The term “midges” may mean:
- Insects according to the official scientific classification, belonging to the midge family.
- Insects belonging to other families, but called midges because of their characteristic appearance and small size.
Both groups include species that are capable of drinking blood and biting people and domestic animals.
Carnivorous midges and insects similar to them in appearance and lifestyle are part of the midges - a group of blood-sucking flying pests. Depending on the area, the species composition of midges may vary, but the bite of any midge looks almost the same. The symptoms and intensity of the reaction are much more influenced by the individual characteristics of the body and immunity of the bitten person. The recommendations for first aid and treatment of midge bites described below are presented for informational purposes; only a doctor should make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, especially for acute reactions.
Pest bite area
In general, midges do not choose where to bite their prey.
They bite wherever necessary (forehead, arms, legs, stomach), wherever they find areas of skin not covered by clothing. Despite this, they can also bite under clothing, in which case you will find bite marks on the thighs and stomach.
Places where pests accumulate are places with high humidity.
They also love hot weather. In the evenings, pests also become more active. Usually, the victims are people who spent the weekend at their summer cottage. Interesting fact
During the war, a person sentenced to execution served his sentence as food for midges. He was brought to a place where pests were concentrated, undressed and tied up. The condemned man died a painful death from numerous insect bites.
vile midge
The photo shows a midge greedily biting into human flesh. A small, harmless-looking insect leaves behind a terribly itchy swelling and a scar that will remind you for a long time of the time spent in the taiga or tundra.
Midges are a family of Simuliidae of the order Diptera (this order also includes mosquitoes). There are more than 1,500 species of midges, they are distributed everywhere except Antarctica, desert arid areas and some oceanic islands. In Russia and the CIS, especially many midges live in the taiga and tundra zones; they also inhabit the steppe and forest-steppe. In places with favorable conditions, midges reach high numbers. Almost all midges are bloodsuckers that attack birds and mammals. These insects prefer a certain type of host: most are birds, many are mammals, and some are less picky.
The body length of adult midges is from 1.2 to 6 mm. The smallest species live in the tropics, the largest - in the northern temperate and subpolar latitudes (the author, by the way, was “lucky” to meet them beyond the Arctic Circle). Midges are diurnal insects, most active in the early morning and at sunset. However, during the polar day, when the sun does not set, midges can fly around the clock. Here temperature becomes the determining factor: it is usually colder at night, and midges hide. Midges are active at temperatures from 8 to 30°C. In addition, the behavior of midges and other blood-sucking dipterans is influenced by the wind. It prevents the imago from emerging from pupae, swarming, and attacking animals. Threshold wind speeds that prevent the attack of midges and biting midges are 1–2 m/s, mosquitoes — 2–3.5 m/s.
Like mosquitoes, only females feed on blood, as this is a source of protein necessary for laying eggs. Males drink exclusively plant nectar. Females also feed on nectar, obtaining the necessary energy from carbohydrates. The eggs of most species of midges do not develop if the female does not drink blood - this is the so-called anautogenic development (see Anautogeny). But there are species of midges (living in subpolar and high-mountain regions) in which the females make the first clutch without preliminary blood feeding, using the reserves of the larval fat body. This type of egg development is called autogenous. The second and all subsequent clutches in such species are carried out only under the condition of preliminary saturation with blood. The larvae of such midges develop for quite a long time - during the entire unfavorable period for the production of adults - managing to accumulate enough nutrients in the fat body. This adaptation allows midges to survive and reproduce in conditions in which the usual life cycle characteristic of the family (anautogenic) is impossible. This allowed midges to populate areas with harsh climates, where the likelihood of encountering a blood-sucking object is low.
When searching for victims, females use smell and vision. From afar, they smell the animal and the carbon dioxide it exhales; at a close distance, the insect uses vision, smell and thermoception (after all, we remember that midges feed on the blood of only warm-blooded animals).
Images from the BBC series about the life of a Canadian moose calf “A moose named Madeline”. Midge larvae develop in water and feed on filtered food particles. Millions of adult midges hatch from their pupae and go in search of other food, making life hell for their victims.
Midge bites are very painful, causing burning, itching, swelling, an inflammatory reaction, and sometimes fever. During mass attacks, a severe allergic reaction develops—simulidotoxicosis—which can lead to the death of the victim. In addition, midges carry various diseases: viral diseases of domestic animals, hemosporidiosis of birds, onchocerciasis of humans and animals. Onchocerciasis, or river blindness, can be contracted in Africa, Central and South America.
