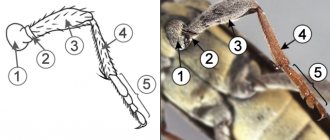
Morphology
Imago . An insect with a strongly flattened body. The wings are lost. The remains of the elytra in the form of small oval plates located on the mesothorax have been preserved from them. The oral apparatus is a three-segmented proboscis with spiny bristles (modified lower and upper jaws). The antennae are four-segmented. [5] The third antennal segment is the longest. The fourth and third antennal segments are much thinner than the second. The eyes are convex. The body is covered with thin short hairs. [2] Legs running, with three-segmented tarsi. [5] The pronotum in front has a deep notch, its anterior angles protrude far forward in the form of wide lobes.
Color and size depend on the degree of saturation. The sucked bug swells, becomes larger, and the color acquires a more saturated red tint. [5] Size ranges from 4.5 to 6.5 mm. The lateral margin of the pronotum is somewhat paler and wider. At the anterior end it is twice as wide as the eyes. The posterior edge of the elytra is cut off almost straight. [1]
Sexual dimorphism . Individuals of different sexes differ in the structure of their genital organs.
Male . The end of the abdomen is asymmetrical. On the left side of the last segment there is a strongly curved copulatory organ. [2]
Female . The end of the female's abdomen is rounded. On the seventh segment, the vaginal slit is clearly visible. On the lateral side of the posterior edge of the fourth segment there is a notch leading into the copulatory bursa. [2]
The egg is goblet-shaped, slightly curved. There is a cap at the upper end. The color is white at first, turning yellow as it develops. [5]
Larva (nymph) . The body size is smaller than that of an adult bedbug. The tarsi are two-segmented. The antennae are shorter and thicker than those of the imago. [5] The first segment is the shortest, the second is shorter than the third. The abdomen consists of eight visible segments. [2]
Phenology of development (in days)
A little about the biological features of the reproduction process
Fertilization occurs when the male simply pierces the female's abdomen with his genital organ and inserts the seed inside it. Over the course of many millennia of evolution, insects still reproduce precisely by the method of traumatic insemination.
The advantage of this type of mating is that the larvae, which will be formed to a certain extent inside the female’s body, can be used as food during the period of starvation. It has been proven that this type of fertilization has made it possible for many species of bedbugs known to entomologists to survive for millions of years.
Females mate only once in their entire lives, which is then sufficient to lay a certain number of offspring. Bed parasitic species have special organs for storing the male's seminal secretions throughout life, which can be consumed in a certain amount as needed. As for males, they are not at all picky in choosing a sexual partner.
A recent experiment by entomologists proved that all adult individuals, regardless of sex, have damage to the abdomen, which indicates that males of these animals can mate even in the same sex order.
Once the male has impregnated the female, she will lay 4 to 10 eggs throughout the day. Their sizes are extremely small and do not exceed one millimeter in length. They are always deposited in the apartment where the female spends all daylight hours. As for bedding species, they will never scatter them in visible places because they care about their offspring. Effective reproduction of bedding species is facilitated by high-quality nutrition. One high-quality meal is enough to lay 20 units of future offspring.
This is interesting! Female bedbugs feed much more intensively than males and manage to lay up to 500 offspring during their lifetime.
The most optimal conditions for the reproduction of bed parasitic organisms are often achieved in the apartment, since in some rooms there may be high air humidity, as well as a temperature of about 25 degrees.
Development
Imago . Leads a nocturnal lifestyle. During the day it hides in various crevices. Vision is weak. The sense of smell is developed. In severe hunger, it can also attack in sunlight. Pricks with the proboscis parts of the body that are not covered by a blanket or clothing. A person almost doesn’t feel the injection. Irritation is caused by saliva injected into the body during sucking.
Capable of fasting for a very long time. The duration of fasting of adults at low temperatures is more than a year. A hungry bug becomes almost transparent and very thin. In search of prey, bedbugs easily migrate from one room to another. They are able to move through the ventilation system, and in the warm season, along the outside of the house. An adult bug moves at a speed of more than 1 m/min, lives up to 14 months, and drinks (female) 7 mg of blood at a time. [5]
The secretion of the odorous glands gives the habitats of bedbugs a specific smell, reminiscent of cognac. Insect habitats are easily identified by the black or brown skins of the larvae. [3]
Mating period . Bed bugs reproduce and develop throughout the year. The female lays from 1 to 12 eggs daily. In total during life - 250–500 eggs. The eggs are glued to the substrate by a gelatinous secretion of the glands. The main places for oviposition are cracks in walls and furniture. [5]
Egg . The development time of eggs depends on the temperature and humidity in the room. At +14–18°С, egg development is completed in 15–19 days, at + 22–26°С – in 5–12 days, at +35–37°С – in 4–6 days. At temperatures below + 10°C, development stops. At -4–7°C, eggs can survive for 1.5 months. [5]
The larva (nymph) goes through 4–5 instars. In a warm room, at +30°C, and with a sufficient amount of food, the first instar larva molts on the 6th day. Further instars last approximately five days each. The entire development takes 28–30 days, at room temperature – 6–8 weeks. At temperatures below this, the development period increases. To move to the next instar, the larva must drink a full portion of blood. Until this happens, the next moult does not occur, and development is delayed. The first instar larva drinks 1/3 mg of blood; subsequent instars drink more. Older larvae can starve for up to 18 months at temperatures below +25–30°C. At +10°C they do not die, at –17°C they live for about a day, at +45°C they die in 45 minutes. [5]
Imago . Adult bugs do not tolerate sudden drops or increases in ambient temperature. Like the larvae, at -17°C they live only for a day; at +45°C they die after 45 minutes. The full development cycle from egg to adult lasts 30–50 days under favorable conditions, and 80–100 days under unfavorable conditions. [3]
Ways bedbugs enter the house
Parasites appear in human habitation for various reasons. If they do not have enough food (the neighbors have too many insects) or places to hide, then the bugs will look for a new object. Sometimes they appear by chance.
