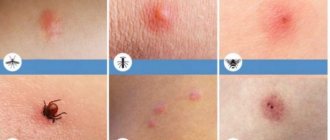
Summer is a wonderful time of year, but the mood is darkened by blood-sucking insects. The mosquito lives almost everywhere. For some people, its marks have no particular effect, others live with severe allergies and scratch their skin until open wounds form. This is fraught with infection.
Mosquito bites also leave bruises and age spots. If repellents do not have the desired effect against killing bugs, it is useful to know how to quickly and effectively get rid of the itch. We tell you how to treat wounds for adults and children, and what to do to relieve itching and redness at home.
Features of mosquitoes
Women and children are most susceptible to mosquito bites.
The first category attracts insects with a special smell, the second - with very delicate skin that is easy to bite through. They attack exclusively female mosquitoes, which require lipids, proteins contained in the blood of warm-blooded animals, to reproduce mosquito offspring. Insect receptors sense warm-blooded prey 3 km away—it’s not easy to deceive insects. The mosquito pierces the skin with its proboscis, injects a substance with an anticoagulant, which clots the blood, so a droplet after a bite never appears on the wound. Mosquito saliva is the cause of an acute reaction in the body. The skin becomes inflamed, a hematoma forms, and hardening occurs. Persons with manifestations of allergies suffer to a greater extent - the puncture sites on the skin hurt and swell.
Malaria mosquito bite
Malaria is a serious disease. One of its possible consequences is death. The carriers of the infection are mosquitoes of the Anopheles species.
Such an insect becomes dangerous in two cases:
- is the offspring of an infected female,
- fed on the blood of an infected animal.
The insect is slightly different in appearance from an ordinary mosquito.
Immediately after a bite, the virus that enters the body does not manifest itself in any way. The usual picture is observed: swelling of the affected area, itching, burning. After 2-3 days everything goes away. The duration of the incubation period varies from 1 to 3 weeks. The determining factor is the resilience of the immune system.
First symptoms:
- increase in body temperature,
- a sore throat,
- feeling of physical powerlessness,
- herpes rash,
- muscle pain,
- convulsive phenomena,
- dizziness,
- constant feeling of thirst,
- migraine,
- nausea,
- pale skin.
At this stage, the disease is often confused with a common cold.
The lack of required treatment leads to a worsening of the situation.
The initial symptoms after a short break are replaced by new ones:
- pain in the liver and abdomen,
- nausea and vomiting,
- decline in hemoglobin,
- loose stool.
Worsening occurs as a result of liver damage and a detrimental effect on blood cells.
The situation requires mandatory qualified medical intervention. In its absence, the following consequences are possible:
- splenic rupture,
- disturbances in brain activity with all the ensuing problems,
- coma,
- fatal outcome.
How and why a mosquito bites
Children and women most often suffer from mosquito attacks. The first because of the thinness of the skin, which can easily be bitten by a proboscis, the second because of the high level of female hormones. The insect can smell human odor for 3 kilometers, so it is extremely difficult to “outwit” a mosquito. Don't try to mask your natural body odor with eau de toilette. If it contains musk, you will become live bait for a swarm of insects.
The blood of birds, animals and humans contains iron and protein. These substances are necessary for the female to reproduce. After landing on the victim's body, the first thing the mosquito does is probe the surface. It then sticks its proboscis into the skin and injects saliva containing anticoagulants. After bites from bedbugs and many other insects, unlike mosquitoes, a red droplet protrudes from the puncture site. Mosquito saliva promotes blood clotting.
It is the injected saliva that causes an acute reaction in the body. People who are allergic to mosquito bites have the worst experience. But even a healthy person can experience a hematoma or hardening. The skin often becomes inflamed and red. All these phenomena are accompanied by burning and severe itching. Scars often remain at the site of scratched wounds. You need to restrain yourself and not scratch the skin, especially if the bite is on the face or other exposed part of the body.
How, when and where do mosquitoes attack humans?
Female mosquitoes need fresh blood from mammals to reproduce. For them, a person is a completely suitable source of satisfying their needs. When bitten, anticoagulants in the insect's saliva prevent the blood from clotting and, if a person does not swat the mosquito in time, it will move away, leaving behind an itchy and swollen wound.
Mosquito
It happens that one person is actually bitten by mosquitoes, while the other remains practically untouched. Insects are more attracted to people with:
- high cholesterol and steroid levels;
- increased acidity of sweat;
- increased sweating;
- high body temperature;
- large volume of exhaled carbon dioxide.
Mosquitoes live in different climatic zones, their activity directly depends on the duration of the warm period of the year. In the tropics, insects drink blood all year round, and in temperate climates from late spring to early autumn. Bloodsuckers are more likely to inhabit areas around water bodies, as well as places where animals gather.
