Spiders are unlucky: few people like them. However, many of them are completely harmless.
You can meet spiders everywhere: in the house, garden, forest or meadow. Some settle on window frames and in secluded corners, others hide in the foliage, having first stretched out a trap web.
Arachnologists who professionally study spiders say that they should never be killed. After all, by eating insects, they take care of the balance of the ecosystem. And if spiders have occupied a home en masse, this will most likely mean that there are a lot of insects in the house.
We will introduce you to the most common spiders in Ukraine and show you what they look like. We will also indicate the dimensions of their body (excluding the length of the limbs).
House spider (Tegenaria domestica)
This is one of the most common spiders. It belongs to the funnel family and loves to live near people. At the same time, tegenaria fulfills the mission of a home orderly: it destroys bedbugs, cockroaches and moths.
The length of the yellowish-brown body of the spider, decorated with a brown pattern, is 6-12 mm. Female house spiders are much larger than males.
Photo: Pinterest
Typically, tegenaria hides in inaccessible places, and comes out in exceptional cases. For refreshment, for example.
Careless spiders
Representatives of this group cannot bite through the skin of a person, because they are too weak to tear off in order to inflict harm. The following can be considered as follows:
- ptachoids;
- crosses;
- haymaker;
- brownie;
- horses.
Most spiders are not human. The stinks live in nature and there is only one thing they want: that no one touches them.
Birds
The biggest spiders. The champion of the middle of them is the goliath spider: the bird, the body of which reaches 10 days. The reach of the goliath's paws is 28 divas. Cover the body with dark-brown thick bristles. For humans, the bird is not safe, but falling stubble can cause an allergic reaction.
Khrestoviki
Krestoviki are large spiders with very large tricute-shaped petals. On the back there are characteristic little ones with a visible cross, giving the name to all kinds of cross spiders. A mixture of gardens, forests, parks and other green spaces. There is a passive waterfall on the clods, weavers in circles. The chrestovik itself robs itself of the butts from the burnt leaves.
Bite safely. A child feels it like a light pinch. Ale turn the baby out and grind the spider with your hands into the snake.
Kosariki
Mowers have no longer become domestic spiders, but “domestic” spiders, and they are not afraid to kill people’s lives. For people, the stench is absolutely harmless and cannot be pinched. The mowers are similar to the mower bug, but they have a drawn-out body, divided into two parts. The bug has a rounder body.
Budinkovy
Follow the family of funnel spiders. Expansion everywhere. Often live in people's homes. The female budinka spider is 7-12 mm in size, the male is 6-9 mm. Zabarvlennya storm. Weave funnel-like borders. Not aggressive to people, but if you stick your finger in the back of your mouth, you can taste it. There will be no residue from the bite.
Skakuni
Jumping spiders are one of the great families. Wider everywhere except Greenland. Spiders of this family create haircuts and actively water during the daytime. Horses have a well-developed hydraulic system, which allows them to change the pressure in the blood and expand the ends. This constant stench can be caused by haircuts that often outweigh their moisture content.
Peacock spider
The original endemic to Australia from the family of horses. Dribny spider is already brightly rozfarbuvannya. The name spider-pavich was taken away from the external copy of this bird: a bright male and a modest female. While keeping an eye on the female, the spider “spreads its tail.” Vin straightens the side scutes of the grass and raises his hind legs from the fire. When the female spiders are absent, they wrap their scutes around the cauliflower.
Tramp
Wool spiders have lost their livelihood because they can’t weave a line and conduct a weed, attacking their prey from ambush. The eyes and methods of watering are similar to those of wolf spiders. The female vikorista webs to weave a cocoon in which to live the eggs. The female pulls the cocoon with her on her back.
Myslyvets bordered
Refers to the family of sparassids - spider spiders. The body can reach 2 div. Variations of fermentation from yellow-brown to dark brown. There was white dark brown on the sides of the body. Expansion in a peaceful climate in the territory of Eurasia. The pond lingers on the banks. A noticeable feature of the product is its ability to move through water and cause water at different times of need. Another name for mislivtsa is fishing, so you can catch a spider and kill a small fish. You can't help the people.
Green spider
It is impossible to determine the destruction of this arthropod, since in nature the “green spider” does not exist. Such is the confusion of various creatures from various canopies:
- jumping spiders;
- mysly spiders;
- spiders-risi.
To see how dangerous the bite of a green spider is, you will soon have to figure out which family of spiders is due.
