Coniferous plants are a spectacular decoration of our gardens. Sooner or later, we all strive to implement interesting landscape design ideas with the help of various spruces, pines, junipers and other conifers. These plants are considered hardy and quite resistant to disease, but, unfortunately, they also get sick and are affected by pests, especially in the first years of life. We will talk about prevention and control measures against diseases and pests of coniferous plants in this material.
Diseases and pests of coniferous plants - prevention and control measures
Bark beetles
Bark beetles can be called the most dangerous forest pests. Most parasites live and develop under the bark of coniferous trees, less often in the thickness of the bark or in the wood, boring holes into them. Bark beetles are small, body length ranges from 0.8 to 12 mm, and the coloring of the pests is modest. At the end of the body there is a flattened bevel, which is bordered by teeth. This is a “wheelbarrow” used to remove waste from gnawed passages.
By boring under the bark the so-called uterine duct, females lay eggs. The hatched larvae, in turn, gnaw their own, larval, passages in different directions from it. At the end of their move, they create a “cradle” chamber in which they pupate. Young beetles, hatched from pupae, gnaw flight holes through which they exit.
Mostly weakened, diseased, drying trees are attacked. Once colonized by pests, they die.
Pest control
Fighting bark beetles is quite difficult. Therefore, it is necessary, first of all, to carry out preventive measures that increase the overall resistance of coniferous plants. To combat the pest, pheromone traps are used, which are attached to the affected tree. All beetles located at a distance of 7 km flock to the smell. After this, the plants with bark beetles are uprooted and burned.
Antipheromones can also be used to repel bugs. They are safe for animals and humans, unlike insecticides. Preparations that are used to combat bark beetles: “BI-58”, “Clipper”, “Krona-Antip” (biological preparation), “Bifenthrin”.
Moli
Order: Lepidoptera (butterflies). Kinds:
- juniper shoot;
- larch cap and miner.
Description:
- almost always lead a twilight lifestyle;
- distinguished by a shaggy large head;
- color - whitish-gray.
Signs of plant infection:
- usually begins in May;
- eaten needles, which moth caterpillars never completely eat, but after them they fall off;
- yellowing of needles;
- white coating on the crown and branches;
- the formation of cobweb nests in which caterpillars live.
How to fight:
- collecting and burning spider web nests;
- treatment with insecticides (Iskra, Komandor, Fufanon).
First of all, the caterpillars of this pest attack young, immature seedlings.
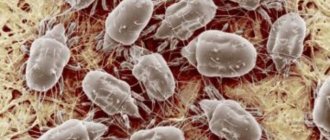
Ticks
Spider mites are one of the most ubiquitous pests. It affects almost all types of plants, except aquatic ones. You can notice ticks on larch, spruce and juniper along the web. Ticks are active in spring and summer, during which they may appear several times.
The size of individuals directly depends on their fatness, the length of females is 0.4-0.6 mm, males - 0.3-0.45 mm. Soft-bodied animals are characterized by an ellipsoidal shape, the upper part of the body is convex, the lower part is flat. Tick larvae are transparent, light green to green-brown in color, with 2 distinct, large dark spots on the sides. The color of females wintering from late summer to spring is orange to bright red. All adult ticks have 8 legs.
Spider mites feed on the contents of plant cells. The presence of the pest is indicated by a thin cobweb and the presence of small white dots on the needles. In case of severe damage, it turns completely white, the entire plant is covered with cobwebs, and a moving mass consisting of the bodies of parasites is visible on the needles.
The main prerequisite for the appearance of mites is low air humidity, so regular spraying of the outer parts of plants is a good prevention of the occurrence of the pest.
Control measures
The most effective way to get rid of ticks is to fight them with modern chemicals. Please note that spider mites are arachnids, not insects. It is useless to use insecticides against it.
It needs to be combated with other drugs - acaricides (Apollo, Flumite, Borneo, Floromite, Envidor) and insectoacaricides (Agravertin, Fitoverm, Akarin, Oberon, Actellik) . To destroy the most resistant individuals, it is necessary to treat with the selected drug several times.
Basic preventative treatment
Regular preventive measures largely depend on what pests appear in your region and even area most often. But there are several mandatory activities:
- in early spring, it is necessary to treat mature trees with a general preventive agent, for example, Iskra or Aliot;
- when the effect of the previous drug has already ended, re-treatment is carried out, choosing a different insecticide;
- when the daytime temperature reaches 17-18°C, treatment is carried out against bark beetles and other stem pests. Treatment is done with Aktara, Aliot, Fitoverm, Inta-Vir or another broad-spectrum drug.