Causes of allergies
Only female mosquitoes attack humans. To reproduce, they need iron and protein contained in the blood. After puncturing the skin, the female injects saliva containing an anticoagulant into the wound. This substance prevents blood clotting, thereby facilitating its absorption. It is to this that the human body reacts as a foreign irritant. The result is redness, swelling, and itching.
On a note!
If mosquito bites were not accompanied by severe itching, then the red spots after them will disappear quite quickly. Scratching the bite site often causes a secondary infection. In addition, spots and scars often remain there. And removing mosquito bite marks requires a lot of time and patience.
How long do mosquitoes live after biting a person?
The length of the insect life cycle depends on many factors. Among them:
- environmental conditions,
- gender (males live less),
- diet (carbohydrate and/or protein).
There is no connection between bite and natural death. Moreover, as a result of many laboratory studies, it has been revealed that the consumption of human blood makes females more tenacious.
However, this is only in theory.
In practice, the insect pierces the skin with its sting and begins to eat. At this time, a person may feel a burning sensation and pain, the intensity of which depends on the sensitivity of the body. Reacting to irritation, the victim notices the “predator”. At this moment, the life cycle of the latter most often ends. From this point of view, the question of whether a mosquito dies after a bite is logical.
What to do if bitten by a mosquito?
The first rule is to be patient and try not to scratch the bite site. Otherwise, the itching will only intensify, and skin damage will occur at the scratch site. If there is still damage, it should be treated with medical alcohol. In addition, in people prone to allergies, an area of inflammation, often significant, forms at the site of the bite. In this case, you should take a high-quality antihistamine.
You should stop the consequences of a mosquito bite as quickly as possible!
- Treat the bite site with alcohol.
- Apply a good antihistamine for external use (in the form of a cream, gel or lotion) to the skin. Pay attention to the composition of the drug; it should contain an analgesic and, for example, miramistin. The product will relieve itching, reduce inflammation and pain.
- If a wound has formed and an infection has entered it, treatment with a salt solution is necessary. Then an antiseptic is applied. To eliminate the risk of suppuration, Vishnevsky ointment or ichthyol ointment is used.
- If your health worsens and your temperature rises, you should additionally take paracetamol.
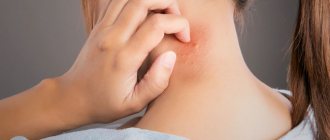
The skin itches after a mosquito bite due to the insect's saliva and special substances in it entering the body. The bite site itches to varying degrees in different people. The common reason for this is the body’s production of histamine in response to any allergen, in this case mosquito saliva. With the help of histamine, the body gets rid of the allergen/poison. In some people, its production occurs too actively, in which case itching, burning and inflammation are excessive.
Mosquito bite: what to fear?
Some species of mosquitoes carry dangerous diseases such as malaria, dengue, Zika virus, chikungunya and yellow fever. Do not think that such insects live only in tropical countries. For example, recently mosquitoes called tiger mosquitoes, which are capable of transmitting dangerous diseases, were noticed in Kuban.
But let's return to ordinary mosquitoes. Could their bites really be dangerous?
Let's start with the fact that some people get bitten more often than others. Just because you hardly get bitten does not mean that for others, encounters with insects do not turn into torture. You too may lose your superpower of being invisible to mosquitoes.
Bloodsuckers search for prey by reacting to chemicals that evaporate from the skin, smell and body temperature. These factors can vary quite widely and change depending on the situation.
Only females bite humans. When an insect's proboscis pierces the skin to a blood vessel, the insect not only sucks in blood, but also secretes saliva. It contains proteins that prevent blood clotting. The human body responds to these proteins with an immune response, causing the bite site to swell and itch.
The immune response manifests itself differently in different people. Moreover, different mosquitoes have different saliva. And if you may not have noticed the bite of one insect, then after another you will suffer from itching for a very long time.
By the way, the consequences depend on the thickness of the skin and the size of the blood vessel at the site of the bite. Young children have thin skin - redness can remain for weeks, and the bite sites can fester.
In rare cases, an allergic reaction may occur when a mosquito bites you. It is called culicidosis and is most often expressed in the appearance of large swelling and redness of the bite site - up to 10 cm (see example in the photo above). There are also “lucky ones” who may experience fever and nausea after being bitten. If you suspect you have an allergy, take an antihistamine with you to your mosquito encounter.
Please note that not only mosquitoes, but also other blood-sucking creatures may be waiting for you in nature. For personal protection, try to choose a product that repels ticks, horseflies, midges, and other people who like to bite.
Allergy symptoms
After relaxing in the forest, you can find many suspicious spots on your body that are not the most attractive color. Some of them may be accompanied by swelling and burning. These spots are left by various insects: mosquitoes, midges, flies or horseflies. Common symptoms of a mosquito bite:
- redness;
- slight swelling;
- strong desire to scratch the skin;
- burning.