Crab spider
It’s also easy to understand how we can talk about the crab pavuka itself. Arthropods come from three families:
- Neocribellatae;
- Thomisidae (side-walking spiders);
- Philodromidae (isopods).
Sidewalker (Thomisidae)
Due to the characteristic manner of moving sideways, these spiders are also called crab spiders. They are one of those species that do not weave a web to catch prey, but attack it suddenly.
Photo: Pinterest
These harmless spiders are found on flowers, where they usually lie in wait for their prey. That’s why they have the appropriate color – camouflage. Experts say that these arthropods are capable of changing it and merging with the environment.
The size of side walkers usually does not exceed one centimeter.
Families
In Russia the following families of arthropods are represented:
- wolves;
- hunters;
- funnel;
- horses;
- cibeids;
- diggers;
- black widows;
- steatodes;
- side walkers;
- knitting spiders;
- orb weavers.
These are not all species of spiders living in Russia, but a significant part of them. Most arthropods are able to live in any conditions. Photos and names of cosmopolitan spiders can be found in the description of the fauna of any of the regions of Russia. Some prefer a dry, hot climate and live in the southern part with an abundance of steppes. Others need water or damp places; such arthropods are usually found in the central part, where there are many forests with lakes and swamps.
Harvester (Pholcidae)
But the length of the harvest spider, which is also called the centipede or window spider, is about 50 mm, but with limbs: it is impossible not to notice and appreciate them. The centipede usually has 6-8 legs, with which the spider moves masterfully.
Photo: Pinterest
Unlike the previous species, the haymaker is a great master of weaving webs. Having caught the victim, the centipede paralyzes it with a special substance.
Reproduction and life cycle
All representatives reproduce by laying eggs. Males do not have a penis. They have to drain the seminal fluid into a reservoir made from the web. They pick it up with the pedipalps. How spiders reproduce:
- Marriage games. If the behavior of the male does not correspond to the species, then the female may mistake the suitor for prey and eat it.
- The male transfers the seed from the abdominal cavity.
- Attached to the female with the help of growths on the limbs.
- Inserts the pedipalp into the female's genital opening and fertilizes. Spider sperm are packed in sacs.
- The seed capsules end up in a sperm storage container.
- From there, the fallopian tubes lead to the ovaries, which can be paired or unpaired.
- The eggs grow on the surface of the ovaries.
- The ripened ones move inside them.
- From there they go out through the oviducts.
- The female wraps them in a web, hides them or carries them with her everywhere.
- The eggs hatch into completely unformed individuals. At this stage they are called nymphs.
- Newborns grow and molt up to 3 times.
Many species of spiders care for their young. A South Russian tarantula takes eggs out of a burrow and warms them in the sun. After hatching, it loses interest in children.
Wolf spiders do not abandon their brood even after birth. Small arthropods climb onto their mother. They live under her protection until they get stronger. And the offspring of Coelotes terrestris do not leave their parents for a whole month. There are also cuckoo spiders that drop their eggs into other people's nests.
The life of spiders is very dependent on the weather. They are accustomed to performing important tasks on the same days every year (mating, laying eggs, settling the young). But if they foresee worsening weather, they change plans. They can even hang their web at a different angle, sensing the approach of a hurricane or thunderstorm. Nature has endowed spiders with an amazing sense of smell. These creatures can anticipate bad weather 7-8 hours in advance.
Horse (Salticidae)
This is another attacking spider. Weaving webs is not his strong point. In its arsenal there is a sticky thread, with the help of which the spider quickly jumps onto the back of the insect. Having dealt with the victim, the horse returns to its original position.
This unusual spider, reaching 6 mm in length, can also turn its head. This helps him grab passing prey on the fly.
Photo: Pinterest
Arachnologists testify that the jumping spider distinguishes ultraviolet light using special “sensors” on its body.
What to do if you are bitten
First of all, you need to remain calm and call a doctor. It is advisable to catch the spider and place it in a durable container. This will help the specialist determine the type and degree of poisonousness of the spider. Then you need to try to prevent the poison from spreading throughout the body. Ice is applied to the bite site, and the bitten limb is raised higher. The wound needs to be treated with an antiseptic.
