The moose fly, or moose tick, is a representative of the Bloodsucker family. The ectoparasite has two other names: moose louse, deer bloodsucker. It feeds on the blood of warm-blooded animals, although it can harm humans, but competent control will help to avoid negative consequences.
moose fly
Natural habitat of the moose fly:
- North America;
- european part of Russia;
- Siberia;
- Primorsky Krai;
- north of China.
The number of insects in a certain area directly depends on the number of elk and deer.
Moose fly: description of appearance, photo
The parasite has an external resemblance to flies until it sheds its wings.
Appearance of a moose fly
What does a fly or moose louse look like:
- individual length – 3–3.5 cm;
- flat body shape with a dense shiny leathery cover of light brown color;
- compound eyes, consisting of 2.5–3 thousand facets, are located on the forehead on the sides of the head, occupying 25% of its total surface;
- there are also three simple eyes on the head;
- the oral apparatus resembles the proboscis of an autumn lighter;
- wings – transparent, developed, dense, 5.5–6 mm long;
- legs with asymmetrical claws with thickened hips are located on the sides of the chest;
- The abdomen is elastic, so it can become larger in size after eating.
Useful video
What does a moose fly look like and how to recognize it in the video below.
Sources
- https://ParazitDoma.ru/vshi/losinaya-vosh
- https://misterklop.ru/klesshi/olenya-krovososka-ona-zhe-losinyj-kleshh-s-krylyami-ona-zhe-losinaya-bloha-ona-zhe-muha-kleshh-kak-ponyat-kto-presleduet- zhivotnoe-i-chem-opasno-dlya-cheloveka-osnovnye-metody-borby-s-nasekomym
- https://notklop.ru/vshi/vidy-vshej/losinye-vshi/
- https://zelenplaneta.ru/vshi/losinaya-vosh.html
- https://nasekomye-vrediteli.ru/losinaya-muha.html
- https://nowifi.ru/pervaya-pomosch/ukusy-i-allergiya/153-losinye-vshi.html
- https://netblohi.ru/vshi/sredstvo-ot-losinyih-vshey.html
- https://lifeinsect.ru/ukusy-losinoj-vshi.html
- https://yachist.ru/parazityi/predstavlyaet-li-opasnost-dlya-cheloveka-losinaya-vosh/
- https://hlopklop.com/o-vshah/losinye.html
Why is the deer bloodsucker dangerous for animals?
In large quantities, moose ticks systematically drink the blood of animals, as a result they become restless, stop sleeping and eating normally, as a result of which exhaustion occurs, and the growth of young animals slows down. In addition, regular blood loss can lead to their death.
Deer is the main host and supporter of the deer bloodsucker
The deer bloodsucker can be found on the body of the following animals:
- roe deer, deer, elk, deer - representatives of the family of artiodactyl mammals;
- cattle;
- wild boars, bears, dogs, foxes, badgers, goats, sheep and others - their parasitism was noted.
Insects drink the blood of animals about 15–20 times a day. Sexually mature females feed more often than males. When it comes to pets, it is impossible to specifically prevent the appearance of parasites. A person can save them from the long-term presence of deer bloodsuckers using special aerosols and sprays to kill insects such as flies, mosquitoes, and ticks.
How long do lice live?
The lifespan of lice, among the species studied, is most often 2-4 weeks, the maximum is about 2 months. The lifespan of males is significantly shorter than that of females.
Without food (without humans or animals), lice do not live long: from 1 to 7 days (according to some sources, up to 10 days). The higher the air temperature and dryness, the shorter the lifespan. Newly hatched larvae, having no host, die in a shorter period of time: from 12 hours to 4 days.
Lice can live in water for 1.5-2 days, eggs - up to 3 days. Pinniped lice survive in water because they have special bristles that accumulate oxygen for respiration during the period when the owner is in the water. In addition, parasites live near the nostrils of pinnipeds, and when the owner dives under water, the insect hides in an air-filled nostril closed by a valve.
Are moose flies dangerous to humans?
Moose fly on a person's finger
Moose ticks attack not only animals, but also people, usually in forests, during daylight hours and in calm weather. Often there is a massive attack of parasites on a person, their number can reach up to 120 pieces. in one minute.
Apparently, when choosing an object, the deer bloodsucker is guided by the size of the target, since it has been observed that it attacks children under eight years of age much less often than adults. Moose people are most attractive to moose flies.
When an insect lands on a person, it sits motionless for the first few seconds, and then begins to quickly move around the body, mainly trying to get under clothes or into hair. It will not be possible to get rid of the parasite even with sudden movements.
Insect lifestyle
The deer bloodsucker is a social insect; not only are the parasites capable of creating married couples, but if necessary, they can unite in flocks and attack the victim all together. The habitat of the moose louse is darkness, warmth and high humidity, in other words, the undergrowth. Bright light does not scare them, so the moose lice is a diurnal insect. Having tracked a deer or elk by smell (the fly also has excellent eyesight), the louse flies onto its skin, buries itself in the fur and can live like this for the rest of its days. Since entomologists have not yet studied this insect quite well, there is a version that the deer fly, elk louse and elk bloodsucker are not different forms of one insect, but different insects in principle.