These signs are a normal reaction of the human body to mosquito saliva entering the bloodstream.
After some time, the swelling subsides, the itching goes away, and the redness disappears completely. However, some people are more sensitive to stings. Signs of vasomotor rhinitis (thickening of the nasal mucosa) and bronchial asthma (severe suffocation) may appear. In this case, you must urgently call an ambulance. To quickly provide assistance to the victim, you need to inject Prednisolone intramuscularly. If you know that you or your loved ones have increased sensitivity to insect bites, be sure to take 1 ampoule of the specified medicine with you.
HIV transmission by mosquitoes
The question of the possibility of transmission of the human immunodeficiency virus by the bloodsuckers in question is terrifying. But this applies only to persons ignorant in this area. Given the knowledge of medicine and entomology (the science of insects) this is a myth.
Factors preventing infection:
- HIV does not live outside the human body. Staying in unfavorable conditions leads to the death of the virus with a 100% probability. Therefore, animals and insects cannot be its carriers.
- The mosquito’s body is “tuned” exclusively to absorb blood. The structure of its proboscis (sting) makes the reverse process impossible.
If such a terrifying prospect were real, the number of HIV patients would grow exponentially.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines include drugs that block histamine receptors, which are responsible for allergies. New generation drugs have no side effects and can be used by children. If you know that you are hypersensitive to insect bites, take an antihistamine before going outdoors. The drug relieves itching, relieves swelling, and neutralizes skin redness.
The most popular antihistamines:
- "Altiva";
- "Tigofast";
- "Cetrin";
- "Cetrinal";
- "Aleron";
- "Glenset";
- "Alersis";
- "Alergomax".
The most common form of release is tablets. Some medications come in the form of a nasal spray or drops for oral use. For children, drugs are available in the form of syrup. Allergy injections have the fastest effect. Drugs available in injection form include Diphenhydramine, Suprastin and Tavegil. In case of severe swelling of the respiratory system, it is necessary to administer the drug intramuscularly.
Potential danger
A man tries to fall asleep to the buzz of a mosquito. Does not work. He gets up and tries to track down the predator. Having lost hope, he goes to bed, covers his head and falls asleep. Having fallen asleep, it opens up, and in the morning wakes up with several itchy “blisters”. This is the best you can expect from mosquitoes.
The situation is less rosy when serious side effects occur. The latter includes a severe allergic reaction.
It may manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- increase in body temperature,
- general malaise,
- severe swelling,
- migraine,
- labored breathing,
- dizziness,
- change in heart rate,
- blood pressure surges,
- nausea,
- anaphylactic shock.
The risk of developing such a response increases due to factors such as:
Read also: Rhubarb root: medicinal properties and contraindications, treatment of hepatitis, diarrhea, weight loss
- decreased productivity of the immune system,
- tendency to allergies,
- meeting with the special species of insects in question,
- a large number of simultaneous lesions,
- pregnancy and young age (due to increased susceptibility of the body).
The temperature from an encounter with bloodsuckers can rise above 39 degrees. In this case, seeking medical help is extremely necessary. This is especially true in cases where several side effects are observed simultaneously.
The required drug treatment is prescribed after interviewing and examining the victim, with the obligatory inclusion of drugs to reduce the temperature.
In children, the possible harm is complemented by several other aspects:
- high probability of scratching with subsequent formation of wounds open to the penetration of various bacteria (as a result, antibacterial therapy may be required),
- increased moodiness in infants in response to unpleasant sensations.
However, the main danger is the possibility of infection by various viruses. This becomes possible as a result of a bite from a healthy person after a patient.
How to relieve inflammation
For some people, mosquito bite marks go away for quite a long time: dark spots that appear after scratching wounds and pimples can remain for more than one month. To get rid of bites, you need to use special medications and folk remedies.
On a note!
You cannot mask traces of mosquito attacks with powder or foundation during the inflammatory process. Such actions contribute to clogging of the wound and its decay.
Content:
- Mosquito bite: what to fear?
- How to treat a mosquito bite: remedies and ointments for itching. How to treat a bite for adults? The best means
- How to apply mosquito bites to children?
- Folk remedies that relieve itching and redness
- According to the naturalness of the base
How to relieve itching after a mosquito bite
It may take a couple of experiments to figure out what works best for you. If this is a pharmaceutical drug, then follow the instructions on the package.
Wipe the affected area with an alcohol wipe
You can relieve itching after a mosquito bite if you immediately treat the bite site with ethyl or isopropyl alcohol. It has a cooling effect when dry. However, it is not recommended to use it often - alcohol dries and irritates the skin.
