Bedbugs and fleas belong to the so-called synanthropic organisms - parasites, whose existence is closely connected with humans and their homes. Some insects have become so adapted to the conditions of rural settlements and cities that they have completely disappeared from the wild. This lifestyle is especially attractive to pests in regions with a variable climate. Cold winters can be safely experienced in heated rooms where food is always plentiful.
When blood-sucking insects appear in an apartment, their presence quickly becomes obvious. They need to eat, and to do this they need to get out of hiding and bite people or pets. At first glance, it is not always clear who exactly bitten, but this issue can be sorted out if you know how. What is the difference between flea and bed bug bites, what signs can be used to identify pests and how to get rid of them, read the material below.
Causes
Fleas can attack a person if there is no other food source (animal or bird) nearby. However, there are also types of insects that parasitize only on humans.
The cause of flea bites is their sudden appearance in a person’s home (regardless of sanitary conditions).
Fleas can appear spontaneously:
- from pets;
- get into the apartment from the street, with dirty shoes;
- move from neighboring apartments, basement, attic, non-residential or technical premises through open windows, balconies, doors;
- be brought into the house after walking pets or when mice or rats appear in the house.
Any type of flea that lives on warm-blooded animals and birds can attack humans:
- dog, cat, chicken, rat fleas - parasitize on different types of animals;
- human fleas - appear in the house, hiding in the hair of the skin;
- earth fleas - breed in the upper layers of the soil, in the house they are localized mainly on furniture, behind baseboards or wallpaper, in carpets;
- bedding - live in bed linen and furniture upholstery, bite mainly at night;
- sandy - live in sandy soils of coniferous forests, they are distinguished not only by the fact that they bite through the skin, but also penetrate under the skin of the victim.
Insects live and breed in the fur or feathers of animals that are ideal for their habitat, or in fleecy surfaces and fabrics (blankets, rugs, bedspreads), as well as in cracks in walls and other secluded places in the house. And although they bite a person, they do not live on his body.
Why do fleas bite?
Fortunately, humans are not suitable “housing” for fleas, because fleas need thick hair to keep them safe. It is for this reason that parasites settle on dogs, cats, and in rare cases, birds. But despite this, fleas bite both animals and people. After the parasite tastes human blood, it returns back to the pet.
The question, “Do dog or cat fleas bite humans?” directly depends on the number of parasites. In the case of a small amount, an animal is enough for them. But if fleas are not noticed in time, or ignored altogether, then their number grows, and accordingly, sooner or later, one pet will not be enough for them. That is, a person for them is just a new source of food.
Transmitted diseases
A flea bite on a person, a photo of which clearly shows the visible consequences of an insect attack, is dangerous not only for its external signs and discomfort.
Fleas are carriers of various diseases, including those fatal to humans. Thus, rat fleas are considered one of the reasons for the spread of plague epidemics that destroyed medieval settlements and entire cities.
