Lice are unique arthropod insects whose life is directly related to the human body and blood. They live all over the world. The scientific name for lice is Anoplura. Lifespan is a little over a month. Lice are very difficult to get rid of, they multiply quickly, and their larvae cannot be destroyed with most modern drugs.
In Rus', it was believed that a person with a large number of lice on his head was very lucky and happy. And according to Slavic superstitions, lice dream of money and wealth.
Nowadays, few people would agree that having lice is a great happiness. On the contrary, these parasites are very feared, and the word “lice” does not have the most pleasant connotation. People infected with lice try to hide the symptoms and do not tell anyone about what happened. It is believed that these insects only live in the hair of people without a specific place of residence. But that's not true. In this article we will tell you in detail about the lifestyle of lice, where they come from, what troubles they can bring to a person, who most often gets them, as well as how to properly remove lice and nits at home using chemicals and folk recipes.
Appearance of lice
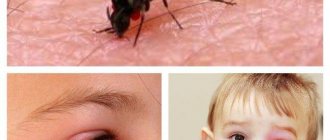
Lice are very small creatures, ranging in size from 0.4 to 5 mm, with a pronounced abdomen, but a small head and chest. The eyes are very small, vision is poor. Oriented by smell. Males are smaller than females. Surprisingly, lice have wings, but they are so small and atrophied that they are unable to fly.
The oral apparatus of lice is of the piercing-sucking type with a proboscis and two needles. When a louse feeds on blood, its proboscis extends from the head capsule and attaches itself to the puncture site of the skin. There are also hooks on the proboscis to securely fix the parasite on the victim’s body. When bitten, saliva is released, which prevents blood clotting and causes irritation and itching on the victim's skin.
Please note: lice cannot completely penetrate human skin. Only the proboscis penetrates the epidermis and pumps out blood.
Attachment to the hair is provided by tenacious and strong three pairs of legs with claws. Lice move at a speed of about 20 centimeters per minute. Lice attach their offspring in the form of nits (i.e. larvae) to the hair using a strong adhesive substance. The female can lay several hundred eggs, which will hatch in 4-16 days under comfortable conditions.
What threat do they pose?
The immature nits themselves do not pose a threat, with the exception of the unattractive appearance of the hair and white formations in it. But when the louse begins its parasitic life, symptoms appear that can significantly worsen the quality of everyday life. These symptoms include:
- almost constant itching of the scalp;
- infection of scratches and wounds, their infection and suppuration;
- sleep disturbance;
- inability to concentrate;
- irritability, nervousness.
Sometimes typhus or age-related typhus can become a complication of pediculosis. Infection of damaged skin after a louse bite, which is dangerous to health, occurs as a result of contact with the waste products of parasites, that is, with liquids and feces. The main unpleasant consequence of infestation with lice and nits is constant discomfort and apparently dirty hair.
Features of the life cycle of lice
Lice are extremely tenacious: they can easily withstand the low temperatures that a person finds themselves in, and with him they can stay under water for a long time. Evolutionarily, insect parasites have developed so much that nits, as their eggs are called, are much more resistant even to chemicals than adults, as well as larvae. With a special composition, they are firmly glued to a hair or thread of clothing, from where they are quite difficult to remove.
The lice's diet consists entirely of blood, which they suck, and the person feels itching on the skin from the bites. The insect lives for about 38 days, during which time the female lays about two hundred eggs. After a week, young individuals emerge and continue to develop.
These features of the life cycle of parasites are what we pay attention to when fighting them: lice are removed within a month. The more effective the drug and the more thorough the hair treatment, the faster you can get rid of lice and nits.
Symptoms
Pediculosis can be detected by visual examination.
- More common head type of disease. To examine a person, you should sit him on a chair under a bright light and use a fine comb to examine strands of hair. Unlike dandruff, lice eggs are difficult to remove from hair, and when crushed they make a characteristic clicking sound. Clinical manifestations of pediculosis depend on the age of the patient, the degree of damage, the type of pathogen and its location.
Lice: photo in hair
Head lice is accompanied by severe itching. The patient scratches his head all the time. At the sites of bites, the skin is damaged and covered with crusts; such lesions are observed behind the ears, at the temples, and on the back of the head. The hair follicles are inflamed. On the head of a child or adult, you can find lice eggs - nits that are white, gray or yellowish in color.
- Clothes This type of disease affects the skin surface of the back, neck, abdomen, lower back, groin area and armpits. Parasite bites cause small rashes similar to mosquito bites.
Photos of linen (body) lice bites
Often they are accompanied by pustular inflammation and scars. Over time, body lice leads to peeling of the skin.
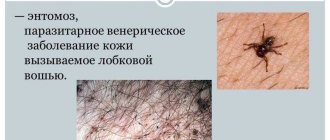
- Pubic the form of the disease is characterized by slight itching, round spots of a grayish tint at the bite sites.
Lice are often found at the root of the hair and do not move much.