Apply honey to the bite area
Honey is a natural antiseptic with wound healing properties. It has been proven to reduce inflammation from bites. But don't apply it outdoors to avoid attracting more flying insects. In addition, sugar can accidentally attract something more dangerous than mosquitoes (for example, wasps).
The most significant disadvantage of honey is that it is a potential allergen. Therefore, it should never be given to small children (under 3 years old)
Make oatmeal lotions
Oatmeal has active ingredients that help soothe itching and reduce allergic reactions. Unprocessed (colloidal) oatmeal from regular Hercules flakes is best suited for this.
- Brew a small portion of oatmeal;
- Let it cool;
- Apply oatmeal paste to the affected area;
- Rinse off with warm water after 15 minutes.
Honey can be added as an additional ingredient to double the therapeutic effect. After this, moisturize your skin with cream.
Use an iced tea bag
The antitumor effect of green and black tea can be useful not only for swelling of the eyes. They help relieve itching from insects. Soak the tea bag and then chill in the refrigerator. Hold on the bite site for about 15 minutes.
Use finely chopped garlic
Garlic contains such powerful antibiotics that they even kill salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus and E. coli. This is extremely useful to protect the mosquito bite site from infection. However, do not rub garlic directly into the wound! This can only increase inflammation. It's best to dilute the garlic with something neutral (like coconut oil or honey) and then leave it for a few minutes.
Cause of itching and bumps from bites
The mosquito injects its saliva into the puncture site. This substance is perceived as a toxin.
The natural response is an allergy. It manifests itself as unpleasant sensations of varying intensity.
Therefore, the victim “itches” after the bite, and develops bumps and redness on the affected areas.
Inflammation from a bite, spot, swelling, itching - this is a normal reaction of a healthy body to injected poison.
With regular encounters with the insects in question, the body is able to develop a habit of protein saliva and not feel any discomfort at all. Whereas with rare and few lesions, a person may not find any relief from itching.
External preparations
Sometimes, after a mosquito attack, ugly red spots appear on the body and face. After some time they disappear without a trace. The duration depends on the individual characteristics of the body. For some people, the spots disappear within 10 minutes; for others, they disappear only the next day after they appear. You can get rid of marks using special ointments and creams. They are indispensable if you have to go to a cafe or on a date.
Ointments relieve swelling, disinfect the wound, and prevent scar formation if you have managed to scratch the bite site. The medicinal substance inhibits the process of inflammation. The tumor does not increase, the itching completely disappears, the tissues do not swell or become inflamed. Creams are considered the best form of release for external use. Thanks to the fatty component included in the composition, creams are deeply absorbed into the skin and ensure rapid transport of the medicinal substance to the source of inflammation.
The best ointments to get rid of mosquito bites:
- zinc ointment;
- "Psilo-balm";
- Mosquitall;
- "Fenistil" (available in gel form);
- "Levomekol";
- "Soventol";
- Akriderm.
After a mosquito bite, the first task is to stop the inflammatory process. It is necessary to relieve swelling, which will lead to the disappearance of redness. All proposed medications should be applied as soon as possible after the bite is detected. “Fenistil” is also advisable to use in case of secondary inflammation (rash or urticaria).
Ointment "Rescuer" is very popular. Some people believe that it is advisable to apply it to inflammation that appears after a bite. “Rescuer” has a calming effect on injured skin, disinfects the wound and has a cooling effect. If a tumor has formed at the site of the bite, it is better to use Levomekol or Fenistil ointments.
How to avoid bee and wasp stings?
- Do not leave cut fruits and sweets on the table.
- Immediately remove cores and crusts into a sealed trash bag.
- The container for compotes/juices must have a lid.
- Teach children not to drink from the bottle, especially from opaque containers. First you need to pour it into a glass and inspect the contents.
- Do not use perfumes or creams with sweet or floral scents.
- Do not wave your arms to ward off wasps and bees.
- If you have already stunned the wasp, take it as far as possible without touching it with your hands, since the insect may still be alive, they could step on it with bare feet or put a hand on it.
- Use repellents.
Methods for relieving itching and swelling
Consistent actions to eliminate visible marks on the skin will be effective:
- take a remedy for allergic reactions to stop the irritation from the bite;
- get rid of itching and inflammation before masking a mosquito bite. A photo of a fresh injury shows redness and swelling on the skin.
Modern pharmaceuticals offer a wide selection of safe therapeutic and prophylactic drugs that relieve the symptoms of a bite - “Fenistil”, “Bepanten”, “Ambulance”. Creams and gels contain microelements to relieve itching, prevent infection, and accelerate healing. The convenient shape of the tube and lipstick allows you to carry the product with you in your pocket or purse.