| Types of diseases | Classification | Incubation period, days | Carriers of the pathogen | Brief description, symptoms |
| Diseases of the musculoskeletal system | Brucellosis | 7 – 14 | Cattle and small cattle, pigs. | Characterized by joint pain, weakness, sweating and sudden increases in body temperature. Over time, the disease spreads to other organs, covering the nervous, respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and genitourinary systems. |
| Diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular systems | Typhus | 6 – 14 | Small rodents. | Severe headaches, confusion, pink rash, fever, chills, back pain, high temperature. Possible death. |
| Encephalitis | 4 – 21 | Livestock, small rodents, birds. | The virus infects nerve cells, spreading to the brain. May be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, headaches, fever, convulsions, impaired consciousness, loss of sensation in the limbs, and hallucinations. | |
| Listeriosis | 7 – 30 | Pets. | Weakness, fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes, headaches, conjunctivitis, sore throat, rash. The disease can take the form of encephalitis, meningitis. Possible death. | |
| Skin diseases | anthrax | 2 – 4 | Livestock. | The formation of a carbuncle (most often a single one) followed by ulceration and the appearance of a scab, accompanied by an increase in body temperature, fever, weakness, itching and swelling. In the intestinal or pulmonary form, death is possible. |
| Tularemia | From a few hours to 21 days | Small rodents, hares, rabbits. | The infection affects the skin, lymph nodes, sometimes affecting the mucous membranes. Accompanied by headaches, fever, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes, sweating, and pinpoint lesions of the mucous membranes. | |
| Bubonic plague | 2 – 12 | Small rodents, wild and domestic animals. | It is characterized by the presence of a specific bubo (pronounced skin neoplasm, most often in the groin), fever, high temperature, pain in the groin area, and weakness. | |
| Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract | Pseudotuberculosis | 3 – 21 | Small rodents. | It affects the intestines, spreading to the liver, and sometimes affects the joints. The disease is characterized by fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, headaches, conjunctivitis, and a white coating on the tongue. |
| Salmonellosis | From 6 hours to 2 days | Wild and domestic animals, humans. | Acute intestinal infection, accompanied by symptoms: vomiting, weakness, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, dehydration. |
A flea bite on a person can transmit bubonic plague!
Any infectious diseases transmitted by blood-sucking parasites are called vector-borne diseases. Infection can enter the human body not only through the saliva of an insect, but also when scratching an existing bite wound.
However, flea bites can lead not only to infection by a virus or bacteria, but also cause the body to respond to saliva containing substances that prevent the victim’s blood from clotting.
They can cause an allergic reaction and contribute to the development of dermatitis, eczema, urticaria, and Quincke's edema. Children and people prone to allergies are especially susceptible to this phenomenon.
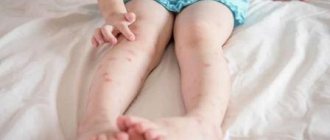
How does a bite appear on the human body?
First, a person discovers very small bubbles on his body that are very itchy, after which they become sores. Each body is individual and swelling can be observed for a different period of time, most often they go away within two days, but if a person has hypersensitivity or an allergic reaction, they may not go away for several weeks. Very often such bites are confused with an attack by bedbugs or lice.
Due to the fact that fleas most often move along the floor and jump to a small height, they attack people in the lower extremities. Therefore, you can often hear that they have bitten the legs; bites appear on the feet, ankles and legs. But it is also worth considering another point: they can attack a person during sleep, then they bite almost all accessible parts of the body, neck, armpits, face. If attacks happen at night, people often think that there are bedbugs in the apartment.
It is quite simple to distinguish such bites; fleas, unlike bedbugs, attack in a chaotic order, punctures on the skin are observed close to each other, but there is no orderliness, as with bedbugs. Of course, the symptoms of a flea attack are also different.
A person experiences quite painful sensations, since a flea does not have pain-relieving enzymes, like ticks and mosquitoes, for example. Swelling and redness appear on the skin, which are located at a short distance from each other. The affected area is very itchy. Most often the attack occurs on the lower extremities.
There is a danger of developing allergic reactions, in which case the person feels unwell and becomes dizzy. A person’s body temperature rises and the lymph nodes become enlarged. The affected areas of the body become inflamed and rot.
Diagnostics
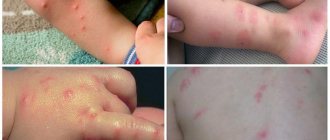
A flea bite is not a disease, and the insects themselves do not always act as carriers of an infection dangerous to humans. However, attacks by these parasites should be distinguished from other blood-sucking insects (methods of prevention and treatment will depend on this), based on visual photographs and existing symptoms that cause discomfort.
