Beetles, also known as Coleoptera (Coleoptera), are an order of insects that number about 400 thousand species. It is considered the largest of all animal orders. In addition, new species of beetles are constantly being discovered.
Beetles are common in almost all habitats except marine and polar regions. They play an important role in their native ecosystems as they feed on plants and fungi, animal carrion, as well as other invertebrates.
Some species are considered crop pests, while other beetles eat them and prevent plant death.
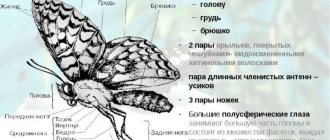
Like any other insect, beetles have characteristic body parts, including a head, an abdomen with six legs, two pairs of wings and a thorax. There is nothing unusual about beetles compared to other insects, but they do have hard jaws.
If we follow the theory of evolution, it can be noted that these living beings have their own physical manifestations of adaptation. From here we can get good hypotheses about what the beetles eat.
Detailed description
Depending on the species, the beetle may have additional eyes. Insects that live in caves, as a rule, lack vision organs. A representative of Coleoptera has a powerful mouthparts designed for grinding food. This organ includes the upper and lower jaws.
Hercules beetles have the most massive mandible. The thorax of a representative of the order Coleoptera consists of 3 segments. In the area of the middle back there are elytra. Beetles have much in common with other representatives of the insect class; they have the following external organs:
- basin;
- shin;
- paws.
There are small dense hairs on the surface of the legs. There are many types of beetles. The most common ones have a uniform brown or brownish-yellow color. Red insects are common.
Less common are species with brightly patterned patterns. Some representatives of the Coleoptera order glow in the dark, they look beautiful and always arouse interest. Females, as a rule, are larger than males and their bodies are more elongated.
Some beetles have very developed mandibles, similar to horns (in this case, males are larger than females). Beetles communicate with each other and protect members of their population. When the male finds a female, he makes a characteristic sound that scares away other types of insects.
The beetle produces vibrations when its front chest rubs against the middle one. Representatives of this class of insects differ in size, but their structure is the same. In nature there are small, medium, and giant beetles. The maximum size of an adult is 21 cm. This species is called the “titan lumberjack.”
Contraindications
Now let's talk about what contraindications there are when using the instructions for treating the healer beetle. Unfortunately, it is not possible to find out whether beetles bring harm or benefit to the human body in the treatment of various diseases.
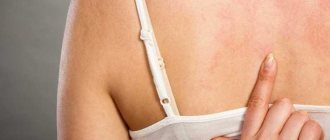
- Allergic manifestations. Taking bugs can cause various types of rashes on the body, numbness of the tongue if they are bitten, and itching.
- The sensitivity of the body itself to bugs and the ability to process them. For example, treatment may be accompanied by pain in the abdomen, head, diarrhea, and various ailments.
- Psychological barrier. The bugs are eaten alive. Not every person can do this without problems. As a rule, you have to cope with nausea, vomiting, and subconscious violence.
There is no scientifically based data on the effect of bugs on the body of patients, therefore contraindications for use are based only on the expected effect produced by insect enzymes and chitin.
Chitosan has the ability to adhere to the mucous membranes of the stomach and bind fats, which can cause a lack of fat-soluble vitamins, calcium and magnesium. The listed properties of chitosan, which is formed from the chitinous shell of beetles, make it possible to generalize the circle of people for whom the use of healer beetles is contraindicated:
- pregnant and breastfeeding women;
- children under 12 years of age;
- patients who have vitamin deficiency or mineral deficiency.
As with any other drug or food product, contraindications here concern, first of all, people with individual intolerance to the components of this drug, as well as allergy sufferers.
But there is also a significant difference from other therapeutic agents, which lies in the psychological side of the matter. There are many people who simply cannot bring themselves to swallow live beetles, no matter how they are hidden or disguised. Here everything depends only on the person: whether he can manage to swallow a live beetle or not.
Important! Taking live darkling beetles is strictly contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women, as well as children.
