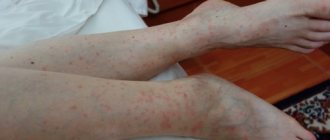
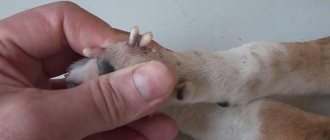
A spider bite is a common and unpleasant occurrence. Since all spiders are poisonous to one degree or another, you should treat this with caution and it is advisable to immediately seek medical help.
Spiders (arachnids) are silent killers that, if attacked, cause instant death to their victim. Patient and calculating, they weave killer nets from invisible sticky threads. Up to 30 thousand species of spiders are known. They live next to humans - in houses, forests, fields, and ponds. And, of course, spider bites are not uncommon, especially if a person is in their habitat.
All spiders are poisonous. Venom glands are located on two head appendages - chelicerae. They need poison to kill and digest their prey. The main prey is insects. In some tropical species, the net reaches 2 m in diameter and can even interrupt the flight of a small bird. They feed on frogs, mice, small birds, fish and even their own brothers - cannibalism is quite common among them. Most spiders are not capable of causing significant harm to humans. Although the venom is strong, its small amount and poorly developed injection mechanism limit the number of species dangerous to humans. The only dangerous ones for people are those that can pierce the skin. The most common species include karakurt (black widow), tarantula, scorpion, hermit spider, cross spider, tarantula spider, and house spider.
What does a spider bite look like?
spider bite at the beginning
spider bite the next day
Most spider bites have common characteristics, such as a small blister in the middle, swelling and swelling surrounding the bite site, and a large circle of redness. On the outside the redness is paler. It is important to note that a spider can only bite once, so if there are several marks, it is likely that it was not the spider that bit, but someone else, or several spiders bit at once. A typical spider bite goes away within a few days and, in most cases, does not require special attention. However, if a large bubble appears, bright redness that quickly spreads to the sides, blue discoloration of large areas of the skin - these are serious signs that need to be responded to immediately and immediately contact a medical facility. In the photo you can see the differences - what a bite from a safe spider looks like and one that is dangerous to health.
What to do if bitten by a spider
- First of all, don't panic! Although all spiders look scary, there are only about 12 species that can have a serious impact on people or animals. The two most dangerous are the black widow spider and brown recluses.
- Check the wound. Pay attention to the site of the bite - whether there is redness, swelling and burning pain. There may be abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, fever, dizziness. The most dangerous reactions are difficulty breathing and shock. If there is anything more than just slight redness and pain, you need to call an ambulance or see a doctor.
- Spider identification - if possible and safe. Some spider bites require serious treatment, including antitoxins. If you are unable to identify the spider, this will be helpful in determining appropriate treatment. It will help a lot if you can catch it in a jar or box (just remember to be safe). Or at least take a photo and show the photo to the doctor.
First aid
- To reduce blood flow in the affected area, it is necessary to secure the arm or leg with a belt or scarf - as if there was a fracture. This will prevent the poison from quickly spreading into the blood and spreading throughout the body.
- Wash the bite with soap and water. Regardless of whether the insect is harmless or poisonous, it should be washed thoroughly as soon as possible. Even an ordinary spider can cause an infection in the wound when bitten.
- Apply a cold compress or ice to the bite site.
- Drink plenty of fluids - this will ensure that the poison is quickly eliminated through the kidneys.
- Take a pain reliever - for example, analgin or ibuprofen.
- And also an antihistamine that will reduce allergic symptoms - itching, burning, rash.
If you suspect you have been bitten by a poisonous spider, you can apply a tight bandage above the bite if it is on an arm or leg, making sure you do not completely cut off the circulation.
The goal is to slow the spread of the toxin, not stop blood flow to the extremities. If the bite is on another part of the body, apply ice and get to a medical facility immediately. Hospitalization is required for most.
Prevention measures
It is worth remembering that a spider bite is quite rare. During the warm period, there are only a few dozen such cases throughout the country. At the same time, about half a million people seek help every year if they are bitten by a tick. Therefore, you should not be afraid of an insect attack; it is enough to take a number of preventive measures.