They are characterized by:
- the appearance of red itchy swellings on the body;
- the spots are located chaotically, but close to each other;
- when scratched, spots and blisters can turn into wounds and remain on the body for up to 2 days;
- if an allergic reaction occurs, bite marks may remain much longer;
- the main places on the human body exposed to insect attacks are the lower limbs;
- fleas bite closed areas of the body, so bites should be looked for under clothing;
- an exception to the rule are fleas that live in a person’s home - they prefer to attack at night, and bites can occur everywhere on the body, including on the face;
- When bitten, a person feels pain, since the saliva of insects does not contain painkillers.
Diagnosis of possible diseases that can cause flea bites will depend on the received primary information about existing complaints and the results of general tests. The effectiveness of a particular method may vary in each specific case.
Diagnostics includes:
- Anamnesis collection - obtaining information about existing complaints, previously identified chronic diseases and the patient’s lifestyle based on his interview.
- Laboratory diagnostic methods:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- serological blood tests.
- Instrumental diagnostic methods are informative in the event of diseases accompanied by inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory and cardiovascular systems:
- radiography (from 120 rubles);
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes, respiratory organs and gastrointestinal tract (from 1000 rubles);
- CT and MRI of the abdominal cavity (from 900 rubles);
- gastroscopy (from 1000 rub.);
- enteroscopy (from 900 rub.);
- endoscopy (from RUB 1,900).
You can undergo an initial examination and general tests free of charge at a public medical institution at your place of registration under the compulsory medical insurance policy. You should apply for further examination at any diagnostic center or clinic in Moscow, depending on the location and price preferences.
How to distinguish bedbug bites from flea bites
Both types of pests feed on blood, however, their bites are similar to each other only at first glance. Bedbugs bite mainly at night; fleas can do this around the clock. To understand how to distinguish bedbug bites from flea bites, study the comparison table below.
During laboratory tests, pathogens of more than 40 viral, bacterial and parasitic infections were found in the bodies, excrement and saliva of bedbugs. Among them are hepatitis, tularemia, typhoid fever, borreliosis, polio, malaria, influenza and other diseases. However, the likelihood of their transmission through bites is assessed as low. It is much more dangerous in this regard to crush the insect and then scratch the bites with dirty hands.
The ability of fleas to transmit diseases through bites, on the contrary, is a proven fact. Parasites provoke pulicosis, transmit helminths, abdominal infections, salmonellosis, tularemia, listeria, hepatitis B and C, plague, and murine typhus. All these pathogens can also be present in the bodies and excrement of pests.
When to see a doctor
A flea bite on a person, a photo of which demonstrates possible variations in its manifestation, may be a reason to contact a medical facility if the following symptoms are present:
- long-lasting spots and regular itching;
- an increase in the area of irritation and the growth of spots into ulcers;
- the appearance of pus on the wounds;
- the occurrence of ulcerations on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- the appearance of weakness in the body, dizziness;
- fever, chills and increased temperature;
- severe swelling at the bite site;
- the occurrence of attacks of suffocation, a feeling of laryngeal congestion;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
The initial examination is carried out by a therapist, who, based on the results of the examination, will prescribe diagnostic measures and, if necessary, give a referral to another doctor: a dermatologist, otolaryngologist, surgeon, gastroenterologist, neurologist.
Why are bites dangerous?
In addition, fleas are carriers of many diseases.
Read more about the danger fleas pose to humans in the article here.
Allergy
The symptom appears most often. It is considered a consequence of the body's reaction to an enzyme that is injected by a flea into the human blood. How severe the allergy will be depends on individual sensitivity. Some patients may experience severe itching, while others may experience anaphylactic shock.
Characteristic signs of allergies:
- Excitability.
- Dermati.;
- Migraine.
- Hyperthermia.
- Unpleasant sensations.
Stains
After a flea bite, dark spots often remain on a person's skin. Most often this is a reaction to an enzyme. They are usually located on open areas of the skin, especially often on the legs.
Initially, the darkening is red in color and small in size, then it begins to grow rapidly, forming a large spot. The affected area has increased temperature and severe swelling. Blistering may occur.
Bubbles
Appear immediately after received microtraumas. The bites resemble small blisters. Most often they are located multiple times.