During the summer, it is important to inspect the plants in order to begin treatment and removal of damaged branches in a timely manner.
There is no need to think that conifers can grow without care and treatment.
They, no less than deciduous plants, need protection from insects. This is especially important for young animals, which easily die due to pests. But regular treatment and prevention will help avoid most problems. If you are unable to provide proper prevention and treatment yourself, invite a plant care specialist. He will take care of your yard, and all you have to do is enjoy the beautiful green plantings. Reading time: 7 min
Scale insects and false scale insects
You can find scale insects on junipers and thujas, and they have also begun to appear on yew trees.
All scale insects have protective shields; they look like plaques on the tree. In an adult female, the scutellum is rounded, about 2 mm in diameter; in the male it is smaller, oblong in shape. Color
pests are reddish brown or dark brown. The most dangerous are females , because the larvae, emerging from the eggs, within a few hours settle over the entire surface of the plant and immediately begin to suck out all the juices from it, the needles are completely covered with scutes.
But it is not these parasites that cause more harm, but false scale insects. The spruce moth is characterized by its large size; it can reproduce quickly and en masse, causing serious damage to plants.
False scale insects differ from scale insects in that the shield covering them on top does not grow together with the insect inside.
If you pick off the shield, the parasite will remain on the plant. The scutes themselves also differ among pests: in scale insects it is flat, in false scale insects it is pea-shaped.
Adults and larvae of both parasites function throughout the year, sucking all the cell sap from plants.
The presence of scale insects can be recognized by the presence of brown or light round scales on the needles, which are difficult to separate from the plant. These are already adults. With severe damage, the needles and trunks of trees and shrubs become covered with plaque, which is formed due to a large accumulation of parasites. The development and growth of damaged plants is delayed, the needles turn yellow and fall off.
When infected with false scale insects, the needles lose their shine, turn brown and become covered with sticky secretions, which attract wasps. The parasite sucks out cell sap from branches and needles. Red-brown or yellow spots appear on damaged areas, leading to the death of parts of the tree.
Pest Control
It is not easy to fight scale insects and false scale insects, since they are protected from external influences by shields. At the initial stage of infection, you can try using a soap-alcohol or soap-kerosene solution . In case of severe damage, use insecticides (“Admiral”, “Aktara”, “Apploud”, “Bankol”, “Confidor”) or insectoacaricides, for example, “Aktellik”. It will be necessary to carry out 2-3 treatments, it is better to do this with drugs belonging to different chemical groups. A week should pass between treatments.
Diseases and pests of indoor plants can lead to the death of your green pet. How and when should you treat your garden for pests? You will find answers to this and many other questions in the article.
You can often find small bugs on cabbage. This is a cruciferous flea flea, methods of combating which are described at https://stopvreditel.ru/rastenij/selxoz/krestocvetnaya-bloshka.html link.
Prevention of diseases of coniferous plants
As doctors often tell us, any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. This message applies to all living things and to conifers, including. Therefore, prevention cannot be neglected. And it begins from the moment of choosing a seedling.
Preventive measures that are necessary for coniferous plants:
- When purchasing a seedling (it doesn’t matter if you buy it in a store, at a market, in a nursery, or dig it up in the forest), first of all, you need to assess the condition of the needles and branches. The shoots and trunk should not have damaged bark or streaks of resin, and the needles simply must be clean - without dried or yellowed areas, without plaque or stains. If a plant is bought on sale - with obvious defects, but cheap - it will require treatment and quarantine. Such a specimen cannot be immediately planted with healthy plants.
- Even if you brought a seemingly healthy seedling into your garden, spray it with a fungicide before planting for prevention. The fact is that many diseases have a long incubation period and the disease does not manifest itself immediately.
- Inspect your young conifers regularly. This is the only way to detect signs of disease or emerging pests in time. After all, the sooner the problem is detected, the easier it is to deal with it, and the greater the chance of the plant not dying.
- Healthy, well-groomed trees are less susceptible to attacks from all kinds of diseases and pests and can more easily cope with such troubles. Therefore, proper planting and care play a crucial role in disease prevention.
Mandatory, but simple care activities that you can do to give your conifers health:
- timely watering;
- applying seasonally appropriate root and foliar fertilizers;
- removing broken or damaged branches;
- mulching;
- preparation for wintering.
Read about the rules for preparing coniferous plants for winter in the article “7 conditions for successful wintering of coniferous plants.”
Hermes
Hermes are a special group of pests that attack pine and spruce. Parasites form on branches
trees, cone-like galls. There are several types of these pests. At the end of June, the early one is active, forming small oval galls at the ends of the branches. Yellow Hermes becomes active in August and develops large green galls. A late species of pest forms large spherical galls in late August-September.