You can relieve discomfort using proven methods:
- apply crushed leaves of parsley, plantain - skin itching and redness disappear;
- rub the affected area with the pulp of a banana peel - the burning sensation and pain disappear;
- lubricate the puncture on the skin with aloe juice - irritation goes away after several procedures;
- wipe the seal with a swab moistened with ammonia - swelling decreases;
- apply a compress of a chilled vinegar solution (one-third of a glass of water, 2 teaspoons of 9% vinegar) - itching is relieved, swelling on the skin is reduced;
- wipe the bite area with essential oil, including clove or tea tree extract, peppermint, and eucalyptus. Before application, it is recommended to mix a few drops of oil with any face cream for a gentle effect on the skin - the antibacterial properties of essential compounds reduce inflammation;
- lubricate the bite with toothpaste - itching decreases;
- Apply a tea bag - swelling disappears and the skin softens.
Inflammation from a bite on the delicate skin of the face is well soothed by a paste of three teaspoons of baking soda and 1 teaspoon of water. The thick mass is applied to the swelling and left until dry. Repeat several times or moisten with soda solution (1-2 tablespoons of baking soda per glass of water). A simple remedy is considered an effective method of relieving inflammation.
If folk remedies seem troublesome to prepare, you can use pharmaceutical preparations. The bite site should be washed with soapy water or wiped with an alcohol solution.
Next, you can use popular tools:
- “Boro Plus” - a composition based on natural ingredients (basil, turmeric, aloe vera, margosa) whitens the skin and eliminates burning sensation. Apply three times a day;
- Zinc ointment - the adsorbent, antiseptic properties of the drug allow you to remove redness and swelling;
- “Tretinoin” is an antitumor agent that eliminates irritation after scratching and small scars. The product has contraindications; you should read the instructions before use;
- “Rescuer” is a balm with the addition of sea buckthorn oil, lavender, vitamin E, and echinacea extract. This safe product can be used by pregnant women and children to get rid of mosquito bites;
- Balm “Star” - reduces itching and inflammation.
Pharmaceutical preparations are applied several times a day until the bite marks are eliminated.
Measures if the bite does not go away for a long time
In most cases, all consequences after contact with the insect in question disappear within 2-3 days. Sometimes this process takes longer.
Possible situations:
- The occurrence of a serious allergic reaction. Mandatory medical intervention is required. As a result of a survey and examination, the pediatrician/therapist will determine the complexity of the situation and prescribe a therapeutic course. Additionally, consultations with a dermatologist, allergist, or gynecologist (if the victim is a pregnant woman) may be recommended.
- Long-healing bites due to scratching. This situation occurs most often in children. The child scratches the affected area. A wound is formed. A pathogenic microorganism enters it. The process of decay begins. As a result of regular treatment with antiseptic agents, the wound heals. A crust forms. The child rips off the last one again, and the process repeats. The result is long-term treatment and scars. In this case, the only correct decision is to choose an effective preventive measure.
- Long healing without pronounced symptoms due to individual reasons. If there is no discomfort, no special treatment is required.
Folk remedies for itching after mosquito bites for a child
It is not necessary to use pharmaceutical products to help your baby get rid of an itchy spot. You can get by with absolutely safe, popular ones. Here are seven remedies that work flawlessly.
1. Ice. The temperature at the site of swelling rises as the body tries to suppress the infection. Cool compresses and lotions can reduce the temperature in the affected area and reduce the severity of the allergic reaction. Use regular ice, but do not rub it on your skin. Wrap it in a scarf in several layers and apply it to the blister for 10-15 minutes. If your baby complains that he is uncomfortable and too cold, increase the number of layers of fabric. The coolness from the compress should be pleasant. Ice packs work as a local anesthesia - they relieve redness, swelling and reduce the feeling of itching.
2. Soda compress. It cools and disinfects the bite site. Prepare a solution of soda at the rate of one teaspoon per half glass of water. Thoroughly soak a bandage, cotton wool or cotton pad in it and apply to the affected area. If there are a lot of blisters, lubricate them with soda solution. In the first hours the product is especially effective. It will also help if itching appears a few days after the bite as a delayed immune reaction.
3. Vinegar solution. Another safe folk remedy is a weak solution of vinegar. Dilute a tablespoon of 9 percent vinegar in a third of a glass of water. Treat the affected areas with the resulting solution. The acid present in it relieves irritation. Apply a cotton swab soaked in the solution to the blister to cool it and relieve any discomfort.
4. Sour cream. Fermented milk products reduce skin inflammation and soothe it, and relieve itching from mosquito bites. Apply sour cream or kefir to the blisters and leave until completely absorbed. While the “lotion” is cool, there is no desire to scratch the blister. When the mixture dries, lubricate the bite areas again. Repeat three to four times until the child feels better.
5. Tea bags. Brew black tea, leave the bag in boiling water for a few minutes, then remove from the cup and cool. Apply to the affected area and leave for 10-15 minutes. Tea leaves contain tannins and tannins. They have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect and relieve local skin irritation well.