Anna, 39 years old, Rostov-on-Don
“There had never been bedbugs in the house before until new neighbors moved into the apartment next door. I think insects crawled over from them, because I once came by as a neighbor, and there was such a specific pungent smell. After that, I immediately covered the ventilation grille with a mesh, inspected all the walls, baseboards and sealed the cracks. After treating the apartment, bedbugs no longer appeared.”
Bed bug on the fabric surface of the sofa
Neighbours
If measures are not taken, insects will constantly crawl from nearby apartments, including bedbugs. This is inevitable, since parasites multiply quickly and need additional food sources. The new generation grows up in 2 weeks under normal conditions.
New things
Bedbugs can live on objects for various purposes, not only in apartments/houses. This explains their appearance among purchased new things. The reason is a violation of sanitary standards at the facility where clothes, equipment, and furniture are stored. The bedbugs will be here as long as there is food.
Bedbugs can also appear on new things.Furniture
When buying an old sofa, bed, or wardrobe, bed parasites may appear. The source is sometimes the belongings of relatives that are accepted as gifts. You need to carefully check the internal surfaces
Pay attention to the back walls and shelves. Inspect the internal structure of the sofa, its upholstery
Bedbugs inside an old sofa
Cloth
If things are stored for a long time, are not sorted or used, and bedbugs have entered the room, then over time these insects will also infest closets and chests of drawers with old clothes. If sold and not inspected very carefully, such things will become a source of bedbugs.
Devices
When parasites are discovered in a new object, the likelihood of nests forming inside furniture and equipment increases. After they occupy the sofa and bed (where a person sleeps), they will move to neighboring areas in search of shelter. A TV, refrigerator, printer, computer, air conditioner - any appliance (if it has been idle for a long time) can become a habitat for insects.
Thanks to their narrow body, bedbugs can hide well
Poultry
Bed parasites attack other animals, birds: cats, dogs, rats, chickens, etc. But parasites consider only humans as their main source of food. The properties of its skin and blood are most suitable for these insects. Alternative food sources are other warm-blooded creatures. But it is more difficult to notice that a chicken coop is infested with bedbugs, so the consequences may be worse (diseases, inflammation of puncture sites in the outer integument of the bird).
Moving to a new place of residence
Secondary housing and new buildings - both objects can be infected with the same probability. In the first case, bedbugs are often already in the room when purchased (they crawled from neighbors or got there by accident). In a new apartment, parasites appear along with the owners’ belongings.
Hidden bedbugs in the seams of an old sofa
Maliciousness
The bedbug is a blood-feeding synanthrope that is closely associated with human habitation. One of the first species to undergo synanthropization at the dawn of humanity and change its host from a bat to a human. [5]
The pest feeds on blood, attacking humans, various animals and birds. It feeds in the larval and adult stages. It causes anxiety to people, interferes with sleep, thereby reducing their performance. Causative agents of various infections (plague, typhus and relapsing fever, tularemia, Q fever) have been found in the body of the bug, but there is currently no accurate data on the transmission of infections to humans. [3]
Laying eggs
The laying of eggs by a female bedbug occurs as follows:
- The first clutch occurs 24-48 hours after mating.
- Each time before laying a new batch of eggs, the female must find enough blood for them to mature.
- If the female’s nutrition becomes irregular, the egg primordia slow down their development until favorable conditions occur.
- The larvae hatch from the egg 7-30 days after laying.
A fertilized female needs increased nutrition and a secluded place. Having found it, she begins laying. It usually contains up to 5 eggs, but under favorable conditions their number can increase to 12. With normal nutrition, the female is able to lay up to five hundred eggs during her life (which is about 15 months).
Bed bug lays eggs
For laying, the female always chooses a secluded, dark and warm place closer to a source of fresh blood. Since this insect is capable of covering a distance of more than 1.3 meters at a time, the nests are always located close to places where people sleep.
Control measures
Preventive actions
The measures are aimed at preventing the appearance of bedbugs and creating conditions that prevent their development and reproduction:
Extermination activities
Insecticides of various formulations are used to kill bed bugs. Ovicidal insecticides are especially effective. Treatment is carried out only in rooms where insects are found. Simultaneous treatment of all adjacent premises is carried out only in hostels and hotels. [3]
When writing the article, the following sources were also used: [4]
Source
Parasite eggs
After fertilization, laying occurs on the fourth day. This usually occurs in hidden places close to a person during sleep and rest. These are the internal parts of: sofas, beds, armchairs, chairs. Where there is no light and warmth.
