Published by: Parazitolog in Parasites in Animals March 5, 2021
Tapeworm in fish is a tapeworm that can cause deadly diseases in humans, for example, diphyllobothriasis. Tapeworm is especially dangerous for children, as when infected with this parasite, a child may experience delayed growth and development, diseases of the circulatory system, and weakened immunity.
- 1 Worms in fish
- 2 Tapeworm in fish - what is it?
- 3 Life cycle of tapeworm
- 4 Types of tapeworm
- 5 Is tapeworm in fish dangerous for humans?
- 6 Symptoms of tapeworm disease in humans
- 7 What does fish look like with tapeworms?
- 8 Tapeworm in dried and smoked fish: how to identify
- 9 Prevention of tapeworm in fish
Worms in fish
Rich in minerals and rare trace elements, fish is a common product in the diet of almost every person.
Few people think about the fact that fish can be dangerous to human health, and this is due to the high risk of infection with worms when consumed by the inhabitants of rivers and seas/oceans.
There are so many diseases that can be transmitted along with worms when eating fish that scientists have divided them into a separate group and called it “fish helminthiasis.” The danger lies in the fact that fish infected with worms are absolutely indistinguishable from healthy ones, and meanwhile, research confirms that all inhabitants of freshwater bodies of water, as well as seas and oceans, can be carriers of eggs and larvae of worms.
Tapeworm in fish. It is worth knowing that even buying fish and seafood in a specialized store does not guarantee the purity of the product. In accordance with regulations, each fish carcass must be checked for invasive contamination.
According to sanitary standards, it is believed that if the number of individuals of non-viable helminths exceeds 5, then the product must be disposed of. A lower indicator allows the product to be sold, but with the condition that before eating it must be subjected to deep heat treatment.
Sexually mature worms, as well as their larvae, can be found in any part of the fish, but most often helminths are found in the liver, gills, muscle tissue, belly or head of the fish. There are also types of parasites that are located in milk and caviar bags!
What to do if you feel bad about throwing away your catch?
It is important to know! If the fish contains a sexually mature parasite, then it is clear that it is already full of larvae.
Unfortunately, this fact does not scare many fishermen, and it’s a pity to throw away another trophy. In this case, they hope to neutralize the fish through careful heat treatment. It is very important to gut the fish and remove the worms with all their segments. The larvae are guaranteed to die if the fish is exposed to:
- Freezing, at a temperature not higher than -20 degrees. At this temperature, fish carcasses are kept for about 3 days.
- Deep salting, using a salt concentration of at least 12 percent relative to the weight of the fish. In such conditions, the fish is kept for at least a week.
- Boil for 30 minutes or fry for at least 15 minutes, first cutting the fish into small pieces.
- Roasting over an open fire.
- Hot smoking for at least a couple of hours.
It should be remembered that small larvae can easily get on both your hands when cutting and kitchen utensils. Therefore, after such work, it is better to wash your hands with soap (laundry soap), as well as kitchen utensils.
Unfortunately, infected fish do not meet high taste standards, since parasites do not allow it to develop normally for a long time.
On a note! Naturally, dishes made from raw or lightly salted fish are considered the most dangerous for humans in terms of parasite infection. Fish caviar, as well as dried fish or cold smoked fish should also be included in the dangerous category. If fish is salted in a low concentration of salt or the heat treatment process is limited, then there is a high probability that the larvae will enter the human intestine and parasitize there for a long time.
This parasite most affects the carp family, and among this family, bream and crucian carp are considered the most vulnerable. In salt water the larvae do not feel as comfortable as in fresh water, although pollock is often found with tapeworm larvae.
Important to remember! Sea fish arrives at retail outlets after deep freezing, after which the fish is also subjected to heat treatment. Such fish can be eaten without fear. If you adhere to the complete technology for preparing fish, as well as comply with sanitary and hygienic standards, then the risk of infection with parasites can be reduced to zero.
To protect yourself from the risks of infection with various worms, it is better not to eat dried fish, as well as cold smoked fish, especially those purchased at the market, since it is unlikely that any seller subjects their products to tests for the presence of parasites. Such fish is not only tasty, but also dangerous to human health.
Tapeworm in fish - what is it?
The tapeworm is a tape parasite that attaches to the inner walls of the intestine with suckers and hooks in its head.
It can reach several meters in size, and survives even with only a head segment. Its entire body is divided into uniform sections that can tear off and leave the wearer's body. The number of these segments corresponds to the number of possible eggs the parasite can lay.
