Lice eaters in dogs are a type of external parasite that is not very well known to pet owners. This is because these translucent small insects are very difficult to detect on the animal’s body. The food for these ectoparasites are particles of the epidermis, dried blood and dog fluff, which is why they are also called lice beetles, skin beetles or itches. Infestation by lice eaters is scientifically called trichodectosis. You need to know all your dog’s “enemies” by sight in order to detect them in time and begin to fight them. In this article we will talk about where a dog can become infected, how to identify parasites and how to deal with them. Let's consider popular industrial and folk remedies and preventive measures.
Ways of infecting dogs with lice eaters
The most common routes of infection are described in veterinary medicine:
- Contact. From an infected animal: when kept together (kennels, dog shelters and hotels), while walking, during mating or a veterinary appointment.
- Other people's care and hygiene items: combs, leashes, muzzles, bedding.
- Grooming. Poor quality processing of cutting tools.
- Offspring become infected from a sick mother.
- Household shoes and clothing. Insects and their eggs can be brought into the house by humans.
High humidity in the dog’s habitat, too infrequent hygiene procedures, and a poor diet contribute to the spread of parasites. Most of the cases of infection occur in the autumn-winter period.
Important! Regularly examine your dog and carefully observe its behavior in order to promptly detect dangerous “intruders.”
Symptoms of canine lice infestation
The clinical picture of trichodectosis resembles the symptoms of infection with fleas, lice and ticks:
- Severe itching of the skin. The animal tries to relieve the itching by scratching itself.
- Changes in coat structure. Dog hair loses its shine and sticks together. The dog looks disheveled.
- Hair loss. Complete baldness is possible on the tail, inner thighs and muzzle.
- The skin in areas of bald patches becomes rough, red, and crusty.
- On the dog's fur you can notice small white grains that move.
- Dermatitis in areas scratched by the dog.
- Extreme thirst and loss of appetite.
- Behavioral changes: sleep disturbances, aggression, anxiety, loss of attention.
- Decreased immunity.
- Delayed growth and development (in puppies).
Why is trichodectosis dangerous for a dog?
Causes functional disorders in the animal's body.
- Reduces immunity.
- Weakens the skin barrier function.
- Causes complete baldness of the dog.
- The causative agents of the disease are carriers of leptospira, fungi and helminth eggs.
Due to the fact that the clinical symptoms of many parasitic diseases are similar, it is important to correctly diagnose.
Photo gallery
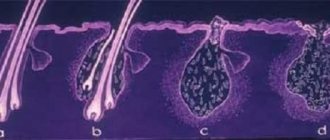
Photo 1. Lice eater under a microscope
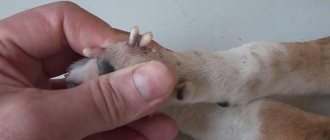
Photo 2. Lice beetles on wool
Photo 3. Poison beetles under a microscope
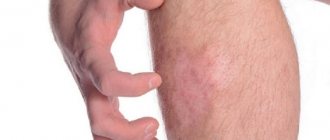
Photo 4. The dog and the consequences of the “work” of lice eaters
Photo 5. Bald patches on a dog
Photo 6. Lice eater close-up
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of trichodectosis consists of a visual examination of the animal's fur, on which lice eaters of various stages of development can be found (adults, larvae, eggs). To facilitate this activity, the dog is heated with an electric lamp or in open sunlight so that the insects crawl to the surface and become more visible. To exclude other pathologies of parasitic origin, scrapings are taken from the skin and examined microscopically in a veterinary clinic.
Symptoms of pathology
Symptoms of ringworm appear 4-6 weeks after the patient becomes infected. A red spot appears on a smooth area of skin of a child or adult. It rises above the surface and has smooth boundaries. Over time, the size of the lesion increases. The surface becomes covered with nodules, blisters and scabs. The spots develop into rings that can intersect or merge with each other. The diameter of skin formations ranges from 5 to 30 millimeters.