Note! Another name for the insect is Palembus or Argentine beetle. According to Wikipedia, it is widely used in Tibetan medicine as an alternative way to get rid of diseases.
This method of healing is suitable for people who are desperate to look for other healing options.
| Name | Description of treatment |
| Bronchial asthma | Reducing nighttime coughing attacks, alleviating the course of the disease, reducing medication intake |
| Oncology | Alleviating the patient's condition, prolonging the period of remission |
| Parkinson's disease | Fighting slowness, reducing jitter |
| Osteoporosis | Improving organ function, removing pain |
| Joint diseases | Reduced tissue swelling |
| Stress | Toning the body, improving mood |
| Other diseases | Gastrointestinal pathologies, diabetes mellitus, decreased immunity are successfully treated with darkling beetles |
Habitat
Beetles are found all over the world, they live in forests, steppes, deserts, and tundra. Insects rarely live where there is permanent snow; they are not found in Antarctica. Beetles are found:
- in black soils;
- in the bark of trees;
- in deciduous cover.
Some species inhabit deserts. Such insects are adapted to different environmental conditions. They forage for food at night.
Most representatives of the Coleoptera order prefer to drink fresh and slightly salted water.
Rules for handling a pet
Swimming beetles - adults and larvae are real predators with strong and sharp mandibles. We must not forget about this when dealing with beetles. It is better not to pick up insects with your bare hands; if they sense danger, they will try to bite or release a special protective secretion. There are glands on the sides of the swimmers' bodies that produce a caustic, milky-white liquid. It is poisonous and smells unpleasant. There is no danger to human health; just wash your hands with soap. When changing the water in the aquarium, the beetle is removed with a net.
The bite of the larvae is especially unpleasant; you should not catch or handle them. The offspring are much more aggressive than the adults.
Observations
Swimming beetles are active insects; they explore the bottom of the aquarium with interest. The need to surface to replenish their air supply makes their behavior active. The beetles quickly get used to humans and swim when approaching the aquarium. Their lifespan is 2-3 years.
Nutritional Features
Beetles are divided into 2 types: predatory and herbivorous. The former eat their brothers and their larvae, the latter feed on mushrooms, seeds, fruits, and the bark of tree crops. Many representatives of arthropods are pests of garden plants. They destroy the fruits and drink the juice of the leaf blades.
It is important to know what beetles of other species eat. They feast on the leaves of vegetable and fruit plants. The most common pest is the Colorado potato beetle, which eats crops of the nightshade family. However, some Coleoptera are forest orderlies. They feed on dry and rotting leaves.
Certain species of beetles eat animal remains. Some insects love wood and pollen. Depending on the species, an arthropod may only feed in its larval stage and go its entire life without food.
The insect affects the state of the ecosystem. Adults, as well as larvae, process wood, improve plant photosynthesis, preventing the development of diseases. Without beetles there would be no humus, plants would not be able to pollinate. In nature, there are more than 350 species of these insects, among them rare ones, little studied by science.
Reproduction
The mating period occurs in the spring; after wintering, adults look for a pair for copulation. The male is held on top of the female using suction cups and bristles on the legs. During prolonged mating, only the partner has the opportunity to breathe. The female has to be content with oxygen obtained from the water as a result of gas exchange. It is not uncommon for females to die after several matings in a row.
Eggs are laid on the underwater part of plants. The female pierces plant tissues with her ovipositor and places large (up to 7 mm) eggs in them. The total number of masonry is 50-100 pieces. After 2-3 weeks the larvae appear. They have a spindle-shaped body, a large head, and an elongated abdomen. There is no mouth opening; the sickle-shaped mandibles have channels for injecting enzymes and sucking out juice. The predatory larva moves with the help of three pairs of legs. Before pupation, it moves onto land. The pupa is the only terrestrial developmental phase of the diving beetle.
Characteristics of ground beetles
The species includes more than 20,000 subspecies (groups of insects). Predatory and herbivorous ground beetles are common. The most famous subspecies is called “humpbacked peon” . His body is large, black, and has a metallic tint. The size of an adult does not exceed 18 mm.