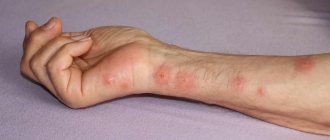
Human reaction to a moose tick bite
Swollen red spots - a reaction on the human body after being bitten by an elk fly.
The deer bloodsucker, or elk fly, has a flat body with dense cover, and tenacious marigolds are located on its legs. When it settles under clothing or in a person’s hair, it begins to drink blood immediately, and in some cases, after 30–60 minutes.
Each person can react differently to a moose tick bite: one feels nothing, another experiences painful sensations, sometimes quite strong, which are accompanied by itching and burning. And manifestations on the skin depend on individual or acquired sensitivity to insect saliva. Observations have shown that people who have been systematically exposed to deer bloodsucker bites for many years have a much stronger skin reaction.
Lifestyle of a bloodsucker
The forest fly is active during the day. After emerging from the pupa, young individuals hide in the grass and low bushes. They are capable of waiting for prey for a month. They detect the approach of animals by smell and movement. They quickly fly into the air and land on the owner's body.
The deer fly examines the “terrain” for several minutes, climbs into areas with a thick, long coat of fur - the back, neck, and sheds its wings. It clings to the skin with its claws and bites. It digs in with its proboscis and sucks out about 1.5 ml of blood at a time. After the first meal, the ability to mate appears.
How to protect yourself from moose flies?
Overalls and mosquito nets are means of protection against moose flies.
Despite the fact that moose ticks drink human blood, they are not carriers of serious diseases, for example, encephalitis and Lyme disease. To protect yourself from them in the forest, you must take precautions.
Requirements for clothing to protect against deer bloodsucker:
- Clothing must cover all areas of the body. The best option is a jumpsuit. The cuffs on the jacket and sweater should fit snugly to the wrist or be secured with an elastic band.
- You should put a mosquito net on your head, which will prevent insects from getting into your face and hair. If you don't have one, you can use a scarf or hat.
- Moose flies are easier to spot on plain colored clothing.
- Use repellents that contain at least 20% DEET.
Epidemiology
It should be taken into account that deer bloodsuckers feed on the blood of the same animal species that feed adult ixodids and occupy the same habitat as the main carriers of Lyme disease, as well as the fact that various types of dermatitis develop on human skin, including erythema, accompanied by inflammatory, sometimes long-lasting, phenomena, as well as indications by some authors of cases of non-tick-borne parenteral infection with Lyme disease. Studies of the intestinal contents of bloodsuckers and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays using monoclonal antibodies have shown that at least 27.6% of hungry winged deer bloodsuckers contain spirochetes, the causative agents of Lyme disease, and in the autumn-winter season the percentage of infected flies reaches 80%.
What to do if you are bitten by a moose louse?
Removing an elk tick from human skin with tweezers
If in the forest a tick gets into the hair or under clothing and burrows into the skin, it must be removed immediately.
Three ways to remove bloodsucker from deer skin:
- Using tweezers or thin tweezers, take the insect by the abdomen and gently twist it counterclockwise, gradually removing it from the wound.
- A time-tested and effective remedy for moose flies is vegetable oil. After the product gets on the parasite’s body, the supply of oxygen is cut off, as a result, after about 10–15 minutes, it will begin to break out in search of air.
- You can remove the tick using a regular nylon thread. To do this, you need to pass it under the insect’s abdomen and tighten the loop, preferably closer to the head. Then swing it in different directions and take it out. The bite site must be disinfected.
Morphology and developmental biology
Lipoptena cervi also has other names: deer bloodsucker, moose fly, moose tick.
Winged insect, gray-brown in color, up to 7 mm long. The oral apparatus is a piercing-sucking proboscis. The proboscis is usually retracted into the head, except when feeding. Compound eyes are 2 times longer than wide. 3 longitudinal veins are visible on the wings.
The body of the insect is dorsoventrally flattened. Ticks have a soft, leathery abdomen with poorly defined segmentation. Claws on the paws allow them to hold firmly on the fur or plumage. By mechanically piercing an animal's skin, lice can be carriers of blood parasites.
The lurking bloodsucker attacks from trees within a radius of 50 m. It sheds its wings onto the animal’s body. It feeds on blood for 5-7 days, after which copulation (mating) occurs. In 2-3 months, the female is capable of giving birth to up to 30 prepupae, which, covered with a hardened larval shell (puparium), then turn into pupae. The pupae fall into the soil, where after 86-160 days they turn into young winged bloodsuckers. By the end of September the first puparia appear.
For the development of the insect, a warm temperature is required - up to +16ºC.
The attack on animals begins at the end of July and continues until the onset of stable frosts. The largest number of bloodsuckers on moose is observed from October to February.
Up to 1 thousand bloodsucker parasitize an adult moose. Most flies are found in the neck, back and sides.
From February to July, the population of deer bloodsuckers decreases. In July, the animals completely get rid of last year's flies. But with the onset of swimming time, when animals, fleeing from midges, are completely immersed in the reservoir, the number of insects increases.