6. Calendula tincture. If the bites are few, treat them with an alcohol solution of calendula. Alcohol disinfects the inflammatory focus and reduces redness and swelling, and calendula fights pathogenic microflora and dries out wounds. Use a cotton swab for treatment, apply the product pointwise - directly to the seal. There is no need to wipe large areas of the child’s skin, as alcohol dries it, and in small children, treating the body with an alcohol solution can cause poisoning.
7. Clay mask. If you have cosmetic clay, white or blue, use it to reduce your baby's inflammatory response. Dilute the clay with water in the usual proportions to a thick paste and apply to the inflamed areas. Leave until completely dry and do not remove when crusts form. Under such a compress, the skin remains moisturized, and the active substances of the clay fight the inflammatory reaction.
Regular brilliant green will help relieve itching, reduce swelling and redness, and also prevent the development of bacterial complications. Apply it to the blisters for three to five days until the seals disappear.
Other reasons
In exceptional cases, itchy pimples on the body, like mosquito bites, appear due to vascular and blood diseases. With this scenario, the rash resembles small bruises, which over time can merge into larger bluish formations.
Meningococcal sepsis is another rare cause of a condition where a rash appears, similar to insect bites. Such a rash can be diagnosed exclusively in a child and is a complication of meningitis, indicating the generalization of the pathological process. Each spot is located on a hyperemic surface and very quickly becomes necrotic. If the baby does not call an ambulance in time, he may die in a matter of hours.
What to anoint the skin after mosquito bites for adults
You can use the same safe folk remedies recommended for children. And herbal medicines that can be found in your home medicine cabinet.
Tea tree oil. It has a pronounced antiseptic effect, relieves irritation well, reduces swelling and helps suppress bacterial microflora at the site of the bite. Apply tea tree oil to the blisters with a cotton swab. The product has a distinct odor, and after application the area may tingle or burn. This reaction takes place within a few minutes.
Before using, make sure you are not allergic to tea tree essential oil. Use confidently if you have already used it before in cosmetic and skincare procedures. Or test the reaction to the product on a small area of skin: apply to the back of your hand, wait five minutes. If irritation does not occur, the product is suitable for you.
Alcohol solution. This can be boric alcohol, salicylic alcohol, regular cologne or vodka. Alcohol reduces the intensity of inflammation and relieves itching. Wipe the bites with a cotton pad soaked in an alcohol solution or apply it pointwise with a cotton swab.
Folk remedies
There are not always special means on hand to treat mosquito bites. You can get rid of discomfort without them. There are several effective ways to relieve itching from fresh mosquito bites at home.
Water
The itching will become less pronounced if the affected area is immersed in cold water or rubbed with an ice cube. This is an effective first aid for bites, and not only from mosquitoes.
You can use lotions of solutions (hold for 10-15 minutes):
- soda: a tablespoon per 200 ml of warm water;
- vinegar: tablespoon per 10 ml of water. Natural apple cider vinegar is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10;
- saline: prepare a paste and apply to affected areas for 10-15 minutes.
To relieve discomfort from mosquito bites, lotions made from strong green or black tea help. You can apply squeezed out fresh tea leaves and cover the top with polyethylene.
Essential oils
Essential oils effectively relieve inflammation and irritation, relieving discomfort on the skin.
How to relieve itching after mosquito bites:
- tea tree;
- carnation;
- mint;
- Melissa;
- thyme;
- eucalyptus;
- lavender.
You can wipe the affected area with pure oil or prepare an ointment: stir 5-10 drops with two tablespoons of low-fat cream.
Such drugs can only be used in the absence of asthma or allergies, otherwise the discomfort will be aggravated by skin manifestations or shortness of breath.
Milk and honey
To prevent the bites from itching, it is recommended to immediately lubricate the skin with honey. This will help neutralize the anticoagulant venom injected by the mosquito. After about 15 minutes, the itching will subside. Milk has a similar effect.
If you have sour cream, fermented baked milk or kefir in the house, they can also be used as an antipruritic compress. You need to soak a piece of gauze and apply it to the bitten areas for 15-20 minutes.
Pasta, tea and herbs
Menthol toothpaste is an effective remedy for mosquito bites. The only negative is that it can cause irritation and burns on sensitive skin.
The most affordable way to relieve itching is a tea bag. It needs to be soaked in hot water, cooled and applied to the affected area.
Decoctions (in the form of lotions) effectively relieve itching:
- chamomile: pour 250 ml of hot water into a tablespoon, leave for 15 minutes;
- sage. The decoction is prepared in the same way as from chamomile;
- calendula: 10 g, pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes;
- oak bark: 3 tablespoons, pour 200 ml of water, heat in a water bath for 25 minutes.