The best way to avoid being bitten is to avoid the spider. These arthropods should not be handled so as not to provoke an attack. Regular cleaning and maintaining cleanliness will allow you to promptly get rid of insects that accidentally appear at home.
When going outdoors, you need to use special repellents that can repel spiders. Clothes must be closed. If you plan to spend the night in the forest, you should take with you a canopy or mosquito net, which will prevent insects from accidentally crawling inside.
What to do if you are bitten by a poisonous spider
Recluse spider bite
One of the four spiders whose bite poses a danger to humans is the recluse spider. The brown recluse is generally not aggressive and generally bites people as a defense mechanism, usually when a person's leg or arm accidentally gets too close.
Brown recluse
The brown recluse has a clear fiddle pattern on its back in the midsection of its body - pictured.
Recommended topic:
- Scolopendra (centipede) bite photo, symptoms, what to do
- Bitten by a hornet, symptoms, what to do at home
- Bitten by a wasp - what to do at home
The venom of the recluse spider contains powerful cytotoxins and hemolytic enzymes that destroy red blood cells. Although the sting is not usually painful at first, there is a burning sensation similar to a bee sting for the first few minutes. A small white blister may also appear.
Additional symptoms usually develop two to eight hours after a recluse spider bite. Sometimes it takes up to 12 hours for symptoms to develop. Signs:
- severe pain at the site of the bite;
- severe itching;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- fever;
- muscle pain.
Local symptoms
Initially, you may see slight signs of redness in the area affected by the bite.
recluse spider bite
In most cases, the skin at the entry site then hardens and scar tissue may take several days to form. More severe local reactions also occur and can cause blistering, discoloration of the skin, and necrosis of the skin area.
Treatment
Because The reaction to a recluse spider bite can be sudden and severe; it is necessary to contact a specialist to prescribe treatment. A visit to the doctor should not be delayed until symptoms appear; see a doctor as soon as possible. If possible, the spider should be caught and brought to a doctor or emergency room for evaluation. There are no known antivenoms for brown recluse bites, so your doctor may prescribe pain relievers, antihistamines to relieve itching, or recommend icing the bite to reduce pain and swelling.
Signs and superstitions
Hermit spiders, like the rest of their relatives, are associated with many signs and superstitions.
It is believed that the spider that lives in the house completely absorbs the negative energy accumulated in the corners. People have long believed that trouble and misfortune await a family that kills a spider.
The house in which the spiders settled was considered rich and happy. The belief is based on a reasonable explanation: arthropods prefer to live in dry and warm rooms. A wealthy farmstead is characterized by the creation of suitable conditions for spiders to live.
They also try to link the behavior of arthropods to signs:
- if you are hiding, expect rain;
- In warm, dry weather, spiders actively build webs, catching your eye more often.
If an arthropod is found in an uncharacteristic habitat - the bathroom - this is associated with expected problems in your personal life or financial losses.
Many people attach importance to the direction of movement of the animal in relation to the person. If the arthropod moves towards you, good news is expected, otherwise bad news.
Spiders in dreams
In dream books, the spider acts as a key figure determining the destiny:
- Gypsies believed that dreaming about a spider meant great luck;
- Miller's dream book - to career growth, a large cash bonus, positive assessment from management;
- according to Vanga - to scandals, serious disagreements;
- the Spaniards believe that arthropods dream of a loss of reputation associated with a scandalous story, a meeting with an ill-wisher;
- French belief - to treason.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=wjEnV1UeGD8
Despite the various interpretations of beliefs and superstitions, the hermit spider is a dangerous animal for humans in direct contact. Therefore, reasonable preventive measures and knowledge of the animal’s behavioral characteristics will not hurt in order to protect yourself from undesirable consequences.
Cross spider bite
The cross is a small creature harmless to humans that lives quietly, hunting insects that fall into their nets. The sharp poisonous fangs of the spider are primarily a tool for hunting and serve to protect it from other spiders. The victim, falling into the trap, is quickly paralyzed by the poison, and then the spider devours it. The cross spider looks quite harmless - it is distinguished by its characteristic cross pattern on its back. The color varies from green to gray, depending on the habitat. The cross is very common - it lives almost everywhere.
It can only bite a person by accident. Their teeth are not able to damage hard skin, but thinner areas of the body are not a problem. Most often, this situation can arise while walking in the forest, picking mushrooms or traveling. Cross plants grow quickly and can reach impressive sizes in late summer.
