April in Moscow and the Moscow region this year turned out to be quite warm, spring in 2022 came on time and a large number of Muscovites went for a ten-day weekend outside the city. Along with nature, ticks have also woken up - carriers of dangerous diseases and simply unpleasant parasites. They begin to wake up immediately after the snow melts, and the air temperature warms up to +3 degrees. Already at the beginning of April, tick bites were recorded in some areas of the Moscow region, thereby marking the beginning of the tick activity season.
How to protect yourself from ticks when going out into nature or to the countryside? In which areas of the Moscow region in 2022 are ticks most active and can transmit encephalitis? Let's figure it out.
Nothing about ticks
Many people consider ticks to be insects, but in fact they belong to the class of arachnids. In the modern world there are more than 50 thousand different species. Some of them pose no threat to humans, others can cause a little harm, and there are representatives that are carriers of various diseases fatal to humans and animals. Therefore, you need to fight ticks, use protective equipment when going outside, and immediately destroy them if they are infested at home. The size of ticks does not exceed 3mm. As a result, they are not easy to detect. Mite species are divided into two large groups based on food preferences: saprophages and predators. Saprophages feed on organic debris. They cause more harm in agriculture. But predatory species, on the contrary, feed on animals and plants. It is this species that poses the greatest threat to all living organisms. There are species that simply drink blood and fall off, but there are also those that carry dangerous viruses that are fatal to humans.
Ticks can live without food for up to three years. Therefore, during cold periods, all vital processes in their body slow down, which allows them to calmly survive the winter. Despite the fact that in winter the risk of catching a tick is very small, such cases still exist. If autumn is warm, then their activity continues this season.
Ticks live everywhere. Some species are quite rare, others are more common, but the species' habitat covers the entire planet. Even in water there are representatives of parasites. But still, the main places where they accumulate are forests and meadows. Premises for storing agricultural products are also favorite places, but such species are generally not dangerous to humans. Pets are particularly affected by ticks. After walking with your pet, be sure to inspect it for parasites. Some species live in houses, so precautions even at home will not be superfluous.
What types of ticks are there?
Species of ticks are divided into groups: parasitiforms, acarymorphs and harvest mites. Haymaking ticks do not include many species in their group. These are the largest representatives of the order, but they are quite rare. Their habitat is forest, tropics. They lead a hidden lifestyle and are located in hard-to-reach places.
Parasitiform ticks are the most dangerous and pose the greatest threat to animals and humans. Representatives of this species jump on a person and suck blood. This species is a carrier of various viruses dangerous to humans. Their active season is from May to September. Their habitat is very wide and they are found even in countries with cold climates.
Acarimorph mites are the largest group. It accounts for 30 thousand varieties. This group includes both predatory parasites and saprophages.
Tick season
The peak of tick activity occurs in May-June, when the weather in the Moscow region and the capital remains warm, but not hot. Then there is a decrease in tick activity by month by mid-summer, and an increase in the number of bitten ticks begins again in late August - early September. The tick season coincides with the period of dacha work, so it is summer residents and gardeners who are at risk.
To reduce the risk of being bitten at the dacha, sanitary and epidemiological services offer services for treating the area from ticks in the Moscow region. The cost of this procedure depends on the area of the land plot and ranges from 1,500 to 3,000 rubles. In addition to protecting the area from bloodsuckers, you need to protect yourself. Every person should inspect his body after being in the garden or garden for the presence of crawling or already attached arthropods. When working on the site, it is recommended to treat skin or clothing with special tick-repellent agents.
Important!
A tick bite that is not a carrier of infection can cause a severe allergic reaction in a person.
Ticks in the Moscow region
Ticks in Moscow in 2022 - 2022 can also be found in any park area. The prevalence of this parasite is difficult to control, so you should avoid walking on lawns, among bushes, away from paved paths. The administrative website of the capital indicates which parks have been treated against ticks in Moscow. But this does not mean that there is 100% confidence that these places do not pose any danger.
On a note!
You need to be careful while walking in Izmailovsky, Bitsevsky parks, and Losinoostrovsky Nature Reserve. In the summer months, when ticks are dangerous in the Moscow region and Moscow, before going to large forested areas you need to use special repellents against bloodsuckers.
How to choose a drug for treatment?
Our company’s specialists use imported and Russian-made liquid and dry anti-tick products in their work. In particular, German drugs from Bayer, products from NPO Garant (Samara), and Shchelkovo Agrokhim are used.
