- home
- Guinea pig
- Guinea pig health
02/14/2019 When purchasing a pet, you must make sure that it is in absolutely healthy condition. You need to find out everything from the seller, and also examine the pet yourself. Suitable and proper care is important for any animal; if it is not provided, the guinea pig may become ill or become infected with parasites. Ticks can cause serious harm. They are found in the fur, on or under the skin.
How to tell if your guinea pig has subcutaneous mites
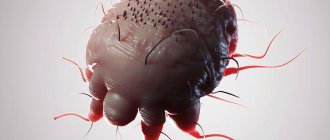
The subcutaneous mite in a guinea pig is a parasite that lives under the skin of very small sizes. A pet can acquire ticks from contact with another pig and not show that it is infected for a long time. The parasite is activated when immunity decreases. For this reason, ticks are most often found in children, old individuals, pregnant females and pets that are kept in improper conditions.
To identify the disease, you need to do a scraping. He may give an incorrect result, saying that the animal does not have parasites. Larvae can be seen only in half of the possible cases. But if symptoms of infection appear, then treatment must be started immediately. Owners may confuse parasite infection with an allergic reaction. However, if the pet really has an allergy, then signs of the disease do not appear.
Sarcoptic mange
If your animal itches a lot, tears the skin until it bleeds, and grayish crusts appear on the affected areas, this is nothing more than sarcoptic mange. The causative agent of this disease is a mite of the Sarcoptidae family.
These are microscopic parasites with a length of 0.2 to 0.3 mm. The body is round. The parasitic zone is the Malpighian layer of the skin.
Insects with chewing mouthparts gnaw passages in the skin. Clot-shaped growths (chaetes) appear on the surface of the skin in the affected area. Due to them, the tick is held on the surface of the skin.
The source of infection is hay or grass that healthy animals eat after sick ones.
Diagnostics
It is possible to determine that guinea pigs have this particular parasite by looking at bald patches and wounds in the area of the face and lower extremities. An accurate diagnosis is made in a clinical setting. A scraping is taken from the affected areas of the animal and examined under a microscope.
Treatment
Acaricides are used to kill ticks and treat the disease they cause. The main active ingredient in such preparations is the substance selamectin. The house in which the sick animal lives is treated with a solution of soda or vinegar, then irrigated with Barsik or Frontline.
The old litter is disposed of, and the new one is filled in only after the pallet has dried. A few hours after disinfection, the animal is returned to its cage. Treatment of this disease is recommended under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Infection and manifestation
For guinea pigs, the greatest danger is the subcutaneous mite. It causes the animal to experience severe itching and constantly itch, sometimes until it bleeds. After this, hair falls out in the foci of the disease. You may notice a decrease in appetite, which can cause the body to become exhausted. At first the pet will behave restlessly, and then become apathetic. When immunity decreases, the tick begins to attack. Most often, old, pregnant and young individuals become infected. If you do not treat and let the disease take its course, then, most likely, the pet will soon die, being exhausted and poisoned.
Animals become infected on the street or from other animals. It is curious that the subcutaneous type of tick is able to wait for the right time under the skin for several months. It is activated when the immune system is seriously weakened.
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor makes the diagnosis based on external symptoms and accompanying complaints of the patient. Most often, the disease affects the glands on both sides. Sometimes the symptoms of the disease practically do not appear, except for inflammation of the salivary glands. Once ill, a small patient may refuse to eat, he may experience dry mouth and inflammation behind the ears.
The child is hospitalized only in case of complications or an epidemic. At home, the patient must be isolated from family members for 10 days and kept in bed.
It is necessary to adhere to a dairy-vegetable diet, grind food to reduce pain when swallowing, eat in small portions and drink plenty of warm teas, decoctions, and fruit drinks. You should avoid sour juices and fatty foods.
Doctors often prescribe:
- antipyretic,
- antihistamine,
- vitamins.
Gargling with a soda solution and dry warm compresses applied to the throat area are indicated. To relieve pain, you can tie a warm scarf around your neck and make a warm oil compress with heated vegetable oil.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes physical therapy, for example, ultraviolet radiation, diathermy. In severe cases, intravenous detoxification therapy with glucose solution is prescribed.
You can get a referral for them and undergo them at the children's clinic or at the SANMEDEXPERT clinic in Moscow Central Administrative District at the Baumanskaya metro station.
Prevention
To avoid mumps, a vaccination is necessary, which is done in any children's clinic according to the vaccination calendar, that is, after a year, often together with the measles and rubella vaccine. However, if a child has a decrease in immunity, for example, with leukemia, then the vaccine is contraindicated. Vaccinations for small allergy sufferers are given with special care. Normally, vaccination should be carried out under the supervision of an allergist.