They stretch webs of web between the trees at the height of a human face. An inattentive mushroom picker falls into the network being laid and completely destroys it. Then the insect, willy-nilly, tries to escape or hides under clothing. At the moment, we can accidentally crush the insect and then the spider bites.
Sometimes such situations occur during sleep. Spiders are nocturnal creatures and often move around looking for good hunting spots. A sleeping person, feeling a slight tingling sensation on his body, instinctively trying to scratch himself, crushes it, exposing himself to a bite. Erythema or swelling may occur on the body in the affected area. Usually these symptoms go away on their own.
The poison of the cross does not cause any harm to humans. However, people with allergies or sensitive to spider toxins should consult a doctor.
Tarantula
The bite of a tarantula (Lycosa, Theraphosidae) does not pose a danger to humans, but may be accompanied by pain and swelling. After being bitten, the animal performs a defensive maneuver, while shedding hairs from its abdomen. Small hairs getting into the eyes and skin cause pain and urticarial rash. A type of tarantula is the tarantula spider.
Tarantula spider
There are 400 species of tarantulas of different colors. From cobalt blue to gray or dark brown, sometimes black. The tarantula reaches sizes from 9-10 to 17-23 cm, although its body is no more than 10 cm. The rest is on the legs. Tarantulas live a very long time - from 25 to 40 years, but this depends on the gender of the spider. He is one of the most terrible spiders (outwardly) - his weight is 80 grams! The tarantula spider does not spin a web like others, but chases prey with its long legs and paralyzes it with a toxin. It feeds on small insects - grasshoppers, beetles, spiders, and even small lizards.
Incredibly, the spider has eight eyes - two in front and two each on the left, right side and back! They usually dig holes in the ground and build a house there.
Tarantulas are poisonous, but most types of venom are not strong enough to seriously harm anyone.
A tarantula bite can be compared to a wasp or bee sting. In most cases, this is harmless, although a person who has an allergy may react like a bee sting. Recently, some people have started keeping the tarantula spider as a pet. It can bite a person through negligence when trying to escape from the terrarium. First aid is no different from others - you should consult a doctor if there is an allergy or signs of wound infection.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis is based on the toxic effect of poisons - neurotoxic and necrotic (cytolytic), as well as the development of allergic and infectious reactions in response to a bite. Effects may be local only or with additional systemic reactions resulting from neurotoxicity.
The effect of spider venoms resembles strychnine , but is much weaker. After excitement, a loss of strength occurs and paralysis . The toxic complex biochemical mixture contains neurotoxic substances that paralyze the nervous system, as well as hemolytic substances that destroy the blood. Their main task is to kill and paralyze the victim, as well as protect and scare away the aggressor.
The mechanism of action of Latrotoxin, a component of most neurotoxic poisons
By its nature, it is a presynaptic neurotoxin, since the point of action of Latrotoxin is the presynaptic nerve ending. There, the dimeric toxin is able to contact protein receptors with a molecular weight of ~95,000, as a result of which the resulting complex induces the permeability of biomembranes and becomes a channel for calcium cations - triggering the release of neurotransmitters and accelerating this process by 1000-1500 times. When reserves are depleted, after 30-50 minutes a complete block of neuromuscular transmission occurs. This ultimately leads to overstimulation of the muscle motor neuron ganglia.
Karakurt
Karakurt (Latrodectus tredecimguttatus) is a poisonous spider that lives in Moldova, Crimea, and Central Asia. Females that have a pair of tubular poisonous glands located on the upper jaw are dangerous to humans. The poisonous segment (chelicerum) ends in a movable sharp claw with an opening for the duct of the poisonous gland. The female has a spherical, dense black abdomen with reddish spots. The length of the karakurt is about 10 mm.
Symptoms of poisoning with karakurt poison
After a bite, a small, quickly disappearing spot is formed. After 10-20 minutes, severe pain develops at the site of the lesion, which spreads to the abdomen, lower back, and chest. Severe mental agitation, headache, dizziness, suffocation, nausea, vomiting, weakness, shortness of breath, cyanosis, tachycardia, arrhythmia are observed. Severe drooling may begin. Possible respiratory arrest.