I would like to warn you right away that there are no safe poisons, so you should not let children and animals out onto the grass for 3-5 days. The presence of people and animals on the site for 5 hours is strictly prohibited.
You need to select the concentrate for processing individually. Much depends on:
- processing conditions;
Before use, the dry preparation must be diluted with hot water (from 60 C). If there is no way to heat the water on the site, then you will not be able to use such a product.
- coatings;
If there is a lawn on the site, then you should not use dry products. If there are sunny days after treatment, the product will burn the grass. It will not be possible to restore such a lawn. Therefore, to maintain the coating, it is better to choose liquid concentrates.
When ordering, take into account the characteristics of people and animals living on the site. If the treatment is carried out on the territory of a children's camp or the residents have a tendency to allergies, then it is better to choose a hypoallergenic drug.
Bayer has such a tool. It is effective in killing ticks, but is safe and does not have an unpleasant odor.
Tick-borne diseases
The bloodsucker of the arthropod subclass is dangerous because it can be a carrier of unpleasant viruses. In the Moscow region and Moscow, the most common ticks are ixodid ticks (Ixodoidea), which can infect a number of serious diseases:
- Tick-borne encephalitis is a dangerous infectious disease that affects the nervous and cardiovascular systems and disrupts the functioning of internal organs. If the victim is not provided with timely assistance and treatment, the disease can cause disability or even death.
- Borreliosis or Lyme disease is a disease caused by bacteria. They affect internal organs and reduce the body's immunity. If the disease is not treated, it becomes chronic and can lead to irreversible consequences for human health.
- Anaplasmosis is a less dangerous disease that reduces the victim’s immunity and promotes the development of inflammatory processes in the body.
- Ehrlichiosis is a bacterial disease that disrupts the functioning of internal organs. Often the infection causes pathologies and deterioration in the quality of life of the bitten person.
All these diseases can be successfully cured if you seek help in the first 2-3 days after the parasite attack. Immediately after discovering an attached bloodsucker on the body, you need to carefully remove it and take it to the nearest laboratory. There are several medical centers in the capital and Moscow region that accept parasites for analysis. Addresses and names of institutions for Moscow residents:
- Diseases transmitted by ticks
The most dangerous virus is tick-borne encephalitis. In the Moscow region, you can conduct a test for tick encephalitis in Odintsovo, Vnukovo, Mytishchi, Shchelkovo, Dmitrov and other cities. The largest medical institutions near Moscow are:
Danger of ticks
A tick infestation never goes unnoticed. The larger the population, the greater the risk of getting bitten. Insects feed on blood. It is almost impossible to notice an attached tick in the first day.
Insects can provoke the development of an allergic reaction and swelling. The main danger is the risk of contracting infectious diseases. Many of them provoke severe reactions in the body, which lead to disability and death.
Diseases spread by ticks:
- Encephalitis;
- Lyme disease;
- anaplasmosis;
- ehrlichiosis;
- babesiosis (deadly for dogs);
- tularemia.
Tick-borne encephalitis is especially dangerous for humans. You can become infected with it immediately in the first hours after the bite. If medical care is not provided in a timely manner, the consequences can be very serious.
Not only people, but also pets suffer from ticks. Walking on untreated grass or among bushes, in most cases, ends in an insect bite for pets. In addition to the fact that animals can also become infected with dangerous diseases from them, they can bring them into people's homes.
Symptoms of a tick bite
It is quite difficult to notice a tick on the body in the first days. Its bite is painless and does not cause any discomfort. The insect's saliva contains components that anesthetize the bite site, thereby protecting the parasite from danger.
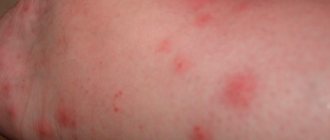
In the first three hours after the bite, a person may feel weakness, drowsiness, loss of strength, and slight chills. After several hours, pain in muscles and joints appears, and body temperature rises. This reaction indicates the onset of an allergic reaction to the tick’s saliva.
Most common symptoms:
- weakness;
- chills;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of swelling at the site of the bite;
- eye reaction to light;
- aching joints;
- skin rashes;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
In rare cases, itching, rapid heartbeat, and decreased blood pressure occur. The severity of bite symptoms, as well as their manifestations, depend on the individual characteristics of the organism and the number of bites.
