Bark beetles belong to a separate group of insects, as they differ in that they eat only wood, live in it and reproduce. Scientists know about 140 species of such beetles that live and breed in Europe. In fact, there are up to 750 species of bark beetles.
In terms of the degree of pestilence, the bark beetle is compared to the Colorado potato beetle, since these insects are capable of destroying large areas of forest if no measures are taken. This beetle prefers to feast on spruce, as well as cedar, pine, fir, etc. Each type of wood eats a certain type of bark beetle, so if coniferous trees do not grow, this does not mean that there is no bark beetle. Therefore, you need to know how to deal with bark beetles.
Description of the pest
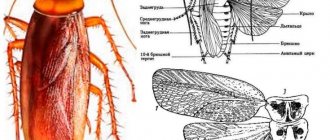
The size of an adult insect is 0.8–9 mm, some tropical species grow up to 1.5 cm. Bark beetles belong to the family of weevils, unlike which they do not have a rostrum. The body of bark beetles is colored black, brown, red-brown. The antennae and paws have a lighter shade.
The compact head with a flat or curved forehead is retracted into the prothorax. Some species may have a bump or small pits on the front of the forehead. The insect's eyes are large, round or oval in shape, often with a notch, due to which they appear to be divided into 2 parts. The antennae are short, geniculate with a compact club.
Bark beetle - appearance
The chest consists of 3 segments. The most important part - the pronotum has an oval, quadrangular, triangular shape. It is most often rounded on the sides and narrowed towards the top.
The surface of the pronotum is covered with tubercles, denticles, and sometimes punctures. Bark beetles have strong, well-developed elytra with dotted grooves. Beneath them are membranous wings.
On the elytra there is a depression (wheelbarrow), through which the uterine passages are cleared of drill flour. The abdomen of the bark beetle is horizontal, often sloping towards the apex. In females it is wider than in males.
The beetles' legs are thin, the front ones are short, digging with teeth on the legs, the hind legs are longer than the front ones.
Life cycle
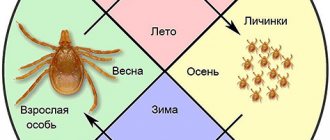
Bark beetles lead a hidden lifestyle ; they spend almost all their time inside the tree. They fly outside only to select a new plant and arrange a nest. Some species fly only in early spring, others are active throughout the summer. Depending on the species, bark beetles have different daily activities. There are insects that fly all day, some only in the evenings at sunset.
For a long time it was a mystery how insects choose the right ones from a variety of trees? It has now been established that weakened plants emit special pheromones and these subtle odors are captured by bark beetles, accurately choosing places to settle. Females burrow into the bark, burrowing into soft tissue. There they lay eggs, each containing 10–100 eggs .
Bark beetle larvae
After 10–14 days, legless, gray or yellow-white larvae emerge from the eggs. Their body is curved like a sickle, covered with small hairs and pads that serve as support when moving. The larvae feed on wood and mold - special fungi with which caring females have previously colonized the wood.
From the tunnels of adult beetles, the larvae make their own passages. They extend perpendicularly from them and do not intersect with the passages of adult insects. The larval course ends with a pupal cradle, from which, after pupation, young beetles fly to the surface. Depending on the species, bark beetles produce 1–2 generations per year.
Reproduction
With the arrival of spring, when the air temperature reaches +10 0 C, the beetles begin to leave their wintering places. Males are the first to come to the surface, in search of a suitable tree for future offspring. The male penetrates under the bark of a tree and there builds a fairly spacious mating burrow. When everything is ready, the beetle begins to emit a special smell - a pheromone, to attract females. From 2 to 4 females fly to the smell.
After mating, the female goes to lay eggs, making her uterine passage in the bark, 8 to 16 cm long and 2-3 mm wide. On the way, she makes a side depression and places an egg in it. Seals the entrance with sawdust and continues working further. In total, the female is capable of laying, on average, up to 80 eggs.
The life cycle of the bark beetle includes 4 stages of development:
- egg – up to 2 weeks;
- larva – up to 3 weeks;
- pupa – a little more than 10 days;
- adult.
From the moment the egg is formed until the young beetle appears, about 60 days pass. It happens that the female has not yet finished laying the uterine duct, and the laid eggs are already moving into the larval stage.
Larva
Having been born, the larva begins to gnaw its individual path, directed strictly at an angle of 90 0 to the maternal passage. The fleshy body of the larva is light, with a yellowish tint and a brownish head, and has a concavity towards the ventral side. There is a noticeable large number of callus-like checkers on it, with the help of which the larva moves, gnawing its way.
At this stage of development, the beetle causes the most damage, because the larvae actively devour the phloem and de-energize the tree, destroying the part through which the sap moves. The larval passages end in a cradle, in which the insect turns into a pupa.