Black widow bite
The black widow spider (Latrodectus mactans) of the genus Latrodectus lives in the United States. The females of this species are very large: the paw span reaches 5 cm, and the body length is 1.5 cm. There is a red hourglass pattern on the black back.
Males are smaller, with a white mark on the back, the small size of the venomous apparatus and mild aggressiveness make them practically harmless to humans. When disturbed, they fall to the ground, fold their paws and pretend to be dead. Female black widows are venomous from the moment they are born. If they are guarding laid eggs or feel threatened, they prefer to attack. Spiders use their venom to paralyze prey, from which they then suck the hemolymph.
The period of post-copulatory passivity of the female allows the male to escape from his partner if she is not very hungry. If the female is hungry, then after mating she eats the “wife”, which is why she is called a “widow”.
Karakurt toxin is a protein with a molecular weight of 130,000. Under its action, ion channels are formed in the presynaptic membranes of nerve cells through which Ca 2++ ions enter the cell. Under the influence of the toxin, exocytosis of synaptic vesicles is facilitated and the release of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), norepinephrine, and acetylcholine is enhanced.
Changes in intracellular homeostasis and an increase in the content of biologically active substances in the blood affect the functional state of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. In case of poisoning with karakurt poison, clinical manifestations develop within 30 minutes. The victim usually feels the sting and describes it as a "puncture". In the area of the spider bite, severe pain is noted, erythema and increased local sweating gradually increase.
Severity
When bitten by a black widow, there are three degrees of severity of the disease.
- I degree; moderate pain at the site of the bite, no general clinical manifestations of intoxication, all laboratory parameters are normal.
- II degree: muscle pain in the bitten limb. Pain spreading to the abdomen when a leg is bitten or to the chest when an arm is bitten. Profuse sweating at the site of the bite. Vital signs are normal.
- III degree: generalized muscle pain in the back, chest, abdomen. Strong mental agitation. Headache, dizziness, suffocation, nausea, vomiting, weakness, shortness of breath, cyanosis, arterial hypertension, tachycardia, arrhythmia. General profuse sweating. Severe drooling. Possible respiratory arrest. Blood tests show increased levels of creatine phosphokinase (CPK), leukocytosis, and proteinuria. In the absence of treatment, the maximum severity of symptoms lasts for 12 hours, the duration of intoxication is 48-72 hours.
in the photo on the left - the bite at the beginning, on the right - on the 3rd day.
Muscle spasms and tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall sometimes become the reason for the erroneous diagnosis of peritonitis and the performance of unnecessary laparoscopy.
Diagnostics
- Clinical assessment
- Careful consideration of alternative diagnoses
Patients often mistakenly believe that they have been bitten by a spider. Typically, a presumptive diagnosis is based on history and physical signs, but confirmation is rare because it requires witnessing a bite, identifying the type of spider (a spider is rarely caught intact), and ruling out other causes.
In non-endemic areas, brown spider bites do not need to be diagnosed without identifying the spider species. Many patients mistakenly attribute the much more common skin infection caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to brown spider bites. Such infections must be ruled out, as should other conditions that mimic spider bites (see table Disorders that mimic spider bites). Severe cases of latrodectism must be differentiated from acute abdomen, rabies or tetanus.
When identifying spiders, their habitat and characteristics are taken into account. Widow spiders live outdoors in sheltered areas (eg, piles of rocks, firewood, haystacks, outbuildings) and are distinguished by a red or orange hourglass mark on their abdomen. Brown spiders live in indoor or hidden areas (eg, sheds, attics, wood storage, behind furniture, under floorboards) and have a violin or cello-shaped marking on the dorsal segment of the cephalothorax from the eyes to the abdomen. This mark is difficult to see even on an intact spider
Lesions simulating spider bites
| Category | Examples |
| Insect bites | Ant bites Bed bug bites Flea bites Fly bites Bites from Reduviid beetles, which represent a large family of predatory insects in the suborder Bedbugs (eg, assassin, wheel, kissing beetles) |
| Bites from other arthropods | Tick bites Ixodid tick bites |
| Skin diseases | Chronic migratory erythema Erythema nodosum Leukocytoclastic vasculitis Pyoderma gangrenosum Sporotrichosis Toxic epidermal necrolysis |
| Infections | Chronic herpes simplex Cutaneous anthrax (anthrax carbuncle) Disseminated gonococcal infection Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus) Septic embolism due to endocarditis or intravenous drug use |
| Injury | Self-harm Subcutaneous injection of drugs |
Features of a scorpion bite
The scorpion (Centruroides sculpturatus) is a poisonous spider widespread in the world. In Russia it lives in southern latitudes. A structural feature of the scorpion, unlike other arthropods, is the presence of pedipalps with claws; at the end of the abdomen there is a curved sharp sting where the duct of the poisonous glands opens. The most dangerous is the black scorpion, its size is 50-100 mm.