Instead of gauze soaked in broth, filter bags can be used. To quickly relieve itching, you can pre-cool them in the freezer - the soothing and anti-inflammatory effect will be more pronounced.
Other means
Folk remedies for mosquito bites:
- lemon and cabbage juice;
- slurry of water and aspirin tablets (diphenhydramine);
- juice of aloe, mint, basil, plantain and kalanchoe;
- onion or garlic gruel;
- balm “Star”;
- boric acid;
- a slice of raw potato;
- bay leaf powder mixed to a paste with olive oil;
- celandine juice or tincture;
- fresh citrus peels (wipe bite areas with zest);
- weak solution of manganese;
- iodine network;
- dandelion leaf or root juice;
- fresh cucumber (apply a slice to the bite site);
- saline;
- ordinary saliva. Its alkaline environment and bactericidal effect will help relieve discomfort. If you smear the scratched bite, the burning will intensify.
Products in the form of a paste should be applied to areas bitten by mosquitoes and left until dry, then rinsed with water. Some people recommend smearing the resulting lumps with earwax.
An original but working way to get rid of itching after mosquito bites: heat a spoon in boiling water and apply it to the blister.
Do not use on children or sensitive skin areas. Another unusual method is to cover the mosquito bite with tape or adhesive tape. This will reduce the sensitivity of the receptors and the itching will subside.
Help options
Traditional medicine offers many means of combating the consequences of mosquito bites.
Cold
For minor damage to the arms and/or legs, treatment may be as follows:
- wrap a cold object/ice in a soft cloth,
- lean against the affected area,
- hold on for a while
- repeat periodically.
The method is based on an anesthetic and anti-edematous effect. Low temperatures inhibit the spread of toxins and localize the inflammatory process. In case of multiple bites, use is not recommended: possible consequences are hypothermia and subsequent cold.
In this way, you can safely relieve swelling and redness in children (including infants) and pregnant women.
Baking soda
The medicinal properties of sodium bicarbonate have determined its active use in many areas. One of which is the solution to the problem under consideration.
You can treat a bloodsucker bite to reduce itching in the following way:
- dissolve 1 teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water,
- in the resulting duet, moisten a cotton pad (alternatives - use a piece of soft cloth, a handkerchief, cotton wool),
- wipe the affected area,
- repeat every hour.
Sodium bicarbonate solution can be used for bites on the face in children.
If a child scratches the affected area, the product should not be used.
If it is not possible to provide assistance in any other way, treatment is carried out around the wound.
During preparation of the composition, its concentration can be adjusted. For children over 3 years old and pregnant women, the proportions indicated in the recipe are suitable. For infants, the amount of baking soda should be halved. For adults, soda slurry is suitable. The latter should be used like this:
- combine sodium bicarbonate and water in proportions 3:1,
- Apply the thick composition in a dense layer to the problem area,
- for convenience, you can cover it with polyethylene and attach it to the skin in any way (optional),
- stand for 10 minutes,
- rinse with running water,
- repeat until the problem is eliminated twice a day if well tolerated.
Read also: Sprouted wheat: benefits and harms, how to use, advice from doctors, use in folk medicine and cosmetology
Possible harm is the manifestation of dry skin. To eliminate this possible phenomenon, you should have a suitable cream on hand. The choice of the latter should be made taking into account the treated area, age and characteristics of the body. A universal option is baby cream.
Tea tree oil
This ether will help quickly relieve swelling and itching. The application procedure is simple: just apply the oily liquid undiluted to the skin. Recommended frequency is every 60 minutes. The duration of therapy is determined individually (depending on the duration of healing).
An alternative to such a one-component product is a duet of tea tree and lavender esters. The combination proportion is 3:1, respectively.
In case of multiple lesions, taking a bath is convenient. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes. The required volume of oil is 10 drops.
Contact with damaged skin is unacceptable, so scratched mosquito bites should not be lubricated.
This ether can be used to prevent “meetings” with bloodsuckers. Possible methods:
- Use an aroma lamp. For a restful night's sleep in the room, it is enough to evaporate 10 drops of ether. You can increase efficiency by simultaneously using half the amount of clove oil.
- Apply to body. Before going outdoors, you should add a few drops of tea tree extract to the body cream you use and spread it in a thin layer over the body (particular attention should be paid to areas not protected by clothing).
Contraindications to tea tree oil:
- individual intolerance,
- age under 3 years (i.e. it is contraindicated for infants),
- period of bearing a child,
- lactation process.
Plants that relieve itching and inflammation
Certain herbs, when used correctly, will also be useful after mosquito attacks. The list of such assistants includes:
- Tansy. Grind the torn leaf until the juice is released, lean it against the painful area, hold it with your hand for 10 minutes (an alternative is to secure it on the body with a bandage / cling film).