Where do encephalitis ticks come from?
In the spring-summer period, Russia occupies a leading place in the number of citizens affected by tick bites. The encephalitis virus is carried by birds, pets and other warm-blooded animals. Ticks become infected from these vectors and transmit the virus to humans through their bite. You can pick up a tick anywhere - both in the forest while walking, and in your own garden or city park. Even professional treatment of summer cottages and city parks cannot 100% destroy all ticks, so there is always a risk of being bitten.
There is a rumor that in the thirties the Japanese planted ticks in Russia; they were considered a biological weapon.
Tick nymph and its danger
The nymph already has 4 pairs of legs, and its size reaches almost 2 mm. This parasite is already moving much more actively, so large animals or birds serve as food for it, and can also attack humans. What is most interesting is that the tick in the guise of a nymph overwinters and only with the onset of spring warmth it turns into sexually mature individuals of different sexes.
Nymphs, like adults, are capable of infecting humans with many serious diseases. Therefore, despite the fact that the tick individual has not yet formed properly, it is quite dangerous.
There are more ticks in the east than in the west
The degree of danger of contracting tick-borne encephalitis within the main tick habitat increases from west to east. Cases of disease are recorded especially often in the southern regions of the Far East. Most likely, this is due to humid, warm summers and the presence of mixed forests.
The most dangerous regions of the Far East:
- Amur region;
- Sakhalin;
- Khabarovsk region;
- Jewish Autonomous Region;
- Primorsky Krai.
What is characteristic: following warming, ticks move from east to west, and the peak of their numbers and activity in different regions varies throughout the season.
Pasture mite (lat. Dermacentor marginatus)
An encounter with a pasture tick can result in infection with tick-borne encephalitis, Omsk hemorrhagic fever, tularemia, listeriosis, Q fever and other diseases. Typically this species parasitizes cattle, but adult individuals often “attack” people.
The pasture tick lives in the south of the European part of Russia, Western Siberia, Crimea, the Caucasus (including Transcaucasia), and the Middle and Lower Volga regions. It is usually found in mountain-steppe regions, but can also live in forest-steppe and mountain-forest areas.
Where do ticks live and what climate do they like?
Ticks can adapt to various environmental conditions and can even survive at low temperatures. But there are conditions that promote rapid reproduction and comfortable life of arthropod parasites.
The carriers of encephalitis and borreliosis are most often the taiga forest tick and the European tick. They prefer habitats where there is grass and shrubs, as well as areas of forest belt with dense vegetation. A safer place for animals and humans is where the grass is low and there is little vegetation. Ticks are not found on paved areas, wide trampled paths and clearings, but they love to wait for prey along paths.
Ticks are found in almost all types of forests, be it birch, spruce or mixed type. Only the coniferous environment is unfavorable for them. Encephalitis ticks live in almost all climatic zones of Russia, sometimes even found in harsh conditions beyond the Arctic Circle because they have learned to adapt to all environmental conditions.
Ticks feel most comfortable in areas with high levels of humidity.
In Russia, encephalitis ticks are found from Siberia to semi-deserts. Many cases of attacks have been recorded in the Moscow region and adjacent territories, in the Caucasus, in the Altai Republic, Volgograd, Kemerovo and Kirov regions. They are most common in the Far East, in the Central regions of Russia and in the Northwestern District.
The best weather for tick development is warm and humid, which is why the main peak of development occurs in spring and early summer . Ticks cannot tolerate dry and hot weather; the scorching sun is destructive to them.
In which regions of Russia are there few ticks?
These bloodsucking creatures are least often found in the Northern regions of Russia, Siberia, the Urals, Magadan, Murmansk, Kamchatka and the Nenets Autonomous Okrug. But this does not mean at all that there are no ticks there and you can forget about precautions when visiting forests and parks.
Is it possible to carry out the treatment without a professional at home?
Amateur gardeners themselves make the decision to carry out the treatment. And they prefer not to involve professionals.
There are many anti-tick products on the market today for home use. But you need to be careful when using them:
- If the dry concentrate is diluted too much, the damaging ability will decrease. After treatment, many insects will survive.
- If the concentrate is not diluted enough, you can ruin the lawn and poison the fruits and animals.
- Treatment cannot be carried out without protective clothing and a respirator.
