Springtails are small pests that many gardeners have encountered. Springtails or podura, as they are also popularly called, usually live in flower pots. This insect prefers to settle in the upper layers of the soil, where there is high humidity. After all, it is excessive watering that causes springtails to appear. A small accumulation of dura will not cause much harm to the plant. However, a rapid increase in the population can lead to damage to the root system of the plant, resulting in its slow growth and even death.
Description of springtail
Springtails, or springtails, are extremely widespread, especially in temperate latitudes, there are many of them in the tropics, they are found both in the Arctic and Antarctic - wherever there are at least mosses and lichens.
This is interesting! Collembolas, or springtails (Collembola) - a subclass of arthropods, in the modern classification classified as cryptognathous. Currently, scientists have described more than 8 thousand species of springtails.
Springtail Tomocerus vulgaris.
These insects most often live among rotting plant remains and in the surface layer of soil, but many also live deep in the soil, often penetrating deeper than other animals. Among springtails, there are also those that live on the surface of plants, and there are even those that have passed on to life on the surface of a film of water.
The number of springtails is also very large. For example, in the soils of forests and meadows there are often several tens of thousands of springtails per square meter. Springtails are very diverse both in body shape and color: as a rule, species that live in the soil and do not leave it are white, springtails that live on the surface of green plants, greenish, but among those living in the forest litter or in the felt of dead herbaceous plants , along with grayish and brown ones, brightly colored or metallic shiny species are not uncommon.
Springtail Orchesella villosa.
Those springtails that live on the soil surface can move in a very unique way. As already noted, on the lower surface of the posterior end of the abdomen there is a special organ not found in other arthropods, the so-called “jumping fork.” In a calm state, it is tucked under the abdomen. Quickly straightening this “fork”, the collembola pushes off from the object on which it sits and makes a sharp jump.
Springtails that stay on the surface of the water (there are some) can jump, pushing off even from the surface film of water - their body is not wetted by water.
White springtails, which always live in the ground and do not appear on the surface, do not have a "jumping fork"; they can only crawl with the help of short chest legs, often not even noticeable when viewed from above. A number of springtails harm plants, such as green smintur onychiura , which eat en masse into the succulent roots of greenhouse plants . Some species probably cause harm indirectly by spreading fungal spores that cause plant diseases.
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of insects in the bathroom, just follow these recommendations:
- Do some minor repairs. Once you've painted, sealed all the cracks and cracks, and sanded the grout, there will be fewer hiding places and ways for pests to enter your home. It will also lower the humidity level.
- Maintain good hygiene. Do not leave wet towels, rags, or scraps of paper on the floor. Clean regularly. Treat seams and crevices with disinfectants. Use bleach once a month when cleaning.
- Determine the humidity level and temperature. To do this you will need a thermometer and a special device. Measurement of indicators should be carried out within 3-5 days. If small bugs appear in the bathroom due to humidity and heat, it is necessary to constantly ventilate the room. If necessary, install a fan to promote air circulation if the ventilation in the bathroom does not cope with this task.
- Do not dry wet clothes or towels on the pipes. Moisture enters the air and settles on surfaces.
- Avoid condensation. If it does form, arrange forced drying and ventilation.
Is it necessary to fight springtails?
In general, springtails are not only harmless, but even useful: they contribute to the decomposition, transformation into humus and mineralization of plant residues and, according to modern data, play a very important role in soil formation. So don’t rush to remove your springtail with the fury of a tiger, as the chemical may be more harmful to your pet than the springtail itself .
Collembola genus Paratullbergia callipygos subfamily Onychiuridae
Green minthurus, alfalfa flea beetle (Sminthurus viridis)
Habitat
Springtails inhabit mainly the litter and upper soil horizons. They prefer damp habitats and are found on tree trunks, rocks, mosses, and lichens. There are specialized species that inhabit the intertidal zone on the seashore, on the surface of reservoirs (Podura aquatica), in the grass (Sminthuridae), on the snow in the mountains (Entomobrya nivalis), in caves, in swamps and other life forms. Deep-soil species live at a depth of more than a meter. Most springtail species are very sensitive to desiccation.
How to recognize collembola?
The size of springtails ranges from 0.2 mm to 10 mm (very few species). Springtails prefer a secretive lifestyle in places with high humidity. They live in the soil, under the bark of dead trees, in leaf litter, and in cracks in stones. Springtails feed on fungal mycelium, bacterial plaque, algae, mosses, and lichens. Only a few species can feed on higher plants. Unfortunately, this is exactly what flower growers are faced with.
