05.01.2016
Predatory mites are arachnids whose endurance and longevity are unique among arthropods. A predatory lifestyle, which involves a constant hunt for fresh blood, has developed in them the ability to withstand hunger and remain active at the same time. We will tell you in this article how long ticks live and how this depends on their living conditions.
- Maximum lifespan by species
- Life expectancy by location
- Life expectancy by diet type
Main types of ticks
- Argaceae. They settle in homes, attack domestic animals, and in some cases humans. It is difficult to remove due to the lack of a hard cover and the head recessed inside the body.
- Subcutaneous.
A very small mite that lives on the body of humans and animals for many years and feeds on dead skin cells. Lives in hair follicles and on the face. Subcutaneous mite - Itchy. It eats through channels in the skin that are invisible to the eye, causing severe itching and redness.
- Forest ticks (European and taiga ticks). They attack directly on humans or spread from dogs. They inhabit the entire territory of Russia, often found in cities, dachas, and private plots. The taiga tick, like the European tick, transmits the most dangerous diseases, including encephalitis and others fatal to humans. What a tick looks like - photo is provided.
- Pasture. It lives in the southern regions and carries encephalitis, plague, brucellosis, and fever. These are Ixodidae and Gamasaceae.
- Armored. They feed on vegetation, mushrooms and their remains, and carrion. They carry helminths (worms).
- Ear. It feeds on the earwax of pets. Such ticks do not attack humans, but cause suffering to animals.
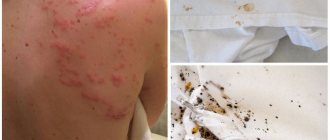
- Dust (bed, linen).
Lives in pillows, mattresses, carpets, etc. It feeds on dead skin particles, dust, down or feathers. Causes asthma in humans. There are dust mites in every home (interesting facts!), and up to 6,000,000 individuals can live in the average bed. In reasonable quantities they do not have a negative effect. Dust mites - Cobwebby.
Herbivorous spider, feeds on plant juices. You can detect mites on indoor plants from the inside of the leaf. Causes plant death. Spider mite - Predatory. Feeds on his classmates. Sometimes used to combat.
- Granary (flour, bread). Causes rot and mold in granaries, warehouses or home closets.
The most dangerous types of insect mites
The main danger of ticks is that they harm human health. Ticks are ectoparasites and causative agents of natural focal diseases. Pests are capable of transmitting various pathogens through the process of sucking blood.
Diseases
The most common diseases carried by ticks are borreliosis, ehrlichiosis and encephalitis. Infections are severe and can cause disability. As a rule, the diseases are chronic in nature and have a long rehabilitation period of up to a year. In addition to the diseases listed above, ticks carry:
- spotted fever;
- tularemia;
- babesiosis;
- tick-borne typhus
The variety of linen mites is not a blood-sucking pest, but these insects are also dangerous to humans. Microscopic excrement of insects along with dust penetrates the lungs and provokes the development of allergic reactions. In combination with a cold, allergies can cause bronchial asthma.
Allergy symptoms
The manifestation of disease symptoms depends on the pathogen that enters the human body after an insect bite. Since pests carry a large number of diseases, each of them is characterized by individual symptoms. In particular:
- Borreliosis is characterized by the appearance of migraines, general fatigue of the body, fever, attacks of nausea and vomiting. The most pronounced sign of the disease is a rash on the skin in the form of a ring-shaped redness.
- Tick-borne encephalitis causes a sharp increase in temperature to 39 degrees. Other symptoms include muscle soreness, vomiting and migraines.
- Ehrlichiosis is characterized by a sudden increase in body temperature and chills, joint pain, and a feeling of malaise. In severe cases, a skin rash appears.
- Symptoms of tick-borne relapsing fever develop gradually over a couple of weeks. Primary signs are insomnia, lack of appetite and feeling weak. Subsequently, the temperature rises, pain in muscles and joints occurs, and a severe rash forms on the skin.
