Pediculosis is one of the highly contagious diseases. The appearance of one person infected with parasites in a team is fraught with rapid infection of the rest.
What causes the high prevalence of parasitic disease? Human lice do not have the ability to move long distances, they cannot fly or jump, but when the need arises, unpleasant insects can move quickly.
The high rate of spread of lice between people is due to the fact that the disease is transmitted through close contact, through clothing and household items.
Let us consider in detail the questions of whether lice can jump, which is associated with the high level of contagiousness of this unpleasant disease.
Head lice
They are also called hair animals, as they live on the scalp. Characteristic signs of this type of lice:
- adult size – from 2 to 4 mm;
- color – gray-yellow;
- body is translucent.
The insect has three pairs of legs, with which they tightly grasp the hair.
The louse lives for about a month. Females lay 5–7 eggs per day. Lice eggs are nits. They are firmly attached to the hair at its very base and look like translucent round capsules. The larva develops in the egg within 7–10 days, after which an adult emerges from the egg. The eggs remain on the hair. It is impossible to distinguish an empty egg from a nit with the naked eye (for more details, see the article “How long does it take for lice to hatch”).
How dangerous is a head louse?
This type of lice is the “safest” for humans. They do not carry dangerous diseases like body or pubic diseases. But these parasites themselves are unpleasant. They have a powerful mouthparts with which they bite through the skin, causing micro-wounds to form into which the insect's saliva gets trapped, causing itching. Also, these wounds can become infected, which leads to the development of skin and other diseases.
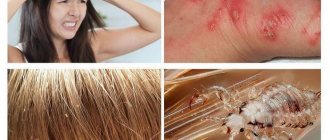
Lice infestation is called pediculosis. Signs of lice:
- severe itching on the scalp - they live not only on the scalp, but also in the beard, eyebrows, mustache;
- bite marks;
- after scratching, crusts appear on the head;
- due to incessant itching, a person becomes nervous and restless;
- with severe damage, the lymph nodes swell.
There is an opinion that lice and nits appear in people who do not maintain hygiene or lead a specific lifestyle. In fact, anyone can get lice.
They are transmitted in different ways:
- in case of close contact with an infected person - less than 50 cm;
- through combs, hats, accessories;
- through bed linen;
- in the pool - a louse can live in water for up to two days.
One adult can reproduce many times within just a few days. When the next generations of lice lay eggs, the hair becomes tangled, tangles form in it, and an unpleasant odor appears. If at least one female remains alive during the fight against these parasites, she will continue to reproduce. With long and thick hair, treatment for head lice can be very lengthy.
Treatment methods
You can get rid of head lice in various ways, and almost all of them are based on the use of special mixtures and combing out the nits.
Having chosen the appropriate tool, you need to:
- Test the drug for allergies - apply a small amount of the product to the inner elbow and wait a couple of hours; if there are no negative reactions, you can start treating the head.
- The drug is distributed along the entire length of the hair (and some products need to be applied to wet hair, while others need to be applied to dry hair).
- The head is then covered with a plastic cap to create a greenhouse effect and speed up the process.
- You need to keep the product from 15 minutes to several hours , depending on the drug chosen.
- The mixture should be washed off with running water, and then it is advisable to rinse the hair with a vinegar solution - to dissolve the adhesive substance that attaches the parasite eggs to the hair.
- Dead insects and their faces are combed out of the hair with a fine-tooth comb.
As for the treatment of pubic lice, the easiest and most effective way is to shave off all the hair. If for some reason this is not possible, it is recommended to use anti-pediculosis ointments and creams.
Body lice are removed in two stages:
- Hygienic procedure - thorough washing with soap and a washcloth,
- Sanitary treatment of all things and linen with insecticidal preparations, as well as the use of high and low temperatures. Clothes infested with parasites can be packed in sealed bags for a month, during which time the insects will die without food.
Body lice
This species does not live on the human body. It lives and hides in the folds of clothing and bedding, which is why the fight against this type of lice is especially difficult and long.