Doll
In appearance, the pupa resembles a beetle. It does not have a cocoon, its body is short, compressed, light in color and soft. The pupal stage lasts up to 2 weeks. If she did not have time to turn into a young beetle before the onset of cold weather, then she remains to hibernate under the bark of a tree until next summer.
The young beetle does not immediately come to the surface. It remains under the bark to receive additional nutrition. Over the summer, one or two generations of young bark beetles may appear.
Over the winter, the newly emerged pest remains near the tree, digging a hole in the ground to a depth of 10 cm within a radius of 3 m. The larvae and pupae remaining under the bark can live at temperatures not lower than -17 0 C.
What does an infected tree look like?
The beetle primarily damages weak and unkempt trees . The presence of cracks and mechanical damage increases the risk of infection. But healthy plants are also in danger if there are massively affected areas nearby.
Characteristic signs of infection are:
- the appearance of small round holes on the trunks in the bark, indicating the flight paths of adult insects;
- accumulation and eruption of white, yellowish or light brown wood flour from holes;
- abundant release of resin on coniferous trees, and strong gum production on deciduous trees;
- frequent appearance of woodpeckers on trees;
- slowing down the growth of shoots, dying off of the ovary, shedding of leaves and needles.
At the final stage of infection, when the tree has no chance to survive, peeling of the bark begins.
Causes of the pest
Prolonged hot weather contributes to the development of several generations and the mass spread of the pest . Scientists note that in conditions of global warming and mild winters, the issue of an epidemic of bark beetles will be relevant. Not only in Russia, but also in Europe, the USA and Canada, the bark beetle has repeatedly destroyed millions of square meters of forest.
The presence of abundant food attracts the pest. Insects will appear if there are a lot of weakened, dry, old trees on the site and in the forest, residues after fires, and stumps, branches and bark have not been removed .
Signs of tree infestation
Wood infested with insects can be detected by the appearance of small holes and fine dust resembling flour in it. To confirm the presence of a beetle, you can pierce the bark of a tree or the surface of the wood with a sharp knife next to the hole you find. If there is a feeling of emptiness, it means that the plant or lumber is definitely affected by the pest.
In addition, its presence can be recognized by its special sound. Light crackling or creaking noises are often heard from wood infested with larvae.
Although the bark beetle looks quite harmless, pest control should begin as early as possible. If this insect appears in the garden, it means that it will soon switch to wooden buildings, since these parasites multiply very quickly.
What trees does the pest attack?
Most species living in Russia rely on coniferous trees for food: pine, spruce, thuja, juniper, larch, cedar . Some of them live only under the bark of trunks and branches, others in wood, and still others prefer to settle under the roots. There are species that damage not only wood, but also pine needles.
Some species live on deciduous and herbaceous plants. Bark beetles attack ash, rowan, hawthorn, dogwood, sloe, elm, aspen, privet, lilac, and rose hips . The bark beetle is attracted to fruit crops: apple, pear, cherry, sweet cherry, cherry plum, plum, grapes .
Some bark beetles settle on herbaceous plants, for example, on fodder clover , damaging their roots and seeds.
Bark beetle in the house - how to deal with it
The bark beetle lives not only in the garden and in the forest. It can live in wooden buildings and structures, and in wooden furniture . The main reasons for this proximity are:
- natural migration of insects in search of better habitats;
- the use of low-quality and beetle-infested materials in the construction of a house, barn, bathhouse, as well as the purchase of infested furniture;
- high humidity on the land and in the house.
If single holes are detected, the passages are filled with insecticides from a syringe. Then the hole is closed so that the liquid does not leak out and the pest does not get out. The treatment is repeated 2–3 times with an interval of 10–14 days. Popular household products are “Neomid Antizhuk”, “Rogneda Antizhuk”, “ PROSEPT Ultra”, “Wood Healer” .
At the initial stages, you can clean the wooden surface and treat it with drying oil, used machine oil, kerosene, white spirit, copper sulfate .
In difficult cases, contact sanitary services for professional treatment of the premises.
Who to contact for fumigation
Fumigation is one of the main specializations. What are the main advantages of the company:
- democratic pricing policy;
- professionalism (all stages of fumigation are carried out in full compliance with existing norms and standards);
- efficiency (processing occurs quickly, which saves client and employee time; he is a member of the “National Organization of Disinfectionists” NP “NOD”, which is a very valuable achievement of many years of work;
- specialists involved in fumigation with pesticides of the first hazard class, which include phosphine, have undergone mandatory training in this process as part of disinfection activities;
- For fumigation, only Magtoxin is used - the most expensive and safe fumigant - magnesium phosphide. Aluminum phosphide and other agents are not used.
To prevent the infestation of wooden structures in a room by wood beetles, choose only thoroughly dried wood, treat the wood at the construction stage with special compounds containing antiseptics, soak it in turpentine (its smell repels pests) and be sure to check from time to time whether there are any passages made in the wood beetles.
