Perhaps the vast majority of people are familiar with stinging hymenoptera and know firsthand how painful and unpleasant contact with them is. In order to properly provide first aid, neutralize the maximum amount of poison, and eliminate the possibility of developing a violent allergic reaction, you need to be able to distinguish between insects and their bites.
This is quite simple, as you can see by reading the article and watching the attached video on the topic.
The wasp's sting is not serrated, so the insect can easily remove it from the skin
General information
Wasps are insects that can be found in different places - both in villages and cities.
There are several varieties of these insects. However, the reaction to their bite is the same: it is very painful and unpleasant, since the venom of all types of wasps acts in a similar way. The ICD-10 code is W57 (bite or stinging by non-venomous insects and other non-venomous arthropods). But in some cases, a wasp or hornet is a particularly dangerous insect. After all, when talking about how dangerous a wasp sting is for a person, it should be taken into account that it can provoke a very acute allergic reaction . Therefore, it is most dangerous for those who are prone to allergies . Multiple bites are especially dangerous. Therefore, it is very important to know how to act correctly if a person is bitten by an insect, and what to do if an allergic reaction occurs. This will be discussed in the article.
Clinical researches
A clinical study conducted by the company together with the Union of Pediatricians of Russia proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily skin care of adults and children with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients.
Many remedies are recommended by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
Sources:
- Reken Martin, Schaller Martin, Sattler Elke, Burgdorf Walter, Atlas of Dermatology, MEDpress-inform, 2018
- Bonifazi Ernesto, Differential diagnosis in pediatric dermatology, Panfilov Publishing House, Binom. Knowledge Laboratory, 2014
- Churolinov Petr, Herbal medicine in dermatology and cosmetics, Medicine and physical education, 1979
Pathogenesis
The venom of Hymenoptera insects contains non-allergenic amines and peptides. They determine the appearance of local reactions to the bite, provoking the inflammatory process and affecting the blood vessels. In addition, the venom contains allergenic proteins (in particular antigen-5), under the influence of which antibodies . If we talk about wasp venom in more detail, it contains the following components:
- Histamine – provokes the development of an allergic reaction (redness, itching, swelling of the skin).
- Phospholipases - destroy blood cells and tissues, stimulating the manifestations of allergies.
- Acetylcholine – conducts nerve impulses.
- Hyaluronidases - destroy cell membranes, leading to an inflammatory process.
- Hyperglycemic factor – increases blood sugar levels.
If an insect stings a person on a peripheral nerve, this leads to disruption of its function.
With increased sensitivity to allergens, a strong local reaction can develop even after one episode. As a rule, an allergy to a wasp sting develops almost immediately - within a few minutes. But sometimes a so-called delayed allergy can develop. Its symptoms appear 10-14 days after the bite.
With multiple bites (10 or more), a toxic reaction occurs.
You can often come across the question of whether a wasp dies after a bite and whether the wasp leaves a sting in the human body. Due to the structural features of the sting of this insect, it can sting many times. The sting is slightly jagged and therefore does not remain in the skin.
Another interesting question concerns how the benefit or harm of a wasp sting manifests itself. As you know, bee stings are used for treatment purposes. There is also some benefit from wasp stings, but only if the person has no allergic reaction to the poison. After all, wasp venom is a stronger allergen than bee venom.
After wasp bites hemoglobin and blood vessels dilate. However, the harm outweighs the benefit, since there is a high risk of developing allergies . Moreover, with each subsequent bite this risk increases.
Causes
There are several varieties of hymenoptera that sting people most often: wasps, bees, bumblebees, hornets. Wasps and bees sting most often. In this case, the bites themselves do not have an adverse effect on the body, but only cause some discomfort and pain. The cause of negative symptoms is an allergic reaction to the venom of such insects.
It is important to remember that wasps sting people for self-defense or to protect their own offspring. It often happens that a person brushes away an insect circling nearby with his hands. This gesture is perceived as aggression, and the wasp stings the person. There is a risk of being attacked by insects even if you are near their nest.
Symptoms of a wasp sting
The symptoms that appear after a bite largely depend on what kind of insect stung, as well as on how the body reacts to its venom.