Symptoms
The main sign of parasite infection is severe itching, pain and hair loss in areas of the skin. Sometimes the skin may begin to peel, the animal becomes irritated if touched and noticeably loses weight. If you touch the source of infection, the pig will feel discomfort and pain.
Therefore, the pet will begin to itch and try to gnaw its own body, which will cause even more harm and unnecessary problems in the form of large scratches and damage. The disease is best tolerated by healthy pigs; sick pets or young animals are much more difficult to tolerate infection.
Symptoms of the appearance of subcutaneous mites in a furry pet:
- severe shedding;
- the color of the wool becomes dull;
- dandruff forms;
- the animal scratches its skin bleeding;
- alopecia occurs;
- infected areas of the skin itch unbearably.
Symptoms and signs
Unfortunately, pododermatitis is a common disease in animals that have suffered mechanical damage to a limb, or have constant contact of a bare area of skin with a poor-quality coating.
The first sign of the disease is slight redness of the skin and swelling. Gradually, the affected area increases, peeling and detachment of dead skin occurs, forming open ulcers. The wounds on the sore paw begin to heal with an unsightly crust, which at the slightest stress bursts, the skin, and the animal’s joint begins to deform.
At the beginning of infection, the animal feels a slight irritation, which over time turns into a burning sensation. The behavior and gait of the rodent changes. Limping, moving sideways, or jumping unevenly indicate severe discomfort. The whining, crying-like sounds that an animal makes indicate extreme pain. The guinea pig refuses to move, loses appetite, does not respond to favorite treats and ignores calls for contact.
Treatment of subcutaneous mites in guinea pigs
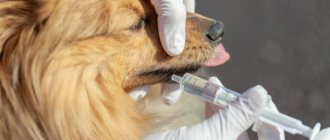
Suitable treatment is prescribed by a professional veterinarian. Initially, a tick infestation is diagnosed by scraping. If the analysis shows no evidence of the presence of a parasite, then the doctor can begin treatment based on the symptoms. If the animal is still very young and therefore not properly tamed, then it is better not to scrape it. Because of this, stress may develop, and then the well-being of the sick rodent will worsen. It is important to remember that your pet may have more than one disease, but several, which worsen the pig’s well-being. In addition to the subcutaneous type of parasites, there are also ear mites in guinea pigs, as well as other diseases that can baffle even doctors with extensive experience. The initial stages of treatment are carried out under the constant supervision of a veterinarian.
You can treat your guinea pig against ticks with Ivermectin injections. Injections are given once a week, the dose of medication is calculated based on the pet’s weight. To cure cubs weighing less than three hundred grams, Otodectin is used. Its dose is also calculated depending on the individual parameters of the individual.
Methods for removing parasites
For treatment use:
- Shampoo. When bathing, apply to wet fur and rub over the entire body so that it does not get into the eyes and ears. The product must be rinsed off well. When it enters the body, the digestion of animals is disrupted. You need to wash the cage and the area near it with the same shampoo, and change the bedding. The procedure is repeated after 10 days to destroy the larvae. When choosing this method of treatment, one must take into account that pigs are afraid of water and experience stress when bathing.
- Spray. The jet is directed onto the skin against hair growth. Most drugs have an unpleasant odor, so it is better to carry out treatment on the balcony or on the street. The pig should be held in your hands until the spray dries to prevent it from licking the medicine.
- Drops. The dose is drawn into a syringe, the needle is removed, the fur is pulled apart and dripped onto the skin, but not onto the wounds. You need to hold the animal in your hands for about 10-15 minutes until the product is completely absorbed.
- Injections. Subcutaneously into the withers.
Basic rules of treatment:
- at the same time it is necessary to process the hair of all domestic animals;
- every 3 days, disinfect cages and bedding (they must always be dry);
- You cannot use several different drugs at the same time;
- the preparations Neostamazan, Ethnomazan, Stomazan, Butox are not used for pigs (they can only treat surfaces - cages, bedding and other equipment).
The cage must be cleaned every three days.
Used against fleas:
- drops – Advocate, Blokhnet, Stronghold, which can be combined with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs;
- shampoo “Nizoral” and others containing pyrethritol;
- sprays – 8 in 1, Frontline, Bolfo.
Do not exceed the dose - this can lead to poisoning of the pig. It is better to buy special preparations for rodents. When using medications intended for kittens, take 0.1 ml of Advocate or 6 ml of Stronghold per 1 kg of pig's weight.
Use flea drops in conjunction with antimicrobial drugs.
The above sprays and drops are used against ticks in the same way, as well as injection preparations:
- Ivermectin. Per kg of weight, 0.02 ml of the drug is combined with 0.2 ml of saline solution. The product is considered difficult to use, since it is difficult to calculate the dose and measure it, and exceeding it is dangerous for the pig’s brain.
