The active season of ticks is in full swing, so hundreds of articles continue to circulate on the Internet telling about where you can find these bloodsuckers, when you should be wary of them and how to remove an attached tick. But can you believe everything that is written in them? Of course not. And today we will tell you about the most popular myths about ticks that everyone around them believes.
- You can protect yourself from ticks using repellents
- Ticks are found only in the forest
- Ticks descend on their victims from trees
- Ticks are dangerous only in May and June
- If you remove a tick right away, it is impossible to become infected.
- The tick can be pulled out with a drop of oil
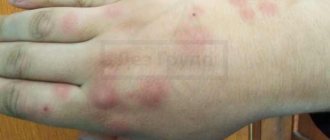
- The bite site is easy to detect
- The tick can lay eggs under the skin
You can protect yourself from ticks using repellents
Repellents can actually protect you from ticks - otherwise why were they invented? However, you should not rely completely on these funds. The fact is that, even if you apply the anti-tick spray according to all the rules, after two to three hours it will completely disappear, so it will have to be applied again and again. But even in this case, you cannot count on 100% protection: repellents can only be applied to clothing, and if a tick gets on an open area of skin, alas, it is unlikely to be frightened by the scent of your jacket.
How does an insect get on a person?
Sometimes a person does not even notice that he has been bitten by a tick, and the problem cannot be detected immediately, since the small dot is almost invisible.
Walking through the park, a person may suspect absolutely nothing, but ticks are already waiting for him. When the insect notices movement, it prepares to attach itself to the victim. Ticks cannot jump, so there is no need to be afraid that it will jump from a distant bush onto clothing.
After a tick lands on human skin, it does not immediately begin to drink blood. First, he will need to find the most suitable place for this. A tick can spend about 3 hours searching for it. It is important to remember that they have favorite places, which include the armpits, areas behind the ears, under the knees and other areas where the skin is especially thin. These areas need to be inspected first and especially carefully. If the tick itself is not visible, but a black bump is found, this may indicate that it has crawled under the skin. Despite the fact that the tick is very small, it easily bites through human skin and then penetrates into the resulting hole.
Ticks descend on their victims from trees
Ticks, by definition, do not climb trees; their “maximum altitude” is no more than 1.5–2 meters above the ground. Of course, a tick can fall on you from a branch, but much more often these arachnids lie in wait for their prey in the grass. Then, with the help of claws and suction cups, they cling to clothing or fur and begin to look for a place to bite, rising upward - this can take the tick from 20 minutes to 1.5 hours.
What not to do
Wrong actions can aggravate a person’s condition and lead to serious consequences. Therefore, it is important to remember what to do is strictly prohibited.
Main mistakes:
- Application of sunflower oil . Do not lubricate the insect with oil. It is not safe. Under a thin oily layer that does not allow oxygen to penetrate, the parasite will actually die. But if the tick remained in the body at the time of its death, then before death it will release a dangerous dose of poison into the human body.
- Use of chemistry . It is forbidden to poison an insect using gasoline, varnish and similar substances. Do not use creams or medicinal solutions. This will lead to the injection of a dangerous dose of poison into the human body in the last minutes.
- Pulling by the tummy . You should never touch the abdomen of a tick. It comes off very easily.
- Sudden movements . Another mistake involves abruptly pulling out the parasite. To remove a tick from a wound, you need to unscrew it. A sudden movement will cause the abdomen to tear away from the tick's head.
- Expansion of the wound . Some try to pick out the wound and eliminate the bloodsucker. This method is very dangerous for several reasons. If a tick ruptures during removal, the infection from the insect’s body will instantly enter the human bloodstream. The large wound left after eliminating the parasite serves as a gateway for infection to enter the body.
Ticks are dangerous only in May and June
The first period of tick activity in Russia begins in early April and lasts until mid-June, and the largest number of bites is traditionally recorded in May. However, we should not forget about the second period of activity - it lasts from the beginning of August to the beginning of... October. And the chances of encountering a tick in the fall are especially high for residents of regions with warm climates. By the way, a tick can attach itself to its victim even in winter. So, in 2011, a five-year-old girl from Rostov-on-Don fell victim to a bloodsucker, and it happened on New Year’s holidays.
What types of ticks are there?
65 species of mites belong to the genus Demodex (lat. Demodex). Each of them has its own preferences for choosing a habitat. The most common and well-known types:
- Folliculorum is the largest mite living in human hair follicles;
- Brevis is a smaller human parasite;
- Sarcoptes is an insect that parasitizes human skin;
- Canis is an insect characteristic of dogs;
- Cati – parasitizes cats.
Both human parasites have a worm-like shape, the only difference is in size. Folliculorum was discovered and described in the middle of the 19th century, and revis in the 60s of the last century. These species are classified as ectoparasites - that is, those that live in the skin. They are present in virtually all people of every race and ethnic group.
The sarcoptes subcutaneous mite gnaws passages in the dermis and causes severe itching. Animals have another group of mites – otodectose mites. They live inside the ears. It has been scientifically proven that these parasites are not typical for humans.
If you remove a tick right away, it is impossible to become infected.