Further treatment depends on the severity of the bite. If no blister appears after eight hours of the bite, there is no severe pain and there are no signs of tissue necrosis, then serious treatment may not be required. If severe symptoms develop, corticosteroids are sometimes recommended. Dalsone, heparin, nitroglycerin and other drugs are also used. If severe necrosis develops, necrotic tissue must be removed surgically, and if a secondary infection develops, it must be treated. The ulcer usually heals on its own, but sometimes skin grafts are necessary. If systemic intoxication has developed, patients are hospitalized.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=wjEnV1UeGD8
In the habitat of recluse spiders, in order to avoid being bitten, it is recommended to be careful with boxes, carefully inspect clothing and shoes, wear gloves when working with firewood, and also seal cracks through which spiders can crawl into the home.
Cross (Araneus)
A very common type of harmless spider. They are easily recognized by the cross-shaped pattern on the abdomen formed by yellow spots.
These spiders are relatively large. The size of females is about 25 mm, males are 10 mm.
What is special about the crosses, besides the painted abdomen? First, they weave huge webs. They themselves usually settle in the center of the web or on the edge.
Photo: Pinterest
Secondly, these spiders are very big gluttons. They try to catch as much prey as possible in their large nets. And sometimes they eat up to 8 insects at a time. Crossies can even catch a massive bumblebee for dinner.
Thirdly, these are still clean people. They skillfully clear their web of everything unnecessary.
Non-hazardous varieties
According to the biological classification, spiders belong to insectivorous arthropods. Their diet consists of what falls into the carefully woven web they prepare. They can sit in ambush for hours, waiting for a fly, mosquito or bee to fall into the trap. Such spiders can be seen in an apartment, in a garden plot, and in a forest or meadow.
Important!
Many people, out of fear of spiders, try to kill them quickly, not realizing that they maintain a kind of balance in the natural environment, actively destroying harmful insects.
Below are photos with names, descriptions of the appearance and diet of existing arthropod species.
House spider
The most common type of spider in Ukraine, living near people, according to the classification, belongs to the Voronkov family. House spiders are distributed throughout the world. The size of an adult can reach up to 1.2 cm, females are usually larger than males. Body color is yellow-brown with a pattern.
The house spider prefers to settle in residential and utility rooms in the house or in outbuildings. Its main diet consists of cockroaches, moths, flies, bedbugs and other domestic insects. In nature, this species lives in grass, fallen leaves, and deep in cracks in the bark of trees.
Interesting!
According to popular belief, an arachnid inhabitant of the house can bring financial well-being. However, according to scientists, the appearance of a large number of spiders in the house signals excessive reproduction of insects.
House spider and common spider
Common cross
The name of the spider comes from its coloring - there are yellow spots on the abdomen that merge into the shape of a cross. In total, there are 1 thousand types of crosses, the most common of them is the common one. The size of females reaches 2.5 cm, males - 1 cm.
Interesting!
Biologists consider them to be the greatest specialists in weaving webs - they are able to weave a trapping net with a diameter of up to 1 m. Then the spider sits in the middle or on the edge of the web and waits for prey. Its gluttony is 7-8 insects per hunt.
Jumping spider
This species of arthropod prefers not to weave, but lies in wait for its prey in secluded places. When she appears, the jumping spider makes an instant jump onto the back of the victim. In order to then return to its original place, it attaches itself with a sticky thread.
Females and males of the jumping spider are the same in size - up to 6 mm. They also have an original feature of their physique, which allows them to turn their heads upward. This helps them successfully catch insects flying overhead. According to biologists, they are also able to distinguish ultraviolet light, thanks to special marks on the body.
Sidewalk spider
Another species that prefers to wait for prey to appear is the flower sidewalk spider. Its size is only 1 cm. But it has a varied body color and is able to change it depending on the situation: from white to yellow or brown (if it lives among trees). Thanks to this ability, sidewalkers are almost invisible in nature.
Interesting!
They walk sideways, like crabs, which is why they got their name.
Spiders of Ukraine
Harvesting spider
Its other names are centipede and window spider. It differs from other species in having very long thin legs that extend directly from the round abdomen. Their number can be 6-8 pieces, length – up to 5 cm.
To catch prey, harvesters weave a web; after an insect gets there, the spider quickly injects a paralyzing poisonous substance into it.
On a note!
Centipedes love to settle near people, mainly in window frames and darkened corners, hanging upside down in them.
Black widow (Latrodectus mactans)
The name of the species speaks for itself. Typically, spiders eat their partners after intercourse.
The black widow is one of the Ukrainian spiders that lives in the ground. They also hide in cracks and hollows. But they can feel quite comfortable settling in a person’s house.
Reaching 20 mm in length, these arthropods are inconspicuous. They are painted black with glitter. There is a pinkish or reddish hourglass-shaped spot on the back.