And most importantly, when purchasing on your own, there is a possibility of purchasing an uncertified drug. This means that the concentrate has not passed safety tests. Using it, you can cause harm to yourself, your loved ones, and pets.
Diet of ticks
Depending on their diet, ticks are divided into:
- Saprophages that feed on organic matter.
Saprophages are involved in the process of converting humus, therefore they are considered very useful living beings. Parasitic mites, whose diet consists of plant sap, cause significant damage to agriculture. They destroy crop reserves at high speed.
Dust or scabies mites eat dead particles of human skin. Barn mites cause serious damage to food stored in warehouses. Subcutaneous mites eat fat that accumulates in human hair follicles. Spider mites suck the juices of various plants, including cultivated ones. Ear mites feed on the fat layer located in the ear canals.
- Predators that parasitize both animals and plants.
Blood-sucking ticks are constantly in their hiding places, where they wait for their potential victim. On the legs of these arachnids there are special claws and suction cups that allow them to cling to clothing, the body or skin of humans or animals. After they land on the body of their victim, they move to their places of vital activity. This could be the armpits, groin, head or neck area, etc. In this case, mites can parasitize the body of other types of mites or thrips.
Ticks, and especially their bites, are quite dangerous for humans, since parasites are carriers of fatal diseases such as encephalitis and others that are no less dangerous.
Ticks can remain without food for 3 years, but if they are very lucky, they become quite voracious, increasing in weight up to 120 times after being saturated with blood.
The 5 Most Dangerous Ticks in the World Watch this video on YouTube
Pliers: description
Such representatives of the arachnid species are not large in size, as they grow in length up to 3 mm and no more. The average size of these living creatures is in the range of 0.1-0.5 mm. Ticks, like all arachnids, lack wings. Adults have up to 4 pairs of legs, while juveniles have only 3 pairs of legs. Ticks also do not have eyes, but this feature does not prevent ticks from sensing their prey at a considerable distance, thanks to the presence of a special sensitive apparatus. Depending on the structure of the body, ticks are divided into several groups: leathery, with a head that is fused to the chest, and also with a head that is movably connected to the body (armored). Depending on this, each group breathes in its own way: the first 2 groups supply oxygen to their organs through the skin or trachea, and the last group breathes through a special organ.
Types of ticks with photos and descriptions
Scientists know about more than 40 thousand species of ticks, which are divided into 2 main groups. For example:
- Parasitiforms, such as gamasid, argasid, nutallium and ixodid ticks.
- Acariformes, such as scabies, hair, feather, marine, freshwater, thyroglyphoid, acaridia, oribatiformes, sarcoptiformes and thrombidiformes.
- Haymaking ticks are also isolated as a separate group.
Main types of ticks and their description:
Ixodid ticks
They differ in that their body is covered with reliable chitinous plates. Moreover, they can have quite impressive sizes. There are species that reach a length of up to 2.5 cm. This type of tick prefers to parasitize in temperate latitudes, where they hide in the leaves of trees and shrubs. Therefore, they are found on almost the entire Eurasian continent. Potential victims of ixodid ticks are wild or domestic animals, as well as humans. If it gets on the skin of its victim, it will be able to feed on blood for several weeks. The female is quite fertile, as she is capable of laying up to 17 thousand eggs per season.
Argasid mites
They prefer to live in crevices of various buildings and outbuildings, and can also live in bird nests, which birds do not use. Their potential victims are poultry and animals, although they can also attack humans. They are often found in chicken coops. Argas mites bite quite painfully, and a profuse rash appears at the site of the bite and unbearable itching occurs. This parasite is characterized by soft skin, and the head protrudes slightly beyond the body and seems barely noticeable.
Armored mites
They are found on the soil surface, although there are species that live in trees. These ticks are not parasites, since they feed on natural food, in the form of mushrooms, lichens, living plants and their remains, and they also eat various carrion. Despite this, oribatid mites pose a certain danger to both birds and animals. The fact is that they can infect with various types of helminths, including tapeworms.
Gamasid mites
They settle in bird nests, chicken coops, and also in rodent burrows, since they parasitize on them. This parasite lives for a little more than 6 months, growing up to 1 mm in length. During this period of time, the parasite can cause serious damage to poultry farms. Their vital activity leads to significant loss of feathers in birds, as well as the appearance of extensive scratching on the skin.
