Home Tips for summer residents
Almost every summer resident has currant bushes, but it is rarely possible to grow a rich harvest and keep the foliage healthy. The bud mite is the most common pest that attacks currants. It sucks the juice from the leaves, the bush begins to hurt and bears fruit poorly. But there are 9 effective ways to get rid of this mite without harming the plant, which even a novice gardener can handle.
- 2 Use a gas burner
- 3 Laundry soap
- 4 Planting onions and garlic
- 5 Mixture of ash and tobacco
- 6 Walnut leaves
- 7 Remove affected buds
- 8 Pour boiling water over the bush
- 9 Use chemicals
Onion and garlic infusion
The kidney mite cannot tolerate the smell of garlic or onions, so to combat the pest, you can prepare a tincture according to the following recipe:
- take 100 g of peeled onion and garlic, chop on a fine grater;
- put the pulp in a 10 liter bucket of water;
- mix everything thoroughly until smooth, cover with a lid and leave for a day;
- strain the infusion through doubled gauze.
Spray the foliage, branches and tree trunks with the prepared solution, starting in early spring. This will destroy the larvae that survived the winter.
This garlic and onion infusion is also effective against aphids and herbivorous caterpillars.
Signs of plant damage by currant mite
- Winter: Some of the buds on the plant are greatly enlarged.
- Spring: Shoots develop unevenly, some are severely stunted. The leaves on them are poorly developed and deformed. Some of the round-shaped buds did not produce leaves or shoots at all. The plant blooms poorly, there are few flower clusters.
- Summer: Affected bushes lag behind in development. The shape of the bush is sloppy, some of the shoots are twisted and underdeveloped. There are few fruits, some of them fall off before reaching full maturity. Starting in August, some of the buds begin to enlarge and become rounded.
- Autumn: Buds on the plant vary in size. Some of them are enlarged and round in shape.
Bud mite on currants
Use a gas burner
Another effective method is fire treatment. You need to point the gas burner at the bush, keeping a distance of 10 cm from the branches. Movements should be fast so as not to burn the bush, and directed from top to bottom.
Healthy buds have dense scales that protect them from fire. Buds affected by pests, on the contrary, are open and porous, so the heat will penetrate inside and destroy the bud mite along with the larvae.
Currant varieties resistant to bud mite
If you are tired of the eternal battle with the currant bud mite, you should think about replacing the currant varieties you grow with ones that are resistant or relatively resistant to this pest: Irmen, Pamyati Michurin, Early Potapenko, Pamyati Potapenko, Shalunya, Sevchanka, Nightingale Night, Belorusskaya sweet, Leningradskaya sweet, Riddle, Kipiana, Leningrad giant, Nara, Oryol serenade, Otradnaya, Chernysh, Black pearl, Vigorous.
Currant varieties with complex resistance >>>.
There are many varieties of black currants of Russian, Belarusian, and Polish selection on sale. You just need to find out which of them are zoned specifically for your region. However, as the bush ages, the resistance of currants to damage by bud mites decreases.
How to deal with currant pests without chemicals >>>.
Laundry soap
Soap can destroy kidney mites due to its high alkali content.
Preparation of soap solution:
- rub 200 g of soap, dissolve in 0.5 liters of water and leave overnight;
- In the morning, add 150 ml of sunflower oil to the mass, stir until smooth;
- Dissolve the resulting mixture in 10 liters of water, pour it into a sprayer and begin processing the bushes.
Spraying should be started within an hour after the final stage of preparing the solution. Later, the soap emulsion will begin to separate.
How to get rid of a pest
The bud mite is an insidious pest that spends most of its life cycle inside the buds of the currant bush. Tick control is most effective during the period of migration of tick larvae in search of a new refuge. The main measures to destroy the pest using folk remedies and industrial preparations are carried out in the spring and autumn.
Folk remedies
Adherents of organic farming prefer to fight bud mites using folk remedies that are effective in the early stages of pest infestation. Decoctions and infusions prepared with your own hands are safe and can be used during the flowering and fruiting period of currants.