The mandibles of the humpback peon are well developed. The insect leads an active lifestyle, but cannot fly, and feeds on solid plants. Its legs are elongated, thanks to them the arthropod runs quickly. The ground beetle is distinguished by large elytra, and its abdomen is protected from the negative influence of the external environment. The insect is found in Egypt, Tunisia, Africa, France, central Russia, and also in Ukraine.
Enemies of the swimmer
The consequence of the appearance of beetles in fish farms or artificial reservoirs can be the extermination of large numbers of fish. However, there are also creatures who eat the swimming beetle in a pond with great pleasure - these are various invertebrates, large fish, birds and mammals.
In moments of danger, swimmers secrete an unpleasant-smelling liquid, which has a deterrent effect.
The larvae of diving beetles also have enemies. We are talking about an aquatic parasitic insect - an ichneumon fly, which has the strange name of prestwichia. Having discovered the egg of a diving beetle, the female ichneumon lays her eggs in it. The resulting parasite larva will eat the insides of the victim's egg until it turns into a pupa. The already formed adult equestrian is released into the world.
Weevil or elephant
The species is divided into 60,000 subspecies. Insects differ in body shape. For example, it can be cylindrical or in the form of a hemisphere. Weevils have different colors, they can be black, yellow-brown. The pictures show different types of elephant insects.
The most common species is the rice weevil. His body is elongated, slightly swollen, beautiful, because it has a characteristic shine. The chitinous covers of the insect are brown, the elytra consist of thin grooves. The weevil lives in Europe, Asia, Austria, America and Africa.
Temperature and humidity
To keep the medicine beetle, it is necessary to maintain room temperature. These bugs are unpretentious and can live well at temperatures from 18 to 27 degrees. The optimal temperature is 21-24 degrees Celsius. At low temperatures, metabolism slows down and beetles have trouble eating and reproducing.
The optimal humidity for keeping beetles is 65-70%. It should be borne in mind that the pieces of fruits and vegetables that you feed the bugs provide additional moisture in the terrarium. And if it is large, then mold may appear. But mold should not be allowed in the terrarium. Because of it, the death of the bugs begins.
But the terrarium should also not be too dry, since beetle larvae do not hatch at low humidity. Read more about this in the article about breeding beetles for healers.
Predatory beetles
They number more than 45,000 subspecies. The elytra of predatory beetles are short, the body size, as a rule, does not exceed 9 mm. The outer covers of such insects are dark or red-brown. Depending on the subspecies, predatory beetles may have a red or yellow pattern on the surface of the body. Such species arouse the child's interest.
They are distributed throughout the world, more often found in Japan, Canada, Europe, and North America. These beetles feed on the remains of animals and the larvae of other insects. They eat decaying plant pollen and algae found on land.
The most common predatory beetle is rove beetle . The maximum size of its body is 1 cm, it is elongated in shape. Representatives of this species are found in America and Eurasia. Rove rove beetle lives near water bodies, hiding in wet grass. The insect is found in garden plots. It is not a pest, but protects garden crops from the harmful effects of other arthropods.
Human use
The rhinoceros beetle is capable of lifting 850 times its own weight. There were even experiments conducted in Japan and China that were published. Experiments were carried out on remote photography of objects using these insects. The organizers of the experiment attached miniature video and photo cameras to the abdomens of insects.
In addition, specialists managed to achieve radio control of rhinoceros beetles during their flight. Scientists were able to place six electrodes in the muscles and brains of insects. They also supplied a microcontroller, radio signal receivers and batteries. This receiver transmitted the signal to the electrodes. Scientists say such rhinoceros beetles could be used to explore places that are difficult for humans to reach.
Lamellar arthropods
They are divided into 25,000 subspecies. The body of such insects is small, elongated up to 60 mm. Some representatives of the subfamily have an oval body. The chitinous covers of lamellar beetles are dark green with small growths in the form of spines. Such insects eat manure and plant debris.