Many people think that if you pull out an attached tick right away, it will not have time to inject poison into the wound, and in this case it is not at all necessary to see a doctor and have it checked in the laboratory. In fact, this is not at all true: the tick releases poisonous saliva exactly at the moment when it bites its victim. And measures that help prevent encephalitis and borreliosis are truly necessary.
How to remove the parasite?
It is very difficult to detect a tick, but it is even more difficult to remove it from the body if the tick manages to burrow itself. And you need to act quickly, because the longer the tick drinks blood, the higher the likelihood of contracting encephalitis and other serious diseases.
The best way is to contact a specialist. Of course, there is no point in calling an ambulance if you find a tick on your body, but the help of a doctor will not hurt. In extreme cases, you can go to the emergency room.
But not everyone has the opportunity to receive qualified medical care for a tick bite. For example, if the bite was noticed during a hike, that is, far from populated areas. In such a situation, there is nothing left but to try to remove the insect yourself. This must be done extremely carefully, since the tick must be completely removed. Otherwise, you can get inflammation on top of everything else.
When asked what to do if a tick has crawled under the skin, experts recommend using tweezers to remove it. This simple device allows you to reach even ticks that have completely crawled under the skin. Tweezers do not take up much space, so it is advisable to carry them with you in a hiking backpack. Using miniature tongs is very simple. They need to be brought as close to the skin as possible so as to catch the insect right at the jaws. You can try to slightly spread the wound in order to better remove the tick. Next, a circular movement is made with the hand. This is an important condition, since it is in this way that the tick can be completely removed along with the head and nose.
Sudden movements are not allowed, as this can lead to rupture of the tick; if part of it remains under the skin and is not removed, inflammation will begin.
Moreover, if the insect was infected with an infection dangerous to humans, this will increase the chances that its victim will become infected.
If the tick has completely penetrated the skin, you can use special medications to remove it. To do this, you can purchase a miniature hook at the pharmacy, which allows you to pick up the insect under the skin and successfully pull it out. In this case, you need to act very slowly and carefully. It is important to position the hook correctly. The tip is inserted into the hole made by the tick, after which it can be pulled out. The insect itself is fixed between the teeth of the hook, so its body is not injured, does not tear or fall apart. This way you can pull it out entirely.
In the event that there is nothing suitable for removing the tick at hand, you need to find a regular thread. A loop is made from it, which wraps around the attached insect. Then the knot is tightened and the tick is carefully removed from the wound.
Some experts recommend an old and proven method for extracting an insect. In this case, it is necessary to drip paraffin or sunflower oil onto the wound. The tick will begin to choke and come out on its own. This method is quite effective and works well, but has one significant drawback. The point is that the lack of oxygen causes the tick to secrete even more saliva containing poison. As a result, while it is crawling out from under the skin to the surface, there will be so much poison in the victim’s blood that infection will be inevitable if the tick turns out to be encephalitic.
No matter how a tick is removed from a person’s skin, after its bite there will be a wound on the body. It must be processed and disinfected. Even the simplest means are suitable for this. First of all, hydrogen peroxide is used, and then the affected area must be treated with iodine.
How does demodicosis infection occur?
Many readers are interested in whether a tick can crawl completely under the skin. The answer is yes. Demodexes live, feed and reproduce under the skin. This species has two routes of infection - direct contact with an infected person or through common household items: clothing, bedding, towels, and so on.
Demodexes can remain on the surface of the skin for up to three hours. Next, they penetrate the hair follicle or sebaceous gland, where they begin to actively feed on the epithelium and adipose tissue.
Most often, they choose to live on the face, back or cervical region of a person. On the face, the area of the nose, eyes, eyelashes and eyebrows are mainly affected. However, Demodex can live on any part of the body.
Types of mites under human skin
There are only two types of ticks:
Demodex is the most dangerous species. Ticks are small and have a transparent body, so detecting their bite remains extremely difficult. There are also those ticks that can live on the human body for years and not have any negative effects; they feed with the help of dead cells, which allows them not to die. But in those moments when a person’s immunity weakens, it becomes very dangerous.
The tick begins to act when a person has:
- Stressful situations;
- Long-term state of an empty stomach;
- Being in the cold for a long time;
- Temperature.
The location can be the face and head, as well as the place under the hair.
Ixodids are hard ticks that transmit encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain. In order to reproduce, it needs to consume blood. As long as the temperature does not exceed 5 degrees, they are not dangerous. The maturation of the larvae can be extended by several years as well as several months.
Appearance has:
- Black color;
- Hard shell;
Basic methods and methods of treating demodicosis
If you find similar signs in yourself, you need to contact a dermatologist who will prescribe an adapted comprehensive treatment. The structure of the insect's body and reliable three-layer shell makes it difficult to combat it.
Complex therapy includes taking antibiotics if necessary, antiparasitic drugs, drugs to restore the normal functioning of the digestive system, as well as drugs to regulate the activity of the sebaceous glands and antiseptic substances. However, the most effective way to prevent demodicosis is preventive measures and impeccable personal hygiene.