There are several types of tapeworms: bovine and pork tapeworms, dwarf tapeworms, dog tapeworms, and wide tapeworms. The differences between them are the method of entry into the human body and the size of the worm itself.
Many people believe that parasites in the intestines lead exclusively to rapid weight loss, but this symptom can be considered the most innocent. The most dangerous thing is suppression of the immune system and the development of secondary diseases.
What worms do crucian carp have?
Crucian carp is a freshwater fish, which means that it is much more likely to become infected with worms than marine inhabitants.
The most common parasites:
- Wide tapeworm - a flatworm, the larvae of which, penetrating into the human body during poor-quality processing of the catch, cause a sharp increase in body temperature, headaches and painful discomfort in the abdomen. Long-term treatment for this helminth can lead to cirrhosis of the liver and even death.
- Ligula vulgare - a tapeworm, reaching a width of up to 4 centimeters and a length of up to 0.8 meters.
- Cat fluke or Siberian fluke - a parasite from the group of liver flukes that enters fish through river mollusks. A person becomes infected by eating improperly cooked fish. The worm affects the liver and pancreas, which leads to severe and irreversible consequences in the body and even death.
- Anisakidosis — the larvae of this parasite are very dangerous for humans. This type of worm lives in the peritoneum of fish.
- Chinese fluke - liver fluke, in an uncomplicated form of the disease causes intestinal disorders, severe pathology - damage to the liver and pancreas.
- Pinworms - small-sized (up to 1 cm) worms that parasitize in the lower parts of the intestine (usually in the rectum). A person experiences severe itching in the anal area, which intensifies at night.
- Trematode Metagonimus yokogawai, reaching up to 2.5 centimeters in length. It causes a serious disease - metagonimiasis, which is accompanied by intestinal disorders, and in severe cases, affects the brain.
- Cestode of the genus Diphyllobothrium - a tapeworm that grows up to 10 meters in length causes a dangerous disease for humans - diphyllobothriasis.
- Tapeworm Bothriocephalus gowcongensis, up to 35 centimeters long, relatively safe for humans, because fish suffer more from it.
- Nematode Philometroides lusiana is a red helminth that is safe for humans and parasitizes in the scales, swim bladder, scale pockets, and kidneys of carp fish. Causes enormous damage to fish farming farms.
- Trematodes and flatworms causing various types of diplostoma. Pathological changes can be found in various parts of the fish’s body.
- Helminth Philometra fasciati - red worms up to 10 centimeters long. After their removal, the fish, having undergone thorough heat treatment, is suitable for consumption.
- Trematode Opisthorchis felineus - the causative agent of the dangerous parasitic disease opisthorchiasis. Its focus is in the area of the liver, pancreas, and bile ducts. In an advanced stage, it can cause severe liver damage.
Parasites localized in fish are dangerous not only because they cause diseases of its internal organs, but also because they can infect a person who eats it without first thermally treating it. But in addition to dangerous worms for humans, crucian carp also contain worms that are relatively safe for humans, with which the fish itself is infected.
Did you know? According to estimates by the World Health Organization, a huge number of people on the planet are infected with one of three types of parasitic worms. 1 billion 200 million people suffer from enterobiasis, 700 million from trichocephalosis, and 900 million from hookworm.
Life cycle of tapeworm
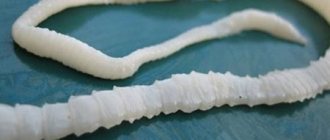
Externally, beltworms look like yellowish or white worms about a centimeter thick and 5 to 8 centimeters long. At the front end of the worm there are special organs with which it attaches to the organs of its host.
The life cycle of plerocercoids begins with the fact that sexually mature worms lay eggs in the intestines of fish-eating birds (pelicans, gulls, cormorants, etc.). From there, the eggs of parasitic worms fall into bodies of water, where larvae hatch from them.
Helminth larvae are swallowed by the first intermediate hosts - microscopic crustaceans. Fish eat crustaceans and become infected with ligulosis themselves. In the body of fish, worms grow to significant sizes and at the end of their life cycle enter the intestines of birds.
The general life cycle of a tapeworm is approximately the same for all parasites:
- eggs fall onto the soil, grass or into water with the feces of the last carrier (many easily survive wintering and remain viable);
- in the process of feeding animals, eggs enter the body of intermediate hosts; the developed larva of the parasite spreads through the circulatory system into the muscle tissues and internal organs of the animal;
- Through meat, the parasite enters the human body, where it develops into a full-fledged adult, which begins reproduction for a new development cycle.