Garlic infusion helps to successfully fight kidney mites:
- the middle head of garlic is cleared of its covering membranes;
- the cloves are crushed into a pulp using a garlic press, placed in a 10 liter container with warm water;
- the mixture is infused for 5-6 hours.
A filtered solution with a sharp, pest-repellent smell is sprayed onto the bushes and soil around the tree trunk.
Red pepper decoction . Recipe for making the product:
- 100 g of red hot pepper are crushed, combined with 1 liter of water;
- the mixture is put on fire, boiled over low heat for 5 minutes;
- The broth is cooled and allowed to brew in a dark place for 24 hours.
Before use, the prepared concentrate is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10.
Herbal infusion . 200 g of dried dandelion grass or wormwood leaves are poured into 2 liters of boiling water and left for 5-6 hours in a dark place. Before use, the concentrated solution is diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio. Berry bushes are treated with the prepared infusion.
Tobacco infusion . The recipe for preparing the product is simple:
- 200-250 g of tobacco dust or tobacco leaves are poured into a bucket of hot water;
- insist for 24 hours;
- filter through several layers of gauze;
- the prepared solution is used to spray currants.
Folk remedies have a cumulative effect and act gradually. The desired effect occurs after repeated treatments.
Industrial products
Mite larvae become active and migrate along currant branches at the end of spring (at +18˚C) during the period coinciding with currant flowering. At this time, pesticides cannot be used; they are harmful to pollinating insects.
Spraying of plants is carried out during the period of bud protrusion and after the end of flowering of the crop, but no later than 21 days before the start of berry picking. Repeated treatment against the pest is carried out in the fall.
Industrial preparations effective against kidney mites:
- “Tiovit Jet” is a combined product with acaricidal and fungicidal properties, produced in the form of water-dispersed granules, easily soluble in water. To treat currants, 30 g of the drug is diluted in 10 liters of water, the solution consumption is 5-10 liters per 100 m².
- “Golden Spark” - the drug is produced in the form of powder or liquid in ampoules. The product quickly destroys the pest and does not cause resistance. For spraying, take 40 g of product per 10 liters of liquid.
- "Fufanon-Nova" is an organophosphorus insecticide with enteric contact action. To prepare a solution for spraying, 12 ml of the drug is dissolved in a bucket of water.
Treating currants with colloidal sulfur gives good results. The event is held in warm weather before the bush begins to bloom. 10 g of powder is diluted in a bucket of water, the solution is sprayed on currant bushes and the soil around the tree trunk is watered.
Bioacaricides are new generation drugs that are safe for humans if the instructions for use are followed. The effectiveness of the products increases sharply at air temperatures above +18˚С. The death of pests occurs 12-48 hours after spraying. Currants are treated with biological products 3 times at weekly intervals, the last procedure is carried out five or more days before harvest.
Bioacaricides that destroy kidney mites:
- "Akarin" is a biological product with a protective effect of 30-40 days. To spray currants, 4 ml of the product is diluted in 2 liters of water.
- "Vertimek" is a biological insectoacaricide that penetrates plant tissue, causing paralysis and death of parasites. For treatment, 2 ml of the drug is dissolved in 2 liters of liquid, the protective effect lasts up to 3 weeks.
- "Bikol" - available in powder form. Preparation of the working solution: 70 g of the product is diluted in a bucket of water.
After harvesting, potent systemic insectoacaricides are used to destroy the currant pest: “Phosfamide”, “Nitrophen”, “Sunmite”.
In advanced cases, it is necessary to apply radical pruning of the bush - all infected shoots are removed. Then the base of the bush and the soil are treated. Full fruiting of the cured currant bush is resumed after 2-3 years.
Pour boiling water over the bush
This method is similar to treating bushes with a gas burner, but in this case boiling water is used.