What diseases and infections are carried?
Fleas can transmit the following infections through blood:
- Anthrax.
- Tularemia.
- Encephalitis.
- Plague.
- Salmonellosis.
Prevention
Preventive measures against flea bites are aimed at preventing the appearance of insects in a person’s home, and include:
- regular cleaning of the premises, including in hard-to-reach places;
- if insects have already appeared in the house before, you should carefully seal the existing cracks (in windows, walls, under baseboards), and lay out dried plants that repel fleas (tansy, mint, wormwood);
- carefully check the fur of pets for the presence of parasites;
- purchase special flea collars and other means of protection against parasites for animals;
- carry out timely cleaning of bedding and rugs for animals;
- wash animals' paws after walking outside;
- Once a month, carry out general cleaning with a soda-soap solution, which repels insects.
If trouble cannot be avoided, you should call the sanitary-epidemiological service or another pest control service to professionally eliminate the problem.
Disinfection of bedbugs and fleas
Professional extermination of insects by sanitary service specialists is called disinfestation. Treatment is carried out using expert class products - insecticides. Sometimes the service appears as disinfection of bedbugs and fleas, but this is a misnomer. Disinfection is the destruction of bacteria, viruses and odors. When ordering pest baiting from the SES, it is not necessary to know specialized terminology. It is enough to tell the consultant which parasites need to be removed.
If bedbugs and fleas live together in a room, apartment or house, you can get rid of them with one treatment. Disinsection is carried out using cold fog. The method is based on the use of automatic generators that transform the liquid insecticide into a cloud of small, volatile droplets, hence the name of the treatment. Cold fog:
- has high penetrating ability. The droplet size varies between 5–80 microns. The powerful sprayer of the device delivers them even to the most inaccessible areas - crevices, cracks, cavities;
- settles evenly. Uniform coverage is critical for processing efficiency. Insects have no areas where they can hide from the effects of drugs;
- acts on resistant pest populations. An insecticide with any active ingredients can be poured into the generator tank. This allows you to select products individually to solve the most complex insect problems;
- sprays quickly. A torch is a jet of insecticide in an automatic generator that can hit a distance of up to 10 meters. Processing a prepared room of 30 square meters is done in less than a minute;
- has a prolonged effect. The products continue to kill insects for 30–40 days after application. Even if the eggs survive somewhere, the hatched larvae will quickly die from the residual effect of the insecticide.
has been baiting fleas and bedbugs in Moscow and the Moscow region since 2014. Disinsection can be done for an apartment, private or apartment building, or commercial premises. The cost of processing will depend on the size of the object. You can find out more by calling the SES contact numbers. Leave a request for a free call back from the Dez Group operator using the form on the website - a service specialist will call you back within 5 minutes.
Treatment methods
A flea bite on a person (a photo and description of which is usually enough to recognize it) most often does not require any specific treatment, and the main methods of therapy come down to independently eliminating the unpleasant consequences after it.
Medications
For flea bites, you should use products that relieve itching and disinfect damaged areas of the skin.
They are usually available in the form of ointments, gels, and solutions for external use:
- Sulfur ointment is an antipruritic drug with antiseptic properties. You can apply it to the affected areas up to 3 times a day, but not more than 5 days. Not suitable for use by children under 3 years of age. Cost – from 20 to 50 rubles.
- Fenistil gel – a remedy for various insect bites and allergic reactions that occur, which can be used by children (over 1 month of age). The ointment is applied 2–4 times a day until symptoms disappear. Price 400 – 800 rub.
- Sinaflan - hormonal ointment has decongestant and antibacterial properties, soothes irritation after insect bites. Apply to the affected areas 1 – 3 times a day, for no more than 5 days. Use in infants is permissible under medical supervision. Price 50 – 90 rub.
- Flucinar gel is a potent hormonal drug, approved from 2 years of age. It is recommended for adults to apply the gel 2 times a day, for children – 1 time, in a thin layer. The duration of use should not exceed 5 days. Not recommended for use on the face. Cost 200 – 400 rubles.
