is ready to mate, and this can be easily understood - you need to tickle her in the spine area, the rat should arch her back and shake her ears.
At the end of estrus, rats begin a period of sexual heat, this is easy to understand by watching the pet - the rat will stretch out its hind legs and spin around the male, they will show interest in each other - licking and sniffing the partner.
The rat is in heat
The main difference between female rats and other animals is the absence of vaginal bleeding, due to the fact that their red blood cells are not visible. But, like other animals, the rat is sensitive towards the male during estrus.
The duration of estrus is determined by several factors - the environment and the individuality of the rat's body. For example, light during the day and at night can affect the cycle and cause it to become unstable, or a new neighborhood, and as a result, stress can also play a role. When planning a pregnancy, this should be taken into account.
Regarding the frequency of estrus - in rats bleeding occurs every 5-6 days, lasting about 15 hours. To understand when a rat is in heat, it is worth observing its genitals. During estrus, her perineum is moist and open, and when she is not in estrus, the perineum is dry and tightly compressed.
Sexual heat in males
Males become fully sexually mature at the age of 5 months, from this period they will respond to the mating games of the female. It is quite simple to understand that a male is interested in a female who is in heat: he will sniff her, lick her and try to mount her.
Housing for a pregnant female
It is recommended that the pregnant female be placed in her own cage a week before giving birth. Aquariums are the safest place for a rat to give birth. If you have a wire bottom or a cage with sides, babies may fall out or slip out of the cage, which can cause injury. Or death if they get stuck, cannot free themselves, or fall to the floor below where other animals can reach them.
Safe crates for babies are those with a flat bottom and 0.5 cm or less between slats.
Some pregnant females can live with other females without any problems. But some pregnant females are very defensive and may attack their other cage mates. It is best to place the nursing mother separately from others.
Some pregnant females begin building nests almost immediately after realizing they are pregnant. Others will wait until the last week to make a nest. Sometimes they build a nest when the young are born, or some don't build a nest at all.
It is best to provide pregnant mothers with a home, a needle, or a box to hide in. They are more comfortable if they have a darker place to rest.
Do not introduce new rats to pregnant females, they may react strongly and harm themselves and other rats.
If pregnant rats are kept together in the same cage, they are likely to mix up their litters. In rare cases, females may engage in a tug-of-war with the cubs, injuring them; if this occurs, separate the females.
What to feed?
Rats are practically omnivores, but there are foods that benefit them and those that are not recommended for consumption. Moreover, rodents should not be fed exclusively grain crops. To ensure normal functioning, it is important that their diet is varied and balanced. A good owner is always attentive to his pet's nutrition.
What you can feed your rat at home:
- grain crops;
- beans;
- nuts;
- dried fruits;
- boiled and raw meat;
- fish;
- cheese;
- boiled eggs;
- cottage cheese.
Decorative pets should not be given fruit seeds. Some of them contain a toxic substance - amigladine. During the decay process, it releases hydrocyanic acid, which can cause acute poisoning. Most amigladin is found in the seeds of persimmons, apricots and citrus fruits. It is not advisable to feed them almonds and berry seeds.
The list of non-recommended products for rodents includes the following:
- White cabbage;
- turnip;
- eggplant;
- radish;
- a pineapple;
- banana;
- sorrel.
What you need to know about childbirth
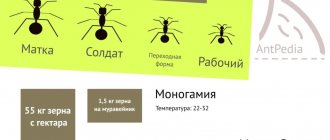
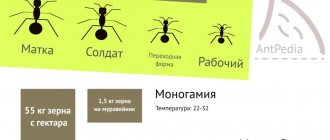
Rats give birth to litters of 6-12 medium-sized pups. They can have up to 24 children. Rats have 12 nipples, so it can sometimes be difficult for mothers to feed their babies.
A pregnant mother will begin to bleed lightly before giving birth. The mother will lick each baby, chew the umbilical cord and eat the afterbirth.
Labor usually lasts 1-2 hours. If your rat labors for more than an hour without pushing out any babies, call your veterinarian immediately.
In rare cases, mothers may eat babies who die during childbirth. This is because in the wild, dead babies can attract predators; the female tries to protect the rest of the family from predators. In very rare cases, a mother may eat live babies if she is not feeding properly or if she thinks they are sick.
Artificial feeding
If the female refuses to self-feed or dies during childbirth, the offspring can be produced using infant formula. It is prepared as follows: 50 ml of regular high-fat milk (or condensed milk) is mixed with 1 spoon of the mixture and 0.5 calcium tablets. They use insulin syringes without a needle, which are convenient for feeding babies. The portion must be gradually increased. If possible, it is advisable to place the newborns with another female, but on condition that she accepts them.
Breeding rats is an interesting activity that allows you to learn more about the life of a rodent.
What you need to know about baby rats
Rats are very vocal and, as a rule, squeak a lot. The mother rat will carry her babies with her teeth (in her mouth), this will not harm them. In the first week, babies are mostly dependent on their mother, but will try to crawl.
Rats are born hairless and pink. On day 3, you may begin to see hints of baby markings and some fur growth. They are born with their eyes and ears closed. The ears of rats are folded towards the head and appear almost completely attached to the head at birth and gradually open and widen. Their ears will open fully at about 9 days.
It will take about 10-14 days for the rat to become covered in light fur. Rats take 10-14 days to open their eyes. Babies will become very active when they open their eyes and begin to explore.
Babies begin chewing food at about 2 weeks of age. Usually immediately after opening the eyes.
Infants should not be separated from their mother before 3 weeks. 4 weeks is the recommended weaning age. Females can stay with mom and males with dad after weaning.
Bathing
Despite the widespread belief that pet rats love water, they are far from fond of bathing. Water procedures can be complicated by the animal’s pronounced resistance, but some pets are tolerant of this procedure - it all depends on individual characteristics. You need to bathe an animal in the following cases:
- if the wool has an unpleasant odor;
- if the rodent is unwilling or unable to care for itself;
- when infected with parasites.
At what age do they begin to reproduce?
The optimal age for these rodents to begin breeding is 4–5 months. At this time, they reach sexual maturity and are able to have healthy offspring. In females at the age of 6–8 months, the pelvis may narrow, after which they are unable to give birth on their own. In this case, a caesarean section is used, after which the female is discarded, as she will no longer be able to give birth on her own.
Repeated fertilization is possible 3-4 weeks after the end of feeding the babies of the previous offspring. And males are ready for sexual intercourse always and at any age, and can begin to mate even in adolescence.
Rats in heat
Estrus in females occurs every 6–8 days and lasts about 12–14 hours. At this time, the animal behaves nervously, constantly moving, often chaotically. The rodent's labia swell from the rush of blood, which causes unpleasant sensations in the form of itching. In addition, mucous discharge appears.
Did you know? Rats in their normal state are able to jump to a height of 80 cm, and during stress they can “fly up” two meters.
The behavior of young females (2–3 months old), which imitate sexual intercourse, is interesting. It is believed that these caresses have no special connection with erotic attraction to another individual of the same sex. Most likely, this is “friendly support”, when another female imitates the male’s attack by touching the “partner’s” back, which brings pleasure and orgasm.