Subcutaneous mites
They live under the skin of humans or animals, causing a lot of discomfort. However, if parasites are not properly controlled, they can live for years, causing severe itching and irritation. The female lives no more than 3 months, but during this period she lays an average of 100 eggs, from which viable individuals emerge in just a couple of days.
Scabies mites
These are parasites that can cause a difficult-to-treat disease called scabies. At the same time, ticks parasitize both humans and animals. The problem is that parasites make a lot of tiny passages in the skin of a person or animal, which leads to itching and redness. Ticks feed on skin secretions. Adult ticks live no more than one and a half months, but during this time the female manages to lay eggs several times.
How dangerous is a tick larva to humans?
After about 2-4 weeks, tick larvae emerge from the eggs, which have a direct resemblance to adult individuals. The only differences are their small size (only 0.5 mm) and the presence of 3 pairs of limbs, since adults have 4 pairs.
The body of parasites is not yet fully formed and some elements may be missing. The larvae appear in the warm season, so during this period they are most active. Since the larvae are still very small, they are not able to rise to a significant height. In this regard, their food items are rodents, hedgehogs, lizards, etc. Digging into the body of its victim, the larva consumes blood for 6 days, after which it falls off and ends up on the ground. The next stage of its development begins - the nymph stage. The larvae are not particularly affected by flooding and can remain under water for up to a month.
According to American scientists, the bite of a tick larva is as dangerous as the bite of an adult. This is especially true in relation to ticks, which carry dangerous diseases such as encephalitis.
What diseases do they carry?
The tick can be the host of many pathogens. But the most famous of them are the tick-borne encephalitis virus and the causative agent of Lyme disease , or, as it is otherwise called, borreliosis . The fundamental difference between them is that the virus is not affected by antibiotics. Vaccination can be done against encephalitis ticks . But this is a last resort. Usually it is done only to forest workers and once every five years to residents of areas where ticks are common.
There is so much talk about tick-borne encephalitis because it can be very dangerous - causing severe illness with meningitis and encephalitis. But in reality it is not as common as borreliosis. In total, tens of thousands of people turn to specialists for tick bites per season. Of these, about a thousand suffer from borreliosis, and less than a hundred from encephalitis.
How often should the treatment be carried out?
Treatment on the site must be carried out annually. The drugs do not have a cumulative effect. Moreover, it is better not to use the same concentrate for several years in a row, because the mites' perception of it may decrease.During the year, it is enough to spray the product once. The exception is when it has rained for 3 to 5 days. In this case, you need to call specialists again.
On the Internet you can find recommendations for processing 2 times a year or every month. We recommend that customers be careful with the amount of concentrates used and not spray more than 3 times a year.
Dangerous areas on the map of the Moscow region
In Moscow and the Moscow region, statistics are kept every year on the number of registered tick bites and the presence of dangerous viruses in their DNA. According to this information received in September last year, no cases of tick-borne encephalitis were recorded in Moscow and the Moscow region. Based on data obtained over past summer seasons, a list of dangerous areas on the map for ticks in the Moscow region and Moscow in 2022 was compiled:
- the first places were taken by the districts of Ramensky, Serpukhovsky, Kolomensky - in the territory of each of them more than 800 cases of attacks by arachnid parasites were registered;
- in Lyubertsy, Naro-Fominsk, Dmitrov and Noginsk regions, the number of bite cases exceeds 500;
- In the Chekhovsky, Pushkinsky districts, and in Orekhovo-Zuevo, tick bites in 2022 are expected in an amount not exceeding 300 cases, as was the case in 2022.
On a note!
According to data for the last summer season, among the 15,857 registered reports of victims, about 4 thousand of them were bitten children. 5958 parasites were delivered for the study. The presence of borreliosis pathogens was confirmed in 15% of cases, 3.5% of ticks were infected with anaplasmosis bacteria, and ehrlichiosis pathogens were found in only 0.3% of the parasites studied.
The number of ticks in the Moscow region in 2022 depends on several factors. In the case of very hot and early summers, the parasites should be less active. They also do not like very rainy weather, which often occurs during the summer months in the metropolitan area.
The map for encephalitis ticks in the Moscow region in 2022 was created based on data for previous summer seasons. Despite the absence of recorded cases of encephalitis infection, there is a likelihood of the presence of encephalitic parasites in the Dmitrovsky, Taldomsky districts, and Dubna. Epidemiologists studying the question of whether there are encephalitis ticks in Moscow have been keeping statistics for the last few years. So far, not a single case of infection with a dangerous infection has been recorded.