It is best to protect yourself from midge bites with clothing that fits tightly to your body and a mosquito net soaked in repellent. If you have already been bitten, disinfect the wound, apply ice in case of swelling, and if an allergic reaction occurs, take allergy medicine. You can also wipe the wound with ammonia - it neutralizes the active substances of saliva, and the bite site will stop itching.
The saliva of midges has analgesic, vasodilator and anticoagulant activity. It contains the enzyme apyrase (see Apyrase), which destroys ATP and ADP, which stimulate platelet aggregation. Apyrase activity in males is insignificant, which is not surprising. In addition to apyrase, saliva contains substances that inhibit some blood clotting factors (and). Also, components of saliva influence the immune response by suppressing the stimuli of cell-associated cytokines. Suppression of the immune system likely facilitates the successful transmission of pathogens through blood feeding.
The proboscis of midges, unlike mosquitoes, is short and only pierces the surface of the skin, plunging to a depth of up to 0.4 mm. Then saliva is secreted, which promotes bleeding, and the midge sucks the blood from the resulting wound (the mosquito, with its long proboscis, sucks the blood directly from the capillaries). The proboscis consists of a labrum (upper lip), a pair of mandibles (upper jaws) and maxillae and hypopharynx (see Mouthparts of insects). All these parts bear sharp hook-shaped teeth.
To feast on blood, the midge needs to perform a series of exciting actions. First, the teeth of the labrum and hypopharynx engage the surface of the victim's skin, stretching and fixing the area. Next, the mandibles come into play, moving like scissors and cutting the skin. The mandibles overlap each other and divide the proboscis canal into two ducts - for the absorption of food and for the secretion of saliva. The bend of the labrum expands the wound and plunges into the hole. The teeth at the top of the lacinia - parts of the maxilla - serve to securely anchor the proboscis. The lacinia retractor muscles allow the head and hypopharynx to sink deeper into the wound. Blood is sucked from the wound under the epidermis using the muscles of the hypopharynx and pharynx, allowing the proboscis to work as a pump. When the midge has eaten, the labrum straightens, the maxillae contract and the proboscis emerges from the wound.
The structure of the mouthparts of the midge Simulium
sp.
in a scanning electron microscope. A
- micrograph of the head.
The skin-piercing structures ( Ma
- mandibles,
Lc
- lacinia) of the short proboscis are hidden behind the labrum (
Lr
) and labella (
Lb
).
Numerous sensory setae are visible on all structures. Mxp
- maxillary (maxillary) palps.
B
- cross section of the proboscis in the middle part.
Fc
is a food canal formed by the labrum (
Lr
) and one mandible (
Ma
), the second mandible covers the groove of the hypopharynx (
Hy
), through which saliva flows.
The labium ( La
) encloses the piercing structures laterally. Figure from the article: H. W. Krenn, H. Aspöck, 2012. Form, function and evolution of the mouthparts of blood-feeding Arthropoda
Eggs, larvae and pupae of midges develop in clean flowing bodies of water - from small streams to large rivers (sometimes they can also develop in stagnant bodies of water). Adult insects live in biotopes with tall grass, shrubs and trees. The development time from egg to adult is from two days in the tropics to several months in northern latitudes, and even up to a year in drying up reservoirs. Diapause helps to survive unfavorable conditions. In the tropics there are up to 16 generations per year, while in temperate latitudes there are usually 2–6 generations. The lifespan of adult females is 3–4 weeks, sometimes 2–3 months. Females hatched from pupae can fly away (actively and passively, with air currents) over distances from several hundred meters to several kilometers and even hundreds of kilometers (in air currents over plains, oceans, and large river basins).
Larva ( left
) and pupa (
right
) of a midge. Worm-like larvae live in water and attach to aquatic vegetation, stones, and branches hanging into the water. Often the substrate becomes anthropogenic debris, and such a substrate is populated by midges even more densely than the natural one. They are secured with the help of a viscous secretion of the salivary glands and two attachment organs, which are rings of hooks. According to their feeding method, the larvae are filter feeders. At the front end of the body, a large fan is visible on which food particles settle. It consists of several dozen rays - outgrowths of the cuticle. The size of the larvae of different types of midges is from 3 to 12 mm. The larvae breathe in water through the integument of the body, and the pupae have a special respiratory organ (in the photo it is in the form of long threads). Its structure is unique for insect pupae. Photo from lifeinfreshwater.net
Male midges live on average no more than a few days. Which is not surprising: the female copulates only once in her life, and fertilization of all eggs occurs with sperm stored in the spermatheca. The task of males is to find a female during swarming during their short lives. Therefore, their eyes acquired an unusual structure: they are divided into two zones - the upper one, made up of large facets, and the lower one, made up of small facets. Large facets make it possible to distinguish moving females against a blue sky (see picture of the day Double eyes of flying insects).