The presence of lice always makes a person disgusted with himself. Itching interferes with sleep, the patient quickly gets tired and gets irritated over trifles. He develops apathy, depression, and psychosis .
More than 75 thousand parasites can cause human death, however, psychological and neurological factors sometimes become the cause of death.
Reproduction
A single mating of adults leads to complete insemination of all eggs of the female, who will be able to lay more than hundreds of nits over the rest of her life. Re-pairing is not required.
If just one fertilized female louse lands on a person's hair, after two weeks there may be 10 to 50 lice on the head.
Within a few hours after insemination, the female begins to lay eggs, attaching them to her hair, about 2-5 eggs per day.
Louse lays eggs on hair
After 7–11 days, the upper lid of the egg bursts and the nymph hatches. She begins to suck blood almost immediately after hatching, thanks to which she reaches adulthood in 8 days. If the louse does not find a food source, after about 18 hours it loses its ability to suck blood due to dehydration and dies.
Short description
Lice (called Anoplura or Siphunculata in Latin) belong to the suborder of ectoparasites and belong to the order Lice. The main source of food for these insects is the blood of the host (human or animal), which they suck after piercing the skin.
Doctors call the disease caused by lice “pediculosis.” In general, 3 types of these parasites most often live on the human body (head) and near it. These include: head, body and pubic lice, which differ in location. Let's describe each of them in more detail.
What do they eat?
Lice feed exclusively on blood (mainly human), their oral apparatus is adapted specifically to pierce the skin and pump out blood. Other power sources are not available to them. They cannot feed on hair, skin or dandruff as some people believe.
Lice feed about 5 times a day every 2-3 hours. In one suction, a louse can drink approximately 0.5 mg of human blood. Saturation with blood allows parasites to reproduce and lead an active life.
How long do lice live and what causes them to die?
As mentioned earlier, the average lifespan of lice is 38 days . At the same time, a louse can go without food for 10 days if the ambient temperature is 10-20 degrees Celsius.
Lice die at elevated temperatures - from 44°C .
These parasites are able to survive in water for about two days , floating on the surface. This is how they are transmitted from person to person in the pool. Cold water is also not scary for them.
Lice cannot survive on a person's head if they are shaved bald. They will have nowhere to hide and secure offspring, and adult individuals will be immediately discovered and destroyed.
Some modern drugs can remove lice in one or two applications. We will talk about the choice of drugs below.
Where do lice come from in humans?
Lice spread mainly through direct contact with an infected person, mainly in families, in kindergartens and schools, dormitories, and holiday camps; to a slightly lesser extent through various items: combs, brushes, hats, scarves, personal items and bedding. If lice get on the collar of your clothes, they can crawl onto the clothes of other people in shared lockers or changing rooms.
Lice can even be transmitted through pool water if an infected person has swam there. Lice are able to survive on the surface of the water for up to 2 days, waiting for a new victim.
Pubic lice are most often transmitted during sexual intercourse, less often when swimming in a pool, and body lice through clothing or underwear.
Who gets it most often?
Most often, lice appear on the hair of children 2 - 12 years old . The reason for the relatively easy transmission of lice in children in this age group is that children often touch their heads when playing games and do not bother to use personal hygiene products. A child can calmly dry himself with someone else’s towel or comb his hair with a friend’s comb.
Does the appearance of lice depend on the time of year?
As surprising as it may seem, in winter the incidence of head lice is higher than in other seasons. This is probably due to the fact that in winter they wear hats, and children often try on other people's hats. In the summer, haircuts are usually shorter, and there is much less clothing on which lice can spread.
Prevention
The use of special medications does not protect against re-infection with parasites. Therefore, it is important to follow preventive control measures, which include the following recommendations:
- It is necessary to regularly examine the hair and skin of a person who has recently suffered from the disease.
- It is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene, regularly wash clothes and bed linen, and iron them.
- You should wash your hair at least once every seven days.
- You need to use only your own things and not share them with another person. You cannot wear someone else’s headdress or use accessories from people you don’t know well.
- It is necessary to avoid casual sex and close contacts with strangers.
- It is necessary to periodically clean outer clothing and upholstered furniture, and ventilate the rooms.
- It is necessary to limit communication with people who live in unsanitary conditions.
- It is recommended to take a bath with essential oils. Their smells drive away lice.
Schools and kindergartens conduct regular inspections to detect lice in children's hair.
But none of the preventive measures provides one hundred percent protection against the disease, because you can become infected with it at any time and anywhere. Video:
How can you tell if you have lice?
Symptoms indicating the appearance of lice on the head:
- Itching that gets worse at night.
- Pink spots on the scalp with a small red dot in the middle are signs of lice bites.
- Small beige or white “pebbles” on the hair are nits. Fixed very tightly. The presence of nits indicates that the lice infection occurred several days or even a week ago. They cannot be crushed and are quite difficult to tear off from the hair.
How to get rid of lice?