Scorpion venom binds to sodium channels in cell membranes, causing neurons to re-activate. This is accompanied by a prolongation of the neuronal action potential at the synapses of the autonomic nervous system, which leads to an increase in the blood levels of catecholamines, renin and aldosterone.
Symptoms of poisoning from a scorpion sting
The bite causes severe pain, which quickly spreads along the nerve trunks. The victim screams in pain, severe weakness develops, cramps of individual muscle groups occur, blood pressure rises, and the body becomes covered in cold, sticky sweat. A urticarial rash appears in the bite area. In severe cases, motor agitation develops, arterial hypertension turns into hypotension, tachyarrhythmia, ventricular extrasystoles, vomiting, profuse sweating, priapism, and salivation occur.
Increasing visual impairment, ptosis, involuntary contractions of the tongue muscles are noted, and speech becomes slurred. Within 2-3 hours after the introduction of the toxin into the body, breathing is impaired and pulmonary edema develops. Death occurs due to the phenomena of increasing acute cardiovascular and respiratory failure.
When assessing the degree of toxicity of arthropod venom, the following was noted:
- tarantula venom is less toxic than that of karakurt and scorpion;
- The poison of karakurt and scorpion (belongs to toxalbumin) is more toxic than snakes (~ 15 times). However, fatal poisonings are much less common. This is due to the smaller amount of poison.
allergic reaction to a scorpion sting
Black Eresus
The beautiful ladybug spider inhabits vast territories of Russia, found from the Rostov region to the Novosibirsk region. Having chosen a burrow once, black eresus rarely leave it. The instinct of reproduction pushes sexually mature males to take such a step, and caring mothers crawl out to warm the cocoons with future spiderlings in the sun. Eresus can bite only in case of self-defense. The consequences will be extremely unpleasant, but not fatal. At the moment of the bite, the person experiences severe pain, then numbness. You may experience sensitivity to pressure for a short period of time.
Treatment
To reduce the spread of venom from the bite site throughout the body, immobilization of the limb is indicated. The pain is relieved by performing a novocaine blockade, and painkillers are administered: non-narcotic and narcotic analgesics. Cold is applied to the bite area.
Hormones, antihistamines are administered: blockers of H1 receptors (promethazine (diprazine), chloropyramine (suprastin), etc. and H2 receptors (cimetidine, ranitidine (acylok), etc., vitamins. When excited, benzodiazepines are prescribed. If a karakurt is bitten, an anti-karakurt drug is administered subcutaneously serum. In severe cases, equine immunoglobulin (IgG) is administered. The antitoxin (from horse serum) prevents the venom from binding to presynaptic membranes and remains effective even 46 hours after the bite.
When a scorpion stings, calcium channel blockers and ACE inhibitors are prescribed.
Propranolol (anaprilin) effectively and quickly stops tachyarrhythmia, but does not improve hemodynamic parameters. In case of respiratory depression, oxygen is supplied; in case of acute respiratory failure, artificial pulmonary ventilation (ALV) is performed. https://medicalit.ru/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/otshelnik.jpg https://medicalit.ru/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/otshelnik-300×272.jpg2020-09-13T17 :49:31+00:00 adminPoisoning with venoms from snakes, insects, fish, the bite of a spider is a frequent and unpleasant case. Since all spiders are poisonous to one degree or another, it is necessary to treat this with caution and it is advisable to immediately seek medical help. Spiders (arachnids) are silent killers that cause instant death of their victim in the event of an attack. Patient and calculating, they weave from invisible sticky...admin [email protected] Medical literature online