The process of destroying the kidney mite is as follows. Tie the bush branches into a bundle with twine, without squeezing them too tightly. Pour boiling water into a watering can with a sprayer, then raise the watering can 2 cm from the top of the bush and water the branches.
This treatment should be carried out in early spring before the buds open. On average, one bush should require a whole bucket of water.
How dangerous are bud mites for plants?
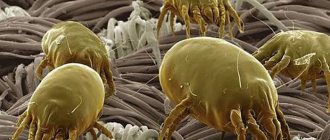
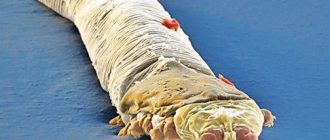
The currant bud mite is a representative of the group of four-legged mites. All of them are smaller than 0.5 mm, and the currant one, even more so, is only 0.2 mm in length. Most four-legged ticks are very sensitive to low air humidity and high temperatures. Therefore, they live in the buds of plants and inside various formations of shoots (witches' brooms) or leaves (galls and felts), which are formed due to the activity of these parasites.
At the moment of flowering of the currant, the affected buds begin to wither, and the female mites climb to the surface. This is the only moment in their life when they are not protected by bud scales. Having left the bud, the pests look for young shoots and buds in the axils of the leaves, penetrate them and begin to feed and reproduce. At least three generations of parasites are born before autumn. The damaged kidney increases in size, swells and takes on a rounded shape. It will no longer be able to produce either full-fledged shoots or leaves.
Moreover, this type of mite actively carries various diseases that weaken currants, including the notorious mycoplasma, which causes double currant flowers. Bushes oppressed and weakened by mites are actively affected by stem pests: small species of longhorned beetles, borers, glass beetles.
More information about the dangerous currant stem pest:
Currant glass >>>
Diseases and pests of red currant >>>.
In winter, the pest waits out the cold under the protection of bud scales. In the spring, at the first warming, ticks begin feeding and reproducing again. By the time the currants bloom, they have time to produce two more spring generations. The time of budding and flowering of currants is coming. The affected buds begin to die, the hungry parasites again leave their cozy shelter in search of young shoots and new tasty juicy buds. They can travel through the affected bush in the thousands. They are carried from plant to plant by the wind, insects, birds, as well as people on their hands, tools and clothes. The more mites on the currant, the more buds will not wake up next spring.
bud mite on currants in summer
If you do not fight the pest, the plant will die!
How to plant and care for black currants >>>.
How to properly plant and care for red currants >>>.
What to feed blackcurrants and when >>>.
Preventive methods
Preventive treatments do not guarantee protection against kidney mites, but significantly reduce the risk of infection. Choose varieties that are highly resistant to this disease - they also get sick, but rarely. For propagation, use cuttings that are strong and healthy. In the off-season, inspect the bushes and remove any buds that look suspicious. Carry out preventive treatments against pests and diseases using chemical and biological agents in a timely manner.
Any donated or purchased seedlings must be disinfected with hot water before planting - soak them for 20 minutes at a temperature of 40 degrees.
For prevention, it is recommended to plant cloves or aerated garlic bulbs densely in the currant rows. The plant secretes phytoncides, which ticks do not like. It is advisable to plant every spring - in this case, protection will be as effective as possible. Regularly inspect not only currant plantings, but also gooseberry bushes. Buy seedlings from a trusted manufacturer. Find out about ways to grow Troy onions in this article.
Biological preparations for ticks
Biological products can also be used against ticks. Their active ingredients are strains of fungi that destroy the pest without causing harm to humans. However, when using such products, one must remember that their effectiveness is visible only at a temperature of +15 degrees and above.
The following bioacaricides have found wide use among domestic farmers:
- Boverin;
- Fitoverm;
- Bicol;
- Akarin.
Similar biological products can be used for spraying currant or gooseberry bushes every 10 days, but it is advisable to alternate them in order to eliminate the habituation effect of mites.
Characteristics of an insect
The kidney mite settles in colonies, its population gradually increases and begins to fill the kidney. The result is the stopping of leaves and shoots in development, infection of the buds, which become sources of viral infections.