Midges make up part of the midges, the biomass of which is enormous. It seems obvious that these insects were created solely to bother other animals. However, predatory larvae of other insects and fish feed on midge larvae, and some birds, such as wagtails, feed on adult insects. For humans, larvae serve as an indicator of the cleanliness of reservoirs, and the number of adult insects indicates a sufficient amount of vegetation surrounding the reservoir. Also, adult insects, feeding on the nectar of flowers, pollinate plants (interestingly, the flowers of such plants imitate the smell of animal skin).
Despite the bloodthirstiness of the Simuliidae family as a whole, there are also harmless midges. There are 37 known species that do not feed on blood at all: the oral appendages of females are reduced to one degree or another and are not capable of piercing the integument of vertebrates. Most of these species live in the north and mid-latitudes of the Holarctic; in the Southern Hemisphere they are much less common.
Finally, watch this cartoon:
The cartoon about annoying midges was made in 1991 based on the song “The Black Fly Song” by Canadian author and performer Wade Hemsworth, in which he talks about his war with these creatures during a summer geodetic expedition in Northern Ontario
Maybe you'll feel a little less sad that summer is over.
Photo © Nikola Rahmé from flickr.com.
Yulia Mikhnevich
Consequences after a midge bite
The reactions that can be caused by a bite are different.
A person who has never complained of allergic reactions may also suffer. Reactions are divided into local (itching, which is unbearable, redness and subsequent swelling, if the midge has bitten the lower limbs, the person’s gait may be difficult); general (high temperature, weakness in the body, headaches. And if you have a tendency to allergic reactions, then in this case the body may become covered with blisters not only in the affected areas of the skin).
The swelling itself may go away within a few days. But the itching may torment you for several weeks. Itching can develop into scratching, which will also take a long time to heal on your body.
What medications will help a child at home?
Almost every mother in her home medicine cabinet has Zvezdochka balm or cosmetics used after insect bites: creams, ointments, pencils. It is better to always take such preparations with you on a walk so that, if necessary, you can quickly apply them to your baby’s wound.
As soon as the parents notice that the child has been bitten by an insect, and the affected area is itchy and painful, it is necessary to disinfect this area of skin. Solutions of Furacilin and Chlorhexidine have antiseptic properties. When rinsing the eyelid at home, you need to be extremely careful to prevent the drug from getting on the cornea.
How to relieve swelling?
The bite of a black midge causes severe swelling of the skin. The following remedies will help alleviate the victim’s condition:
- first you need to rinse the affected area with cold water in order to eliminate any remaining poison as quickly as possible;
- You need to apply a cold compress to the swollen area;
- anoint the redness around the wound with Fenistil, Advantan, Zvezdochka or Rescuer balms, Boro Plus;
- Furosemide tablets and injections can relieve extensive tissue swelling;
- in case of a bite in the eyelid area, if the eye is swollen, vasoconstrictor eye drops Polynadim or hydrocortisone ointment will help relieve swelling (we recommend reading: what to do if a child has swollen eyes?).
Elimination of itching and redness
To relieve allergy symptoms (itching and redness), oral administration of antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin, Diazolin) and the use of local agents (Fenistil-gel, Advantan) are indicated. Alcohol compresses or lotions with novocaine cope well with itching.
If the bite site is very itchy and there are no antihistamines at hand, in this case Corvalol or Valocordin will help treat the disease. You need to apply a few drops of the product to the itchy area, and within a few minutes it will stop itching.
Treatment of allergies to midge bites
To block the manifestation of an allergy to an insect bite, it is necessary to take an antihistamine as quickly as possible. Such drugs begin to act 15-20 minutes after administration, and the effect lasts throughout the day.
If this is not the first time an allergic reaction has occurred in your baby, it is recommended to take an antihistamine for several days until the characteristic symptoms completely disappear. In this case, it is better to visit a doctor so that he can prescribe the appropriate drug treatment, calculate the dosage of the drug and the duration of its use.
Antipyretics and other drugs for symptomatic treatment
It happens that the baby’s condition after an insect attack is accompanied by weakness and hyperthermia. In this case, the doctor prescribes additional medications to eliminate symptoms:
- antipyretics (Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol);
- anti-inflammatory medications;
- in severe cases - antibacterial drugs;
- wound healing ointments.