This type of lice has a translucent body measuring 3–5 mm; they are dirty white in color and darken when saturated with blood. In terms of lifestyle, they are more reminiscent of bed bugs, since most of the time they hide in clothes or bedding and can make their way into the thickness of mattresses, pillows, and blankets. This is where the eggs are laid. They do not live directly on human skin or hair, but go there only to feed. Bites most often appear on the upper body - neck, shoulders, back and lower back.
A body louse - or as it is also called, a linen louse - lives for about 35 days, the female can live up to 45 days. During her life cycle, the female lays about 300 eggs. Development to adulthood takes no more than a week.
Infection with body lice occurs much less frequently than with head lice. It is often associated with an antisocial lifestyle, poor hygiene and a rare change of clothes and bed linen.
You can become infected with body lice:
- when trying on clothes;
- when wearing clothes of a sick person;
- when sleeping in a bed infested with lice;
- in crowded places with close contact with the carrier.
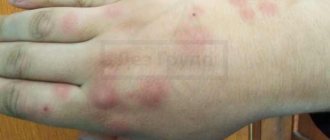
Linen lice also cause lice, just like head lice. This is expressed by bites, and they are not in the form of punctures of the skin, but lice can cut off micro-pieces of skin with their jaws. These bites take 4 or more days to heal. At the same time, they itch very much. The parasites' saliva causes hives. It contains a secretion that prevents blood clotting. With severe damage, body temperature rises.
Since linen lice can move from one person to another, they can also carry pathogens of dangerous diseases, such as typhus, etc.
Prevention
To protect yourself from infection, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- avoid close contact with infected people;
- refuse casual sexual contacts;
- use only your own household items - combs, hairpins, scarves, etc.;
- change clothes regularly and wash them at high temperatures;
- carefully examine the scalp of yourself and your child;
- use special repellents if necessary;
- Apply anti-lice shampoos in small quantities from time to time.
You should not perceive lice as unpleasant but harmless bugs that can only cause itching at the bite sites . These blood-sucking parasites can carry severe infectious diseases, provoke allergies and cause rough skin. Lice must be dealt with immediately as soon as insects or their metabolic products are noticed.
- about the author
- VK profile
Pubic lice
This is the third option of what kind of lice a person can have. They live on the hairline, but not on the head, but in the groin and armpits. They are attracted to these places by the secretion secreted by the apocrine glands.
These pests are smaller in size than body or head pests. Their length is only 1.5 mm. The body is light brown, flat, not elongated, like other types of lice, but more round. Their paws are designed to move along hairs with a triangular rather than circular cross-section.
The pubic louse feeds every 4 to 5 hours, so bites when infected with this type of lice are multiple.
The peculiarity of pubic lice - also called flat lice - is that they lay eggs at temperatures from 20 to 40 degrees. At higher or lower temperatures, they cannot breed. The human body temperature is ideal for them.
They cannot live outside the hairline, so the simplest way to combat them is to completely shave off the hair.
Infestation with pubic lice is also pediculosis, but its special type is phthiriasis.
Signs of phthiriasis:
- severe itching;
- bite marks, blisters and small hemorrhages in their place;
- traces of parasite activity on underwear.
Representatives of this type of lice also live for about a month. During her life, the female lays about 300 eggs.
In addition to the discomfort that pubic lice cause, they can be carriers of sexually transmitted diseases. They carry syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, etc.
You can become infected with this type of lice:
- during sexual intercourse with a carrier;
- just in close contact;
- when wearing clothes of a sick person and using his personal belongings;
- in common areas - swimming pools, baths, saunas, solariums, public restrooms, etc.
What are they needed for?
Why did lice appear? Why do nature need them at all? Surely this question was asked by every person who happened to encounter them. All living beings are useful in some way. Every animal and insect plays some role in the biosphere of the planet. What about lice? Do lice have any significance in nature?
There is an assumption that these parasites were included in the food chain at the beginning of their existence. They may have been larger and more nutritious than they are now. Over time, they became smaller and at one point fell out of the social life of the planet. Now they are just parasites. Harmful and certainly useless to anyone.