Disease prevention
Salt water is a less favorable environment for the life of tapeworm, which is why it is less common in marine fish. Accordingly, to avoid infection, it is better to avoid eating river fish. If this is not possible, then you should exclude dried, especially home-made, smoked (cold-processed), lightly salted, and raw fish from your diet.
If you have eaten bream and are not sure of its quality, then it is better to go to the pharmacy for antiparasitic drugs: Fenisal, Pirantel, Piperazine. These drugs have a destructive effect on the tapeworm's body, preventing its organs from developing normally.
Did you know? Some types of tapeworms can destroy 95% if they don't have anything to eat.
Tapeworm is a dangerous parasite that can harm any living organism. It is better to avoid contact with it, and if it already happens that it has entered your body, take measures to destroy it.
Types of tapeworm
Bovine tapeworm: A parasite that is considered one of the longest to live in the human body is the bovine tapeworm. As an intermediate carrier before humans, it parasitizes cattle; humans, in any case, remain the final infected host.
Tapeworm in fish. The maximum recorded length of an individual bull tapeworm is 22 meters, but the average is 12 meters. With a thickness of 2 mm, even such a long intestinal parasite can exist in the human body for many years without causing serious discomfort.
These worms do not have their own digestive system, but absorb nutrients directly through the body. Infection occurs due to insufficient heat treatment of meat, because the eggs of the parasite are found in the muscle tissue of cows. Employees of meat processing plants, slaughterhouses, farms and food processing plants are susceptible to teniarinosis (infection with bovine tapeworm).
Pork tapeworm parasite: A smaller parasite, the pork tapeworm, causes the disease taeniasis. The localization of the disease is East Asia, Latin America and Africa, and in Russia – the Krasnodar Territory. The intermediate carrier before the human body is pigs, and it does not matter whether they are wild boars or domestic farm animals.
Taeniasis is dangerous because humans are the last carrier, which means that the colony of worms
will multiply until it destroys the host. Due to the way it is attached, pork tapeworm can damage the walls of the intestines or internal organs.
Broad tapeworm: what is tapeworm in fish? This is a tapeworm - a wide tapeworm that enters the human body with raw or poorly processed fish meat. It rarely exceeds several meters in length, but this makes it no less dangerous for the life of its owner.
The life cycle of this parasite is more varied than that of parasites of cows or pigs. The entire chain of carriers and rebirth of the tapeworm is as follows:
- The worm egg in water degenerates into a larva;
- coracidium settles in small crustaceans;
- the fish’s body becomes infected through feeding on crustaceans;
- the parasite spreads to all tissues of the fish’s body (bream, perch, carp);
- a person becomes infected through meat or fish by-products.
As you can see, humans again remain the final carrier (along with animals that eat fish, such as cats), which means there is a particular danger of the parasite being in the body. What are fish tapeworms and what diseases do they cause to humans? These are anemia, anemia, problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Due to a decrease in the number of beneficial microorganisms, the nervous and immune systems are suppressed.
Fish susceptible to parasites
Freshwater fish, marine fish, those living in the oceans - all these fish are susceptible to infection by parasites (helminths, larvae). But sea inhabitants are infected less frequently than in rivers or ponds, since sea waters are saltier and colder, and there are no favorable conditions for the development of parasite larvae.
crucian carp
Crucian fish of the carp family. The meat is valuable, healthy, tasty. It is white, it contains a lot of protein, fat, and microelements. Fish is fried, baked, steamed.
Peeling of scales, dropsy, and bulging eyes are diseases of crucian carp that are not dangerous to humans.
Fish suffer from severe rubella (aeromonosis) at the beginning of summer. When purchasing, you must carefully inspect the carcass.
From crustaceans, crucian carp becomes infected with a disease such as argulosis. Infectious viruses enter the fish's body.
Helminths (flatworms) cause bothriocephalosis in crucian carp, from which the fish dies.
The appearance of a rash on the carcass of young crucian carp indicates the disease ichthyophthyriosis. It is advisable not to eat fish infected with these diseases.
From crucian carp, people can become infected with helminths, which cause many problems with the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and heart. Worms settle in the body of crucian carp both in the belly and outside.
Lerneosis is one of the diseases of crucian carp, the causative agent of which is crustaceans (anchor worms).
Ide
Belongs to the carp family. River fish, found in lakes, can live in slightly salted water. Lives throughout the Russian Federation. The meat is tasty, but there are a lot of bones, like crucian carp. Ide is often infected with helminths. Opisthorchiasis is a disease typical of ide. Suffers from the same diseases as crucian carp. It all depends on the habitat.