The most common representative of the subspecies is the sacred scarab. It is distinguished by a smooth convex round body, painted black. The body size of a male individual does not exceed 35−37 mm. A special feature of the scarab is its large teeth located in the area of the front legs. Representatives of this species live in Bulgaria, Spain, Georgia, Cyprus, and Africa. They feed on plant debris.
Breathing process
Beetles, which spend almost all their time in water, breathe atmospheric air. When diving, they capture a supply of oxygen, which must be replenished after 10 minutes. The swimmer exposes the rear end of its body, contracts its abdomen and pumps air into the tracheal system. Insects can partially obtain oxygen from water. The larvae breathe in a similar way; they expose the end of their abdomen with spiracles from the water. The required amount of air depends on the temperature of the water; in summer, beetles often emerge; in winter, they can remain at the bottom of the reservoir for a long time.
Leaf beetles
The species has 32,000 varieties. Insects have an elongated or spherical body of a rich blue or golden color. The size of the female’s body does not exceed 16 mm.
The most common representative of the subspecies is the mint leaf beetle . It has a small, smooth, convex body of blue-green color. The maximum size of an insect is 11 mm. The green leaf beetle loves to feast on mint leaves, which is why it got its characteristic name.
Reproduction
The reproduction process of diving beetles intensifies with the arrival of spring. Having left their hiding places, the beetles go in search of a reservoir. In their new habitat, they begin to choose a partner. During the fertilization process, males are not characterized by signs of gallantry. Having discovered a female, they attack her and hold her with the help of suction cups located on the front legs.
But sometimes one female can mate with several males in a row. In such cases, the likelihood that she will survive is quite low. After all, swimmers are periodically forced to rise to the surface of the water to breathe. Being below at the moment of fertilization, the female is deprived of this opportunity. But the male, being on top, can linger near the surface and get the necessary amount of oxygen.
You should also take into account the fact that the mating process takes much longer than the insect can stay under water without air. Therefore, if the female does not manage to get up in time, she may simply suffocate from lack of oxygen.
After mating, the female begins laying eggs. At one time she is capable of laying up to a hundred eggs, and up to a thousand in a season. She lays her eggs on the stems of aquatic plants in the water. After some time, small larvae are born, which are so voracious that they begin their hunt almost from the moment of birth.
Unusual longhorned beetle
There are more than 23,000 subspecies in nature. The mustaches of arthropods are long, exceeding the size of the body by 3 times. The average body size is 15 mm. Most representatives of the subspecies are small, but there are also giants, which include the titan woodcutter.
The insect weighs 25 grams. The head of the woodcutter is elongated, slightly flattened, the body is brown, but there are also black varieties. There are 3 spikes on the front back of the woodcutter. The male lives up to 36 days. The largest woodcutter beetle was recorded in South America.
Breeding at home
Oddly enough, the malicious pest darkling beetle, which thrives in flour, bran or cereals, still requires, albeit small, effort when specially grown.
Conditions of detention
These insects feel best at room temperature in a semi-shaded area. For their high-quality reproduction, a minimum of 400 individuals are required, which are usually placed in a half-liter glass jar, at the bottom of which a 5-centimeter layer of wheat bran is placed. This is the beetles’ home, which partly serves as their food supply.
Mating season
Male representatives of the insect class fight with each other, occupying the most comfortable places. Males actively forage for food and often fight for females. Beetles are higher insects; their reproduction requires complete transformation. The egg passes into the larval stage, which becomes a pupa and subsequently develops into a full-fledged individual.
The female hides the eggs in fallen leaves or places them in stones. The larva can hatch in the bark of a tree, in curled leaves.
The eggs are usually white, green or yellow. On their surface there is a thin leathery shell. The size of the egg depends on the type of beetle in question. On average, it lives 15-20 days, after which it turns into a larva.
Larvae can be seen in the soil and tree bark. They are:
- yellow;
- white;
- pinkish.
The outer integument is brown or green and may have brown spots on the surface. The larvae differ not only in shape, but also in body structure; they are often elongated and dense. Some of them look like worms.