The plant is poisonous - this method of suppressing symptoms after encountering insects is not applicable for pregnant women and children.
- Plantain. It is used similarly to tansy and is permitted during pregnancy and for infants.
- Mint. Place the dried leaves of the plant in gauze (it is better to fold it in several layers) and tie it. Place the “knot” in boiling water and boil for up to 5 minutes. Cool and squeeze out excess moisture. Use to wipe problem areas.
This treatment is safe for pregnant women and children over 3 months of age. For infants, prior medical consultation is required.
The dried plant can be stored at home permanently.
This is convenient for those who live in apartments and do not have their own garden plot.
Soothing tea for little ones
Severe mosquito bites in an infant can cause increased moodiness. As a result, appetite decreases, sleep patterns are disrupted, and the voice may “sag” (with prolonged screaming). It is possible to prevent such developments. To do this you should:
- determine a suitable and affordable treatment method,
- carry out a whole course of therapy (one procedure produces the desired effect in rare cases),
- At the same time, introduce soothing tea into your diet.
The latter can be purchased ready-made in pharmacies. An alternative option is to prepare an herbal drink at home.
From birth, children are allowed fennel tea. The recipe consists of the following simple steps:
- pour 1 teaspoon of seeds into the selected container,
- pour in 200 milliliters of boiling water,
- let the liquid cool down,
- remove the grounds,
- start using (“introducing” infants to the drink should begin with minimal doses).
Disguise methods
After removing the pronounced redness, itching - signs of the inflammatory process, you can begin to mask the remaining traces of mosquito bites. First, apply a thin layer of foundation or BB cream to the area. The treated area is covered with light powder.
How to disguise a mosquito bite photo.
Redness can be successfully neutralized with a greenish camouflage pencil or additionally covered with concealer.
In the sun, mosquito bite marks may become darker, so it is recommended to use sunscreen to block ultraviolet rays. Mineral cosmetics with a reflective effect give excellent results.
Resourceful people with a sense of humor offer their own ways to disguise a mosquito bite; photo jokes reflect unique solutions to this summer problem.
Going out into nature, to bodies of water, involves the use of protective equipment against insect bites. Showing forethought will reduce the number of mosquito attacks, the severity of skin irritation after bites, and protect against allergic reactions. The main thing is that you don’t have to figure out how to disguise a mosquito bite, a joke to distract the attention of people around you.
How to get rid of the consequences of a bite video
What helps against mosquito bites
Throughout our lives, we encounter several different types of parasites. But the most dangerous and unpleasant of all are those that are capable of stinging. Despite the life expectancy of such a bloodsucker, a drug is needed to alleviate its condition. After all, most often the bites itch mercilessly, and the lump from them acquires an impressive size.
Photo source: shutterstock.com
What helps against insect bites? In such situations, you should not pierce, especially in nature. Why? The hint is simple - this is fraught with infection. Therefore, safe means are needed here. Various antihistamines will help relieve itching at the site where the mosquito stung. So, the following medications provide good relief:
- "Zodak";
- Zyrtec (especially in the form of drops);
- "Tavegil";
- "Suprastin";
- "Loratadine", etc.
They effectively stop an allergic reaction to a mosquito bite in an adult or a child over 1 year old. But some drugs are suitable for infants. Tablets also cope effectively with the task. But the liquid version will allow you to achieve positive results faster. Sometimes such drops are used as external agents. They need to be applied to the cover around the problem area. Lubricated and waiting. No need to rub! After 5-7 minutes, the irritation will pass.
Useful tips
You can reduce the serious consequences of a small mosquito bite by showing your will - not to scratch the affected area. The release of histamine when scratching causes even greater itching. Additional damage to the wound increases the risk of infection, which means that the next day you can expect a large blister with signs of suppuration. Disguising the trail of a mosquito feast will become much more difficult.
Sources
- https://mymedic.clinic/biologicheskie/kak-zamaskirovat-ukus-komara.html
- https://klopkan.ru/komary/kak-izbavitsya-ot-sledov-ukusov-komarov/
- https://stolichki.ru/stati/kak-izbavitsya-ot-ukusov-komarov
- https://med-post.ru/prochee/kak-izbavitsya-komarinyh-ukusov
- https://apest.ru/komary/ukusy-komarov/izbavitsya-ot-sledov-ukusov-komarov/
- https://medvisor.ru/articles/problemy-s-kozhey/komarinye-ukusy/
- https://riafan.ru/1299510-narodnye-sredstva-ot-zuda-posle-ukusov-komarov-rebenku-chem-pomazat-chtoby-bystro-snyat-otek-i-pokrasnenie
- https://parazitdoma.ru/drugie-parazity/sredstva-ot-ukusov-komarov
[collapse]