The moose louse feeds 15-20 times a day, sucking 0.3 mg of blood. Males feed less frequently than mature females. Lice parasitizing on an adult elk in numbers from 3 to 5 thousand are capable of sucking up to 50 g of blood, which leads to exhaustion of the animal. Animals are forced to stand in ponds for a long time to escape flies and scratch themselves on trees. Because of this, they develop extensive dermatitis, complicated by microflora. Infection of animals with elk lice provokes the disease lipoptenosis.
How to get rid of deer bloodsucker
There are two ways to combat moose flies.
Industrial methods
Treating the area with various chemicals. Currently, a large number of chemicals have been developed that do not harm plants, animals and people.
Spraying chemicals in a gaseous state onto an area allows you to treat even hard-to-reach areas, leaving no chance for parasites to survive.
To kill moose flies indoors, it is treated with carbon dioxide by spraying onto various surfaces. Thus, not only they, but also other insects will leave the building. In the liquid state, the temperature of carbon dioxide is −50ºС.
Traditional methods
To prevent insects from accumulating on private property, it is necessary to regularly mow the grass, since, as a rule, they live among tall plants. Moose flies do not like moisture, so it is recommended to spray trees, shrubs and lawns with water. You can add alcohol or regular garlic to it. Wormwood and tansy also successfully help cope with parasites.
Question-answer section
To avoid collisions with moose parasites, it is necessary to learn more about the peculiarities of their life activity. All questions can be asked to an entomologist on the website online.
How is it different from a real tick?
Alisa, 34 years old, Rostov-on-Don. “The main difference is the wings of the moose bloodsucker. But if she has already attacked you or an animal, then the wings are shed. You can count the legs – a true tick has 8 of them. In addition, the limbs themselves of arachnids are thin and shorter.”
There is a moose flea in my hair, what to do, how to get rid of it?
Olga, 38 years old, Vladimir “When an elk tick attacks, it is somehow easier to notice and remove it on the skin. How do you remove it from your hair?” “The principle is the same: use tweezers or thread, in this case you need to ask one of your relatives to do it. It is necessary to open the area first so that the hair does not interfere.”
How to identify a moose flea bite?
Vera, 36 years old, Moscow. “Externally, I can, in principle, distinguish the bloodsucker-elk tick. How can you recognize its bite? “The main difference is the formation of a papule at the point of skin puncture. In addition, immediately upon being bitten there is pain (but not in all people) and a burning sensation.”
Deer bloodsucker in the apartment! Is it possible?
Vera, 35 years old, Kirov. “I often find blood-sucking pests in my apartment. How do they get there if they live mainly on animals in the forest and households?” “It’s very simple - parasites attack birds, so they spread quickly. Sometimes such pests are brought home on clothes. I hope you manage to get rid of them."
Preventive measures
The smell of sweat and warmth are especially attractive to moose lice. Therefore, for a trip to the forest you need to choose the appropriate clothes. The most reliable option is a special protective suit that reliably hides all parts of the body. It is desirable that it be made of thick fabric, have cuffs on the legs and sleeves, as well as a collar that fits well to the neck.
To protect the most exposed part of the body - the head - you can use a mosquito net. It is indispensable during forest walks in the summer. You can also protect yourself from moose fleas using specialized products, such as repellents.
Many users note that not all of them are effective. Therefore, when purchasing them, you should opt for a powerful drug that has a noticeable odor and a high saturation of active ingredients.
Experts recommend using Deta or Taiga sprays. All clothes need to be treated with them so that bloodsuckers can smell the smell from a great distance and do not even try to consider a person as their potential victim.
Externally, the insect looks like a fly because it is endowed with wings. But unlike it, the moose flea is able to withstand extreme pressure on the body. This is possible due to the structure of the insect - compacted covers of a strongly flattened body, the length of which reaches 3 mm or more. The largest individuals can have a body length of up to 4 mm. The color of the integument is light brown or amber.
The deer bloodsucker differs from its bloodsucking counterparts in other features:
Popular questions
Many people are new to this insect, so they have many questions.:
- Where is moose louse most common? Most often, this parasite makes itself felt in Siberia, the European part of the Russian Federation, China and Scandinavia.
- How long is the life cycle of an insect? The maximum elk louse lives is 5-6 months. It usually dies in the spring, after an active breeding period.
- What animals can it live on? Animal feeders for moose lice can be: moose, deer, and deer. They are also found in the fur of smaller animals (bears, foxes, wild boars). Most often, such pests settle on wild animals, but sometimes they can also be found on livestock (goats, cows, sheep).
The moose louse usually attacks fairly large, moving people, and it does not perceive children or stationary people as victims. Once on the human body, the moose louse first freezes and then begins to move quickly. Quite painful bites can be felt almost immediately. But some people hardly notice them. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
If a person has been attacked by elk lice and has discovered such parasites on himself, then he should quickly get rid of them.
After the extraction procedures, the victim must bathe and wash his hair thoroughly, as well as wash his clothes. It is also advisable to use antiparasitic agents based on insecticides, and if complications develop, consult a dermatologist.