Ixodid ticks are very numerous (almost 1000 species), but two species pose a real danger to humans: the taiga tick and the dog tick. The taiga tick (Ixsodes persulcatus) lives in Russia and some European countries. The dog tick (Ixsodes ricinus) is common in Europe. The dog mite is moisture-loving; its eggs can develop in an aquatic environment. Both of these species often attack humans. Adults are most active in spring; activity decreases in mid-summer. Larvae and nymphs suck blood in summer.
The body structure of both species is similar, it has 4 pairs of limbs and is protected by a shell. The oval body, 1-10 mm long, tapers towards the head and is conventionally divided into a gnathosoma (proboscis or mouthparts) and an idiosoma (abdomen). When saturated with blood, the tick acquires a spherical or ovoid shape.
The main bloodsuckers are females; the peculiarities of their physique and the ability to greatly increase in size allow them to be saturated with incredibly large volumes of blood compared to their body size. Males are smaller in size and are not able to attach for a long time. The color of a hungry parasite is yellow, brown, black.
The digestive system of the parasite consists of: the mouth opening at the tip of the proboscis, salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, intestines and anus.
Ticks can pose a threat to humans only in one case - when they are carriers of diseases. Through a tick bite you can become infected with the following diseases: encephalitis, typhus, hemorrhagic and Q fever, scabies, ehrlichiosis. The names of these diseases alone are terrifying, not to mention the consequences. How long do ticks that carry such diseases live?
Ticks can confidently be called the laziest arachnids: they travel several tens of meters in their entire life. Moreover, an interesting fact: the female needs more blood and time to saturate. A couple of days are enough for the male to replenish his reserves and go to digest the incoming food.
How long can a tick live in an apartment?
- Temperature regime.
- Indoor air humidity.
- Sexual maturity of an individual.
- The amount of vegetation in the house (as many types of mites feed on plants).
- How often is cleaning and ventilation carried out?
How can you tell if there are ticks in your apartment?
the appearance of bites on the body (concentrate on the skin: if there is a dried bloody dot, then this is probably a tick bite); multiple black spots on sleeping objects, appliances and furniture (people often confuse these with dirt, but this could be mite droppings).
You can also use a magnifying glass and a flashlight to determine the presence or absence of ticks in the house. It is necessary to lay out the bed, turn off the lights and examine the room with these objects.
Ways to combat ticks in an apartment
You need to know that it is impossible to completely get rid of ticks, but you can prevent their reproduction.
To do this, you need to do the following:
Do wet cleaning of the apartment regularly using a 20% saline solution, paying special attention to furniture. Maintain air humidity within 40 percent, as this will create unfavorable conditions for ticks to live.
Maintain air humidity within 40 percent, as this will create unfavorable conditions for ticks to live.
Down and feather pillows should be replaced with padding polyester.
Floors should be washed with water containing a small amount of salt to disinfect the room.
Ventilate the room regularly (in addition, you can use air ozonizers).
Vacuum cleaners, air purifiers and air conditioners will also help in the fight against ticks.
If you don’t know how to get rid of ticks in an apartment, you don’t need to panic and think that this is a hopeless situation. It is enough to adhere to the above rules, thereby you will protect yourself and your loved ones from the harmful inhabitants of your home.
The 2022 tick season began right on time, and the first victims went to emergency rooms in April. The first ticks wake up and attach themselves to a person usually in mid-April; last year, the first cases of bites were recorded in March, and these are not isolated cases, but the full beginning of the tick season. How is the situation now, in March? Have ticks come out of hibernation or not yet? Let's look at the main periods of activity and ways to protect against them.
How can you tell if a tick has bitten you?