- Otodectin (variation with 0.1% ivermectin) at the rate of 0.2 ml/kg.
Injections are given once every 10 days, 2-4 injections in total (depending on the degree of damage). Ivermectin is applied to inflamed areas of the skin 2-3 times a day. The cage needs to be washed with a solution containing chlorine and the bedding changed.
Often a tick infection is complicated by the appearance of a fungus. It primarily affects the scalp, neck and extremities. It is treated with Chlorhexidine, Lamizine, etc.
We make injections into the animal's withers.
Help against lice and lice:
- sprays Bars, Celandine, Bolfo, Dana, Akaramectin;
- Ivermectin injections (if there are a lot of parasites);
- Advantix drops, Frontline, Advocate.
If nits are present, the treatment is repeated after 2 weeks. Insecticides kill only adult insects.
The least toxic are pyrethrin-based preparations, such as 8 in 1 sprays and Beaphar. They can be used to treat pregnant and lactating females and cubs weighing up to 500 g.
Sprays against lice and fleas destroy only adult individuals, but not nits.
Seek help from a veterinarian
Not really
After treatment
When infection with a subcutaneous parasite is confirmed, the pet needs treatment, and its home needs careful treatment. To ensure that parasites no longer spread, it is necessary to create a quarantine and immediately treat animals that show signs of illness.
The situation will not improve in a matter of moments, so you need to be patient. It is possible to completely cure your pet only after 2–4 weeks, it all depends on the severity of the disease. It is best to add useful elements to your pet’s diet to strengthen the immune system. Try not to use flea and insect repellents - most of them contain pesticides that are dangerous to rodents.
Are ticks dangerous for people?
The harmful mite in guinea pigs does not pose a danger to humans. It exclusively infects guinea pigs.
lice eaters
This is another type of parasite that differs in that it can feed not only on particles of the animal’s skin, but also on its blood. Due to the small size of the parasites, it is quite difficult to detect them with the naked eye; you will have to use scraping. The first signs include hair loss of the animal, as well as itching. An animal's reduced appetite threatens death from exhaustion. The danger is that lice can get on the animal even with careful care, for example, through the owner’s clothes or toys from the store.
Comprehensive treatment measures include treating all animals that have previously been in contact with or are close to an infected individual, even if they do not show signs of infection.
Akaromectin, Bolfo and Bars spray can be used as medical assistants in the fight against lice eaters. Due to the fact that bathing is considered extremely stressful for pigs, it is best to opt for a spray, as it will cause them less discomfort. The animal does not resist the procedure and, if necessary, it must be repeated the prescribed number of times. This is usually done by a veterinarian. Lice remedies are also available in human pharmacies, but you need to choose those options that contain the substance permethrin. The largest number of breeders recommend choosing Advocate spray. Due to the content of fewer toxic substances, it is safer for the animal.
Lice eaters are localized in the croup and perineum; they parasitize at the roots of the hair, wrapping their limbs around the hair, and feed on blood, epidermal scales and secretions of the sebaceous glands. As a result, the affected hair falls out. Lice eaters are most active in winter, when the guinea pig's fur becomes thicker and longer, which is a favorable factor for the proliferation of parasites.
Lice feed on blood and are able to actively move around the animal’s body, causing itching. Parasites can be seen with the naked eye when parting the fur, mainly in the head area and around the ears.
Guinea pigs become infected with lice and lice through contact with sick relatives, through bedding and food.
Lice and lice cause itchy skin and severe anxiety in a sick animal, up to the appearance of seizures and convulsions. Fleas with intense infestation can cause inflammation of the skin - flea dermatitis. It is characterized by redness of the skin, baldness, and eczema.
Symptoms of parasite infestation
The symptoms of lice and fleas are almost identical. Inexperienced owners can easily confuse them. Lice most often infect the head and neck.
They are much smaller than fleas. They have an oval body with a characteristic yellowish tint. A characteristic sign of lice is white nits, which are firmly attached directly to the hairs themselves.
But such lice are not dangerous for humans.
There are two types of ticks that infect mumps:
- Itchy.
- Fur.
With mites, the itching is so severe that the baby literally convulses. Such a defeat is a real test for the pig’s body. Pregnant individuals even have a risk of miscarriage.
Symptoms of tick infestation:
- itchy skin;
- rough skin areas appear;
- There are places where hair falls out.
If you start the right treatment, you can get rid of ticks quickly.
If you have any suspicions, it is better to take your pig to the veterinarian. He will accurately determine whether there is cause for concern. He has a microscope at his disposal, under which he can easily detect any parasite on the fur.
Preparations containing ivermectin are used. It is recommended to treat the animal's fur several times at intervals of 7-10 days.
The cage can be treated with sulfuric lime.
We suggest you read: Whitefly in a greenhouse: how to get rid of it using folk remedies