Bream
Bream fish of the carp family. The body is elongated upward and flat on the sides. Bream lives in almost all fresh water bodies. Bream meat is healthy due to its fat content. Bream, like other carp fish, will not be able to avoid infection with helminths.
Perch
Predator, lives in rivers and seas. River perch and sea perch belong to different families. The fish has an unusual color. The meat is tasty and fatty.
Perches become infected with helminths that parasitize their fins, gills, and intestines. Apophallosis and diphyllobothriasis are dangerous diseases transmitted to humans from infected fish.
Sometimes perch suffers from trypanosoma. The disease is characteristic of fish living in Baikal rivers. This disease kills perch, but it is not dangerous for people.
Pike
The pike is a predator that lives in fresh water and feeds on small fish, perch, and gudgeon. Infection with helminths cannot be avoided; pike can become infected from any fish eaten.
Pike suffers from opisthorchiasis, diphyllobothriasis, clonorchiasis, and metagonimiasis.
Tench
Fish tench from the carp family. A distinctive feature of tench is its color change in air from dark to yellowish.
Tench get their food from silt: mollusks, worms, insect larvae, and therefore are also susceptible to infection by parasites, like other fish of the carp family.
Flounder
Flounder lives everywhere: in rivers and seas. She lives at the bottom of reservoirs, an unusual body that gives her this opportunity.
River flounder is brown-green with a white belly. It feeds on food from the muddy bottom: small fish, mollusks, crustaceans.
Flounder suffers from helminths, bothriocephalosis. White worms up to 1 m long parasitize her intestines.
Many people believe that flounder is not infected with helminths. The opinion is wrong.
Is tapeworm in fish dangerous for humans?
Worms that have reached sexual maturity can cause dangerous complications and stop the functioning of vital internal organs. Most often, tapeworm causes diphyllobothriasis, which is dangerous due to intestinal obstruction.
Worm larvae, when attached to the intestinal walls, can infect the mucous membrane, cause hemorrhages, disrupt the digestion process, and also destroy microflora. In addition, the parasite, whose nutrition occurs through the blood, takes vitamin B12 from the body, which is necessary for the normal functioning of organs.
The helminth poses a significant danger to the body of children. The tapeworm often provokes: retarded growth and development of the child; blood diseases; allergic reactions; prolonged diarrhea; deterioration of the immune system.
Tapeworm in fish. Having consumed an infected fish dish, a person does not suspect that he has become a carrier of a helminth, since early infestation does not cause any symptoms or illness. Parasites can be detected through fecal analysis and blood tests.
Having entered the body, the larva reaches the digestive system and attaches itself to the walls of the small intestine with suction cups. It is there that the helminth begins to develop. The plerocercoid, a representative of tapeworms that is capable of growing into an adult worm in the organs of another host, poses a huge threat to life.
Most often, invasion occurs when eating poorly fried and boiled fish, fresh caviar, as well as insufficient freezing. 30 days after introduction into the body, the female parasite begins to lay eggs, the duration of which can last for many years.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
Fish parasites: helminths parasitizing sea and river fish
Worms in fish: are there river or sea fish? Is it possible to eat raw or salted fish with worms?
Tapeworm in humans: what are the signs of infection, can it be in fish and how to treat
What can you become infected with opisthorchiasis when consumed? Dangerous foods
Roundworms in the intestines: signs and symptoms of infection, methods of treatment and removal
What is molluscum contagiosum and how can you get infected with it?
Symptoms of tapeworm disease in humans
Due to the active life of the parasite, pathological processes occur in the intestinal system in people.
The most common signs of infestation appear:
- nausea and gag reflexes;
- painful syndromes in the peritoneum;
- loss of strength, weakness;
- weight loss;
- deterioration of intestinal function - diarrhea, constipation;
- loss of appetite.
Tapeworm infestation is accompanied by a decrease in immunity and the occurrence of concomitant pathologies. The first symptoms should not be ignored: therapy in the initial stages is quick and effective.
What does fish with tapeworm look like?
Tapeworm in fish. If you decide to clean the caught fish, but are surprised to find that there are worms inside it, then the fish was sick with ligulosis. Fish ligulosis is caused by tapeworms and is a dangerous disease that can threaten the existence of fish in freshwater bodies.
If belt worms (belt helminths, plerocercoids) live in the abdominal cavity of the fish, then the fish is sick with ligulosis. The life cycle of worms includes a change of several hosts. The final hosts are fish-eating birds, and fish play only the role of an intermediate host.