The main features are as follows:
- A sharp pain appears.
- Swelling develops. Moreover, the more fat or fiber there is at the site of the bite, the more significant the swelling.
- There is redness near the bite site.
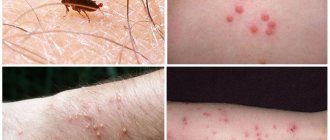
Most people experience exactly these symptoms, which then go away after a few hours. Sometimes people also notice that the bite itches a little later. But even if there is a red spot left and the bite area itches, there is nothing to worry about. If one or more insects have stung, the wasp's venom does not pose a threat to life. However, the body may react more violently if a person is stung by a large number of wasps.
About 1% of people develop an allergic reaction to wasp venom. Symptoms of a wasp sting allergy may include the following:
- Very severe swelling appears, the tumor quickly increases.
- Itching and rash develop throughout the body.
- Nausea and vomiting are observed.
- It becomes difficult for the victim to breathe.
- Severe dizziness .
- The pulse becomes either too fast or slow.
- The person may lose consciousness.
Bites to the lips, tongue, and palate are very dangerous. When swelling develops, it can block the airway, and the victim risks suffocation. It is also important to consider that in people allergic to venom, the first bite can lead to sensitization, that is, a disruption of the immune response. But in the second such case, a number of pathological reactions occur, as a result of which an allergy is noted.
After a wasp sting, various types of allergic reactions may occur:
- Localized urticaria - a few minutes after the bite, the skin begins to itch, and a rash appears on some parts of the body. Slight weakness may develop. The swelling is small.
- Generalized urticaria is a rash that spreads throughout the body, but this condition is not yet life-threatening.
- Quincke's edema is a very serious condition in which the soft tissues of the face swell. If the process spreads to the neck, there is a danger of developing laryngeal edema. This is a dangerous condition in which the upper respiratory tract becomes blocked and a person dies from suffocation.
- Anaphylactic shock is a dangerous condition in which, over the course of several minutes, blood pressure , the pulse increases, and the entire body is covered in a rash. In anaphylactic shock, a person dies from acute cardiovascular failure if help is not provided to him in a timely manner.
Normal body reaction
During the bite, the insect sprays poison under the skin, which causes a defensive response from the body. Instant pain, redness, swelling, swelling around the damaged tissue, and a local increase in temperature appear at the site of the lesion. After some time, as the wound heals, itching of medium intensity is observed. This reaction is present in most victims.
The body itself stops the effect of the poison and restores damaged tissue. Painful symptoms disappear within 24 hours; the speed of healing of the bite site depends on the sensitivity of the skin. Approximately a bruise after a wasp sting disappears in 5-7 days.
The situation does not require special treatment, it is enough to provide the correct first aid. To eliminate unpleasant sensations, folk remedies are used in the form of lotions, wiping the wound, compresses, and pastes.
Treatment with folk remedies
It happens that insects sting in a field or forest, and there are no pharmaceutical products at hand for treatment. In this case, you can use some folk remedies:
- Parsley juice - you need to pick several stems of the plant, rub them and apply the juice that has been released to the affected area.
- Lemon juice – it is recommended to lubricate the skin to neutralize the effect of wasp poison.
- Berries – if you have any sour berries nearby, you can make a compress from them. The berries need to be crushed and placed on the bite site. Vinegar can also be used as a compress.
- Dandelion milk – applying fresh dandelion juice to the area can relieve pain. Using fresh calendula juice is also effective.
- Garlic and onion juice help relieve swelling and pain.
First aid
Speaking about what to do if a wasp stings at home, it should be noted that assistance must be competent and provided in a timely manner. Treatment of a wasp sting, if it stung outside the home, can begin with the use of folk remedies.
First aid for a wasp sting at home should begin with confirming the diagnosis. Before treating the bite with anything, you need to make sure that it is not another insect that stung the person, and that there is no sting in the wound.
If possible, you can try to suck out the poison from the wound. Also, first aid for a wasp sting involves treating the bite site with antiseptic solutions - alcohol or hydrogen peroxide. This helps numb the affected area and reduce swelling.