What signs can be used to understand the severity of a reaction to a midge bite?
Factors that will help you understand how reactions to a midge bite are expressed:
- Age range.
More mature people can easily tolerate midge bites. For children, bites can subsequently affect them in the form of an allergic reaction. Infants suffer the most danger from midge bites. For them, this can develop into a serious illness. - Immunity.
If the immune system is weakened, the reaction to a midge bite can cause allergic reactions. Age range does not matter here. - Increased sensitivity to midge saliva.
All pests contain an irritating reagent in their saliva, the body’s reaction to which cannot be predicted. If the human body is sensitive to this reagent, then insect bites must be avoided. - Pregnancy and lactation.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, a woman’s body is weakened significantly. If before pregnancy a woman tolerated insect bites normally, then during this period there can be serious consequences.
General description of insects
The black midge belongs to the order of blood-sucking insects, like mosquitoes and flies. More than a thousand species of these hymenopteran creatures are known in nature. Midges are small insects that look like a fly, but their body size does not exceed 5 mm. They are common on all continents except northern and southern latitudes in permafrost conditions.
On a note!
The widespread Drosophila flies or fruit flies are not blood-sucking flies and do not bite humans. They are interested exclusively in the fruit and vegetable menu. They often appear in people's homes with brought food and settle in the kitchen. The activity of the fruit midge cannot be called harmless - it lays larvae in rotten fruits and can be a carrier of infections, so it is necessary to get rid of fruit flies in the apartment.
Appearance of midges
Black midges live and breed near sources of fresh water. Very often you can notice a whole cloud of small insects near large bodies of water or even a puddle. Only females are predators. Males feed on nectar and plant sap. Insects hunt people and animals only during the daytime. They live in colonies and very rarely fly alone.
During the bite, the female bites the skin and plunges her proboscis inside. While she sucks the blood, her saliva enters the wound, which contains a substance that prevents blood clotting, as well as enzymes that cause severe itching and swelling. Multiple midge bites can cause a severe allergic reaction, which only doctors and special medications can prevent.
First aid after a midge bite
If midges bite you while outdoors, you must immediately treat them with any solution that contains alcohol.
After this, treat the bite with insect repellent. Nowadays, people do not go on vacation without these funds. If a midge has bitten you at home, the first thing you need to do is treat the wound with folk remedies to prevent the development of swelling.
What antiseptics are recommended for treating a bite?
Chlorhexidine;- Miramistin;
- Boric acid;
- Furacilin solution.
To prevent the swelling from “growing,” you need to apply ice in a cloth wrap to the bite area. If you do not wrap the ice in a cloth, you may get frostbite on your skin.
When is hospitalization necessary?
Medical assistance is required in the following cases:
- The reaction to a bite develops rapidly; available first aid remedies are not effective. It is recommended to contact the nearest medical facility.
- There is a risk of developing anaphylactic shock. You need to call an ambulance.
- Symptoms of intoxication do not subside within 5-7 days when all necessary therapeutic measures are carried out.
After examining the patient, the doctor will decide whether to recommend the patient hospitalization or continue outpatient treatment.
Relieving inflammation
Inflammation occurs when we begin to scratch the affected area.
To completely prevent inflammation, you need to take a comprehensive approach to treatment. Ointments and lotions will give you a positive effect. If it was not possible to remove the inflammation with the help of ointments and lotions, and the inflammation continues to “grow,” then the following maneuvers must be performed daily:
- Treating the wound with soapy water. It is advisable to use 72% laundry soap.
- Lubricate the irritation with any antiseptic. It is important to ensure that this product does not get into the wound itself.
- 2 hours after applying the product, lubricate the wound with ointment (levomekol, you can even use Vishnevsky ointment). It is recommended to lubricate the wound at night.
- After a while, as the ulcer formed after the bite begins to heal, you can begin to make lotions. Flocks of herbs (chamomile, sage, etc.). Wet a cloth with the solution and apply it to the wound.
Important point.
If irritation begins to worsen, consult a doctor. Of particular concern should be the appearance of black spots on the skin.
Traditional treatments (drugs)
Drug treatment follows the same plan as treatment with traditional methods: we disinfect, relieve itching, prevent swelling from spreading, and fight allergy symptoms.