As a rule, tapeworms live in the digestive tract of freshwater fish: bream, rudd, roach, crucian carp and other cyprinids.
A fish infected with tapeworms quickly weakens and exhibits a disturbance in the basic physiological functions of the body, up to complete atrophy of vital organs.
Typically, fish with ligulosis swim upside down or on their sides near the shore or in shallow water - it is easier for them to get food there. Externally, the fish does not look the best. Her abdomen is swollen and quite hard to the touch.
The fish itself, in comparison with its other counterparts, has a much smaller body weight. She is emaciated and underdeveloped. When strong excitement begins on the water, the weakened fish cannot go to depth and remains floating on the surface, where it is nailed to thickets of reeds, snags, etc.
It happens that due to the abundance of worms, the stomach wall of an infected fish ruptures and the parasites go into the water. A final conclusion about ligulosis can be made only after opening the fish and detecting helminths in its digestive tract.
Most often, mass infection of fish with tapeworms occurs in low-flowing water bodies - ponds, lakes, estuaries, etc. Since fish with ligulosis move sluggishly and swim on the surface, they often become prey for fish-eating birds. In the body of birds, worms find their final refuge, where they complete the cycle of their life development.
What species are susceptible to invasion?
The broad tapeworm was found in 47 species of fish. River dwellers most often suffer from helminths: crucian carp, rudd, silver bream, asp, roach, pike. The worm especially often penetrates the body of bream: sometimes, worms are found in the entire catch.
Tapeworm fish are usually found in polluted water bodies. There is a lot of it in areas of the Upper and Middle Volga, a number of lakes in the Novgorod and Tver regions, and the Mozhaisk reservoir. In some ponds in Central Russia, all the crucian carp living in them are infected with worms.
Note! An unpleasant odor emanating from water is the first sign of the presence of a large number of helminths in it. This is explained by the fact that the overgrown tapeworm tears the body of the fish. Their massive death and subsequent decomposition leads to poisoning of the reservoir.
In reservoirs located in industrial regions, tapeworm infection of fish is becoming widespread.
Tapeworm fish can also be caught in environmentally friendly regions (for example, in the Far East). Worms are most often found in salmon species such as trout and salmon, as well as the Caspian Sea roach, an endemic species.
Much less often, the tapeworm infects sea fish: the worm does not like salt water. You can find tapeworm in certain species: pollock, herring, anadromous salmon (chum salmon, pink salmon).
Interesting fact! Some representatives of the ichthyofauna are not susceptible to helminthic infestation. Among them: whitefish, peled, pike perch. It has been noticed: the more of these species there are in a reservoir, the fewer inhabitants in it suffer from helminthiasis.
Tapeworm in dried and smoked fish: how to identify
You can identify helminths in fresh fish by its behavior: the fish swims slowly and sluggishly on the surface of the water; there is a slight swelling in the abdominal area; By pressing on the abdomen, you can see fragments of the parasite.
Infected fish are more common in spring and summer, as well as in early autumn. If you catch a fish with helminths, you should not release it: the tapeworm is capable of leaving offspring. It is difficult to distinguish an infected catch from a healthy one, but the taste of such a product is much worse and there are fewer nutrients.
Tapeworm in fish. Parasites in dried products can live in the form of eggs. Mature individuals do not survive under processing conditions and are found only fresh. When buying dried fish, a person may lose vigilance and not inspect it before purchasing. This can lead to negative consequences.
Therefore, you should purchase fish delicacies from trusted retail outlets, and also check the availability of the necessary documents. In smoked fish, the parasite can continue to exist if the heat treatment is poor. Not all manufacturers follow the smoking rules. If you have doubts about the products you are purchasing, you should refuse to purchase.
How can you get infected?
For full development, parasites require an aquatic environment, so it is almost impossible to become infected with larvae through unwashed fruits or vegetables. In most cases, infection occurs from low-quality fish.
Infected fish have a large, swollen abdomen. When pressed, the worms can come out through the scales. It is best to avoid such a product - even if it is well gutted, the larvae remain in the meat.
A person can swallow helminth eggs. From the stomach they enter the small intestine. Soon, larvae emerge from the eggs and begin to spread throughout the body. Cysts form in which larvae develop, and the functioning of the organs where they are located is disrupted.
If you swallow the larvae, they will live and develop only in the intestines. This form of infection has the most favorable course of the disease and can be cured faster.
Worms in fish do not survive long-term thermal freezing, and they tolerate low temperatures easily. Therefore, frozen fish does not exclude the presence of helminths in it.