Some larvae have a chitinous layer, others do not. The head has hard coverings and a developed oral apparatus. When the larva develops, it molts. Life expectancy depends on the type of female and male, and the climatic features of the area play an important role. The larva can live from 2 months to 5 years. It should be noted that some arthropods reproduce in the larval stage.
Coleoptera representatives of the “Insect” class contribute to the pollination of garden crops. Beetles eat animal remains, resulting in faster decomposition processes. Predatory species are beneficial for the crop because they destroy their harmful counterparts. The importance of beetles in nature and human economic activity is difficult to overestimate. “Forest nurses” improve the ecosystem.
How to be treated
The therapeutic effect of eating darkling beetle is the overall health of the body, improved well-being and strengthened immune defense. The medicine beetle secretes substances that promote general detoxification, as a result of which the functioning of all systems and organs is normalized and functional balance is restored.
- diabetes mellitus;
- asthma;
- Parkinson's disease;
- psoriasis.
According to some data, darkling beetle eliminates pain from cancer, lowers blood sugar levels, and increases the body's resistance in patients with AIDS. After a course of insect therapy, there is a reduction in the incidence of not so dangerous, but unpleasant diseases, such as colds and flu.
Experts in the field of alternative medicine have developed several beetle therapy regimens, which depend on the stages of the disease. All treatment methods involve consuming a certain number of adult witch doctor bugs; the difference lies in the duration of the course.
Due to the fact that the minimum duration of the course of therapy is 60 days, it is recommended to maintain strict control over the number of insects eaten. For these purposes, you can keep a special diary in which you need to record how many pieces were accepted and when.
Due to the lack of statistical data that reflects the results of beetle therapy by healers, it is impossible to immediately start consuming insects in large quantities. The first stage of treatment, the purpose of which is to strengthen the immune defense and improve overall well-being, is preventive in nature and helps to check how the medicine beetle affects the body of a particular patient.
- start taking with 1 piece;
- daily increase the dose by 1 individual compared to the previous day;
- the maximum number of insects eaten is 30 pieces;
- After consuming the maximum dose, the number of medicinal insects should be reduced by 1 piece daily.
The pattern of eating beetles for the treatment of diseases at an early stage is similar to the preventive stage, only the maximum number of individuals eaten is from 40 to 70 pieces. To enhance the therapeutic effect, specialists in the field of alternative medicine offer a slightly modified course of treatment, which involves consuming the maximum dose of beetles for all subsequent days after reaching the middle of therapy.
Cancer beetles are used according to the most complex and lengthy dosage regimen. The therapeutic effect will be noticeable if the dosage of 70 pcs is observed. individuals daily for 140 days. According to alternative medicine, for other serious diseases such as diabetes, osteoporosis, psoriasis, asthma, the medicine bug can also be effective if you follow this treatment regimen.
During the therapeutic course, provocative signs of the body's reaction may appear (fever, fatigue), for which you should be prepared and not stop taking it. This condition indicates the activation of protective mechanisms and the beginning of resistance to the disease.
Chitosan, contained in the hard shell of insects, can provoke an allergic reaction, which is a reason to avoid using medicine beetles. The mild treatment regimen is designed for early detection of the first signs of a negative effect on the body in case of intolerance to biological organisms and the substances they secrete.
Currently, the Argentine medicine beetle is used to treat and improve the quality of life of people suffering from a wide variety of diseases (about 70). These are diseases such as asthma, diabetes, vitiligo, psoriasis, kidney disease, osteoporosis, Parkinson's disease, oncology, arthritis, chronic skin diseases, depression and many others.
According to insect therapy proponent Reuben Deiminger, beetle therapy (Coleoterapia) refers to the consumption of beetles of the genus Palembus beetles, known abroad as the “Palembus beetle” and the “Chinese weevil”, and in our country as the “medicine beetle” or “ medicine beetle" - Palembus Ulomoides dermestoides.