Each time eggs are laid in a new place, which increases the likelihood of survival of the offspring. Externally, eggs look like grains of rice - white oval-elongated capsules. On top they have a sticky jelly-like substance that provides them with fixation to vertical and horizontal surfaces.
There are hundreds of similar clusters of eggs. Because of their dense shell, they are resistant to negative external factors, which is why they are so difficult to destroy. Pesticides used to treat living spaces cannot penetrate inside the egg coating. We must wait until they hatch and re-disinfect.
In such a situation, microencapsulated pesticides with a prolonged spectrum of action are used. The harmful effect lasts up to 3-4 months
To detect nests, it is important to carefully inspect hidden places with a flashlight before sanitizing
what type of development do bedbugs have?
Bed bugs - insects from the order Hemiptera (Hemiptera) - live everywhere: on grass and trees, on soil and in water, and there are also those that parasitize animals and humans. The oral apparatus of bedbugs is of the piercing-sucking type. This is a jointed proboscis adapted for sucking liquid substances. In a calm state, it is tucked under the head and directed back. It is very typical for bedbugs to have scent glands. Their secretions can have a signaling value - ensuring the meeting of individuals of the same species - or have a protective function - scaring away enemies. Development in bedbugs occurs with incomplete transformation. A female bedbug at room temperature, 2 days after blood-sucking, lays 1–2 eggs per day. Oviposition lasts 5 days and stops until a new portion of blood arrives. Eggs are laid in the same places that serve as a refuge for bedbugs: various crevices in wooden objects, in folds of paper, fabrics. Larvae are usually similar to adult bedbugs in both appearance and lifestyle.
Harm to humans. The attack of bedbugs on people deprives them of normal sleep and rest. The saliva released during a bite causes itching, burning, and redness of the skin. Usually the bug pricks several times before it finds a suitable place for sucking; the duration of sucking in adult bedbugs is about 15 minutes. There is no reliable data on the importance of bedbugs as disease carriers. But it is known that they can preserve pathogens of plague, typhus and relapsing fever, tularemia, and Q fever.
Source
Harm to humans and animals
Bites from this type of bedbug are absolutely safe for humans and animals. These insects rarely bite people. They are often confused with forest ticks. Bites are not capable of causing acute pain or allergic reactions.
The infestation of forest bugs sometimes leads to losses. They can parasitize crops and garden plants.
The mouthparts of forest bugs are adapted to use plant juices as food.
The invasion of forest bugs into city apartments is temporary. This behavior is provoked by forest fires or sudden changes in temperature and humidity levels. Each time, bedbugs always return to their natural habitats. You can protect your home during periods of increased activity of forest bugs with mosquito nets. Mechanical removal of individuals that have already appeared in the room gives good results.
The secretion produced by the mammary glands contains a special acid. It makes the forest bug's secretions poisonous to some insects.
An interesting fact is the use of forest bugs in folk medicine. They are often used in the form of an alcohol infusion to treat severe forms of alcoholism.
Do you suffer from horse flies? You need to know which horsefly remedy is most effective. Do you know why a gadfly bite is dangerous? This article will be of interest to you.
Do you have scabies and want to figure out where you got it from? Interesting material at the link.
How bedbugs reproduce - all about blood-sucking parasites
Blood-sucking parasites cause serious harm to human health. They settle in sleeping places, wall cracks and other parts of the room. Residents of the apartment do not see how bedbugs multiply; they suddenly encounter a large colony of insects that has grown in the immediate vicinity. To prevent infection of the premises, it is necessary to study information about the characteristics of the reproduction of parasites.
Video: forest bug close-up ????
Considering that such a pest resembles representatives of other species, it is recommended to watch a video that allows you to learn more about the features of the appearance of the forest bug.
Read further:
Bugs on currants: effective methods of destruction
Types of forest ticks - 10 photos, description, habitat. How dangerous and what you need to know when encountering a parasite
Cruciferous bug: photo, description, reproduction, how to save the crop and how to get rid of the bug
Bed bug, everything about the insect: description, photo, where they are found, where they come from, methods of control
Italian bedbug - everything about the insect: description, photo, breeding methods
Bed bug reproduction rate
House bugs are lurking blood-sucking parasites of humans. It is quite difficult to detect their appearance in an apartment in a timely manner. Insects lead a secretive lifestyle, but at the same time actively increase the size of the colony. How quickly do bedbugs reproduce? In favorable conditions, at a temperature of 26-30°, 30-42 days are enough for parasites to transform from an egg into a mature individual. Given the high fertility of females, the number of pests grows exponentially. Entomologists have calculated that one female lays 250-500 eggs during its life.