How to detect a tick on the body and can the pest crawl completely under the skin?
As you know, it is in the spring that the likelihood of a tick bite increases most. Despite its small size, it can pose a huge danger to humans. We are talking about terrible diseases that are carried by ticks. It is worth noting that in certain regions the likelihood of getting problems from a tick bite is much greater than in other areas. Ticks are most dangerous in the spring. During this period, the risk increases significantly.
If a tick just sits on a person’s skin, this does not pose serious problems for the body. However, if a tick has crawled under the skin of its victim, then you should worry about serious diseases. The deeper the tick digs into the skin and the longer it drinks blood, the more likely it is that an infection will affect the body. In addition, how the tick is removed from the skin also plays a huge role. If this procedure is performed incorrectly, this can cause not only blood infection, but also the onset of an inflammatory process at the wound site.
Preventive measures
To protect yourself from ixodid tick bites, you must take precautions while walking in nature. Particularly dangerous periods are spring and early summer. At this time, ticks are especially aggressive, as they experience severe hunger after hibernation.
When going for a walk, you need to take all precautions to protect yourself from getting ticks on your body. To do this you need to follow simple rules:
- Choose clothes that cover almost the entire surface of the body. Ticks live in tall grass, so they first fall on their feet. Gradually they rise up, trying to find a bare area of skin. When walking you need to wear long trousers and closed shoes.
- Clothing should be worn in such a way as to prevent the entry of parasites. The bottom of your shirt or T-shirt must be tucked into your trousers. Pants legs should be tucked into socks. The shirt must have long sleeves. If it is cool, you should wear a light jacket with a hood. If it is hot, then the head should be protected with a cap or hat.
- During a walk, clothes should be periodically inspected in order to notice parasites in time. If you are going to spend the night in the forest, you need to inspect your sleeping bags and tents.
- It is advisable that clothes for hiking be light in color, since it is harder to notice ticks on dark ones.
- Currently, there are a large number of protective drugs that can repel parasites. These are special gels, sprays, aerosols, ointments. You can buy them in a store or pharmacy. The most popular: “Biban”, “Taiga”, “Picnic-Antiklesch”, “Tornado”, “Deta-Vokko”.
Methods for diagnosing demodex mites
There are several methods:
- Tests in the laboratory - a scraping is performed or a part of the hairline (eyelash or eyebrow) is taken. The laboratory assistant places the material to be examined on glass and examines it under a microscope, and only then makes a conclusion.
Tests are taken only in the first half of the day, since the chance of diagnosing it at this time is much higher. This method will cost from 500 – 1500 rubles, depending on the clinic and the city where the analysis is performed. The good thing about this method is that you study many parts at once;
- The eyelash test is performed only by an ophthalmologist. Using tweezers, take both the upper and lower eyelashes and place them in a test tube. A specialized solution is added to the test tube and the test is performed. The cost varies from 300 to 500 rubles.
- Biopsy - a drop of a specialized substance is applied to glass and attached to the site of a possible bite for 30 seconds. Cost from 1000 to 2000 rubles.
You must first prepare for the tests by refusing:
- Cosmetics;
- Wash your face twelve hours before the procedure;
- Washing your hair;
- Eye drops.
How to reduce the risk of a tick bite
It is known that anyone can pick up a tick, regardless of gender and age. To neutralize yourself, you should get vaccinated at the clinic.
However, when such an opportunity is not available, you should try to observe the following preventive measures:
- In the forest, it is necessary to avoid places with accumulation of vegetation and dry pine branches. When heading out into nature, you need to remember that pests do not like humidity. In addition, their aggressiveness will depend on the lighting. In gloomy weather they do not bite, nor do they bite at night.
- In the evening, after completing the walk, you need to take off your clothes and carefully examine them and examine your body.
- When there is no overalls available, you need to wear plain, light-colored clothes when outdoors. The tick will be clearly visible on them, the pants are tucked into the boots, and the head is covered with a cap.
- When a person notices a tick crawling on the skin, it must be immediately caught, thrown into boiling water or burned. Then examine the skin to see if there is a puncture or a black dot. If it was found, you need to treat it with iodine.
Vaccination is the most reliable way to protect against ticks. After it, the body will recognize the disease cells and counteract them.
When a tick crawls over the body but still does not bite, it can infect a person through the affected parts of the body or wounds. An ordinary scratch can sometimes cause dangerous consequences. For timely detection of the virus and initiation of therapy, it is necessary to monitor symptoms. Preventive measures must be observed. This is the only way to avoid infection with borreliosis or encephalitis.
Causes of demodicosis
An opportunistic tick begins to activate in the presence of the following reasons:
- Unhealthy eating. Excessive content of glucose and easily digestible carbohydrates in tissue and blood cells causes activation of the tick, since this substance is an excellent nutrient medium.
- Sharing common household items or clothing.
- Passive lifestyle. This leads to a decrease in the body's resistance.
- Treatment with antibiotics and hormonal agents.
- Presence of chronic diseases.
- Stress and nervous tension.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Use of low-quality cosmetics, leading to clogging of sebaceous ducts, glands and follicles.