Lice are the source of many unpleasant symptoms, the main one being itching
What other types of lice are there?
As mentioned above, each type of lice lives only on “its” victim. In addition to human lice, people have to deal with pests on their pets. Lice eaters live on dogs and cats. Their difference from human lice is that lice eaters do not feed on blood, but on dead skin flakes and animal hair. In terms of symptoms, lice-eater infestation is similar to human lice. It is also expressed by severe itching. Lice eaters do not spread from pets to humans.
Lice don't just live on cats and dogs. They can live on mice and rats, sheep, horses, pigs and other animals. All types of lice have the same structure. Vary in size. The largest are pork hematopins, whose length reaches 5 mm. And the smallest are hoplopleurae, which infect hamsters whose size does not exceed 1 mm. Also, species can differ in color, although they are all brown-gray, and when saturated with blood they darken to black.
All types of lice have the same nits - capsules in which the larvae develop. They are round and translucent, attached with an adhesive substance to the base of the hairs.
Can parasites swim?
It is generally accepted that lice infection can occur after visiting a swimming pool or other source of water, especially natural bodies of water. It should be emphasized that the physiological structure of the parasite is such that they are only capable of running quickly. Lice cannot jump or swim. But for some time they can remain viable when in water.
This fact is easy to prove practically. When bathing a pet infected with parasites, lice move in large quantities onto the pet's face, which is due to the lack of swimming ability and fear of water.
It is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of lice infection during bathing, but this possibility is minimal. Infection can only occur if there are a large number of people in a small pool, when lice have the opportunity to easily move from one head to another. The ability to jump and fly does not matter in this case.
How to deal with all types of lice
Traditional methods of control can only work in the initial stages of infection, when there are not very many pests yet. For treatment, essential oils with pungent odors are used, as well as cranberry juice and vinegar. They make wraps with these products, wash their hair with them, and treat the skin. Another method is temperature. It is believed that lice die at -8 degrees.
But in case of severe infection, such methods are useless. You should use professional and effective pediculicides, for example, Medilis-BIO, Medilis-Permifen, Medilis-Malathion. They are used to treat the hair and skin of adults and children, as well as clothing and bedding.
Do nits jump?
So, nits are lice eggs. It’s worth saying right away that at this stage of development, individuals are completely deprived of the ability to move. They don't jump, fly, run or even crawl.
Females attach the nit to the hair, using an adhesive substance, thanks to which it is securely attached until maturity. After maturation, the young individual leaves the shell, and it remains on a thread.
In the nit stage, individuals do not require nutrition; in addition, their shell reliably protects them from the effects of all negative factors. They easily tolerate temperature changes, and if nits find themselves in unfavorable conditions for further development and maturation, they hibernate. During hibernation, the formation of the parasite stops; as soon as conditions become favorable, they continue development.
Myths
In this section, we propose to dispel all the myths that float around these insects:
- Lice can jump. As has already become clear, these creatures cannot move in this way. We have already discussed in more detail above whether lice jump.
- Lice live in dirty apartments. This is true, but only partially. Of course, lice don't crawl on the floor there. But, as a rule, residents in dirty houses do not observe basic rules of personal hygiene.
- Only children can get lice. This is an unfounded claim. The chances of infection through contact with a sick person are the same for both adults and children.
- It is possible to become infected only through sexual contact. The pubic variety of parasites is transmitted in this way. We described above how infection occurs.
- These insects can be transmitted from pets. We propose to discuss this issue separately and in more detail.
Diagnostics
Despite the high level of development of modern medicine, the only way to diagnose the disease is through examination. It is regularly held in all educational institutions (schools and preschools). The diagnosis is confirmed only when living individuals are detected, and not nits. Infected children are excluded from attending educational institutions and are sent for examination to a dermatologist.
The specialist conducts an examination using a Wood's lamp (for head lice) or a slit lamp (for clothing parasites). Sometimes microscopic examination of hair, nits, or live specimens is performed. A modern diagnostic method includes videodermatoscopy, which allows you to capture enlarged lice in a photo or video.