Mating Features
Bed bugs reproduce by traumatic insemination. A male who has reached sexual maturity pierces the integument of the female's abdomen with a sharp copulatory organ. During fertilization, he holds his partner with his limbs. Aggressive males attack not only adults, but also nymphs. Cases of injury to male parasites and other insects (cockroaches) caught in the path of an excited bug are not uncommon. After the puncture, it releases sperm; it remains in the body of insects for a long period. When the gametes enter the body of a male, they are mixed, preserving the genetic material to the benefit of the species.
In representatives of the species Cimex lectularius, between the 4th and 5th abdominal segments there is a notch on the side leading to the copulatory bursa. But the partner does not always hit this exact place with the needle-like genital organ. The unusual method of reproduction looks dangerous to the life of the female. A wound remains at the puncture site, and pathogenic bacteria enter the body.
Nature provides a compensation mechanism. The female body has a special Berlese organ. This neoplasm plays the role of a seminal receptacle. The seed is stored in it for some time. The tissue contains a large number of immune cells that quickly stop invading bacteria. In 2 hours they cope with any pathogen. A special antibacterial enzyme is produced inside the Berlese organ, which preserves the health of females.
Interesting fact. In 1897, zoologist Ribaga discovered an unknown organ in the stomach of a female house bug. The scientist suggested that it serves to create sounds. Upon further examination, there was a supply of sperm inside. The zoologist discovered Berlese's organ, but incorrectly determined its purpose. Only at the beginning of the 20th century did entomologists learn about the traumatic insemination of bedbugs and draw conclusions about the function of the organ.
The entry of male reproductive cells into the body cavity in an extreme situation helps females survive. In case of prolonged hunger, the supply of gametes is spent not on fertilization, but on nutrition. The body digests them instead of protein from the blood. Sperm enter the reproductive organs along with hemolymph. After the eggs are fertilized, the female begins laying eggs. She attaches it in dark crevices. The process occurs daily, the number of eggs laid ranges from 1 to 12.
Information. Before copulation, the male bug needs to suck blood, the female feeds before laying.
What do harmful garden bugs look like and what do they eat?
There are a sufficient number of garden bugs known to parasitize cultivated plants. Moreover, there are known species that cause harm to fruit and berry crops, so to speak, from birth. And there are representatives of individuals who are born to eat wild plants, but at the first opportunity they gladly switch to feeding in nearby gardens and vegetable gardens.
- Green forest bug, popularly called the green garden bug. Here is a living example that easily switches to feeding on garden plants. From birth, it successfully feeds on forest trees and shrubs, but at the first opportunity, with great desire, it will move to your garden plot and will eagerly begin to eat raspberries first, and then everything else.
- The cruciferous bug is an even more harmful and dangerous species of insect, called northern eurydema by specialists. This type of bedbug has external similarities with an ordinary soldier bug, but it causes colossal damage, because feeds on the leaves of radishes and radishes, cabbage and watercress and similar plants. After an invasion of the cruciferous bug, these plants generally die.
- The pear bug - upon meeting it, at first glance everyone admires its lacy and unusual appearance, and is affectionately called the pear bug. However, the nature of this species is insidious and dangerous for pear and apple trees, quince, apricots, plums, cherries and others. The abundance of insects leads not only to the loss of fruits by trees, but sometimes to the loss of the trees themselves by gardeners.
- Berry shieldweed - we have already talked about it above, we will only repeat that it harms the harvest of berries such as black and red currants, however, it will not refuse white ones, raspberries and gooseberries, chokeberries and some others.
- The cucumber bug is very small, no more than 3 mm in length, mainly located on the underside of the leaves and at the same time jumps well and far. That is why you will have to work hard in the fight against the destruction of this bug. The cucumber bug quickly infests large greenhouses, feeding not only on cucumbers, but also on tomatoes, eggplants and sweet peppers.
- The bug is a harmful turtle - we have already mentioned this species. In its classic form, it is practically not scary for gardeners and gardeners, since its main diet consists of cereal plants. However, if food ceases to exist for him, he will easily switch to other plants and, in the company of his brothers, can visit garden plots nearby with fields.
- The horse fly bug is a fairly small insect that has an inconspicuous appearance, but it can cause significant damage to almost all garden plants. Experienced farmers call it “the scourge of all problems.”
- The ringed predator can mainly be found in areas where apiaries are located. The hunter directly hunts the bees themselves, sits on the flowers, awaiting his prey.
Type of development of bedbugs
Representatives of the order Hemiptera are insects with incomplete metamorphosis. There is no pupal phase in their development. Stages of bed bug development:
Information. At temperatures below 5°, parasite eggs do not develop. In this state they remain viable for up to 40 days.
Information. Each stage of metamorphosis requires blood nutrition; without the supply of protein, the process is delayed.
Information. The lifespan of adult house bugs in favorable conditions is 12-14 months.
The full development cycle of a bed bug takes 40-100 days. The large variation in timing is due to the temperature factor. Together with nutrition, it accelerates or inhibits the development of insects.
The development cycle from the egg phase to the adult is called generation. In bed bugs it is multiple; scientists do not give the exact number of generations during continuous reproduction. In natural conditions, insects' life cycle is affected by seasonal changes in weather conditions. Synanthropic parasites in apartments are in comfortable conditions, without sudden temperature fluctuations. They breed all year round.