Female Hermes feed on tree sap and lay eggs on them. The emerging larvae harm the kidneys, deforming them. Then galls develop in these places.
On the outside, these parasites are covered with a downy growth, making it difficult to combat them, for which systemic insecticides are used, for example, “Aktara” and “Commander”.
Aphids
Order: Hemipterans, or arthropodous.
Kinds:
- spruce root;
- green spruce or Sitka;
- gall yellow and red;
- juniper;
- pine;
- thuja.
Description:
- small insects whose body size does not exceed 2-3 mm;
- special proboscis that pierce shoots and leaves;
- can be either winged or wingless;
- The color is most often light pale greenish or brown.
Signs of plant infection:
- white fluff;
- sticky hands after rubbing it;
- growth slowdown;
- shortening shoots;
- shedding of needles;
- drying out of conifers.
How to fight:
- spraying plants with insecticides: Aktara, Formate, Karbofos, Neoron, Iskra;
- if after two treatments with the same drug (with an interval of 10 days) the pest remains, it is recommended to change the product to another;
- if the lesion is small, folk remedies can also cope with it: a solution of potassium soap and an infusion of wood ash.
The outcome depends on the scale of the lesion. If there are few pests, chemical insecticides will destroy them in 20 days. If the invasion resembles an epidemic, prepare for the fact that you will have to part with the plant.
Sawflies
Spruce trees are attacked by sawflies:
- Canadian,
- Serbian,
- European,
- occasionally prickly.
As a rule, spruce trees do not suffer much from these parasites; next year their needles are restored. Sawflies cause more damage to pine trees; sometimes you can find entire nests of insects on the branches. Weymouth pine, cedar, mountain and common pine are most often attacked.
The insect's abdomen is connected to the thorax motionlessly, without the help of a stalk. The ovipositor of females looks like a saw, with which they cut plant tissue and lay eggs inside.
Externally, sawfly larvae look like caterpillars.
It is they who eat young shoots of coniferous plants from May to the end of June, after which the branches look scorched and die.
Controlling these pests is not difficult. The main task is to see the caterpillars in time and take measures to destroy them. “BI-58”, “Aktellik”, “Decis” and “Fury” will help with this.
How to increase the immunity of coniferous plants?
A deficiency of essential microelements negatively affects not only the appearance of the plant, its general condition, development, but also its ability to cope with various diseases. Conifers suffer from insufficient supply of necessary elements as follows:
- there is not enough nitrogen - the needles grow poorly and have a pale color;
- iron deficiency - turn yellow and sometimes turn white;
- lack of phosphorus - they turn red.
To increase the immunity of coniferous plants, it is necessary to use fertilizers, preferably special ones for conifers. The fact is that ordinary mineral fertilizers sold in stores are intended for fruit and berry crops, and the application rates are calculated specifically for these plants. Conifers have different needs, and the standards for them are much lower.
When applying fertilizers, it is best to alternate root feeding with foliar feeding, which is often forgotten. But it is through the leaf (and the needles are precisely the leaves) that the plant better absorbs many microelements.
Do not forget that fertilizers containing nitrogen are applied only until mid-summer, since this element causes shoot growth. From the second half of summer, you can feed with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers with other microelements, excluding nitrogen - they will help the shoots to ripen, and the plant will successfully survive the winter.
Such preparations as “Zircon”, “Super Humisol”, “Immunocytophyte”, “Epin-extra”, “Nikfan” will help improve absorption and normalize the balance of microelements. These biological products also improve root formation, increase the immunity and resistance of plants to various stresses - bad weather, attacks by pests and diseases.
Prevention of diseases and pests of conifers is, first of all, proper care. © Fine Gardening Magazine
Gray mold (rot)
This disease is caused by the fungus Botrytis cinerea and is manifested by the formation of ash-gray cobwebby mycelium on the needles. The mycelium can exist for up to 2 years and at the same time infect new parts of plants. The development of the disease occurs in the fall, and by spring the mycelium grows into the root system of young seedlings, causing tissue death and death. The disease develops especially actively in conditions of increasing humidity and thickened crops, in places where moisture accumulates and in shaded areas.
Measures to prevent and combat gray mold
|
Rust diseases
Rust affects most conifers, and its subspecies differ slightly from each other. Yellow-orange spots appear on trees and shrubs affected by the fungus, then spore-bearing bags are formed from the mycelium, and brown growths appear on the needles. Typically, rust appears on conifers after it has formed on grass crops. The needles gradually turn yellow, dry out and fall off, the plant looks thinned out and even slows down in growth over time.
Rust prevention and control measures
|