If you notice signs of the destructive “work” of wood beetles in your home, do not despair - take immediate action before the structure receives significant damage. And most importantly, do not try to cope with an insect infestation on your own - call pest control specialists, since only they can clear your homes of pests.
Means of struggle
Chemical and biological agents
Seedlings are treated with pesticides before planting and adult plants after flowering, when the mass flight of females begins. Insecticides act on the pest only at the initial stage. All above-ground parts of the tree are treated with the solution 2 times with an interval of 14 days. The active substances of the drugs should fall on the branches, leaves, and trunks.
Clipper
New generation contact-intestinal insectoacaricide. Refers to pyrethroid drugs. Does not accumulate in tree tissue, effectively fights the typograph bark beetle and other pests inside the trunk.
Used for spraying and intra-stem injections. The drug is diluted with water to obtain a 3% solution or used in concentrated form, taking into account that the consumption rate of the drug is 2.5–5 ml per 1 square meter. m. trunk.
BI58
In the fight against bark beetles, they use both an independent insecticide and in a mixture with the drug “Clipper”. The solution is prepared at the rate of 10 ml of product per 10 liters of water.
Confidor Extra
An insecticide based on imidacloprid acts on the digestive system of the pest. The dosage of the drug is 0.5–1 g per 10 liters of water.
Boverin
Microbiological insecticide based on the mycelium of an entomopathogenic fungus. The spores germinate into the body of the pests and release toxins that are harmful to the bark beetle. To treat plants, 100 ml of suspension is added to 10 liters of water.
When fighting bark beetles, you need to use pheromone traps with caution . Forest pathologists warn that in small garden plots they will give the opposite result. Beetles from all over the area will flock to the garden, since pheromone traps are designed for large forest areas.
Traditional methods
Trap belts are placed on trees twice a season. The optimal timing will be April-May , and for the destruction of the second generation of the pest - July-August .
After spring pruning, the trunks and branches of trees are coated with an insecticide prepared at home. To do this, take 6 parts of vegetable oil, 3 parts of paraffin and 2 parts of crushed rosin. Melt the paraffin and add rosin to it. The mixture is stirred until smooth, vegetable oil is added and the solution is heated for 10 minutes.
Why is it harmful?
Adult females and beetle larvae damage the bark of trees. When the female is ready to lay eggs, she gnaws through the wood to the bast (some species of the pest - to the sapwood). There, the female gnaws out a rather large (for her size) oval chamber, where she lays eggs. It is called the uterine.
When the larvae hatch, they begin to gnaw their way out, diverging in different directions from the camera. Since there are 20–40 eggs in one clutch, there will be the same number of “trenches” made by the pest.
Females and larvae of the bark beetle damage bast and sapwood. This has the most negative effect on garden trees and often leads to their death.
Basts are the “vessels” of plants. It is through it that water with inorganic substances dissolved in it flows from the roots to other parts of the tree. And then - organic compounds, including glucose, produced during the process of photosynthesis, disperse along the phloem from the leaves. Violation of the integrity of this tissue leads to the fact that some parts of the plant are left without nutrition. As a result, their death begins. As a result, the entire plant may die.
Sapwood is a tissue that stores stored nutrients. It helps plants survive the cold season. If the sapwood is damaged, the tree does not have enough resources for spring restoration, when the leaves have not yet blossomed, but nutrients are already needed. The plant may die.
Species of beetles that feed on conifers often lay eggs in houses and other buildings made of pine, spruce, and larch. The passages made by insects make the wood less durable and contribute to the onset of the rotting process.
Prevention
All preventive measures can be defined as sanitary and health measures.
- The area is kept clean: dry, diseased branches are cut down in a timely manner, and stumps are uprooted.
- On old trees, the trunks are sanded before the insects begin to fly out. The larvae are not afraid of the cold, but cannot tolerate bright light and dryness, so without a protective bark they quickly die.
- Fallen leaves and dry grass are also collected and burned.
- Constant care will strengthen the plants' immunity and increase their resistance to the bark beetle. The trees are watered, fed regularly, and the crowns are thinned. The soil in the tree trunk circles is dug up and loosened.
- If the pest cannot be controlled on infected plants, then such trees are disposed of to avoid an epidemic.
- Bark beetles have a wide range of predators. Birds and beneficial insects will help regulate their numbers.
Due to the massive proliferation of certain types of pests, huge forests and plantings on private plots are dying. Supervision of the condition of trees, compliance with sanitary rules, and proper use of chemicals will prevent the destruction of plants.
You will learn more about how to deal with the bark beetle in the video.
Preventive measures
Caring for your trees can prevent bark beetle infestations.
- Annual pruning of dry, diseased branches.
- Whitewashing trunks with lime.
- The use of chemicals to treat trees during the beetle flight period.
- Making traps from freshly cut trees, cut into small pieces. They can be placed in different parts of the garden, the beetles will choose them to reproduce. After the bark beetles settle, the traps need to be burned.
- Attract birds, they will happily feed on a variety of parasites that can settle in the garden.