To reduce the severity of intoxication in a child or adult, he must be given clean water to drink. You should also drink as much as possible throughout the day. The liquid helps remove toxins from the body faster.
Cold helps relieve swelling after a wasp sting. If you have been stung by a wasp and you need to remove the tumor, then before applying any medication to the bite site, you should apply ice from the freezer or a cold compress. A compress with a soda solution also helps relieve swelling.
Treatment for this condition involves taking antihistamines. If an insect stings a child or adult, you should take a tablet of this drug. However, it is better to discuss its use with your doctor.
If your arm or leg is swollen, you should try not to make sudden movements. The bite site can be wrapped with a sterile bandage. This will help relieve pain and stop the spread of poison.
After a wasp bite on an adult or child, you can also smear the area where there is redness and itching of the bite with any ointment that contains hormonal components. It is advisable to treat the bite site after the antiseptic has been used. A specialist can tell you in more detail how to treat a wasp sting.
If vomiting begins or the person loses consciousness, he should be placed on his side.
In case of an allergic reaction, which can occur with multiple insect bites, a hornet bite to the head, etc., a feeling of heat and lack of air appears. In this case, you should remove all tight clothing, lay the person horizontally, and provide him with an influx of fresh air.
At the first manifestation of an allergic reaction, you should immediately call an ambulance. If there are indications, the patient is given injections of dexamethasone or adrenaline .
As for what to do, if after a wasp sting your arm or leg is swollen, and there are no medications at hand, then in this case it is worth using folk remedies. You can lubricate the affected area with any means that helps relieve swelling: juice of sour berries, garlic, onions, etc.
Prevention
To prevent insect bites, you must adhere to the following rules:
- If a wasp flies nearby, do not wave your arms or panic. It is important not to make sudden movements so as not to provoke an attack.
- You should not walk barefoot on the grass while in nature.
- It is important to be careful when consuming food outdoors. Sweet foods, as well as fruits and soda, can attract wasps.
- In places where there are a lot of insects, it is better not to wear very loose clothes and loose hair, so that wasps do not get entangled in them.
- Picnics should not be held in areas where there are many wasps swarming.
- If a bite does occur, do not scratch the affected area.
What to do if a wasp stings your face – cheek, lip, eye, nose, tongue?
These insects usually sting the arms and legs. However, they can also bite on the face: cheek, lip, eye, nose, tongue, and mucous membranes of the oral cavity. It is very dangerous. If an insect flies into the mouth, frightened by unusual conditions, it will sting again and again until it uses up all its reserves of poisonous secretion. If there is nothing wrong with moderate swelling of the tongue and lips, except discomfort and problems with swallowing, then swelling of the larynx and nose can lead to suffocation.
Damage to the eye is fraught with inflammation of the eye and mucous membranes. Bites to the face and neck are considered the most dangerous. If measures are taken untimely or incorrectly, the victim may die. To prevent this from happening, a person bitten on the face by a wasp must be immediately taken to the nearest medical facility.
Consequences and complications
The consequences of a wasp sting, like the consequences of a hornet sting, are dangerous for those who are prone to allergies.
Swelling may develop in the affected area, which quickly increases. If your hand is swollen, this condition does not pose any particular danger. But when such a reaction develops, airway obstruction may occur in the larynx or oral cavity.
An allergic reaction can manifest itself in the form of anaphylactic shock, which is likely to result in death.
Other consequences and complications depend on where exactly the person was stung by the insect. glaucoma , iris atrophy, etc. may later develop
Danger signs
Signs of anaphylactic shock
Two percent of people are hypersensitive to bee venom. For them, an encounter with a bee is extremely dangerous, but wasp toxins do not cause a violent reaction or anaphylactic shock.
If an allergic person is bitten by a bee, then you should immediately take a double dose of an antihistamine and take the victim to the clinic without waiting for negative symptoms to appear.
Pay attention to dangerous clinical manifestations:
- rapidly developing swelling and hyperemia;
- shortness of breath, lack of air, respiratory failure;
- lowering blood pressure;
- changes in heart rhythm;
- nausea, dizziness, vomiting;
- severe weakness, loss of strength;
- coldness of extremities, cold sweat;
- panic, fear of death;
- faintness or loss of consciousness.