Two-toothed shieldweed
The two-toothed stink bug belongs to the “forest” group, but is not a pest.
The two-toothed stink bug is a predator that feeds on insects, including its own relatives. In case of hunger strike, he can make do with plant juice. The body color of this insect is brown. A distinctive feature is two sharp spikes on the “shoulders”. The habitat is the same as that of its victims, that is, open forest, shrubs, grass. When you see brown or brown bugs on raspberries, there is no need to rush to destroy them immediately. This may turn out to be an assistant out hunting.
On a note!
Some predatory species of these beetles are specially bred to be released into farmland.
The spread of parasites in the apartment
Experts warn that one adult female is enough to colonize a home with synanthropic blood-sucking parasites. Without information about how bedbugs reproduce, it is not clear that if one parasite appears, how will it produce offspring? Female bedbugs are able to retain sperm throughout their lives, using it in parts to fertilize eggs. After one copulation, they give rise to an entire population without partners.
To actively reproduce, the parasite needs regular blood feeding. A bedbug attacks a person every 2-5 days. Feeding lasts up to 15 minutes, while the female drinks up to 7 ml of blood. She comes out of hiding at night or early in the morning at 3-5 o'clock. The instinct of self-preservation tells parasites when the victim is sleeping and does not pose a threat. After saturation, the insect doubles in size. Having received a high-protein diet, the bug goes into a crevice in the bed or other furniture, where it lays its first eggs. From now on this process will be continuous. Read about the harmfulness of insects in the article “Bed bugs: appearance of blood-sucking bugs, and what harm can they cause to health?”
In the apartment, blood-sucking heat-loving parasites find ideal conditions for life and reproduction. They take root in any room, even with perfect cleanliness. Insects require several conditions:
From the first eggs laid, sexually mature females will appear in 1-1.5 months, ready for procreation.
Where to look for adult bedbugs and offspring
Parasites make a kind of nest near the feeding site. You can find it by smell; bedbugs have odorous glands, from which an oily liquid with a sharp, unpleasant aroma is released. In the process of communication, insects send signals to each other by secretions from the glands. Their composition is close to the chemical formula of pheromones. The presence of a colony is also indicated by black dots left on the surface of furniture or walls. These are insect excrement; the more there are, the more numerous the group of parasites.
The most likely areas where insects can be found:
The appearance of parasites in an apartment is always unexpected. The first sign of their vital activity is bite marks on people’s bodies. Particular attention should be paid to rashes and wounds in the form of paths in children. Bed bugs often enter homes with old furniture purchased from individuals or in a store. They are brought in in the seams of bags or the folds of clothes from their trips. They can even move into the house through ventilation ducts. At the first signs of infestation in the room, begin fighting parasites. It is better to prevent their reproduction than to fight a large colony.
Source
Habitat
Garden bugs have chosen as their habitat areas where various crops are planted, orchards with fruit trees, and forests. Garden bugs are widespread and varieties can be found on every continent except Antarctica.
What does it eat?
The diet of the garden bug is the green part of cultivated plants, fruits and foliage of fruit trees, as well as cereal crops.
Signs of appearance
Regular inspection of plants will help you notice the presence of harmful bugs in the area in a timely manner. At an early stage, you can notice the larvae, which are localized on the back of the leaves. If the lesion is already beginning to gain momentum, then small holes can be seen on the leaves of trees, shrubs and garden plants.
Flower bugs are widespread in Russia, in the countries of Europe and Central Asia, as well as throughout the world. They live in grasses, shrubs, trees, and forest floors. Some species use bark beetle tunnels. Predators can often be found in grain warehouses and other places where their potential prey lives. They overwinter under fallen leaves, in tree bark, and in animal burrows.
What does it eat?
For example, Antokoris oakgrass feeds on the nectar of female willow inflorescences from early spring, as well as the wintering stages of small herbivorous insects. In summer, the predator extracts nectar from flowering grasses, feeds on the secretions of aphids, and continues to destroy insect larvae and eggs. Antokoris is very voracious and, according to research, is capable of destroying up to 95% of wintering eggs of fruit mites.
During the attack, the predatory bug pierces the body of the victim with its proboscis and injects digestive juices into it. After the insides of the insect are digested, the bug sucks them out using the same proboscis. Tiny predators feed once every 5-10 days, larvae more often - every 3 days. If necessary, they can go without food for much longer and even go into suspended animation. During dry and hot periods, bedbugs feed more often, realizing an increased need for water.
The full breeding cycle of bed bugs - what prevents them
Bed bugs love to live in apartments and private houses, poisoning people's lives with an unpleasant odor and constant bites. They feed exclusively on blood, including human blood, domestic animals, rats, and mice. Poorly protected from parasites that feed on them, for example, riders, or external factors. Therefore, bed bugs have an interesting reproduction process.
Parasite eggs
After fertilization, laying occurs on the fourth day. This usually occurs in hidden places close to a person during sleep and rest. These are the internal parts of: sofas, beds, armchairs, chairs. Where there is no light and warmth.