The moment of ixodid tick suction often goes unnoticed because it is painless. After some time, the affected area swells, turns red, and itching and pain begin. Symptoms may persist for several days. The most attractive body parts for parasites, in descending order:
- Ears and area behind the ears;
- Neck, armpits;
- Lower back and abdomen;
- Groin.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Ant and aphid type of relationship
The most characteristic appearance of an insect bite occurs when infected with Lyme disease: erythema in the form of a large spot up to 10-20 cm in diameter. Soon the edge of the spot becomes overgrown with a noticeable red outline, and its center turns white or blue. After a day, the erythema becomes crusty, and after 2 weeks, visible symptoms disappear. 1-2 hours after the parasite has been sucked in, the following sensations occur:
- Temperature increase;
- Weakness;
- Joint pain;
- Cardiopalmus;
- Itching;
- Enlarged lymph nodes, etc.
These signs are most pronounced in children and the elderly, those suffering from any diseases.
People who do not have pets or who rarely relax in nature will not immediately be able to identify the symptoms of a bite from a dangerous parasite, especially at home. You should know that even when the skin is pierced, there is no pain, since nature has endowed this type of arthropod with a powerful anesthetic contained in their saliva. You can find out that a small pest has attached itself to a person if you see it or by certain signs:
- Unexplained chills;
- Increased fatigue and drowsiness;
- Photophobia.
Ticks in the apartment: what to do? If the insect has already attached itself to the skin, you should urgently take all measures to remove it and treat the wound with an antiseptic. Under no circumstances should the parasite be thrown away, as it is subject to mandatory testing in the laboratory of the sanitary-epidemiological station in order to exclude the possibility of infection with encephalitis or Lyme disease. After primary medical care, you need to go to a clinic or any medical facility for a blood test.
DIY devices are available in the form of plates with a teardrop-shaped hole and spoons or hooks with a V-shaped slot. The embedded tick must be pryed as deep as possible under the head and carefully pulled out using twisting and rocking movements. All tools are small in size and can be used as key rings. Products available include Tick Twister and Trixie hooks, Ticked Off spoon, Pro-Tick and Tick Key plates.
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis
If you are planning a trip to a region exposed to a high risk of infection with tick-borne encephalitis, think in advance about protecting your body. Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis should begin in advance - in the fall. Immunity to encephalitis is developed after three vaccinations with an interval of 1 month. There is currently no preventive vaccine against borreliosis, only against encephalitis.
Will any bite from an infected tick give a person encephalitis or Lyme disease? No, not every bite from an infected tick will cause illness. It all depends on:
- time, how long the tick sucked blood;
- virus concentration in the tick body;
- characteristics of the microorganism;
- human immunity.
Think in advance about the safety of your family and pets, even before traveling to your dacha or to the forests of the Moscow region. Thus, you will save yourself and your loved ones from possible serious health problems. Have a nice holiday!
Useful article, thank you! 2I don’t like it, delete it!
Where do ticks live and where do they come from?
The habitat of ixodid ticks is quite diverse, which indicates a high degree of adaptability to various living conditions. Some species prefer forests and shrubs, others have adapted to the steppe zone, others live in mountainous areas, etc. There are even species that have chosen various buildings and premises as their habitat.
The pasture type is divided into 3 groups: those with one owner, two or three. Most of them lie in wait for the owner, being in the upper part of the grass. The duration of tick blood sucking at different stages of development is different: larvae suck blood from 3 to 5 days, nymphs from 3 to 8 days, adults (adults and the most voracious individuals) - from 6 to 12 days.
Ixodid ticks are the record holders for fertility among all types of arthropods, and are capable of laying several thousand eggs. The development cycle until reaching adulthood is 2-4 years for northern species, 1 year for southern species. Insects are able to withstand negative temperatures and go without feeding for a long time.
How do Ixodid ticks live?
In the warm season, another dangerous tick becomes active - the ixodid tick. It is dangerous due to the spread of deadly diseases - tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis. Lives in tall grass, on the lower branches of bushes. Found in the wild, among urban civilization.
If you find a tick at home or notice it on the balcony, it must be mercilessly destroyed. In the future, take care of protecting the premises. Treat the balcony with insecticidal repellents or a spray with essential oils. For 1 liter of water, 5 drops of geranium, lemongrass, eucalyptus, lavender or orange oil. Spraying with a home remedy should be repeated every 3 days during the parasite activity season.