Dangerous areas for ticks on the map of the Moscow region
During the tick period, the safest areas of the Moscow region in terms of the number of calls from victims are considered to be the eastern and southern ones:
- Odintsovo;
- Mozhaisk district;
- Shakhovsky district;
- Kashira district;
- Troitsk and others.
It is impossible to say for sure whether there are encephalitis ticks in the Moscow region. The virus can be brought from other northern neighboring regions: Yaroslavl, Tver, Ivanovo. Bloodsuckers are able to travel distances through transport or while on the human body.
Incubation period of the disease
The incubation period from the moment of infection to the onset of symptoms of this disease occurs from ten days to two weeks. Moreover, the incubation period may be longer if a person has been vaccinated against encephalitis, which is given in childhood.
There are two stages of this infection:
- fulminant, when initial symptoms occur within the first twenty-four hours. In the absence of prompt medical care, people quickly fall into a coma and may die due to paralysis of the central nervous system;
- protracted, when the incubation period can last a month, and sometimes even exceed thirty calendar days.
The first symptoms of the disease, often a week after relaxing in nature, are headache, nausea, vomiting and fever, which reaches forty degrees. The person also feels weak. After the first symptoms, paralysis, pain in the nerve endings, convulsions and loss of consciousness begin to appear.
Treatment of tick-borne encephalitis
Treatment of people who have become infected with tick-borne encephalitis occurs according to general principles, regardless of the presence of vaccination or the use of specific drugs that contain antibacterial antibodies.
During acute periods of the disease, even if it is mild, it is necessary for the patient to remain in bed until all symptoms of intoxication have passed. Almost complete immobilization and non-active transportation leads to minimal pain and, accordingly, improves recovery prognosis. It is also important to remember the need for a balanced diet for the sick person. The diet can be prescribed if dysfunction is detected in the stomach, intestines and liver.
In addition, many patients with encephalitis experience an imbalance in the vitamin balance and need to consume vitamins B and C. Therefore, at least three hundred milligrams of ascorbic acid should be administered daily, which will stimulate the functions of the adrenal glands and improve liver function.
Where does the encephalitis tick live?
It is impossible to distinguish an encephalitis tick from a regular tick by appearance. To find out whether there is a virus in his blood, he is sent to a laboratory for examination. The spreaders of the infection are ixodid ticks, especially European forest and taiga ticks. In a hungry state, the size of the arachnid’s body does not exceed 3 mm; as it feeds, the abdomen increases in size.
In the wild, the parasite lives in grass and on the lower branches of bushes. Prefers bright clearings, but without direct sunlight. Natural habitat:
- spruce, birch, deciduous, mixed forest;
- City Park;
- unkempt vegetation near the house;
- meadows;
- pastures.
The parasite does not tolerate coniferous forests, low grass - less than 7 cm in height, asphalt, compacted roads.
It feeds on blood and waits for prey on the grass and lower branches of bushes - up to 1.5 m. It can remain in a hungry state for several months. At the sight of a potential victim, it becomes more active - it falls from the branches onto the animal’s back, clings to a person’s clothing, and crawls out of the grass.
Encephalitis ticks
On a note!
Borreliosis is transmitted by a bite through saliva, encephalitis - through blood. If the parasite's head comes off if the parasite is removed incorrectly, infected blood gets into the person's wound and illness will follow.
Will ticks wake up in 2022?
The tick season begins when the snow melts from the ground, the soil begins to be warmed up abundantly by the sun, and the air temperature remains stably at +10° C. During the winter, the parasites go into suspended animation - an analogue of animal hibernation in insects. In this mode of seasonal hibernation, a tick can live up to 8 years, “switching off” every fall and awakening in the spring.
Are there ticks in February?
If in any specific area on the ground in February the snow has completely melted and direct sunlight constantly and for a long time falls there, ticks may wake up at this point, even if it is 3-5°C outside.
Exit from suspended animation works automatically, like a button - where suitable conditions appear, the awakening process starts. In Moscow and the Moscow region in February, such conditions almost never occur, so ticks coming to life at this time are a rare and unlikely occurrence. You can find out whether ticks have woken up near you in 2022 by observing the weather at the location of your site and through experimentation. Take a white piece of cloth and run it over the budding grass and vegetation. If ticks have awakened en masse, you will see them on the canvas.