Each time eggs are laid in a new place, which increases the likelihood of survival of the offspring. Externally, eggs look like grains of rice - white oval-elongated capsules. On top they have a sticky jelly-like substance that provides them with fixation to vertical and horizontal surfaces.
There are hundreds of similar clusters of eggs. Because of their dense shell, they are resistant to negative external factors, which is why they are so difficult to destroy. Pesticides used to treat living spaces cannot penetrate inside the egg coating. We must wait until they hatch and re-disinfect.
In such a situation, microencapsulated pesticides with a prolonged spectrum of action are used. The harmful effect lasts up to 3-4 months
To detect nests, it is important to carefully inspect hidden places with a flashlight before sanitizing
Life cycle of bed bugs
The bug does not give birth to live young. Females lay eggs, from which larvae emerge and gradually develop into adults. The total lifespan of a bed bug does not exceed 14 months.
The maturation of the insect lasts up to 35 days - this is the incubation period of bedbugs. Under unfavorable conditions, the time frame may increase to 2-4 months.
The stages of development are:
The house bed bug does not waste time pupating, but immediately becomes a sexually mature creature. The type of development is not complete transformation.
Important! The life cycle of bedbugs can extend by 140-150 days if the insect goes into suspended animation, for example, due to hunger or too low an ambient temperature. For larvae this period is slightly shorter - up to 130-140 days.
Pairing
Mating of bed bugs occurs like this: the male catches the female with a special proboscis that resembles a small needle, pierces her chitin on the abdomen, and then fills the partner with sperm.
He fertilizes up to 150-200 females per day. Sometimes it mistakenly tries to mate with larvae and other males. Females mate once in their lives. A huge amount of seminal fluid enters her body, which is enough for the entire life cycle.
Interesting! The seminal fluid can be used by the female as food during periods of hunger.
3-4 days after mating, the female lays the first batch of eggs. Their size is approximately 1 mm, occasionally reaching 1.5 mm. Such small sizes make finding bedbug eggs difficult.
Parasite eggs are very strong and persistent. They reliably protect the developing embryo from:
If adult insects and larvae quickly die from the effects of certain special pesticides, then the eggs almost always remain in a viable state even after professional treatment of the room.
Nymphs
Outwardly, it is an adult bedbug, but smaller in size and with transparent chitin. The nymph is constantly growing and moving a lot. She needs a lot of food. They feed on the same thing that adult bed bugs feed on—blood. The larvae have smaller food portions than adults, but they “attack” their victims more often due to the need for a large amount of energy for growth.
Interesting! The nymph's bite is very painful. Only adult bedbugs have antiseptics in their saliva; larvae do not have an anesthetic substance.
Adult bedbugs
The size of an adult insect ranges from 4 to 6 mm. The color of the parasite's body depends on when it last fed. If the meal was recently taken, the insect is black in color. As the food is digested, the bug lightens in color and turns light brown when hungry.
Interesting! Only adult insects spread unpleasant odors. The larvae lack glands that secrete a smelly secretion.
Reproduction and lifespan
Bedbugs mate during the warm period of the year - in the spring, the first generation appears closer to summer. Some individuals produce 1 generation of young individuals, others more (2-3). Before mating begins, pests actively feed. After hibernation, they strive to increase their energy level, which will allow the female to lay a clutch; the male facilitates this. In one approach, the bug can leave 30-100 eggs on the leaf (from the back) or fruit.
Mating process
Eggs
They are round-shaped formations, flattened on both sides. The edges of the lid are visible, through which the larvae emerge. Forest bug eggs reach 1-1.3 mm in length. Their color may vary, depending on the type of pest. For example, there are green and brown eggs. Sometimes these formations gradually darken as the end of embryo development approaches. Then the eggs acquire a more saturated shade.
Empty shells remain where they were. They are firmly secured with a special secretion that the females secrete during laying.
Laying eggs
Larvae
Insects do not enter the pupation stage. The larvae emerge from the eggs (shells). Young pests are characterized by the same size as eggs. But they develop quickly - in 1-1.5 months. There are up to 5 stages of molting. On each of them the insect grows up to 1-1.5 mm, sometimes less.
The larvae have not yet formed their outer coverings; the need for molting confirms this.
Externally, the larva is easy to distinguish from the imago. Despite some similarities, such pests are still very different from adult individuals. They are smaller, the color is also often different - darker and brighter. Young insects cannot fly or mate.
Forest bug larvae
Bedbug breeding sites
To successfully breed offspring, parasites need the following conditions in a house or apartment:
An apartment building is an ideal option.
A popular breeding ground for bedbugs is beds and sofas, especially those with large mattresses with lots of holes. Insects often breed in numerous cracks in the walls and on the floor, under the baseboard.
Note! Bed bugs prefer to live in colonies. If traces of insect activity were found, for example, feces, egg laying or shed layers of chitin, then the room is infested with parasites.
Laying eggs
After fertilization, the seminal fluid accumulates in a special section of the female and forms into eggs. For regular laying and reproduction, the individual must eat well. One feast is enough for a voracious female to lay 2-3 ovipositions. The female lays from 6 to 10 eggs per day; during her life cycle she is capable of laying about 500 eggs, which allows the insect population to grow rapidly.