If a tick has escaped at home, you need to vacuum the carpets, wash the floor, and carefully inspect the room using a magnifying glass. The arachnid can go without food for several months; the possibility of a bite if the parasite is not detected remains. It is recommended to treat the room with an insecticidal spray, leave it closed for 2 hours, ventilate, wash the floors and furniture with a soap-soda solution.
To replenish energy reserves, the ability to develop, reproduce, lay eggs, and simply live, we need the blood of animals and birds. A person becomes a temporary host, promotes further development, but significantly reduces potential. Therefore, humans are a potential victim for ixodid ticks, but not the main one.
Without blood, the pest can live longer than without water. Environmental humidity plays an important role in the development of larvae, nymphs, and the vital activity of adults.
- Parasites wake up very early, when the air temperature barely rises above 0 degrees Celsius.
- Activate activity at 10 degrees Celsius.
- A favorable temperature for them is no higher than 22 degrees Celsius. Therefore, dry summers and heat within 30 degrees Celsius kill them.
After the bite, the parasite continues to transform, lay eggs, and mate. For a tick, the lifespan depends on the conditions where it then ends up. While walking in nature, a person can pick up a parasite and bring it into his home. The pest sits on clothing for several minutes without moving, then begins to look for open areas of the body.
The parasite can also hide in a car during trips through the forest, on vacation, or with the windows not tightly open in the parking lot near the house. A pet can bring them into the apartment. In a situation where the tick falls off the dog on its own, there is a possibility of biting a person in the future. Parasites can be found on the bodies of cats, rodents, and birds. It is easier to detect through the fur when stroking. After suction, the parasite begins to inflate, forming a noticeable tubercle.
Life of a tick
The parasite sits on the human body for about 3 days, when it has had enough, it disappears. At home, the female will be able to lay eggs and live, but the larvae will not appear, since there are no favorable conditions. Without food in an apartment, an adult can live up to 8 months, but this is only if it is not detected.
We suggest you read: How to get rid of book mites
The tick sits on the human body without moving for about 30 minutes, then attaches itself to places where the skin is thinner - the back, shoulders, neck, armpits, arms. As food arrives, the tick swells within a few days to sizes ranging from a few millimeters to 3 cm. When a parasite bite is detected, a person does everything possible to remove the tick.
Colloquially called bed mites, they do not attack people and can cause allergic reactions. They are very small in size and invisible to the naked eye. They feed on the exfoliated remains of dead corneal skin. How long a tick lives in an apartment depends on how hygiene measures are followed, how and how often cleaning is done, and whether recommendations for the use of preventive measures are followed.
Bed mites are afraid of direct sunlight and low relative humidity. Clean air and timely cleaning contribute to a sharp decline in the population. In favorable conditions it lives for about four months. During their life, they produce a lot of excrement, their total amount being hundreds of times the weight of an adult.
As a rule, the skin of a new person is infected by females by laying eggs, but cases of infection have also been observed at other stages of development. In one day, the female can make up to 3 mm of movement in her body and lays up to four eggs per day. The larvae appear on the third day; after several molts and metamorphoses, the tick turns into an adult in 2–3 weeks.
Lifespan without food
Interestingly, without the blood of the victim, ticks live much longer. This is due to a slowdown in development. The process of complete transformation stretches up to 8 years. How long can a tick live without bleeding?
In the absence of food, ticks fall into a special state that allows them to save energy and metabolic processes slow down. The tick does not live, but exists. In this state, it is able to withstand unfavorable climatic conditions and winter. A tick lives without blood for 10 years. All this time he is waiting for a victim. Once on her body, it begins to actively feed. The blood brings her back to life. The development process begins.
It is difficult to say definitively how long a tick can live. Because everything depends on a lucky chance. It is interesting that with such a probabilistic approach, ticks should have disappeared as a species long ago. But no, they continue to torture animals and infect people with dangerous diseases. And every year their number does not become smaller.