Signs of ringworm include an acute inflammatory reaction. It often develops in children and girls. The lesions begin to peel off intensively. Patients suffering from dermatitis do not immediately identify symptoms of microsporia. Areas of active fungal growth may appear as inflammatory skin lesions.
A common manifestation of ringworm in a child is damage to the scalp. This symptom affects patients aged 5-12 years. Older children experience changes in the chemical composition of sebum. Its elements become dangerous for the microsporia pathogen.
The suppurative type of ringworm is characterized by the appearance of soft nodules on the patient’s skin. The nodes are dotted with numerous abscesses. When they are compressed, purulent contents are released.
Are you experiencing symptoms of ringworm?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Anti-hairworm medications for dogs
To rid a dog of dangerous parasites, a variety of insecticidal preparations are used: drops, aerosols, shampoos, dusts. The course of treatment is quite long - from four to five weeks. This is the life cycle of lice eaters. It is not enough to treat the animal’s fur once; the measures are carried out 2-3 times with an interval of 7-9 days, according to the instructions for the specific insecticide.
Pediculicidal shampoos
To get rid of lice, you can use shampoos against fleas, lice and ticks. The moisturizing substances included in their composition reduce itching and improve the structure of the dog's hair. Medicinal detergents have a pleasant aroma and rarely cause allergic reactions in pets. Shampoos are used to treat dogs of all breeds and ages; use in puppies is allowed.
Popular brands of shampoos against hair lice:
- Lugovoy;
- Phytoelite;
- RolfClub;
- Bars (AVZ);
- Demos-Lux.
Drops against lice
The basis of medicinal products in the form of drops are insecticidal components. Drops are considered the most effective remedy against this type of parasite, because they have a long protective period - the preventive effect lasts up to 6-8 months.
Popular brands of antiparasitic drops:
- Insectal;
- Good Dog (Favorite);
- Prac-tic (Novartis);
- Frontline (Merial);
- GreenFort.
Antiparasitic sprays and aerosols
Preparations in the form of sprays (aerosols) have a composition similar to drops. A distinctive feature of this type of preparation is its high concentration of insecticide.
Popular aerosols against lice:
- Frontline (Merial);
- Bars (AVZ);
- BlochNet (Astrapharm);
- RolfClub;
- Fiprex.
The form and brand of the medicine should be selected by the attending veterinarian, taking into account the condition of the dog, the degree of infestation with parasites, age and other biometric parameters.
Other means
In addition to those described above, there are also other types of products that protect against fleas, ticks and lice - key chains and tablets.
- key fob works by transmitting signals in the ultrasonic range and repelling both blood-sucking insects and ticks. The cost of such a product ranges from 1,500 rubles to 5,000. Manufacturers of such devices assure that the key fob is valid for 2 years.
- In addition to key chains, there is another product that has an insectoacaricidal effect - chewable tablets . The validity period of such tablets is from one (Frontline Nesgard) to three months (Bravecto). The cost of the product is quite high - from 800 to 1500 rubles per Frontine tablet and from 1300 to 1800 rubles per Bravecto tablet.
The tablet is a wet treat that is soaked in the active ingredient. After the dog eats it, the ingredients penetrate through the gastrointestinal tract into the blood and remain there for the entire duration of action.
The advantage of this remedy is that any blood-sucking insect or tick will definitely die if bitten. A significant disadvantage is that if the substance enters the animal’s blood, it cannot be removed until the entire period of action has expired. The only way is a complete blood transfusion.
Tablets should be used with extreme caution for miniature dogs or animals prone to allergic reactions.
How to use medications correctly?
We have already said that the process of completely getting rid of lice eaters takes from 4 to 5 weeks. Therefore, it is so important to strictly follow all the veterinarian’s recommendations regarding the choice of treatment and instructions for its use.
