With redness, itching of the eyelids, the formation of crusts on them and sticky discharge from the eyes, we can talk about the presence of demodicosis. But before making such a diagnosis, you need to find out what eyelash mites are and how to diagnose them.
Demodex is a parasite that lives in hair follicles or sebaceous ducts. The iron bug often lives in the nasolabial area, on the skin of the chin, in the area of the eyebrows or forehead. Less often, the tick chooses the eyelids as its localization site.
Prolonged parasitism of the pest provokes the appearance of blepharoconjunctivitis or blepharitis. Demodicosis has a chronic course and is more often diagnosed in people whose immunity is weakened.
Causes
Normally, from one to three eyelash mites (demodex) live inside the eyelash bulb. In this case, it belongs to the normal microflora. With such a concentration of microorganisms, clinical symptoms do not appear, so a person is not aware of the existence of demodex in the glands of the eyelids.
It often happens that the immune system loses its functionality, this occurs in the following cases:
- poor nutrition with insufficient intake of vitamins, microelements, and minerals;
- frequent viral and infectious diseases that suppress the immune system;
- diseases causing immunodeficiency (congenital, acquired).
When the effect of the immune system decreases, the eyelash mite begins to multiply intensively. If it becomes more than 10 units, clear clinical symptoms arise. This causes an imbalance in the normal microflora of the glandular tissue of the eyelids.
Maintaining personal hygiene if you have demodex
The eyelash parasite is able to move to healthy areas of the body. Therefore, in addition to drug therapy, you need to carefully observe personal hygiene.
If demodex is detected, the following measures must be taken immediately:
- It is necessary to wash and iron bed linen;
The patient needs to separate his things, even washing should be done separately from the things of other family members;
If a person wears glasses, they must be disinfected and wiped frequently;
Risk group
The risk group includes patients suffering from the following disorders:
- endocrine, hormonal imbalance;
- changes in hormonal levels due to adolescence;
- recent treatment for a viral or infectious agent that has caused weakening of the body;
- constant stress, worries;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the superficial tissues of the eyes;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases that reduce the supply of nutrients to the body;
- poor nutrition, causing a decrease in the supply of nutrients, minerals, trace elements, vitamins to the body;
- increased secretion production in the sebaceous glands;
- taking certain medications or applying cosmetic products that negatively affect the sebaceous glands in the eyelid area;
- allergic reactions.
Persons who suffer from the above diseases and conditions are recommended to undergo periodic examination by an ophthalmologist and dermatologist. The sooner the disease is detected, the sooner treatment will begin. This will prevent complications for the tissues of the organs of vision.
Symptoms
Settling in the sebaceous glands, the mite feeds on secretions that protect the eyelids from negative environmental factors and tears. The more demodex is on the eyelids, the more actively the following symptoms develop:
- redness of the skin in the corners of the eyes, which develops slightly at the initial stage;
- secretion from the sebaceous glands in increased quantities, which causes the eyelashes to stick together after sleep, which resembles pus in consistency;
- sensation of a foreign object under the eyelids that is not actually there;
- constant dryness of the mucous membrane, causing irritation and damage to the cornea;
- spread of the inflammatory process to the conjunctiva, cornea;
- swelling in the eyelid area;
- the formation of a vascular network on the cornea, which makes the eyes painful;
- loss of more eyelashes than usual;
- if there is no treatment, the eyelids swell greatly, become significantly red, and lose sensitivity.
If the parasite spreads to other organs and tissues, the inflammatory process will spread to them. But most often the affected area is localized only on the eyelids.
Nutrition tips
If a patient is diagnosed with eyelash mites, then he must be prescribed a certain diet:
- The amount of smoked, spicy and salty foods consumed is significantly reduced;
Avoid chocolate, honey, and alcohol;
Sweets are removed from the diet because they are considered the favorite food of parasites. It is for this reason that their consumption is limited in order to deprive parasites of food.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis for the presence of parasites is carried out in several stages:
- Anamnesis collection. This is data obtained from the words of the patient or his close relatives.
- General examination of the patient. The doctor may assume the bacterial nature of the discharge and prescribe antibiotics. If the parasite is not sensitive to them, they will not help. Treatment requires specific medications. If the doctor does not determine the cause at the first visit, he will order laboratory testing at the second examination.
- Laboratory tests. The doctor takes a smear in the place where the discharge from the eyes or the whole eyelash with bulb is localized. The material is examined for pathogenic microorganism content. Under a microscope, the mite will be immediately detected. Additionally, its quantity is determined. If it exceeds the norm, drug treatment is prescribed.
Only after laboratory analysis can a doctor make a reliable diagnosis. Therefore, it is recommended to take a smear if there is discharge from the eyes.
Treatment
To eliminate the parasite, complex treatment is required. It is important that the patient maintains eye hygiene and takes medications prescribed by the doctor. If there is no effect from them, you cannot replace the drug with an analogue yourself. To do this, consult a specialist.
Eye hygiene
To eliminate excess pus, it is recommended to rinse the eyes with Furacilin 3 times a day. This is a drug that in rare cases causes side effects.
After using it, the skin may be slightly dry. This method is used for up to 7 days, since after this time resistance to the active substance may develop in pathogenic microorganisms.
In the intervals between washing Furacilin, it is recommended to use saline solution. Additionally, they maintain hand hygiene so that the infection does not spread from them to the eye area.
To maintain hygiene in the eye area in persons with a predisposition to mite reproduction, it is recommended to use baby shampoo. It does not cause tears, but destroys pathogenic microflora.
Compresses
For a compress in the eye area, oak bark, chamomile, sage, green tea, and calendula are suitable. They can be used together or separately. They eliminate the inflammatory process, irritation, and have a mild antiseptic effect.