Ticks are rather small arachnids, the size of which sometimes does not exceed 0.5 mm. They have 8 legs and a fused head and chest. That's where we'll talk today.
How do ticks live?
In the forest, for example, a tick climbs a blade of grass or a twig to a height of no more than half a meter and waits to cling to the body of an animal, person or bird. And having seized such a moment, it takes a long time to choose a suitable place for feeding. Having eaten, the female returns to the forest floor and begins laying eggs. From this moment until the appearance of an adult, several stages pass, lasting from three to five years. And during all this time, the tick drinks blood only a few times.
How long does a tick live after a bite?
The chitinous shell that covers the entire body of the arachnid stretches on the abdomen, so the female, for example, can drink quite a lot of blood, as a result of this turning into a large “bean”.
It will take the female almost a week to eat. And then you can fall off to digest the blood and take care of the offspring. Males also do not disdain blood. They need it to support the body until mating. True, they drink much less of it and are full within an hour. And then both of them will need blood only for the next process of procreation.
How long does a tick live without food?
The presence of food leads to amazing transformations of this insect. Thus, argasid mites, which live in dry and warm places and do not pose any threat to humans, have a length of no more than 13 mm without food. But after lunch, these crumbs increase hundreds of times!
The most dangerous ticks for humans are ornithodor ticks, which live in the steppe, desert and semi-desert zones. They can go without food for 10 years, but at the first opportunity they infect the bitten person with serious diseases.
So how long does a tick live?
There are more than 48,000 different ones on Earth. Among them are those that cause diseases, for example, encephalitis or hemorrhagic fever, and those that feed exclusively on plant sap. Its duration depends on their way of life.
A tick bite is not necessarily dangerous. Many of us don't even realize we've been bitten. But it is necessary to remember that there are dangerous individuals in nature.
After all, there are scabies mites and domestic dust mites that feed only on dry flakes of human skin, but at the same time can cause severe allergies.
Regardless of how long a tick lives, we still need to clearly know that attentiveness, cleanliness and composure can help us avoid contact with this insect. When coming home from the forest or returning from the dacha, be sure to examine yourself. If you find a tick on your body, seek medical help. Good luck to you!
05.01.2016
Predatory mites are arachnids whose endurance and longevity are unique among arthropods.
A predatory lifestyle, which involves a constant hunt for fresh blood, has developed in them the ability to withstand hunger and remain active at the same time. We will tell you in this article how long ticks live and how this depends on their living conditions.
Control and prevention measures
Ticks cannot be called too mobile, because on their own they travel less than ten meters during their entire existence. And the life activity, despite the size of the tick, lasts a relatively long time. At least for two or three out of a thousand. The life path of these insects is not particularly diverse and depends on a huge number of accidents and coincidences.
There are more than 48,000 species of ticks in the world. They live on all continents, in a wide variety of weather conditions. And although most of these arachnids do not pose a danger to humans: limiting their diet to soil fungi, plant debris or arthropods, which are larger in size, these insects still have a bad reputation, thanks to some of their relatives, which will be discussed further.
Damage caused by ticks
The main danger of ticks for us lies in their ability to transmit pathogens of dangerous diseases. Diseases such as tick-borne encephalitis, tularemia, tick-borne typhus, hemorrhagic fever, ehrlichiosis, Lyme disease, relapsing tick-borne typhus, Q fever - are frightening by their very name.
Also, these arthropods are capable of making human life unbearable on their own. Some types, such as spider mites, cause damage to house plants and crops. A considerable number of ticks infect pets, causing a lot of trouble for animals and their owners.
Types of ticks
Encephalitis tick, perhaps, occupies the first position in the number of mentions. Many people who have been bitten by ticks wonder what an encephalitis tick looks like, because no one wants to joke with an infection, the complications of which often lead to death. However, encephalitis ticks are not a separate species - all types of ticks infected with encephalitis can be called this. And it is impossible to determine by appearance whether a tick is a carrier of infection or not.
