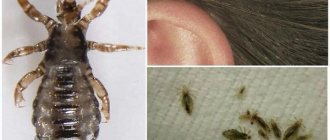
Black lice are one of the varieties of blood-sucking ectoparasites, the appearance of which is caused by the infection of a healthy person by an infected one. Depending on the species of parasites and the specifics of their localization, several types of parasitic diseases are distinguished - pediculosis, phthiriasis.
To remove black lice, it is permissible to use chemicals or safer folk remedies. How to promptly detect infection with pediculosis and phthiriasis, get rid of parasites, and prevent their appearance - we will consider further.
What do nits look like?
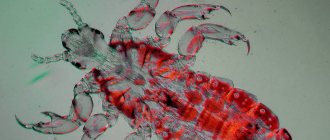
Female lice are quite fertile and are able to lay eggs several times during the day. A nit is a capsule that is covered with an adhesive membrane. It is thanks to the adhesive substance that the egg is attached to the hair. When examined under a microscope, a tail is identified, which fixes the parasite on the hair.
Live and dry nits differ in their appearance. Living eggs are white and glisten when illuminated. After the louse hatches from it, the white shell gradually darkens to a gray-yellow hue, but remains on the hair. This visually leads to the fact that the number of nits significantly exceeds the number of lice.
Treatment methods
There are several ways to rid the skin of nits, lice, and, accordingly, the symptoms accompanying the disease, the most unpleasant of which is the constant persistent desire to scratch your head.
- The mechanical method is combing with a specialized comb with a tooth frequency of 0.2–0.3 mm. This method is the safest. This comb can be purchased at any pharmacy.
- Using shampoo will have a fairly strong effect, removing a significant part of the parasites, and will be an excellent preparation for subsequent combing.
- After combing and washing the head with a special shampoo , some of the nits may remain on the hair. In this case, the removal process can be continued using chemical medications. If you decide to use only pharmaceutical medications, relief can occur within a few uses. They will help get rid of head lice at home.
You should not abuse chemicals, as they can cause significant harm not only to parasites, but also to human hair and skin.
How is a nit different from a louse?
The differences between nits and lice are obvious, since these are different stages of development of the same type of parasite. The nit represents the initial stage, that is, the embryo in the cocoon.
As a result, we can conclude that a louse and a nit have fundamental differences - appearance, feeding method, transmission options from person to person.
Possible methods of transmission of parasites
There are many transmission options, but the leading one is close contact with a sick person. Infection can occur:
- during a hug and a kiss;
- sexual contact;
- while playing together;
- in case of accidental contact of hairstyles, etc.
A child can acquire head parasites as a result of playing together or having close contact with an infected friend. In children's groups they spread instantly. At the same time, the appearance of insects in a child has nothing to do with non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. They appear on both clean and dirty hair.
Parasites also appear through other methods of transmission. Human infection can occur in the following ways:
- adults, as well as nits and nymphs, get onto the hair through shared things - combs, pillows and towels;
- swimming in the same water. Head lice appear in a healthy person after taking a bath in which an infected person had washed before. The insects do not die after falling into the water, but safely move onto the hair of the new host;
- wearing hats together. This method of transmission is especially popular among children. After a child tries on the hat of an infected friend, the appearance of bloodsuckers is inevitable.
Where do nits come from?
Most often, lice are transmitted through close contact, during which the louse moves on to the next victim. The nit cannot move on its own, so this type of infection is less common. This can happen if you share a comb, a hat, a bobby pin, or a hair tie.
Under the age of 12, children are constantly in contact with peers, so the prevalence of head lice in children and adolescents is high. And if a disease is detected in one of the students, it is recommended that all his classmates, as well as their families, undergo treatment.
What threat do they pose?
The immature nits themselves do not pose a threat, with the exception of the unattractive appearance of the hair and white formations in it. But when the louse begins its parasitic life, symptoms appear that can significantly worsen the quality of everyday life. These symptoms include:
- almost constant itching of the scalp;
- infection of scratches and wounds, their infection and suppuration;
- sleep disturbance;
- inability to concentrate;
- irritability, nervousness.
Sometimes typhus or age-related typhus can become a complication of pediculosis. Infection of damaged skin after a louse bite, which is dangerous to health, occurs as a result of contact with the waste products of parasites, that is, with liquids and feces. The main unpleasant consequence of infestation with lice and nits is constant discomfort and apparently dirty hair.
Are there nits without lice?
In some cases, dead nits may still be found without the presence of live lice. This is explained by some detrimental effect on the hair, which led to the death of lice. For example, after coloring your hair with a dye containing hydrogen peroxide (peroxide), which destroys parasites.
In any case, if a nit was found on the hair, then it is worth thinking about the need to use some additional methods of treating the scalp in order to prevent possible relapses.
Symptoms
How can you tell if there are nits? Symptoms of the disease, as a rule, are invisible immediately after its appearance, since they are not very pronounced and a person simply does not consider it necessary to pay attention to them. Despite this, it is possible to detect signs of head lice in the first days of infection.
The following symptoms of infection exist:
- Constant itching that does not go away even with strong scratching of the skin.
- The presence of bites, since the entire diet consists of human blood. To prevent the bites from healing, the parasites inject a special secretion that interferes with the blood clotting process.
- Slight tingling, like a mosquito bite. The sensations of a mosquito bite and a louse bite are the same.
- The presence of white bodies in the root part of the hair.
Of the above symptoms, the most noticeable is itching. Most often, it is this that becomes the reason for contacting a medical specialist or conducting a thorough examination of the head at home.