Description of appearance
Cecidophyopsis ribis is a very small worm, the body of which is no more than 0.04 mm wide and 0.15 mm long.
The pest settles in the buds of berry bushes, where it goes through all stages of its development. Females lay small oval-shaped eggs, usually in the month of March. These eggs are transparent, but then become white or milky. The parasite leaves the bud house after the currants throw out leaves and flowers.
Since the tick is very small, it is almost impossible to see it with the naked eye. The main way to detect a pest is the appearance of corresponding symptoms.
Life cycle
Ticks hatch from eggs that females lay in early spring. The tick does not leave the bud - its main hiding place - until leaves appear on the bushes. Then the pests move on to the leaves and bark, where 99% of the entire population dies. Surviving ticks move to another permanent place of residence closer to June and lay eggs. Five generations can develop in one bud; at a time, the mite lays a hundred eggs or a little less. If nothing is done, the pest will first destroy the crops, then the currant bushes as a whole and move to neighboring plants. Find out about planting and caring for Aflaut onions here.
In Latin, the name for all varieties of currants is ribes. The Spaniards gave it to the plant even before our era.
Prevention
Simple rules help prevent the appearance of pests:
- You need to buy seedlings in specialized stores and licensed nurseries;
- do not take cuttings from infected plants;
- in autumn and spring, carry out sanitary pruning, after which treat clothes, tools, and burn cut branches;
- keep the area clean.
Description of the pest
The kidney (currant) mite differs from other species in a different number of limbs, it has 6, while most other individuals have 8.
This parasite belongs to the gall superfamily, the order Thrombodiformes. The body length of a male varies in the range of 0.03-1.0 cm, in females - 0.05-3.0 cm. The pest feeds on the plant sap of cultivated plants and causes enormous damage to fruit and berry plantings.
Expert opinion
Mityuk Stefania Bogdanovna
Some species of mites are beneficial saprophages. They feed on soil organic matter. This contributes to the rapid decomposition of the soil to the state of humus, improving its composition.
Kidney mite species are pests. Moreover, even a slight presence of parasites in a garden plot can provoke an epiphytotic (mass) outbreak of reproduction, which leads to the rapid death of crops.
The number of parasites in the kidney can reach more than 100 individuals, which makes this species one of the most active. The body of mites is covered with tiny bristles and is divided into the abdomen and cephalothorax.
Save the environment!
The oldest method of exterminating pests was invented by nature itself. Each pest has natural enemies in nature, entomophages, which effectively reduce the number of pests of plant crops. Be attentive to the small workers of gardens and berry fields. When using chemicals, remember that you are also destroying beneficial fauna.
Ticks are effectively destroyed by beneficial insects:
- ladybug (stetorus);
- carnivorous bug;
- carnivorous mite;
- lacewing;
- chalcids (riding insects);
- Phytoseiulus;
- encarzia
- hoverfly and others.
More information about herbivorous mites can be found in the article “Mites are herbivorous garden pests.”
Dear readers! You have become familiar with the main methods of exterminating the currant bud mite, which causes significant damage to berry crops. Not all methods are harmless to humans, animals, and beneficial insects. Before using any of the drugs suggested in the article or purchased, carefully read its effects and decide whether its use is suitable for you. The choice is yours. Offer us your ways to protect berry plants from this and other pests in the comments to this material.
Treatment with chemicals
Treatment of currants with chemicals is carried out in 3 stages:
- The first treatment is done in the spring, when the air temperature is no more than +18 degrees. During these events, larvae that have overwintered and are preparing to reproduce are destroyed.
- The second treatment is done when leaves appear on the bush and the air temperature has risen above +20 degrees.
- The third treatment is carried out after flowering in order to exclude larvae that may have survived after previous treatments.
Spring treatment of currants from diseases and pests
To combat the currant mite, the following drugs are used: Fufanon, Kontosom, Movento, Oberon and others.