At temperatures from 25 to 30 ° C, egg development ends after 5-6 days; at low temperatures, the time increases to 10-15 days. If the temperature is below 10 °C, development stops and resumes if favorable conditions exist. Temperatures below 10 °C can destroy egg laying and stop the reproduction of bedbugs.
One fertilized female, under favorable conditions, can give rise to an entire colony, the number of which in 2 months will number in the hundreds.
How quickly do bed bugs reproduce?
At one time, the female bedbug lays 1-5 eggs, this happens every day from the day of fertilization. It reaches 70 and even up to a hundred pieces per month. Therefore, they multiply quickly.
During the year, the female gives birth to about 700-800 new bed bugs. The total number of parasites is growing continuously, since young insects also reproduce. As a result, within a few months the number of parasites exceeds several tens of thousands of individuals.
The full development cycle from egg to adult is 30-40 days - after that, the first bugs appear if the premises are infected.
Learning to recognize bedbugs in your area
As soon as it is not popularly called - stink bug, currant bug, stink bug, garden bug. All these are the names of one family of bedbugs, numbering about 4000 species.
- If your plants are parasitized by green individuals approximately 1-1.5 cm long, this means that this is the most common tree stink bug. It received this name because it has a kind of “shield” on its back. The bug feeds on almost everything that surrounds it - it can be trees, garden crops, and even the remains of other insects. Often, it can be found among green raspberry leaves, cereals, fruits and vegetables, and young tree shoots.
- The marbled bug is a type of stink bug that lives in southern Russia, Abkhazia and Georgia. It has a brown color, with small dots, hence its name. Causes enormous damage to citrus fruits, apricots, persimmons, grapes and other fruit trees. It also feeds on corn, tomatoes, and peppers.
- The berry stink bug can be identified by its brighter color - it has a “berry” tint, thanks to which it is well camouflaged in the bites of currants, chokeberries, raspberries, strawberries, sea buckthorn, gooseberries and other berries.
- A harmful turtle is a bug that looks like a small turtle, with a characteristic pattern and shape of the shell. It has a gray-brown color and mainly feeds on cereal plants. When his diet is poor, he eats everything, causing great damage to the country's agriculture.
- Also well-known soldier bugs, red in color, with black dots in the form of a pattern, love to create colonies and feed on the sap of almost any plant.
- The cruciferous bug is almost identical to the soldier bug, it has a red cover, with an intricate pattern, and a large black dot on the back. It feeds on lettuce leaves, cabbage, radishes, turnips, and celery. Plants practically do not recover after it.
- There are also other common species - for example, the cucumber bug. If you find beds of cucumbers with wilted, eaten leaves, it means that they liked the cucumbers, and the cucumbers need proper processing.
What prevents reproduction
Females and males reproduce quickly only in a comfortable environment. When unfavorable conditions arise, insects slow down the rate of population increase.
Temperature
The optimal temperature for the development and life of an insect is +25…+30°C. Until the ambient temperature drops to +10°C, bedbugs will continue to reproduce, but at a slower rate.
This process stops completely when suspended animation occurs, i.e. when the ambient temperature drops to +5°C and below. Frost from -10°C is fatal for bed bugs.
Humidity
Bed bugs feel most comfortable in warm and dry rooms. Parasites cannot tolerate high humidity; the optimal indicators for them are 40-60%. Low humidity is easily tolerated by adult insects; they replenish the lack of fluid by increasing the amount of blood they consume.
The eggs run the risk of dying, because if there is a lack of environmental humidity, they quickly dry out and the embryo dies. If the humidity is too high (70% or higher), the eggs are susceptible to fungal infections.
Lack of food
A bedbug can live without blood for 3-4 days, a larva - 2-3 days. But even a month of hunger strike does not lead to the death of the bed parasite. If the insect does not receive food within 14-16 days, it will fall into a “inhibited” state - suspended animation. In this state, all processes in the body slow down, and nutrient consumption is reduced to a minimum.
Important! With the lack of food, the ability to reproduce offspring stops.
Anabiosis
Anabiosis is the next stage of “slowing down” the life activity of the bug. This state occurs at a temperature of 0…+5°C. Too high a temperature does not lead to suspended animation, it kills the insect. The larva dies at +45°C, the adult bug lasts up to +70°C.
In this state, the parasite stops moving, feeding and reproducing.
Do they reproduce without blood?
Bed bugs are very hardy and easily adapt to external conditions. The lack of food in the form of human blood affects all life processes of the parasite, including the ability to reproduce rapidly. However, this does not mean that the lack of food supply leads to the death of the insect. The bug can live without food for up to 3-4 months. Some studies show that this period is even longer - up to six months.
Of course, the absence of blood does not immediately lead to the loss of the insect's ability to reproduce. However, lack of food leads first to a decrease in the number of eggs laid by the female, and then to a complete cessation of this process. The lack of food has an equally negative effect on males. They gradually reduce the number of mating trips until they stop them completely.