- Hydrocortisone 1% is a hormonal ointment for severe itching and irritation, used similarly to Flucinar. Cost 20 – 60 rubles.
- Zinocap ointment - indicated for rashes, including dermatitis and neurodermatitis, up to 3 times a day. Suitable for use in children over 1 year of age. Cost 300 – 800 rub.
- Balm Golden Star - used in liquid form, rubbed into the affected areas to relieve pain and irritation. It is recommended to apply immediately after the bite every 20 - 30 minutes. until the discomfort is completely eliminated. Price 100 – 200 rub.
- Psilo-balm is a gel to eliminate swelling and itching with a cooling effect. Use up to 4 times a day; children are allowed from 2 years of age. Cost 250 – 350 rubles.
- Levomekol - gauze dressings with ointment are used for suppuration at the sites of insect bites until the purulent-necrotic contents are completely pulled out from the wound. Allowed for children from 1 year of age. Price 100 – 160 rub.
- Miramistin is an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agent, applied to bite sites up to 4 times a day, regardless of the patient’s age. Cost 250 – 800 rubles.
- Menovazin is an alcohol solution to eliminate itching, has a soothing cooling effect and contains a small dose of the anesthetic novocaine. It is used up to 3 times a day, and the total duration of the course can be 3 – 4 weeks. Price 12 – 40 rub.
In addition to the above drugs, you can disinfect a bite using alcohol, chlorhexidine, iodine, and brilliant green solution.
In order to prevent the occurrence of an allergic reaction from a bite or if signs of one appear, you should immediately take antihistamines (Zodak, Suprastin, Zyrtec, Cetrin, Loratadine, Tavegil). It is recommended to give them to children in advance, regardless of existing symptoms.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods for flea bites are effective as first aid measures for minor rashes and the absence of allergic reactions. These are affordable products that are always at hand and can temporarily replace medications that are not available in the house.
First aid for bites consists of disinfection and removal of swelling:
- wash the bite site with antibacterial or regular laundry soap;
- apply an antiseptic;
- Apply a cold gauze compress or ice to the damaged area of skin.
Next, you need to use painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Mix baking soda with water to a paste consistency, apply the paste to the bite area and let it dry.
- For children, you can prepare a less concentrated alkaline solution with soda in a proportion of 1 tsp. soda per glass of water. Apply a lotion to the affected areas.
Folk remedies with soda help neutralize toxins contained in insect saliva and prevent the development of an allergic reaction, so they are most effective immediately after a bite.
- Acid-containing products such as lemon or vinegar have disinfecting properties and can prevent the development of infection. To prepare the solution, mix 1 part lemon juice (or apple cider vinegar) with 2 parts water and apply it to the affected skin.
- Aloe juice has soothing and regenerating properties. It is used in its pure form, lubricating bite wounds up to 3 times a day or applying a fresh leaf (after cutting off the top layer of skin on one side) as a compress.
- Black tea is known for similar properties. For bites, you can use regular tea bags, freshly brewed and cooled until warm. The lotions should be kept on the skin for at least 3 minutes.
- Compresses from decoctions of medicinal herbs (calendula, aloe, plantain, coltsfoot, string, chamomile) help eliminate pain and relieve inflammation. For cooking you need 2 tbsp. l. Pour a glass of boiling water over any pharmaceutical plant and cook in a water bath for 10 - 15 minutes. Allow to cool slightly and apply warm (but not hot) lotions to the skin until the composition cools completely.
- Honey for bites is used as an antimicrobial agent that neutralizes toxins. It is applied to the skin in its pure form and left for up to 5 minutes.