Ixodid ticks
- also called hard ticks, for their hard chitinous cover, are the main carriers of encephalitis, and they are most often encephalitic, and more specifically, they are related to ixodids, taiga and dog ticks. To prevent infection, it is necessary, first of all, to know where ticks live, which could carry dangerous diseases, and try to avoid staying in such places.
The ixodid tick loves moisture, so it is more often found in moderately shaded, moist mixed and deciduous forests, for which it is also called the forest tick. At the bottom of a forest ravine, along a forest stream, at a forest edge, as well as along forest paths overgrown with grass, you will probably find more than a dozen ticks.
The ixodid tick is distinguished by its considerable size - up to 25 mm and spends most of its existence among greenery or on the ground. At all stages of life, ticks need to feed on the host’s blood at least once in order to move on to the next stage. Fertilization usually occurs on the body of the host before blood sucking.
Several females are fertilized by one male, who soon dies. Up to a week and a half after fertilization, the female feeds intensively and falls off, laying about 3000 - 5000 eggs over several months. The top layer of soil must be used for masonry.
The larvae remain on the body of the infected person for 2 to 5 days, then they fall off and undergo a molting process, turning into nymphs. Nymphs need from 48 hours to a week to feed, after which, being safe, they transform into adults. Both larvae and nymphs that find a host in May - June move on to the next stage of development in the same year.
Argasid mites
- also known as soft, due to their soft skin, or lurking, due to their closed habitats. The main homes of argasid mites are all sorts of caves, burrows, grottoes, nests and deep cracks. They can also be found visiting auls or villages, where arthropods prefer garbage on the floor, dust, cracks in walls and all sorts of adobe buildings.
In most cases, people are attacked at night, but there are also cases of daytime attacks, away from sunlight.
The life cycle of argasid ticks is somewhat different from that of ixodid ticks. In addition to similar development cycles (egg, larva, adult), argasids, as a rule, have 3 phases of nymphs, the number of which, under unfavorable conditions, can grow to 7.
We suggest you read: How to get rid of aphids on an indoor flower
At any stage of its development, the argas tick feeds on blood. It is capable of starving in the absence of food for up to 14 years, and the lifespan of individual ticks is up to 25. Also, a distinctive feature of these centenarians is the ability to preserve and transmit infectious agents for 10 years.
They are active mainly when it is warm, but indoors, be it a home or a barn, they are active all year round.
Another important difference from ixodid ticks is fast feeding. The Argas tick is capable of satiation in up to half an hour, and infecting with tick-borne relapsing fever in a minute to one and a half minutes. The tick bite is very itchy for several days to several weeks, turns purple, and dermatitis is possible from scratching.
The most dangerous of the Argasid ticks are the Persian tick and the cat tick.
The chicken mite is very small, its body is less than a millimeter long, but its saliva is extremely toxic. After being saturated with blood, the female lays about 20 eggs in secluded depressions or crevices. Three days later, offspring appear, which need a host - a bird - for nutrition and further development. The chicken mite feeds only at night and goes into hiding during the day. Thus, its development, under favorable conditions, does not exceed a week.
Their meetings with humans are extremely rare, but still possible. If there is no bird in the room, the insect will attack the animal or person.
Subcutaneous mite
- is able to live with a person, or rather on a person for many years, absolutely not revealing itself, feeding only on waste cells. However, when the immune system weakens, it multiplies more actively and begins to penetrate deeper into the skin, resulting in skin inflammation. As a rule, the scalp and facial skin are affected by subcutaneous mites.
On average, the life of a subcutaneous mite, or demodex as it is also called, lasts about two months, some females can live up to 120 days.
The average number of eggs is from 20 to 40, from which new representatives of the species hatch after 60 hours. The larvae, feeding on sebum, develop over 36 hours, after which they turn into pronymphs. Pronymphs, after 72 hours of development, turn into nymphs and for the next 60 hours stop feeding and freeze. After which they become imagoes. Adults feed at certain time intervals and after 120 hours become individuals ready for reproduction.