- for disinfection, you can use solutions of Chlorhexidine or Furacilin;
- Ointments with antihistamine components (Levomekol, Lincomycin ointment) will help relieve the symptoms of an allergic reaction, as well as itching, pain and swelling. You can also use antihistamines in the form of tablets (Suprastin), their effect will be longer, but will not act as quickly as ointment;
- Cooling solutions, for example Menovazin, are used to relieve itching;
- for the last stage of treatment, when there is no more itching, the rash and swelling have gone, you can use healing ointments (Argosulfan, Levomekol).
If suppuration appears at the site of the bite, surgery may be required. The doctor will mechanically open the abscess and remove the accumulated pus.
What remedies will help get rid of irritation and itching?
A midge bite causes severe itching, which can develop into nervous anxiety. How to treat it? Folk medicine and traditional remedies come to the rescue.
Ointments and gels
- Fenistil.
- Sinaflan.
- Psilo balm.
- Momederm.
- Betazon.
- Prednisolone.
- Hydrocortisone.
Regardless of their pharmaceutical affiliation, all of the above remedies will help you fight unbearable itching.
Why are insect bites dangerous?
Mosquitoes, ants and fleas, bedbugs and arthropods often bite people. You can encounter them not only in the fresh air; insects easily penetrate into a living room, skillfully hide in it and attack a person. Each of them has their own reasons for biting : for some, human blood is food , which makes it possible to produce offspring (mosquitoes) or move to another stage of development, for others, the bite is a measure of protection . Whatever the reasons why an insect bit you, you need to be careful about the bites and know how to properly provide help.
Swelling after a midge bite. How to deal with it
- Baking soda.
You will get the effect from it: it relieves swelling, lowers the pain threshold and reduces itching. How to prepare the solution? Add 1 teaspoon of soda to 250 ml of water. Wet a cotton swab with the resulting solution and wipe the infected area. - Plantain or parsley juice.
The effect will also help reduce pain and itching. - Essential oils.
It is recommended to use both in pure form and to make a solution. The method of application is the same as described above. How to prepare the solution? 1 tablespoon of vegetable oil and 5 drops of any essential oil. Also wet the swab and apply it to the infected area.
Treating stinging insect bites
- Remove the sting and apply fresh garlic paste; be careful with this product, as a burning sensation may occur.
- You can prepare a natural compress from burdock leaf. To do this, pour boiling water over it and coat it with a thin layer of honey, and then apply it to the bite site.
- A cold compress is also effective in relieving pain .
- Be sure to treat the affected skin with any alcohol-based disinfectant .
- numb the bite site , rinse them and crush them in your palms, apply to the wound. Mint will also relieve swelling and redness.
Any complications after the bite? Treatment options
Signs of complications:
- Heat;
- Headaches and dizziness;
- Formation of pustules in the affected area;
- Spots and scars appeared after the wound healed.
All these symptoms indicate that you are experiencing complications.
You can relieve fever and headache with conventional antiviral drugs (Ibuprofen, etc.). Signs of intoxication - here medications such as enterosgel, white coal will help you.
Aloe.
A folk remedy that will help you replace all pharmaceutical products and save your budget.
How to apply aloe?
Rinse the aloe leaf well and scoop out all the pulp using a spoon. Cut in half and place on a napkin. First, the wound should be treated with any antiseptic; after 15 minutes, apply an aloe leaf to the wound and tie it with a bandage.
Effect:
Aloe not only disinfects and increases wound healing time, but also relieves itching and inflammation of the wound.
If you find spots on the skin, you can use products such as: Bruise off, Badyaga and other products designed to treat bruises and abrasions.
If hardening is detected inside the wound, it is recommended to use absorbable compresses, for example, Dimexide.
Dilute it in water in a ratio of 1:4 and apply a gauze pad soaked in the solution to the cone.
This product may cause skin burns if overused. The optimal holding time is no more than 40 minutes.
Midge life cycle and description
Adult black flies are small insects, 1 to 5 mm in length, ranging in color from black to various shades of gray or yellow.
Adults
transition from egg to larva, pupa, adult stage. The full cycle takes two to six weeks, depending on environmental conditions. Adults are most numerous near breeding sites. The average flight distance of a female is 2 km, for males it is less than half this distance.
Eggs
Males and females feed on nectar, but females require blood to mature their eggs. They feed at dawn and dusk. Some species are active during the day.
The number of eggs produced varies depending on the species, up to 450 eggs in one batch and up to seven batches over a lifetime.
Females lay eggs on vegetation just below the surface of the water. Adults live for several weeks in natural conditions.