The venom of this spider, according to experts, is 15 times more powerful than the venom of a rattlesnake. You should especially be wary of the female black widow during the mating season, when she is most active. Males of the species are less poisonous.
Photo: Pinterest
As a result of the bite, death can even occur, especially if the black widow injected a lot of poison and if the person’s immunity is weakened.
The consequences of a bite have numerous manifestations. These include, but are not limited to, dizziness, diarrhea, shortness of breath, vomiting, nausea, stomach pain, etc.
Features of peacock behavior
Of interest is a male with a bright color. Variegated colors are needed to attract females. The cavalier raises his abdomen and hind limbs and begins to move from side to side, as if performing a ritual dance. Outwardly, all this resembles the movement of a peacock, hence the name. The rest of its life, the spider lowers its legs and folds its “tail.”
After fertilization, it forms a cocoon and breaks off eggs. After a few weeks, a young generation of peacocks appears, which almost immediately begins to live independently. They molt several times, constantly increasing in size. At the last stage, the genital organs are formed. The maximum lifespan of a female is 12 months.
Karakurt (Latrodectus tredecimguttatus)
Here's another truly dangerous spider. Karakurt bites are fatal in four percent of cases. Its venom is 50 times (!) more powerful than that of a tarantula.
The cunning of karakurts also lies in the fact that these spiders are relatively small. The body of females reaches a length of 20 mm, males - 7 mm. Karakurts have a black color. Young spiders have a reddish spot on their abdomen.
Photo: Pinterest
Karakurts live in the south of the country. And if the summer turns out to be particularly hot, they move to more northern regions.
As a result of the bite, convulsions, suffocation, and heart attacks occur.
Harmless
The following families are very common in Belarus: funnelbirds, hunters, sidewalkers and horses. Besides them, you can find 4 species of wolf spiders there. Apart from family and protective coloration, these night hunters have nothing in common with the South Russian tarantula, which is also a wolf spider.
Funnel
Funnelfish live in moist, shaded places, on the forest floor, under snags and at the foot of bushes. They often settle in village houses. People gravitate toward human habitation:
- funeral;
- brownies;
- attics.
Hunters
They live on the banks of reservoirs, of which there are plenty in Belarus. There are only 3 pisaurid spiders found in the country. Spiders hunt with their hind legs on coastal vegetation and their front legs on the water surface. These hunting spiders can glide across the surface of a body of water like water striders.
Tarantula (Lycosa)
Tarantula is the largest spider in Ukraine. Of course, it is nowhere near as huge as the largest spider in the world, the blond teraphosa. The size of this giant, including its limbs, can reach 28 cm.
The body of the tarantula grows to only 35 mm, and together with the legs it reaches 70 mm. It is difficult to confuse it with any other species. The body and limbs of the tarantula are covered with thick brown hair. The abdomen is painted black.
Photo: Pinterest
These dangerous spiders live in forest-steppes, steppes and deserts in the southern part of the country. The most common is the so-called South Russian tarantula, popularly known as Mizgir. He has 8 eyes, each of which sees 360 degrees.
Tarantulas usually live in burrows that they have dug for themselves. The depth can reach half a meter or more. The hunting time of this arthropod is night.
Despite its notoriety, the tarantula does not attack humans. And it bites only in rare cases, when it defends itself, sensing danger.
As a result, the bitten person’s temperature may rise, soft tissue inflammation and an allergic reaction may occur. The skin turns yellow and remains that way for several months.
Reproduction and lifespan
Karakurts are highly fertile. In one year, the female lays at least 1000 eggs. Periodically, there is a surge in birth rates, when females increase the eggs in their clutch by almost one and a half times during the season. Peaks of mass reproduction of spiders occur every ten, twelve or twenty-five years. Species populations increase their numbers sharply.
The mating season of arthropods occurs in mid-summer, with the arrival of heat. At this time, the active movement of karakurts begins in search of secluded places for weaving mating nets. Males scent the web with pheromones to attract a female. Such a web serves temporarily, only for mating spiders, and is woven in corners protected from heat.
Black widows, following natural instincts, eat males after mating and look for a new place to lay eggs. The den is often set up among uneven soil, in various depressions, abandoned burrows of rodents. Karakurt females also crawl into ventilation systems, from where they then enter people’s homes.
At the entrance to the equipped lair, the spider stretches a network of chaotically intertwined threads. She lays eggs inside and hangs 2-4 cocoons with eggs from the web. Nearby there is a horizontal hunting web of an asymmetrical structure. Snare catchers differ from other arthropods in the absence of concentric circles.