Pediculosis will not go away on its own. Over time, the number of insects increases, the number of bites increases, and the itching becomes constant and unbearable. Control methods are divided into two types - mechanical and chemical. Folk recipes can also be classified as chemical methods, but we will consider them separately.
Mechanical methods
Typically, mechanical methods mean hair cutting, shaving and combing out parasites with a comb, but they can also include thermal treatment with a hair straightener or tongs. Hair cutting at the root is the cheapest and most effective treatment method, but it is not suitable for everyone. Women and girls will not want to lose their hair, and not all men are ready to go bald.
Chemical and mechanical methods must be combined. Just treating with a drug from a pharmacy will not be enough; you need to comb out dead lice and their larvae from your hair. The fact is that most drugs are not capable of destroying nits; their shell reliably protects the offspring from chemical exposure.
Don't expect to get by with a regular comb. Nits must be combed out with a special comb with very frequent teeth located almost close to each other.
Chemicals
There are a large number of modern drugs for head lice; they differ in cost, consistency and method of application. The most common types of medicinal formulations can be distinguished:
- Shampoos are the most popular, inexpensive and quite effective products when used correctly and following all the procedures specified in the instructions. Here are some of them: Hygia, Paranit, Lavinal. Shampoos specifically designed for children are sold separately.
- Sprays are more effective than shampoos, but are more difficult to use, are difficult to wash off and can cause unwanted allergic reactions. Usually a comb is included. The most famous: Paranit, Lavinal, Nyuda, Para Plus.
- Aerosols used to treat contaminated clothing. Someone even uses Dichlorvos against lice.
- Creams are less common than shampoos and sprays, but they are not inferior to sprays in effectiveness. Among them: Nix, D-95.
- Combs - designed for combing out bloodsuckers. They differ from ordinary ones in that they have very frequent teeth that detach the nit from the hair using mechanical pressure. But this is an auxiliary product used in combination with chemicals, most often included with the product.
Linen lice are removed by thoroughly washing and ironing bedding or clothing. Temperatures above +60 and below -10 °C are destructive for parasites.
Traditional methods
Although folk remedies can be recommended by most representatives of the older generation, they cannot be called particularly effective. Their main advantage is accessibility, but they can cause harm or, at the very least, be useless. Here are some common folk remedies for lice and nits.
- Kerosene - smear it on your head, wrap it around your hair and leave it for 2 hours. After treatment, the substance must be washed out for a very long time, besides, it damages the hair and can leave a chemical burn on the scalp.
- Cranberry juice has a depressant effect on lice and detaches nits from the hair, as the acid dissolves the adhesive. All that remains is to comb them out with a fine comb.
- Vinegar 6 or 9% acts similar to cranberry juice. Take three tablespoons of vinegar per 300 ml of water and apply the mixture to the scalp. The composition dries out the scalp greatly.
- A mixture of pomegranate juice and mint decoction, in a ratio of 1 glass to 3 tablespoons, is boiled for more than 10 minutes. Moisten the hair with a warm decoction and rub it into the skin.
- Hair coloring will not prevent lice. Only very caustic and harmful paint can kill 40-80% of parasites. This method cannot be considered effective
All folk remedies involve wrapping the head in a towel for up to two hours. But in children it is necessary to check the condition of the skin every 30–40 minutes to avoid burns.
We do not recommend resorting to traditional recipes if it is possible to purchase a safe and effective medicine at the pharmacy.
Stages of lice removal
It is better to first destroy adult insects and nymphs, and then nits. Shampoos and sprays usually contain combs in the package, which should be used to comb out lice and nits after treating the head. If the infection process has just begun, they are combed out within three to five days. Combs with long rather than short teeth give quick results.
If after one wash with an insecticidal agent and combing the insects survive, you should treat your hair again after a week. And comb out again, since initially some nits may not be combed, and larvae will hatch from them.
Carefully study the composition of the drug, pay attention to contraindications, check in advance for an allergic reaction on the skin of the elbow. Follow the rules of use described in the instructions. And best of all, consult a doctor before starting treatment!
Prevention of lice is to follow the rules of hygiene: use only your own things, swim in the pool with a cap and avoid untidy people.
Treatment methods
There are several ways to rid the skin of nits, lice, and, accordingly, the symptoms accompanying the disease, the most unpleasant of which is the constant persistent desire to scratch your head.
- The mechanical method is combing with a specialized comb with a tooth frequency of 0.2–0.3 mm. This method is the safest. This comb can be purchased at any pharmacy.
- Using shampoo will have a fairly strong effect, removing a significant part of the parasites, and will be an excellent preparation for subsequent combing.
- After combing and washing the head with a special shampoo , some of the nits may remain on the hair. In this case, the removal process can be continued using chemical medications. If you decide to use only pharmaceutical medications, relief can occur within a few uses. They will help get rid of head lice at home.
You should not abuse chemicals, as they can cause significant harm not only to parasites, but also to human hair and skin.