Rules that owners of infected animals must adhere to:
- Shampoos are applied to the dog’s wet fur, rubbed in with massage movements and left for several minutes. Heavily soiled areas and matted fur are treated especially carefully with a large amount of detergent. After this, the shampoo is washed off from the animal's fur, the dog is dried, and the dead parasites are combed out.
- Drops are applied to the withers and spine using special pipettes so that the dog cannot lick them off.
- Sprays are used to treat the entire coat, protecting the eyes and mucous membranes from contact with the drug.
Important! The animal is processed in several stages at weekly intervals.
Handling your pet's personal belongings and disinfecting your home
Leaf bugs that have left the fur can hide in any household items, so the fight against them cannot be done without thorough disinfection. All horizontal surfaces must be treated with insecticides or herbal infusions.
Particular attention should be paid to dog toys and bedding. They should be washed in hot water with insecticidal shampoo or treated with steam, and then thoroughly frozen on the balcony. In summer, the required temperature can be found in the freezer. To destroy heat-loving pests, it is enough to keep washed items there overnight.
Prices for drugs against lice
Russia
- Lugovoy (Agrovetzaschita), shampoo, 270 ml., from 165 to 190 rubles;
- Bars (AVZ), shampoo, 250 ml., from 160 to 170 rubles;
- Rolf Club, shampoo, 400 ml., from 300 to 320 rub.;
- Rolf Club, spray, 200 ml., from 490 to 520 rubles;
- Insectal, drops, 4.3 ml., from 185 to 195 rubles;
- Prac-tik, drops, 3 pipettes, from 1100 to 1400 rubles;
- GreenFort, drops, 3 pipettes, from 130 to 190 rubles;
- Bars (AVZ), spray, 100 ml., from 180 to 190 rubles;
- BlochNet, spray, 100 ml., from 170 to 175 rubles;
- Gamma, shampoo, 250 ml., from 110 to 120 rubles;
- Phytoelite, shampoo, 220 ml., from 90 to 100 rub.
Ukraine
- Phytoelite (Veda), shampoo, 220 ml., from 40 to 45 UAH;
- Bars (AVZ), drops, 1 pipette, from 30 to 32 UAH;
- Insectal, drops, 1 pipette, from 90 to 95 UAH;
- Prac-tik, drops, 3 pipettes, from 80 to 85 UAH;
- Insectozol, spray, 30 ml., from 22 to 24 UAH;
- FiproGuard Max, drops, 3 pipettes, from 290 to 300 UAH;
- Foline, drops, 3 pipettes, from 200 to 210 UAH;
- Lugovoy, shampoo, 270 ml., from 100 to 110 UAH;
- Leopard, spray, 100 ml., from 100 to 110 UAH;
- Inspector, drops, 1 pipette, from 280 to 285 UAH;
- Lapushka (Veda), shampoo, 220 ml., from 33 to 35 UAH.
Traditional methods of getting rid of lice in dogs
Lice eaters in dogs are insidious and very tenacious ectoparasites, which are difficult to remove even with industrial insecticides. Traditional methods of control are allowed only at the initial stage of infection in combination with special anti-parasitic shampoos.
Popular folk remedies:
- sagebrush;
- chamomile;
- series.
These plants are used in the form of decoctions for bathing dogs. Treatment of infected puppies with folk remedies is especially effective.
Symptoms
Considering the rapid development of lice on a dog’s skin, symptoms of infection will appear quite quickly. Unfortunately, the microscopic size and colorless, pale yellow color of parasitic insects makes it impossible to immediately detect them with the naked eye. Favorite places for lice eaters to localize on the body of dogs are the croup, tail, back, and inner surface of the limbs.
During the process of active reproduction, parasitic insects cause severe itching, which leads to the dog becoming restless. On the body, especially behind the ears, on the muzzle, at the base of the tail, scratches, scratches, and small ulcers are noticeable, which cause pathogenic bacterial flora to enter the body. Dogs rub against corners, furniture, and chew fur, experiencing severe itching.