Other methods
In the event of an allergic reaction to a bite or an exacerbation of a chronic form of an allergic disease as a result of insect bites, the main methods of therapy are supplemented with physiotherapy:
- electrophoresis or ultraphonophoresis - administration of medications using current or ultrasonic pulses;
- UV radiation and intravenous laser irradiation - used to change blood counts and relieve pain;
- darsonvalization - exposure to current pulses for an antiseptic effect and acceleration of the healing process.
Patients suffering from chronic allergic diseases should periodically visit salt rooms (speleotherapy) and undergo mud therapy procedures.
Also, for any skin rashes (including chickenpox, dermatoses, rubella) and to relieve itching, children are prescribed a cosmetic product with natural ingredients - calamine lotion for external use. It is rubbed into the affected areas 3 to 7 times a day, according to the doctor’s indications.
Appearance of the parasite
Fleas are very different from other bloodsuckers in their appearance. Their length is about 3-5 mm , so it is quite difficult to notice these insects. The body is slightly oblong and rounded, increasing towards the rear. The sides are slightly flattened .
These parasites have a very strong shell made of chitin , making them difficult to crush. The most common color is black or brown. These bloodsuckers have three pairs of legs, with the longest and strongest ones being the hind ones; with their help, adult individuals can jump over distances of up to half a meter.
The entire parasite is covered with small bristles . The head is round in shape, slightly flattened. It has two eyes and two antennae. The insect's mouth is practically invisible. It looks like a tiny proboscis on which powerful jaws are located.
Possible complications
A flea bite on a person, whose photo most often shows small red spots or blisters, is rarely taken seriously.
However, such minor rashes can cause the development of serious pathologies and lead to:
- tachycardia;
- partial damage to the nervous system;
- prolonged heart pain and low blood pressure;
- attacks of suffocation and panic attacks;
- swelling of the trachea, larynx;
- Quincke's edema;
- anaphylactic shock;
- lethal outcome.
In addition, parasite bites can change the psycho-emotional state - a person becomes nervous and irritable, constantly itches, and in places of imaginary bites false pain sensations occur, not accompanied by the redness characteristic of bites. As a rule, this condition goes away when the parasites are completely eliminated.
Flea bites on humans are an unpleasant and quite painful phenomenon, not only from an aesthetic aspect (as evidenced by numerous photographs of the consequences of flea attacks), but also from a medical point of view, since these insects are carriers of serious (and sometimes fatal) diseases for humans.
Parasites can appear unexpectedly even in a perfectly clean apartment without pets, so you should not neglect preventive measures, and when cleaning, sometimes replace ordinary water with a solution of soap and soda.
Author: Anna Lalochkina
Features and danger of flea bites
When a flea pierces the skin and begins to drink blood, a person experiences a strong painful sensation comparable to a needle prick. This effect can be explained by the fact that this parasite, unlike bedbugs and ticks, does not inject natural painkillers into the wound when it bites.
Many of the consequences of flea bites depend on the action of toxic enzymes that the flea injects along with saliva into the bite to prevent blood clotting. Thanks to these substances, blood begins to flow into the insect’s stomach in a thin stream almost independently.
When the flea detaches itself from the bite, the elastic walls of the skin will close and prevent bleeding from escaping, but it can continue under the dermis and lead to the formation of a small hemorrhage. If the concentration of bites in one place is high enough, the bleeding may turn into purpura, which is dangerous in its consequences.
A painful bite is the least of the evils that a flea can cause.
Consequences of a flea bite:
- Severe allergy to an enzyme that prevents blood from clotting. It can range from itching, redness, rashes to swelling and anaphylactic shock.
- The flea itself can serve as a carrier of a huge number of serious diseases.
- By scratching the bite site, a person can infect the wound.
The allergy is usually caused by flea saliva enriched with an enzyme. An allergic reaction occurs in people suffering from hypersensitivity to insect bites in general and flea bites in particular. Children under 12 years of age are most susceptible to it.
Diseases whose pathogens are transmitted by parasites themselves pose a huge danger. Their specificity is largely determined by the type of blood-sucking insect.