To use the compress, the plants are brewed and infused. Cotton wool is soaked in the resulting liquid and applied to the eye area. A person should lie with them for 5-10 minutes. Procedures are recommended to be carried out in the morning and evening.
Medications
To eliminate the parasite, it is recommended to use antibacterial drugs to which it is sensitive. This group includes macrolides and tetracyclines. Medicines that reduce the production of glandular secretions from the eyelids are also used. For example, Isotretinoin.
To identify the exact type of antibiotic to which the tick is sensitive, laboratory testing is necessary. The doctor inoculates microorganisms on a nutrient medium and treats it with various antibacterial drugs.
Medicines
The following medications are used to treat demodex mites:
- Demodex Complex is a product based on natural ingredients (21 medicinal plants) that provides treatment and protection against relapses of the disease through an acaricidal effect, wound healing and anti-inflammatory effect, restoration of the barrier functions of the skin, softening and cleansing it, eliminates itching, relieves redness and narrows pores. skin around the eyes; Demodex Complex includes a special tonic, soap, morning and evening creams;
- eye drops containing zinc;
- Tafazol - antiseptic, anti-allergenic and anti-mite eye drops, treatment lasts for 2 weeks;
- Colbiocin - drops containing an antibiotic are used even in children;
- Eubetal – drops and ointment with complex action (against germs and bacteria);
- Prenacid - anti-inflammatory drops, applied to the conjunctival sac;
- Carbohol - destroy pathogens, applied along the eyelash line;
- eye drops used in the treatment of glaucoma, which have a paralyzing effect on parasites - Phosphacol, Physostigmine, Tosmilen, Armin;
- ointments and creams - Demazol, Blefarogel, Demalan - are applied to previously cleansed skin of the eyelids;
Ointments for the treatment of eyelash mites - tablets or ointments containing Metronidazole;
- as an antiparasitic treatment it is recommended to use: ichthyol, tar, zinc-ichthyol, sulfur ointments, benzyl benzoate;
- antihistamine drops Acular, Okumetil, etc. - help reduce redness and irritation;
- to relieve unpleasant symptoms - Tosmilen, Phosphacol, Armin;
- physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis of the eyelids with the addition of diphenhydramine and zinc sulfate);
- magnetic therapy, Darsonval device (electric current therapy).
Complications
If the patient delays going to the doctor or ignores the use of medications, complications will arise:
- loss of sensation in the eyelids;
- inflammation and spread of the inflammatory process to the structure of the eyeballs;
- formation of abscesses with purulent infiltrate.
To avoid complications, you must fully adhere to your doctor's recommendations. Self-medication is unacceptable; it will lead to a worsening of the patient's condition.
Prevention
To avoid the spread and reproduction of eyelash mites, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- daily hygiene of hands, face, eyes;
- proper healthy nutrition containing nutrients, vitamins, minerals, microelements;
- treatment of clothing with a hot iron, especially for persons with a predisposition to the development of eyelash mites;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases;
- the use of drugs that stimulate the immune system for people with reduced function.
Preventive measures are recommended for persons with immunodeficiency or normal functionality. The above rules will protect the patient not only from tick development, but also from bacterial or viral infection. It is especially important to maintain immune function in the autumn-winter period, when the supply of nutrients and vitamins to the body is reduced.
Excessive production of eyelash mites is a fairly rare phenomenon that develops during a decrease in immunity. If purulent contents form in the eye area, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor. If treatment is carried out on time, this will save the patient from complications.
Parasites on human eyelashes
Treatment of demodex of eyelids and eyelashes
Neglecting the rules of facial skin care leads to the appearance of parasites on a person’s eyelashes, eyebrows, nose and other hairy areas. The skin is an ideal environment for the development and reproduction of microorganisms. Rash, acne, pimples are the result of the life activity of mites and lice.
Lice on the human body
The face is parasitized by Trichinella - dangerous small worms that move from the gastrointestinal tract into the facial muscles, causing trichinosis.
Larval parasites cause dirofilariasis. People become infected through contact with pets - cats, dogs. The larvae live on the eyelash margins, eyelids, and under the skin.
On a note. Sometimes parasites are easy to spot without a microscope.
Danger to humans of eyelash mites
The interciliary mite, demodex, lives in the hair follicles of the cilia, eyebrows, nasal cavity, and outer ear. The face is no exception. It comes from parents in childhood or adolescence. According to statistics, approximately 1/3 of the population is affected in youth, 75% are over 40 years old, and at the age of 60+ only every tenth does not suffer from the disease.
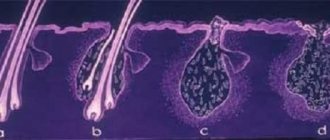
Demodexes belong to the class of arachnids, their dimensions do not exceed 0.2-0.5 mm. The sweat and sebaceous glands of the human body are associated with their lifestyle. Ticks are human symbionts. Parasites can live permanently on the skin without causing harm: a neutral or conditionally harmful form of development.
Favorite places for mites to settle are human eyelashes and eyelids
Increased reproduction of demodex and transition to a pathogenic form is observed under unfavorable factors:
- hypothermia;
- hormonal imbalance;
- decreased immunity.
Females lay eggs near the hair follicle near the eyes. After 60 hours, larvae appear that are unable to move, but feed for 40 hours and develop.
The next stage is the transformation into a nymph, which lives only on the hair follicles.
Additional Information. Demodex feeds on cilia at all stages of development on keratinized epithelial cells and sebum (mites prefer an oily type of epidermis). This is not dangerous. But the waste products of parasites are strong allergens and often provoke a negative reaction in the human body.