The spiderlings quickly, after 10-15 days, depending on weather conditions, are born, but remain in a warm cocoon and do not leave the shelter. The cocoon woven by the female will allow them to escape the cold and survive the winter months. Karakurt cubs first feed on natural reserves, which are placed in their bodies at birth, then, in order to survive until next spring, they switch to cannibalism.
Subsequently, through natural selection, not all of the strongest individuals are selected, only the spiders that survive the test. In autumn, gusts of wind tear the cocoons from the web and spread across the steppe and desert. Nature itself helps to expand the habitat of spiders, sending them on a journey.
Not all females can survive the winter; spiders often die after briefly surviving the eaten males. The lifespan of karakurts, therefore, is approximately a year. But in warm climates, the lifespan increases significantly. With successful winterings, spiders live up to 5 years.
But even in regions with cold winters, high fertility and rapid development of offspring make it possible to maintain a stable population size, and sometimes increase it. Spring warming, around mid-April, encourages the hatchlings to leave their cocoons.
Karakurts are very prolific, they multiply by the thousands in a year.
The winds carry the spiders with the remains of their webs around the area. The young have to go through stages of development and get stronger. Only by mid-June will the new generation become sexually mature, capable of further reproduction, if the life of the spiderlings is not interrupted by herds of sheep and pigs that simply trample them.
The development of a spider goes through several stages. The chitin shell does not allow growth until the next molt occurs and a new larger cover is formed. Males live seven molts, females – nine.
For centuries, karakurt has been successfully fighting for survival and adapting to new places. The ability to distinguish a poisonous inhabitant from its relatives allows a person to peacefully part with it, without harm to both parties.
Argiope
This species is also called the zebra spider or wasp spider because of its bright yellow and black stripes.
Females grow up to 15 mm, males - 7 mm. Their peculiarity is an unusual way of weaving webs: in zigzags.
Photo: Pinterest
An argiope bite causes inflammation. But death is ruled out. Therefore, the zebra spider is classified as a less dangerous species.
It is interesting that previously Argiope could be found mainly in the Black Sea region. They lived in the Kherson and Zaporozhye regions, as well as in the Crimea. But as global warming progressed, these spiders migrated to more northern regions of Ukraine. They even began to be called indicators of climate change.
Main characteristics of arthropods
Arachnids are classified into the phylum Arthropods based on the following characteristics:
- the presence of articulated limbs;
- chitinous outer shell;
- the body is divided into sections.
Arachnids have 6 pairs of limbs:
- 1 pair – chelicerae, which have claws or claws at the ends to capture prey;
- 2 pairs – claws, serve as organs of smell and touch;
- 3-6 pairs – walking legs.
Arachnids lack antennae and antennules; they are replaced by chelicerae and pedipalps (legs). Poisonous glands open on the chelicerae, which serve to protect and hunt prey.
In addition to chitin, the outer shell also contains a wax-like substance that protects the body from the evaporation of excess moisture, thereby maintaining the amount of water in the body.
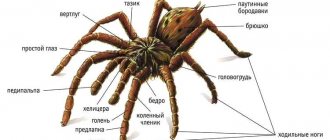
Arachnids have two body parts: the cephalothorax and abdomen. The limbs are attached only to the cephalothorax; on the abdomen they are modified into other organs (arachnoid warts, genital operculum, tactile organs or respiratory organs).
Fig.1. External structure of the spider
Internal Budova
There is no full-fledged circulatory system. Blood also. It is replaced by lymph. There are 3-4 little girls in the heart, which are called ostia. Through the ostia, lymph from the body of the creature enters the heart, and through the arteries of the heart the lymph flows out to the space between the internal organs. From the interstice, the lymph enters the pericardial lobe of the body and turns again in the heart. Lymph contains a mechanism that provides additional acidity to the spider.
Budova pavuka
The dichotomy system has a unique appearance. Legene bags contain plates that look like books. Open the doors wildly, open the lungs, covered with dry crusts. There are also long tracheal tubes that transport acid from the openings to the organs of the spider body.
Being a hijak, the spider has a good effect on the central nervous system and has a significant impact on the brain. In the cephalothorax of the arthropod there are 2 nerve nodes, from which the nerves diverge and lead to the organs of the spider. These are the knots and the brains of the creature.
Tsikavo!
The area of the brain takes up 20-30% of the total area of the cephalothorax.