Earth flea bite
The bite of an earthen flea, which is also called a sand or sea flea, has its own characteristics. These parasites, living in the habitats of birds and rodents, not only bite through the skin and drink blood, increasing the above risks, they make their way into the skin under the nails, laying eggs there. As a result of such actions, the bite site becomes severely suppurated. The larvae grow in this environment, feeding on the resulting pus and surrounding tissue. Itching, swelling, and irritation appear at the site of the lesion. Doctors diagnose sarcopsillosis.
Cat flea bite
Parasites of this species cause many infectious diseases in humans, including even plague, as well as fungal viruses. They can be carriers of cucumber tapeworm eggs, a special type of parasitic flatworm that reaches a length of 50 cm, and other helminth diseases, such as toxocariasis. Helminth eggs enter the flea's digestive tract along with the blood during bites. When a parasite injures a person, they enter his body and the hatched larvae are carried by blood throughout the human body, along the way affecting the lungs, liver and other organs with allergic inflammation.
Rat flea bite
A rat flea bite can have the most serious consequences. This type of parasite spreads plague, endemic typhus and a number of other diseases.
Among the agents carried by fleas that pose the greatest danger are the causative agents of tularemia, typhus, salmonella, encephalitis virus, trypanosomes, as well as anthrax spores. In total, about 200 representatives of life-threatening diseases were identified on representatives of various subspecies of these parasites. Therefore, you can never predict what the next flea bite will turn out to be. Microbes in the body of this insect can exist for more than a year, significantly increasing the number of infected people.
It is important to refrain from scratching the wound, since the canal formed as a result of flea feeding can receive excrement of the parasite and various types of infections left on the victim’s skin, which greatly increases the risk of re-infection. In disturbed wounds, pus may begin to accumulate, which will cause more trouble than the initial bite. The damaged area should be properly treated to reduce itching and the risk of infection.
Can fleas bite humans?
Fleas are ectoparasites that feed on the blood of warm-blooded creatures and leave unpleasant bites on the body. Man is no exception. There are approximately 2,000 species of fleas and many of them can feed on our blood.
A person is bitten by fleas:
- human;
- canine;
- rat;
- felines;
- sandy;
- avian;
- bedding (linen);
- earthen and others.
Host species specificity is important only for insects that parasitize bats. The rest can feed on the blood of any warm-blooded animal, although they prefer to live on the skin of the main host. For example, dog fleas happily feed on the blood of cats and humans. And none of these parasites live on the human body.
Most often we encounter bites from fleas, fleas and human fleas. In second place are cat and dog parasites. Even rabbit and elk fleas can bite a person, although these insects feed on human blood extremely rarely. But there is no reliable information about goat fleas. We don't know whether they bite humans or not.
Bed fleas: how to get rid of them at home?
Blood-sucking insects may be in the house for the following reasons:
- If the apartment is located on the ground floor, then rodents living in the basements can introduce fleas.
- There are pets in the property next door to you.
- The parasites were brought in by the owners themselves, especially if we are talking about those who often have to visit basements or non-residential premises.
Bed fleas, photos of which are presented in this material, jump onto the bed solely to feed themselves. It is quite difficult to detect small insects, but if you make your bed with light-colored linen, you will certainly notice the presence of bloodsuckers.
After processing the animals, you need to start cleaning the apartment. Fleas cannot tolerate the smell of tansy and wormwood, so you can place bunches of grass in the corners of the room. A room in which blood-sucking insects have infested requires wet cleaning, and this should be done using ammonia, vinegar and soap solution.
If traditional methods do not help and the question of how to get rid of bed fleas remains unresolved, the room will need to be treated with special sprays, aerosols or solutions. Preparations to combat various insects are sold in many stores today.
The main thing is to read the instructions before use and strictly follow the recommendations, taking precautions.
In the future, to protect your home from fleas, be sure to purchase special collars for all pets, and place dry wormwood or tansy under sofas and pet beds. This environment will prevent parasites from settling in your apartment.