Identifying these representatives of the animal world is quite difficult. There are many views on the taxonomy of springtails, as a result of which many synonymous names are mentioned in the literature.
The small size and secretive lifestyle of springtails make it difficult to study them. The lack of accessible and complete identification literature on these groups of insects makes it almost impossible for non-professionals to identify springtails.
Fortunately, the biology of soil springtails is similar enough that precise identification is not required. It is enough to know that these are springtails and not to confuse them with other insects (thrips, rootworms) and mites. To develop adequate control measures, if necessary.
Water springtail, or water forktail (Podura aquatica).
Mealybug
Small white bugs in the soil of indoor plants may be mealybugs. The pest can be recognized by the thin web that entangles the leaves of the plant. The insects themselves are up to 4 mm in size, so they are easy to see without a magnifying glass, especially if their population is large.
Pests prefer to settle in the axils of leaves, and +25 degrees is considered a favorable temperature for their active reproduction. Scale insects suck nutritious juice from leaves and stems, which can soon lead to the death of the plant. The following methods are used to combat the parasite:
- Chemical preparations, such as Aktara, Fitoverm, Calypso, Biotlin. Plants should be treated with them according to the instructions indicated on the package.
- Among folk remedies, the advice to treat the leaves with garlic infusion, soapy water, lemon infusion, and horsetail decoction is especially popular.
Mealybugs are easiest to control at an early stage, when the insect population has not reached its maximum size and has not destroyed the plant.
Springtail structure
Springtails got their name due to a special jumping organ (jumping fork) located on the underside of the abdomen. The fork is held in a “cocked” state by a special hook. If necessary, the fork is released and, hitting the ground, throws the collembola forward and upward. Some springtail species have an elongated fusiform body shape. They are traditionally called fools . The other part is distinguished by a rounded abdomen and a spherical body; they are usually called sminturs . In a strict sense, this is not entirely correct. Sminturs are only part of the springtails that have this spherical body shape.
Springtail larvae completely repeat the body shape of adult individuals, differing from them only in size and maturity.
The color of springtails (podur and smintur) is very diverse. Most species have a whitish, gray, yellowish, or brownish color, sometimes with a metallic sheen. Representatives of some genera may have a marble pattern, or less often, one or more transverse stripes. Some mints may have a clear dot pattern.
When growing indoor plants, most often found are white, grayish in color, sometimes with a greenish or silver-metallic sheen.
Is the pest dangerous?
Many people are puzzled by the question of why double-tailed milk is dangerous for humans. The damage caused by double-tailed insects includes not only damage to indoor plants, vegetables in the garden, as well as fruits and berries in the garden.
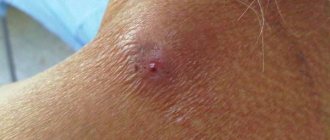
The presence of pests in the home increases the risk of spreading infectious bacteria during a bite. After all, double-tailed fish bite quite painfully, pinching soft skin tissue with their claws. Large specimens with such a grip can even damage the integrity of the skin, resulting in the appearance of two barely noticeable wounds. A photo of a double-tailed bite can be seen below.
Double-tailed bite
Symptoms of a double-tailed bite in humans may be as follows:
- The presence of microscopic wounds at the site of the bite, which are accompanied by severe itching.
- As a result of scratching, the damaged area begins to redden and swell.
- People with allergies may develop fluid-filled blisters. The process of opening the vesicles is accompanied by severe painful sensations. In such places, long-term non-healing ulcers can even form, causing a person great discomfort.
The question of what to do if bitten by a two-tailed fish arises by itself. Despite the fact that the insect is not poisonous, the situation cannot be ignored. Treatment for a bite involves treating the damaged area with an antibacterial or disinfectant, followed by taking an antihistamine. If your general health worsens, you should consult a doctor. Neighborhood with such insects is undesirable for humans, so they should be gotten rid of using folk and chemical means.
Harm from springtails
Single damage caused by a few podurs cannot cause much harm to the plant. Large poduras (1-1.5 mm) can only cause real and significant damage to seedlings. The seedlings at the stage of opening the cotyledon leaves are completely eaten by springtails.
Green smintur, alfalfa flea.
The harm from poduras is also significant in cases where there are too many of them and the room temperature is low. Plants weakened by unfavorable conditions slow down their growth and development and cannot regenerate normally. In such conditions, multiple damage caused by podras becomes an open gate for a wide variety of fungal and bacterial infections, which can not only weaken, but also destroy part of the plants in your collection.