Larvae
The larvae are worm-shaped, creamy white, approximately 2 to 5 mm long. They need water, air, food. They are not strictly aquatic or terrestrial and cannot develop without moisture. Present in and around salt marshes, swamps, on the banks of streams, ponds, and in dirty substrates. They feed on small organisms.
The larvae do not develop inside humans or other animals.
Some species can produce their first batch of eggs without their first meal (blood).
Simulium slossonae flies four to eight miles from its breeding site in search of food, then returns after feeding to reproduce and lay eggs. Thus, the problem can be transferred over considerable distances.
If a midge bites you on the face. What to do
The favorite place for midge bites is the face and neck.
They especially like to bite in unprotected places on the body (the mouth and around the eyes). If a midge bites in these places, you will feel the effect immediately when the poison enters the blood.
The eye will immediately begin to swell, which can lead to short-term vision loss.
If the site of infection is the area of the lips, then the lip will immediately begin to enlarge and it becomes problematic to talk.
Face
– a dangerous area for pest bites. If this happens, you must immediately take measures to prevent the development of complications:
- Apply antiallergic cream to the affected area of skin. In this case, drugs from the corticosteroid group are suitable;
- It is necessary to drink as much water as possible in order to remove all toxins as quickly as possible.
- Apply a compress of grated potatoes to the sore spot. This product will help cope with itching and cool the skin;
- Parsley juice will help deal with swelling. Wash fresh herbs, chop finely, place in clean gauze and squeeze well. Apply a damp swab to the bite site.
Important point. Never rub your eyes with your hands. If the mucous membrane is inflamed, the percentage of infection penetration increases significantly.
Experts' opinion
Based on the results of clinical studies, La-Cri products, including cream for sensitive skin, are recommended by the St. Petersburg branch of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia. The effectiveness, safety and tolerability of the products have been proven by a clinical study. The cream is also suitable for daily skin care of children with mild to moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
It has been clinically proven that La Cree cream for sensitive skin reduces itching and irritation, relieves skin redness, moisturizes and gently cares for the skin.
Sources:
- I.A. Gorlanov, L.M. Leina, I.R. Milyavskaya, Skin of newborns: differential diagnosis of pathological conditions, features of care
- N.D. Odinaeva, G.V. Yatsyk, I.A. Belyaeva Correction of dry skin in newborns, Pediatrics journal, 2011
- B.A. Shamov, I.G. Safiullina, A.B. Beshimova, T.B. Shamov, Differential diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, Journal of Practical Medicine, 2011
- Fokina R.A., Atopic dermatitis: stages of development of classification forms, Siberian Medical Journal, 2007
What you should never do after a midge bite
- Household chemicals. Anything containing chemicals is strictly prohibited. The exception is laundry soap.
- If ulcers appear from scratching, they must be handled carefully. Do not allow alcohol solutions to get into open wounds.
- If a midge bites a baby. In this situation, consult a doctor immediately. Do not take self-medication, this can turn into a tragedy, since the baby does not have a strong immune system.
- Minimize scratching. If you really want to, it is also advisable to abstain. This can lead to infection in the infected area of skin.
- Corticosteroids should not be applied to an open wound. They cause a burning sensation and slow down tissue regeneration processes.
What not to do?
- You should absolutely not scratch the bite site. The more you scratch the bite site, the more itching appears and the swelling becomes greater.
- Do not wash the wound with synthetic detergents.
- Like all types of wounds, a bite should not be smeared with brilliant green and pure alcohol. If you treat a bite with brilliant green or alcohol-containing solutions, you must do this carefully and only around the open wound.
- You should not experiment with antibiotics and strong antihistamine tablets on your own.
- Apply hormonal ointments to the wound itself. Moreover, if antihistamines or antibiotics were prescribed by a doctor, such prescriptions should not be neglected under any circumstances.
In what cases is it necessary to urgently consult a doctor?
It is necessary to seek medical help if:
- You have tried all the methods, but nothing helps, and the effect of infection only intensifies, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
- If there is a possibility of developing anaphylactic shock, call an ambulance immediately.
- If you follow all the recommendations and do everything according to the instructions, but the symptoms do not disappear, it is also recommended to consult a doctor.
What are the dangers of skin lesions and how to treat them?
If the bite is treated incorrectly and untimely, the following complications arise:
- allergies (the appearance of a rash, nausea, weakness, fever - signs of such a reaction);
- inflammation of wounds (severe itching provokes scratching, and if infected, the damaged area festers);
- loss of vision (if bites in the eye area are treated incorrectly, there is a risk of vision loss).