Are there nits without lice?
Such a case is possible, but very rare. The discovery of empty nit capsules, where there are no longer living individuals, makes you think carefully about the situation. The answer to many questions is that measures to combat head lice were applied either on purpose or by luck.
There are no living specimens on the head, as they died as a result of some impact. One of the types of such effects is painting with a mixture containing hydrogen peroxide, or bleaching hair, as a result of which the peroxide destroys lice and nits.
Development period
A nit is the initial stage of louse development. The louse develops from egg to adult within 2-4 weeks. During this time the following periods are observed:
- egg (nit);
- larval stage;
- 1st and 2nd order nymphs;
- adult parasite.
After a week or a little longer, the nit becomes a larva. The ripening period depends on temperature conditions. So, the most favorable temperature is the human body, that is, 36.6 degrees with minor fluctuations. But if you don’t wear a hat in the cold or the heat is unbearable in the summer, then the life cycle of lice slows down, but does not stop.
Once the louse has emerged from the outer shell of the cocoon, it begins to feed. And literally after 2 days the female is ready to reproduce. During her life, the female lays many eggs - 80-150 nits. In favorable conditions (air temperature +30), the number of lice increases tens of times in just a few months.
FAQ
Often, parents faced with the problem of childhood lice have the following questions:
Expert opinion
Eve
hair stylist
Ask a Question
The child was found to have nits, but no lice, why can this happen?
This situation is possible if the infection occurred very recently, that is, only one adult could have landed on the baby’s head, which immediately laid eggs. At the same time, the louse itself (especially if there is one or only a few of them) is quite difficult to notice. This is why it seems to parents that there are nits, but no lice.
Do dead nits click?
As noted above in the text, dead louse eggs do not produce a characteristic click when pressed on them . This is one of the distinguishing features between dead and living nits.
In conclusion, it should be noted that immediately after discovering nits on the head, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment for head lice. It doesn't matter whether they are dead or alive. In any case, lice eggs must be removed from the head.
- about the author
- VK profile
What do they eat?
A nit, that is, an egg from which lice will hatch in the future, does not need nutrition. The egg shell contains all the necessary microelements for the development of larvae. Only after the larva leaves the cocoon does it begin feeding - it makes a small wound in the human scalp and sucks out a drop of blood.
After lice bites, wounds form, which can sometimes be confused with urticaria, an allergic reaction, or sweat rash. But do not forget about possible infection by parasites.
How to detect?
The louse for laying eggs rises along the hair to a height of about 3 centimeters. It is at this height that you should look for nits. In rare cases, the egg may attach to the scalp. This occurs as a result of it falling from the hair after mechanical impact.
It is extremely rare for a louse to lay nits on a hair that already has masonry. But if more than one nit is found on one hair, then the number of lice has reached incredible proportions and it is necessary to immediately take measures to destroy them.
To search for the parasite's nest, you should start from the occipital region. It will be easy to spot light eggs and dry shells on dark, straight hair. Examination of curly blond hair will be a little difficult. While the larvae are almost mature and ready to leave the shell, the nit becomes dark brown in color and blends in color even with dark hair.
Inspection of the hair on the head should be carried out using a comb, which will facilitate the process of combing the hair and dividing it into individual strands.
Reproduction
Lice reproduce by laying eggs on the scalp. A sticky secretion that hardens well in air, promotes good attachment to the hair and further helps to better preserve the future generation. Such increasing offspring require large amounts of energy from adults, so they feed a lot, 3 to 10 times a day.
Lice have a strong and multi-layered shell. It helps protect against high temperatures and certain chemicals.
The incubation period of nits found on hair is from 5 to 9 days. Insect reproduction depends on external influences. The more a person is in a cold room, the longer the parasite grows.
The ideal temperature for lice breeding is 24-30 °C. If it drops below 20, the reproduction process slows down or stops altogether.
The transition to adulthood occurs in 19-23 days. During this time, the larva goes through all stages and becomes capable of reproduction. Parasite reproduction proceeds very quickly. Females mate with males immediately after emerging from the nymph stage. One mating is enough to fertilize all the eggs. Then she lays 2-4 eggs a day. Over the course of her life, one female lays about 140 nits.
How to distinguish from dandruff?
A person who is not familiar with lice may confuse nits with dandruff. There are several significant differences that will allow you to determine the true cause of the appearance of white spots at the hair roots.
- Dandruff flakes have different sizes and irregular shapes. The shape of the nits is round and smooth. The size of each egg is practically the same.
- Dandruff easily moves along the length of the hair and is also easily removed. But the sticky shell of the nit holds it firmly at a certain height from the scalp. To remove a nit, you need to grab it firmly with your nails and pull it off the hair. When pressing with a fingernail, a distinct click is heard.
- Dandruff flakes can be found on the collar of a shirt, on the shoulders of outerwear. Nits can leave the head only with the hair.
- The main symptom of lice is severe itching, and if dandruff is present, it can cause minor skin irritation.
- The localization of dandruff is concentrated on the crown of the head, but the favorite places for laying nits are the frontal, occipital and temporal parts of the head.
It should also be noted that dandruff is a purely personal problem of an aesthetic nature. But pediculosis becomes a problem for the entire person’s immediate environment (family, team), since the parasites are constantly in search of food and will not miss the chance to spread to new pastures.
To clarify the diagnosis and determine the exact source of deterioration of the hair condition, it is recommended to consult a specialist with a medical education - a dermatologist.