Dandruff and light scales indicate that the dog is infected with lice eaters.
Causes of dog infestation with lice eaters:
- severe itching;
- the appearance on the body of grayish-white small scales resembling dandruff;
- deterioration of coat condition;
- change in the dog's behavior;
- the appearance of hairless areas on the body, bald patches;
- anemia of the mucous membranes.
When dogs are infected with lice eaters, the coat becomes disheveled and loses its natural shine. On long hair, small knotted lumps are noticeable. Dogs become restless due to lack of normal sleep and rest. Puppies and adult animals are reluctant to follow commands and refuse to participate in active games.
Parasites lead to the development of inflammatory processes in various structures of the dermis, the appearance of allergic reactions, which are accompanied by a decrease in appetite, a slight increase in temperature, lethargy, apathy, and weight loss.
Bald patches and scratching as a result of severe itching are a symptom of a dog being infected with lice eaters.
Lice eaters can provoke a decrease in immunity, cause exacerbation of chronic, latent infections and diseases, and lead to the activation of opportunistic flora that provokes mycoses and onychomycosis. In places where parasitic insects are most localized, the skin becomes rough, dry, and tight. Dirty-gray crusts, scabs, and scales may be noticeable in the affected areas.
Important! To make sure that your dog is infected with lice eaters, you need to warm up the fur with a UV lamp for several minutes or, if it is summer, take a walk in direct sunlight. Heat-loving parasites will definitely begin to move to the tips of the hairs, and they can be seen upon careful examination of the body and coat of the pet.
In especially severe cases, when dogs are heavily infested with lice eaters, insomnia, inappropriate behavior, complete refusal of food, and increased thirst are noted.
Severe damage to a dog by lice eaters
Prevention
Preventive antiparasitic treatment of a dog and its habitat is not reinsurance, it is a way to save your pet from a severe debilitating disease.
Prevention measures:
- Barrier. Try to protect your dog from unwanted contact with stray animals.
- Antiparasitic collar. Use special collars when walking your dog.
- Animal hygiene. Keep your dog's environment clean and bathe your dog regularly. Wash and replace bedding promptly. Carry out preventive treatment of enclosures, kennels and dog habitats with insectoacaricidal agents.
- Visual inspection. Regularly carefully inspect the body and coat of the animal.
Following these simple rules will help protect your pet and you from the harmful effects of parasites.
Important! Remember that it is easier to prevent an infection than to treat a dog for a difficult-to-treat infestation.
Are lice eaters in dogs dangerous for humans?
Lice eaters prefer one owner, so a person cannot become infected from their pet. But this does not mean that they pose a danger only to the dog. If a person comes into close contact with an infected animal, accidental insect bites may occur. These bites are dangerous because the parasites are carriers of many fungal and bacterial infections. In addition, insects carry worm eggs, so the likelihood of helminth infection is high.
Therefore, as soon as you notice the first signs of parasites in your dog, contact your veterinarian for a diagnosis and treatment. Immediately carry out insectoacaricidal treatment of all premises where the dog is. Strictly observe personal and animal hygiene measures. This way you can save your dog from illness, and protect yourself from possible dangerous consequences.
Biology
Trichoderma is transferred to a dog from a cat, relative or rodent. In order for a female lice eater to lay eggs, she needs blood. The parasite's mouthparts are only suitable for gnawing; the parasite cannot suck blood. This opportunity is provided to him by the dog itself when scratching the itchy skin. If a flea, having drunk blood, leaves the animal to lay eggs, then the lice eater spends its entire life on the dog or moves to the cat.
Depending on the outside air temperature, the development cycle of Trichoderma from egg to adult insect capable of oviposition lasts from 3 to 4 weeks.
Fungi and bacteria settle on the scratched skin, the activity of which increases the itching, and new scratching occurs. There is more food for insects. The larvae actively feed on the fur, and the dog develops bald patches.