To prevent complications, measures must be taken immediately. Immediately after discovering a bite you should:
- Wash the wound with water and laundry soap. You should not use other soapy products (gels, shampoos), as this may contribute to the development of allergies.
- Blot excess water with a napkin.
- Treat the wound with an antiseptic (Furacilin, Chlorhexidine).
- If the pain is intense, take a painkiller and an antihistamine (Paracetamol, Claritin, Suprastin, Tavegil).
- Cool the bite area with ice.
On a note. Netizens who have encountered a similar problem recommend applying Zvezdochka balm to the damaged area.
If the bite occurs in the eye area, you must:
- Rinse the damaged area with cold water.
- Relieve swelling with a special ointment, for example, Fenistil Gel.
- Cool it with a compress.
- You should consult a doctor as bites in the eye area are especially dangerous.
Compresses
A compress applied to the damaged area in a timely manner will greatly facilitate subsequent treatment and speed up recovery. This method will help relieve inflammation and relieve itching. There are many recipes for wet dressings, but we will focus on illustrating the most famous of them.
Dandelion compress:
- Grind the fresh leaves of the plant until the juice is released.
- Apply the resulting pulp to the bite site.
- Secure the compress with a bandage or plaster.
- Change every three hours.
In the same way, a compress is made from the leaves of parsley, plantain, and basil.
Potato:
- Take one raw potato.
- Cut into slices or grate.
- Apply to the skin and secure with a bandage.
- When the potatoes are hot, replace them with a fresh portion.
This recipe, like the previous one, is also suitable for eliminating the consequences of bites in the eye area.
Soda:
- Dilute a teaspoon of the substance in half a glass of water.
- Soak the bandage in the solution.
- Apply to the damaged area of skin.
- Keep until dry.
- If necessary, repeat the procedure.
You can also use ice and menthol products as a compress, including toothpaste, which perfectly cools the skin.
Photo gallery: ingredients of effective compresses
A compress of grated potatoes is a popular method in folk medicine for relieving skin inflammation.
Thanks to a compress of soda, severe itching is relieved in places where midges bite.
A chamomile compress will soothe and tone damaged skin.
Pharmacy drugs
Purchased anti-bite remedies are divided into three groups:
- Ointments.
- Gels.
- Creams.
They differ in consistency and speed of absorption of the active substance. Ointments and creams are made with a fatty base, which means they are absorbed slowly but remain on the skin longer. Gels have a quick effect, as they are water-based and easily absorbed.
Important to remember. Ointments and creams leave stains on clothes due to their fatty base, so they should be used carefully.
Table: characteristics of popular products with ratings based on customer reviews
| A drug | Price | Grade | Active substance | Action | Contraindications |
| Fenistil | 360 rub. | 3,9 | Dimetindene - 1 mg |
|
|
| Bepanten | 200 rub. | 4,7 | Dexpanthenol – 1 g | Tissue regeneration |
|
| Rescuer | 154 rub. | 4,8 |
| Healing | Hypersensitivity to components |
| Menovazin | 70 rub. | 4,9 |
|
|
|
| Levomekol | 130 rub. | 4,7 |
|
|
|
Photo gallery: effective drugs for treating damaged skin
Rescuer balm contains only natural ingredients
The substance dexpanthenol in Bepanten ointment heals and restores the skin
Fenistil gel has antipruritic and antiallergic effects
Treatment of the consequences of bites in children
In children, various types of symptoms are more intense than in adults. They also have a harder time not scratching their itchy skin, so there is a greater risk of wound infection.
If a child is bitten by a midge, follow these rules:
- Rinse the wound thoroughly.
- Apply a baking soda compress using a cotton pad and hold it in place for a short time. This will prevent you from scratching the bite area.
- Bathe your child with sea salt. This procedure will help relieve itching from numerous bites.
- After this, treat the patient using special means.
Important to remember. When choosing an ointment for your child, read the information on the packaging. It is necessary to use medications in accordance with the age category to which the patient belongs.
Since not all ointments are suitable for treating small children, use tea tree oil - it relieves itching and reduces irritation. While relaxing in nature, carefully monitor your baby. If he starts to itch, examine the skin for bites so that the child does not have time to scratch the damaged area.
If swelling and redness are severe, consult a therapist or allergist. Self-medicating in this situation is dangerous, because children's immune system is weak, which makes the risk of complications higher.
Video: helping a child with midge and mosquito bites
What to do if signs of allergy appear
Children, pregnant and lactating women, as well as people predisposed to such reactions are susceptible to developing allergies.