At the end of the reproduction process, the males die, and the females lay eggs in the hair follicles.
Scabies mites, also called scabies, are the cause of such an unpleasant disease as scabies. Until recently, the prevailing belief was that, in addition to prolonged direct contact of the skin of an infected person with the skin of a healthy person, the scabies mite can migrate using household appliances and accessories, however, at present experts are unanimous in the opinion that the scabies mite does not use this method of spread.
Also, there are often claims that the scabies mite is transmitted sexually, which is not entirely true, since sexual intercourse itself does not play any role in the transmission of scabies - prolonged direct skin contact is the only method of infection due to a number of features:
- female scabies mites are active and come out only at night,
- It takes an average of half an hour for a tick to drill into the skin of a new host.
- conditions outside the host's body are extremely unfavorable for itching - 21°C and humidity from 40% to 80% - kill it within a day and a half.
Ear mite
It is quite rare in humans; its usual carriers and feeders are dogs and cats. It can get into the house on shoes, from stray animals living on the landing, or on your hands if you pet an infected animal and then your pet. Ear mites can cause us only short-term discomfort, because they are not able to live long on the human body. Although, sometimes ear mites are called ixodid or subcutaneous mites that have settled in the auricle.
Ear mites that live in the ear canals of pets can sometimes migrate to the owner's head.
The larva, hatched within 4 days after oviposition, uses sebum and earwax as food for about 7 days and becomes a protonymph and then a deutonymmph. The deutonymph reaches puberty and is ready to mate even before it has decided on its own gender. And only after the fertilization process will she turn into a female and lay eggs, or turn into a male and mate with other deutonymphs.
What does a tick look like on the body?
The attached tick is located in the center of a red or bluish spot about 1 cm wide. When you see it, it seems as if the parasite has deeply drilled through the skin, and its head part is completely in the body. The tick is attached only with the help of its proboscis. Since its surface is equipped with teeth, it is very difficult to remove the insect.
The body protruding from the outside can be invisible, small and oval-flat (if the parasite has not yet had time to suck) or in the form of a swollen ball of impressive size (if it has been sucking blood for a long time) - up to 1 cm.
Scabies mite
Representatives of this type of mite are the causative agents of an unpleasant disease - scabies. If we consider the complete life cycle of the scabies mite, it becomes clear that the human body acts as an intermediate host. This type of tick lives near humans and domestic animals and attacks at different times of the day.
When it comes into contact with the skin, the proboscis “bores” the tunnels for movement and obtaining food, which causes irritation and itching of the skin. The scabies mite does not tolerate high humidity and low temperatures. Such conditions can destroy it within 24 hours, although their life expectancy is already extremely short.
The period of tick activity: when does it start and how long does it last?
Early melting of snow and persistent warm weather in March contributed to the early awakening of ticks.
The first tick bite last year was recorded on April 3, and in 2022 - on March 3 in the Chelyabinsk region. General tick activity is usually observed from April to October. When does tick season start? The onset of tick activity begins in April - May, when above-zero temperatures were recorded and the snow melted.
When does tick season end? The end of the season usually falls between September and October, when the weather is cool and damp. In 2022, the tick season ended in November, and this year it will end the same if there are no weather anomalies.
Are ticks active now? In the central region of Russia, Ukraine, the CIS countries and Europe, ticks emerged from hibernation and went in search of food, so they can pose a threat to humans and domestic animals.
The most favorable conditions for tick activity:
- Air temperature +18-20 degrees;
- 80% air humidity.
Typically, tick activity reaches its active phase in mid-April, it comes out of hibernation and begins to actively hunt and reproduce. In June, the population begins to decline due to dry and hot weather. The second wave of the activity phase occurs in August, September and sometimes October; it is weaker than the spring wave, but bites are just as likely. Warm autumn delays the tick's hibernation, and if the first frosts occur in September, the tick season can be considered over.
Have you been bitten by a tick? No, never 46%
Yes, once 46%
Yes, twice or more 8% Voted: 50