In Moscow and the Moscow region, as a rule, the tick season begins in March and ends at the end of September or October. These are approximate guidelines; in fact, the process of waking up and falling asleep of ticks starts and stops due to the climate in the current season.
Where are encephalitis ticks found?
The habitat of ixodid ticks covers the continents. They live almost all over the world, in all climatic zones. They quickly adapt to the most extreme conditions and are found even beyond the Arctic Circle. The greatest number is in tropical and subtropical forests with tall grass and high humidity.
In temperate climates, arachnids live everywhere. In Russia, the habitat begins with taiga and ends with semi-deserts. Regions endemic for tick-borne encephalitis are Karelia, the Far East, the North-Western District, the Volga region, most regions of the Central District. The distribution map of tick-borne encephalitis is updated annually, but in the above areas, the danger of an epidemic always remains at a high level.
Important!
Parasites appear in early May and disappear at the end of October, when there is a persistent decrease in temperature indicators. They are extremely active in dry, humid climates – long spring, rainy summer, warm autumn. They are not found in the hot summer when temperatures rise above 30 degrees Celsius. Optimal climatic conditions are temperature 15-25 degrees Celsius, high humidity.
Encephalitis ticks
How to protect yourself from ticks
No remedy or method of protection against ticks guarantees 100% safety, but combining several approaches at once helps to significantly reduce the likelihood of bites and transmission of infections as a result.
- Use tick repellents and acaricides regularly.
- When going into the forest for a walk or picking mushrooms, wear light, closed clothing on which ticks will be easy to spot.
- Do not lie on the grass without a blanket, do not place hammocks, garden chairs, swings or tents near bushes and thickets.
- While in nature, periodically inspect yourself for insects crawling on you and brush them off.
- If you have pets, consult with your veterinarian on the best way to protect them from ticks and purchase tick repellent drops, spray and/or collars.
- Teach your young children about ticks, why they are dangerous and how to be careful in nature to avoid being bitten.
- Regularly mow the grass in your dacha; the shorter it is, the less likely it is that ticks will hide in it.
- Carry out acaricidal treatments of the entire summer cottage in spring and autumn yourself or order the appropriate service from the SES.
What should I do if bitten by a tick
First of all, you need to remove the tick either at the nearest emergency room or with your own hands. What exactly should you do if you are bitten by a tick, and there is no way to quickly get to the emergency room?
- Wear disposable gloves or take a clean piece of gauze folded in several layers or a cotton pad.
- Gently, slowly rotating around its axis, pull the tick out of the wound, holding it as close to the head and surface of the skin as possible with your fingers, tweezers, thread or a special tick remover (sold at the pharmacy).
- Disinfect the wound, for example, with hydrogen peroxide.
- If there is a black dot left in the wound - this is the head of the tick, it needs to be treated with iodine and not picked, the skin will soon reject it on its own.
- Place the tick in a test container or similar sealable container, along with a cotton pad or piece of gauze lightly moistened with water.
It is important not to crush the tick when removing it. This is necessary to submit the pest for analysis to the laboratory, which must be done immediately after you have removed the pest. Ticks are accepted for analysis by commercial laboratories, for example, Gemotest or Invitro, or the Centers for Hygiene and Epidemiology of Moscow
or
Moscow region
.
note
At the moment, analysis of ticks for the presence of pathogens of encephalitis, borreliosis, anaplasmosis and ehrlichiosis is always carried out for a fee in all laboratories.
If laboratory analysis reveals causative agents of any diseases in the tick, you can begin treatment even before the first symptoms appear, which will significantly increase the chances of a mild course of the disease and a quick recovery.
What to do with pets
The same goes for pets. Cats tolerate tick bites more or less easily and without consequences compared to dogs, however, it is advisable to take care of protecting your pets even before going to the countryside or going out into nature. Consult with your veterinarian about the best way to protect your animal in your particular case. It also makes sense to contact a veterinarian after a bite, especially if you observe changes in your pet’s behavior and well-being. The special risk group includes all dogs without exception, purebred, very young or old animals, as well as cats and dogs with chronic diseases.
Prevention and protective measures
To reduce the risk of Muscovites and residents of the Moscow region being bitten by a tick, parks in Moscow are being treated for ticks in 2019. Specialists from sanitary and epidemiological stations have been sent to public gardens and parks to destroy “unwanted guests” using special chemicals.