Returning to proper nutrition leads to the rapid restoration of all functional abilities of the beetle. This includes the ability to reproduce.
Methods for controlling green woodworm
Various methods are used:
- chemical (based on insecticides);
- folk
When wood bugs appear in an apartment, how to get rid of them - this problem is solved in a completely different way.
How to poison an insect so that it does not come back
If pests have only recently settled on the site, there are still few of them, or the garden has not yet been infected, then home remedies are used for prevention purposes:
- mustard solution in water (ratio 1:10);
- onion infusion: fill a bucket with peels (up to half), fill with water to the top of the container, after 5 days use the finished product, filter first.
In addition, chemicals are used:
- Aktara;
- Karbofos;
- Karate Zeon.
Green stink bugs can be poisoned using both insecticides and traditional methods.
How to get rid of bedbugs on the balcony
These pests do not need to be killed at home. It is enough to help green wood bugs fly out through the windows. Then you should take care that they do not return - they fill the gaps in the frame structure of the balcony. To drive insects out of cracks, use strong-smelling products, such as tansy and essential oils.
TansyFeatures of appearance and nutrition
The most common garden bugs that summer residents find on their plots are pear and cruciferous, berry and cucumber, green and ringed bugs, as well as horse flies and harmful bugs. All these representatives have one feature in common - the secretion of secretory fluid, which has an unpleasant specific odor.
The forest green bug has a bright color, which allows it to be invisible among foliage and grass. In autumn, the insect's body changes color from green to brown. It is interesting that garden bugs of this type eat absolutely any plant. They like to feast on park and wild plantings, as well as shoots of garden plants or shrubs. In addition, they are frequent “regulars” of raspberry fields.
Appearance of the Green Woodbug Cruciferous bugs typically live in the leaves of lettuce, radishes, or radishes. They are easily recognized by their black and red color with a symmetrical pattern, reminiscent of another common type - the “soldier”. The pear bug has an unusual appearance: in addition to its light brown color, the body is decorated with a translucent edging, and the back is decorated with an interesting pattern. Its presence on trees is evidenced by destroyed vegetation and rapidly falling leaves.
Berry stink bug can be found on the leaves of currants, raspberries or gooseberries. It differs from its relatives in its pentagonal body shape with round corners. Thanks to their color, they have the ability to hide in bushes, remaining invisible to humans. The size of the cucumber bug (2-3 mm) also gives it the ability to harm cucumbers, tomatoes, eggplants and sweet peppers growing in garden beds for a long time with impunity.
Gardeners can very rarely encounter the pest bug on their plots. Typically, the insect lives in crops of cereal plants, which constitute their diet. But horseflies feed on different types of plants, so they harm both fruit trees and vegetable crops. Fighting it is quite a difficult task, since it is not immediately detected due to the green color of its body, which allows it to remain invisible on the leaves.
The ringed predator does not pose a threat to plants. He usually lives near apiaries and hunts bees. This bug waits for its victim, hiding in the flowers of plants. The insect is easily distinguished from other hemipterans by its bright black and red pattern on its back.
Bee hunter - ringed predator
How to get rid of uninvited guests in the house. Types of pest control chemicals
If there are blood-sucking insects in your home, you need to get rid of them as quickly as possible. Such pests are susceptible to chemicals - insecticides. Poison is delivered to habitats in different ways:
aerosols are popular due to their high efficiency, such preparations are sprayed over all surfaces (except woven products), the death of pests occurs in a few minutes/hours; concentrated liquids - used to prepare a working solution, it is important to follow the recipe, the ratio of insecticide and water must not be violated, this may cause a decrease in the effectiveness of the product; crayons - applied to surfaces where insects usually are: along baseboards, on furniture frames, back walls of cabinets, chests of drawers, paintings, photographs;
- powders have the disadvantage of being able to treat only horizontal surfaces; in addition, preparations in this form do not allow full use of furniture and objects - particles are carried everywhere;
- hot and cold fog are relatively new types of products, sprayed using special equipment, which releases a fine suspension that remains in the air for a long time;
- smoke bombs are the most toxic method; according to the principle of action and structure, the released substance resembles a gas - the insecticide particles are so small that they penetrate everywhere.
Fog is considered one of the effective methods against bedbugs.
Harm or benefit of a bug
Let's consider how harmful forest bugs are or maybe they are beneficial?
Harm
I would like to say right away that the forest bug is absolutely harmless to human health, unlike its fellow bed bug, which feeds on the blood of people and animals. The main harm caused by a forest visitor is the spoilage of berries, from which the insect sucks out the juice, and in addition leaves a sharp unpleasant odor on them, after which the collection and consumption of such berries becomes impossible; or rather, you can collect them, but there is unlikely to be a desire or appetite to eat them. The poison injected by insects into the stem of the plant is destructive for young shoots.
Benefit
But here’s what’s interesting: that very specific smell also brings benefits to a person; it is known that vodka infused with bedbugs is used by people to treat alcohol addiction, the taste of vodka is preserved, but the bedbug “aroma” of drinking such a drink causes a persistent aversion to alcohol in the future. The bug's "aroma" can repel other insects that are unfavorable to humans.