The main features of beetle therapy are as follows:
- This is a cheap way to maintain health, since you can breed these bugs yourself
- This is a complementary therapy and does not replace traditional treatment. It supports and complements traditional treatment.
- This is not medical therapy, so remember that if you are under the supervision of a doctor, you must comply with all his requirements.
The data was collected from reviews of people suffering from various diseases and published on the Internet.
- The condition is relieved
- Bronchospasms decrease or stop
- Nocturnal attacks stop
- The need for asthma inhalers is reduced or completely eliminated.
- Pain is reduced to a state of simple discomfort
- Improves overall organ function and quality of life
Parkinson's disease
Muscle rigidity and tremors are significantly reduced. Slowness disappears. It cannot be said that a person has been cured of the disease, this can only be stated by doctors, but the condition is improving.
Cancer is one of the most serious diseases that affects millions of people. And of course, in an effort to be cured, people use the medicine beetle to treat cancer. And although it is impossible to claim a cure for particularly severe forms of cancer in stages 3 and 4, many people who used beetles for the treatment of oncology wrote that they received relief from their condition.
When treating joints with medicine beetles, their mobility increases and swelling decreases. Painful sensations recede. The pain reduces to a feeling of discomfort and may disappear altogether. A decrease in pain occurs by the 10th day of taking medicine beetles, and sometimes even earlier.
As pain subsides and joint mobility returns, the body’s energy increases, good health returns, and mood improves.
In many cases, depression is associated with a violation of the mineral and vitamin balance in the body. When treated with the Argentine beetle by a healer, your mood improves and a sense of well-being returns. Of course, along with beetle therapy, to combat depression you need good nutrition, consumption of vitamins and minerals, exercise and walks in the fresh air.
When you adhere to a healthy lifestyle, following all of the above recommendations, depression recedes.
Currently, many people take medicine beetles, trying to alleviate their condition and recover from a wide variety of diseases.
The medicine beetle is drunk to treat skin diseases such as psoriasis, dermatitis, etc. This bug is widely used to treat gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes, etc.
Such a wide range of applications for these beetles comes from the fact that the substances released by these beetles when they enter the stomach presumably have an effect on the entire body as a whole, activating the immune system and helping the body cope with various difficulties.
But do not forget that although beetles in many eastern countries are simply consumed as food, beetle therapy is still a means of traditional medicine. Doctors are treating us and we must adhere to their recommendations. In addition, there are some contraindications to treatment with beetles, which you can find in this article.
Video from TV channel TV 2
Even in ancient times, insects were used as medicine against various diseases. As for medicine beetles, they were previously grown only for reptiles, wild birds, and various animals. But over time, the fact was noticed that by eating these insects, sick (even cancer-stricken) animals and birds were cured. This prompted scientists to conduct clinical research.
According to traditional medicine specialists, medicine beetles are useful because:
- Dissolving in gastric juice, insects die and release biological substances that have a beneficial effect on the immune system.
- Chitosan, contained in the shell of beetles, kills various pathogenic bacteria, starts metabolism, has hemostatic properties and can improve blood condition.
- Females contain rejuvenating pheromones in their bodies.
Treatable diseases
Now let’s figure out what diseases the medicine beetle treats. It is believed to help cope with diseases such as:
- Osteoporosis, by eliminating pain and normalizing the functioning of all organs.
- Cancer. True, not at the final stages. But lovers of alternative medicine believe that taking insects helps increase the period of remission and alleviates the patient’s condition.
- Depression. They often occur due to a lack of vitamins, microelements and nutrients in the body. Beetles give a person strength and lift his spirits.
- Bronchial asthma. Treatment helps reduce nighttime attacks, helps to avoid medications or use them extremely rarely, and also improves the condition of the entire body.
- Parkinson's disease, helping reduce sluggishness and tremors.
- Joint disease. As a result of taking the medicine beetle, their mobility is restored, tissue swelling is eliminated and pain is relieved.
The instructions for treatment with a medicine beetle are simple, but at the same time, the effect is obtained only with long-term therapy.