On a note!
Tick extermination in Moscow is carried out from March to May, when they are just emerging from winter hibernation.
To protect yourself from the possibility of contracting encephalitis, you can use a special vaccine. This vaccination must be given before ticks appear in the Moscow region. The vaccine is given in two stages: the first injection is administered 2-3 months before ticks begin to bite - in November or December. Then the second vaccination is prescribed after 1-2 months. And only after it, after two weeks, immunity begins to act. The third injection is given after 12 months, then the vaccination is repeated every three years. Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis in Moscow is carried out in budgetary, commercial clinics.
The situation with ticks infected with the equally destructive infection borreliosis is worse - there is no vaccine against the infection. In case of infection, treatment with antibiotics is carried out. To prevent bloodsuckers from biting a person, you need to dress appropriately for a walk in the forest or park:
- choose closed clothes with long sleeves;
- tucking pants into socks, a jacket or shirt into pants;
- gather long hair in a ponytail or braid and put on a headdress;
- wear plain, light-colored clothing, which makes it easier to catch ticks.
Special acaricidal agents in the form of aerosols that repel bloodsuckers will also help. It should be remembered that after each visit to nature it is necessary to carefully examine the body for the presence of attached parasites.
Why is it worth ordering treatment for ticks at the sanitary and epidemiological station of Moscow and the Moscow region?
- We have accreditation from Rospotrebnadzor.
- We work according to SanPin standards.
- We work with individuals, individual entrepreneurs, LLCs and legal entities.
- We can handle any volume. Our specialists are ready to treat a 6-acre dacha plot, the territory of a recreation center or a summer camp.
- We are trusted by companies that hold public events: we ensured safety from ticks at the Nashestvie festival and at the Military-Historical Reconstruction of an episode of the Battle of Borodino.
You can order processing by phone, via email or online form.
Precautionary measures
- To avoid ticks, it is important to protect yourself in advance. Avoid untreated areas of forests and parks; it is advisable not to visit places with tall vegetation during the period of activity.
- If you happen to end up in such a place, you need to cover all exposed areas of your body with clothing as much as possible, and be sure to wear a hat. The picture shows the most favorite places where ticks bite.
- You can also use protection, such as repellents, which are sold in any supermarket.
- When you arrive home, be sure to check yourself and your loved ones for ticks. Clothes should be washed in hot water, because the larval forms are invisible to the eye and can reach you already at home.
- If a tick has embedded itself, take the measures listed in the previous subheading as soon as possible. In no case should you ignore the symptoms and blame everything on the flu, because the first signs of encephalitis at the initial stage are not much different from it, but the consequences are many times worse!
Is the anti-tick medication harmful to people and animals?
As already mentioned, there are no completely safe anti-tick concentrates. Treatment is carried out with toxic substances.
Therefore, you must adhere to the following rules:
- do not be present when spraying;
- if possible, do not visit the site for 3 - 5 days.
Remember! Ticks enter the area with mice, rats and other rodents, as well as cats and dogs. Therefore, it is not enough to carry out the treatment; you need to limit access to the site to strangers, wild and stray animals.
Ticks in the Moscow region 2022: dangerous areas
Only Taldomsky and Dmitrovsky districts are considered endemic for tick-borne encephalitis in the Moscow region. At the same time, ticks are found and annually bite people in absolutely all areas of the region, but either do not transmit any diseases at all, or transmit some other tick-borne infections. Unfortunately, there are no accurate statistical data reflecting the full picture. You can see where ticks live in the Moscow region in 2022 and see how far dangerous areas are from you on the map.
Sources
- https://kleshei-net.ru/kakie-byvayut-kleschi/
- https://apest.ru/kleshhi/kleshhi-v-gorodah/kleshchi-v-podmoskove-i-moskve/
- https://felisov.ru/kleshchi/otkuda-poyavilis.html
- https://prusakam.net/kleshhi/
- https://felisov.ru/kleshchi/v-podmoskove.html
- https://kurer-sreda.ru/2020/05/15/556648-karta-rasprostraneniya-kleshhevogo-encefalita-v-2020-godu
- https://Dezoff.ru/kleshhej/kleshchi-v-2020/
- https://apest.ru/kleshhi/kleshhi-v-gorodah/gde-obitayut-ehncefalitnye-kleshchi/
[collapse]