Causes
Springtails in flowers
Springtails settle in indoor flowers only when there is a favorable environment for their habitat. Usually a fool attracts:
- excessively wet soil, excessive watering and a poorly equipped drainage system are some of the important reasons for the appearance of springtails;
- damp air in a room or greenhouse;
- presence of moss;
- excessive use of organic fertilizers;
- rotting remains of natural fertilizers; tea leaves in combination with stagnant water in the soil or tray are especially dangerous;
- low temperature in the room.
How to get rid of springtails?
Podura are almost always present in volumes with mature plants, and it is not necessary to conduct a directed fight against them with normal agricultural technology. The main measure to combat outbreaks of podar numbers can only be compliance with the conditions of correct agricultural technology for growing plants.
The substrate should not contain a large number of actively decomposing components (unrotted leaves, tea leaves, decorative sawdust). The volumes must have good drainage to prevent stagnation of moisture in the soil. Watering is moderate, as the soil dries. The volume of the pot should correspond to the size of the root system. The place not occupied in the near future by plant roots will be occupied by fungi, bacteria, algae, the earth will turn sour, and fools will breed.
The number of duras remarkably restrains a number of predatory mites, which are also almost always present in the soil.
If there are too many springtails, change the soil to a new one. If history repeats itself, then reconsider the soil composition and watering regime.
In cases where you need to take urgent measures to reduce the number of poduras, you can use systemic insecticides (Mospilan, Aktara, etc.). You can restrain and somewhat limit the number of fools by also adding citramon or askofen to the water for irrigation (half a tablet per 2-3 liters of water).
Centipede from the class Symphyla and springtail Poduromorpha.
When sowing Saintpaulia and Streptocarpus seeds, the soil must be thoroughly steamed. The container in which the seeds are sown must be sealed and have no drainage holes accessible to the pest. It is especially important to comply with these requirements when there are few seeds or the germination rate of the seeds of a given hybrid is very low.
Did you like the article? Share with your friends and like!
Facebook Twitter VKontakte
NEWS DELIVERY BY MAIL IS CONVENIENT
When you subscribe, you will receive an email about new articles posted on the site over the past two weeks.
Mechanical methods of struggle
Poor quality care, accumulations of dried leaves and excess moisture create ideal conditions for the growth of houseplants. Therefore, to eliminate pests, it is necessary, first of all, to regulate watering, which is the main cause of increased soil moisture. Deprived of their usual and comfortable living conditions, springtails will no longer disturb the plant.
There are other ways to get rid of the fool:
- It is very important to comply with indoor humidity levels. To do this, you should ventilate the room more often, dry clothes outside, and provide access to sunlight. A special device that absorbs excess moisture will help regulate the humidity level.
- Sprinkling the soil with ash or sand is one of the most effective methods of killing podura. It can be used for almost all plantings. The exception is plants growing in acidic soil. These include camellia, gardenia or azalea.
Camellia, gardenia and azalea - To get rid of pests, just place the pot with the plant in water. After that, all that remains to do on its surface is to collect the floating springtails.
- Particular attention should be paid to the drainage system. After all, it is the clogging of the holes at the bottom of the flowerpot that causes water to stagnate. A few pebbles, which are placed at the bottom of the pot when replanting the flower, will help to avoid this.
- Replacing the substrate is another effective method to get rid of springtails. It is important not only to remove the contaminated soil, but also to thoroughly rinse the root system.
- You should also not use organic fertilizers too often. Residues from tea leaves or ground coffee can cause the development of mold or mildew, so they are added to the soil no more than once a week. After 2-3 days, the organic particles are removed and the substrate is carefully loosened so that the soil is enriched with oxygen. It is important to eliminate all factors that contribute to soil decay and mold.
- There is another original folk method of getting rid of the fungus, which is safe both for the plant and for the person himself. To do this, you will need a raw potato, which is cut into two parts, each of which is placed cut side down on the substrate. If you lift these halves after a few hours, you will see a lot of pests on them. After which the bait should be shaken off or washed off with water and the “bait” should be installed again.
Reproduction and development
Springtails are dioecious animals. They have external fertilization with a complex behavioral mechanism accompanied by “rituals”. The male deposits a spermatophore on plants or soil, and the female captures it with the genital opening. Eggs are very sensitive to environmental humidity. Development without transformation: springtails emerge from the egg, similar in structure to adult individuals. Many species of springtails, mainly deep-soil ones, develop parthenogenetically. Springtails molt several times throughout their life.