Signs:
- polymorphic rash, characterized by the appearance of heterogeneous spots;
- acute erythema - a sensation of dense nodes under the skin, up to 5 cm in diameter;
- increasing swelling of the tissue at the site of the bite.
What to do:
- Relieve swelling with ointments or compresses.
- Take an antihistamine.
- If signs of swelling do not disappear within a day, you should consult a doctor.
Rarely, after a bite, anaphylactic shock occurs or Quincke syndrome (extensive swelling of the skin) develops. In such cases, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, as there is a risk of death or coma.
Signs of anaphylactic shock are as follows:
- pressure drop;
- convulsions;
- uncontrolled urination;
- loss of consciousness;
- heat;
- headache;
- intense local reaction.
Quincke syndrome is characterized by the following symptoms:
- enlargement and swelling of soft tissues;
- the swollen area feels hard to the touch;
- after pressing on the bite, a hole remains;
- pale skin;
- decreased blood pressure;
- tachycardia (rapid heartbeat);
- intense sweating;
- confusion;
- lack of coordination;
- anxiety, fear.
Important to remember. Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor. Trying to solve a problem on your own is dangerous and can be fatal, as can failing to seek help in a timely manner.
Photo gallery: allergic reactions to midge bites
The development of anaphylactic shock can occur over a period of several seconds to 5 hours
Quincke's edema due to insect bites occurs only in 2% of cases
In 20% of cases, anaphylactic shock is fatal
How to avoid midge bites
Midges bite unnoticed and it is not always possible to feel their bite, so if you know that you are going to travel to nature or to the country, be sure to take precautions:
- Don't wear perfume. This attracts midges.
- Dress to show as little skin as possible.
- It is better to wear clothes made from natural fabrics.
- Apply products that repel midges. Please read the instructions before applying.
- The smell of food also attracts pests. When you sit down to eat, be sure to cover as much of your body as possible with clothing.
If you live in an apartment or house, you can also become victims of midges.
This is where electric fumigators will come to your aid.
If you take all protective measures, then you will not be afraid of any pests and the summer will pass 100%.
Description of the appearance of a bloodsucker under a microscope
Those who managed to see a photo of a mosquito under a microscope clearly state that it looks scary and repulsive. His body no longer looks as smooth as it seems. It is all covered with small bristles. With their help, he orients himself in space and establishes a connection with the surrounding world.
Most noteworthy is the head, which in photographs under a microscope looks like something alien. The first thing that catches your eye when looking at it is the large mosaic eyes. The structure of the visual organ under a microscope looks very interesting. These are many small fragments that together make up a whole faceted eye.
The structure of the oral apparatus also attracts no less attention. An enlarged mosquito has a developed and branched apparatus
It consists of the upper and lower lips, jaws and proboscis. Even the nose of a mosquito is not a strong needle, but several flexible tentacles. It is with their help that the bloodsucker finds a blood vessel under the skin.
The midge is considered the most common insect on Earth. When magnified under a microscope, the midge looks somewhat like a fly. Its size, on average, is 2 - 3 millimeters, with an isolated case when the dimensions reach 6 mm. The body of the insect is gray. After biting a person or animal, the midge becomes saturated with blood and its body changes to a reddish hue. The midge has a curved chest covered with small hairs.
The abdominal cavity is a single system consisting of 9 segments. On the outer part of the midge body there is a pair of fairly large wings. If you look closely, you can see dark patterns on the wings, giving the midge a grayish color. Thick and densely packed veins are covered with small fibers over the entire area. The paws are dense and small like those of a midge. One pair of legs is located in the upper part of the abdomen, and the other two, bent and covered with villi, are located in the lower part. The head of the midge is always turned down, many antennae are visible. The eyes occupy a large area of the insect's head, being located on the side.
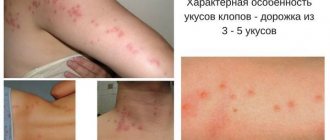
Symptoms of a midge bite
Symptoms of a midge bite depend on its composition. Most often in the bite area it is:
- Redness
- Itching
- Edema
- Tissue compaction
- Burning
- Papules formation
- Dull, sometimes throbbing pain
- Increased skin temperature
- Allergy
If you are bitten by several types of midges at once, the bites and sensations from them may vary. The more insects there are, the more dangerous the situation and the more violent the body’s response can be. This is one of the biggest problems of encountering midges. Bites, which individually would not cause much discomfort, begin to be inflicted in tens, hundreds, or even thousands.