Goliath tarantula
The impressive size of the spider determined its formidable and powerful name. The Goliath tarantula is rightfully the largest spider in the world.
Thirty-centimeter legs and a massive furry body will impress even the bravest daredevils.
The largest spider in the world chose the green thickets of the tropical forests of the South American continent as its habitat. Ambushing its prey, the spider plunges its sharp fangs deep into it.
The spider's diet includes insects, amphibians, and certain types of snakes, but it does not eat birds, although it bears that specific name.
Below you can watch an amazing video of this beautiful and huge spider.
Funny classification
Among lovers of great bird spiders, we have divided the candidates into categories based on their outstanding characteristics:
- For the cobs. There are a lot of spiders that we like to demonstrate on video. These arthropods sit calmly on the ground, and when they get wet, they move around completely.
- For those who have slipped through. If the spider of this group is about to leak, then the ruler can only tell you directly where the creature is located.
- For professionals. The loss of the spider is noted for its presence in the place where it was sitting quietly. Where you go is known only to the arthropod itself.
Spiders
The rest of the group suggests that not all breeds of spiders are yet to die. It’s easy to catch a sweet spider, because you don’t suspect that it’s here.
Non-dangerous and poisonous species of spiders in Ukraine: what to expect from an encounter with arthropods?
Spiders in Ukraine are very diverse. Some of them prefer to live in human homes, while others hide from prying eyes among plants or under fallen leaves. Some species are safe for people, annoying only with cobwebs in the corners of the house and causing unpleasant emotions in impressionable people, while others are poisonous, and it is better to avoid them. So what is it like – the world of Ukrainian arthropods?
Popular message topics
- Indoor rose
The rose can rightfully be called the most beautiful and beloved flower of man. Indeed, there is no more delightful and elegant plant on our planet. A flower belonging to the rosehip genus of the rose family, - Tree (Elm)
Elm belongs to the trees of the Elm family. Asia is considered the birthplace of the tree. From where it spread to Siberia and the Volga region, to the Urals and the Caucasus, and to some European countries. Found in mixed forests, - Drum - a musical instrument
A drum is a kind of musical instrument belonging to the percussion class. Today, the sound of drums is widely used in music of various genres. Entire drum kits were even created to accompany rock music.
General information
According to geographic zoning, Ukraine is located in the Palearctic region, where the European and Mediterranean subregions are distinguished. The first subregion, at the same time, covers almost the entire territory of the country, while the second (Mediterranean) locally affects only small river valley, reservoir and coastal areas.
European subregion
Forest cat
The European subregion includes the following zoogeographical provinces, each of them has its own faunal complex:
- Mixed forests are the habitat of such animals as: common viper, lizard, crested newt, grass snake, wood grouse, hazel grouse, black stork, snipe, wood sandpiper, woodcock, woodpecker, thrush, tit, hawk, vole, gray mole, beaver, hare , common and small shrews, wild boar, otter, red deer, wolf, forest cat.
- Forest-steppe areas are the habitat of roe deer, red deer, tree snake, steppe viper, crested newt, speckled ground squirrel, gray partridge, hawk, fox, woodlark, badger, marten, wild boar, two-colored bat, great horseshoe bat, crucian carp, pike , bream, catfish.
- Common in the steppes: green frog, water snake, steppe viper, yellow-bellied snake, lark, steppe eagle, steppe crane, gray partridge, ground hare, small gopher, rat, small mole rat, nutria, gray ermine, hamster, vole, European marmot, mouflon, doe.
- In the Carpathians you can find rarer species: Alpine and Carpathian newts, spotted salamander, black woodpecker, golden eagle, squirrel, wild boar, otter, red deer, wolf, lynx, forest cat, fox, brown bear, bison. The Crimean mountains are home to the rock lizard, leopard snake, sea gull, rock pigeon, southern nightingale, black vulture, red deer, mouflon and other species.
Mediterranean subregion
Extrazonal valley-river, reservoir and coastal areas belong to the Mediterranean subregion very conditionally - they are dominated not by the Mediterranean climate, but by the natural conditions of the steppe and forest-steppe, somewhat transformed by the presence of watercourses and reservoirs created on them. This category includes the coastal areas of the Dnieper, Dniester and other reservoirs, the Dnieper-Bug, Danube, and Dniester floodplains. A characteristic feature of the fauna of these territories is their close connection with water bodies, forming a rich and diverse fauna, consisting of fish resources, waterfowl and other representatives of wetland fauna.