Like many living creatures, pigeons are often attacked by small parasites, which not only cause discomfort to the birds, but are also carriers of various diseases. Some of the pigeon parasites are also dangerous to humans, so every breeder must be able to recognize harmful insects in order to exterminate them in a timely manner. Otherwise, parasites on pigeons can cause the death of all winged wards.
Description and characteristics of bird fleas
Fleas in birds are rare. Lice should be excluded immediately, since parrots are not carriers or carriers of such parasites. Insects quickly take root on the bird’s body and multiply rapidly.
Interesting! Initially, fleas lived only on chickens, but quickly moved to the feathers of pigeons and parrots.
Insects get onto the plumage in various ways. Most often, infection occurs in the warm season after visiting the street. It is extremely rare for poultry to be bothered by fleas or cat fleas. But they do not live long on feathers. The likelihood of infection increases if there is:
- poultry houses (ducks);
- home chicken coops;
- dovecote.
Fleas get indoors on human belongings, but it is not difficult to move into a cage and onto a parrot’s feather.
Appearance and life cycle
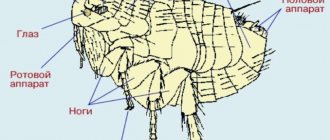
Fleas that interfere with the lives of parrots and pigeons are practically no different in appearance from cats:
- rounded;
- flattened on the sides;
- brown color of the body;
- three pairs of limbs;
- 4-6 mm in size.
Pigeon fleas can only harm birds. They are not dangerous for cats and dogs. Parasites initially settle in their nests.
Reproduction
One mature flea is enough for the parrot to be left with itching and discomfort within a month. Initially, its location is a nest. This is where she lays her eggs. After 14-21 days, young individuals actively live on the bird’s body. Mating occurs exclusively on feathers.
What do insects eat?
The study of the flea victim is carried out with special antennas. But punctures on the body are made using the nose part - a special proboscis. After suction, saturation with blood lasts from several minutes to 5-6 hours.
Interesting fact! Flea infestation can occur from a cage that has previously been used. Parasites can live in it for a long time even without a bird. The fact is that they are capable of being in the stage of suspended animation, but after the appearance of the parrot’s warm body, they awaken and lead an active lifestyle.
Prevention measures
To maintain the health of pigeons and protect birds from parasites, experienced breeders recommend taking the following measures:
- Maintain cleanliness: remove dirt and droppings, wash feeders and drinking bowls.
- Systematically carry out disinfection, and if insects are detected, disinfestation.
- Fill holes and cracks in the walls of the poultry house - these are favorite habitats for ticks and bedbugs.
- Provide a proper and balanced diet for birds, including vitamins.
- Prevent contact between domestic birds and wild birds: street pigeons should not be allowed to eat or drink from pets’ bowls.
No one is immune from infection by parasites, including domestic pigeons. The best thing a breeder can do for their pets is to eliminate the possibility of infection in advance by regularly carrying out preventive measures and measures to eliminate parasites. If trouble does occur, you should contact a veterinarian, who will recommend a means to kill harmful insects.
Transmission routes
The danger of infection can be expected literally anywhere. Reason: fleas are able to jump 30 cm forward, and up to 20 cm in height. But fleas appear on pigeons more often, since they are always outdoors, in contact with wild birds. In apartment conditions, the bird may not become infected at all if the owner monitors the hygiene of the house (cage) and the health of the parrot.
The appearance of fleas on the feathers and body of a pet is rare. They get into the apartment:
- on things, shoes;
- if there are other pets, then on the fur after a walk (dogs and cats) they can only bring bird parasites into the house, but do not become infected themselves;
- ventilation system. Parasites live in places with high dampness: basements, attics. They get into the ventilation shaft quickly;
- when buying food in a store or market. The culprits are other birds that are sold in the pet store.
Attention! It is almost impossible to protect a parrot or pigeon from flea infection. Only prevention prevents parasitic infection by 90%.
Types of pigeon parasites and signs of infection
Wild birds are considered the main source of parasite infection in domestic pigeons. Street pigeons, living in the attics of old buildings and often feeding on scraps from garbage cans, are not clean, so they are often attacked by various insects.
There are several types of pigeon parasites:
- down-eaters;
- fleas;
- mites;
- bedbugs.
All of these species are considered carriers of disease and cause severe discomfort and damage to the health of birds. In addition to the listed varieties that live on the body and in the plumage, there are also worms whose habitat is the gastrointestinal tract of pigeons.
Breeders of domestic birds are advised to carefully ensure that their birds do not have contact with wild relatives. Otherwise, the chance of infection with parasites is high.
To protect your pets, it is important not only to care for and care for birds, but also to be able to recognize the presence of parasites by the behavior and condition of pigeons.
Most insects prefer to settle on the back of the bird's neck, where they are difficult to reach.
Down-eaters
Down feather eaters are a type of insect that feed on feather scales, causing discomfort and causing unbearable itching. Periods reach 3 mm in length, have a light brown body color and a developed mouth. The main signs of the appearance of feather eaters in pigeons:
- the pigeon constantly cleans its feathers;
- the feathers of the wards fall out.
If you notice that the birds are acting restless and constantly cleaning themselves, you need to examine your pets for the presence of light brown small parasites. The fallen feathers have a stitched appearance.
Fleas
Many living creatures suffer from fleas, and pigeons are no exception. This is the most common type of parasite found in poultry. Jumping from one pigeon to another, fleas quickly move and infect the entire flock. Parasites feed primarily on the blood of the victim, biting through the skin.
Fleas reach 1–3 mm in length and have a dark brown or black body.
Painful insect bites cause severe itching. Fleas lay eggs with enviable regularity, from which larvae soon emerge. Parasites are especially dangerous during the breeding season of pigeons, when it is possible to infect both mother and chicks. Fleas can remain viable for a long time without food, waiting for a new victim.
Ticks
Pigeons can be attacked not by just one tick, but by several species, the infestation of which is fatal to birds. The following types are distinguished:
- Pigeon mite. Insects with a spherical body shape that are active at night. Feeding on the blood of birds, ticks increase in size, growing up to 10 mm, so a well-fed tick can be easily detected by visual inspection. Parasite bites cause almost no pain in adult pigeons, so the birds behave normally. But chicks with a weak immune system perceive infection differently - they weaken and may even die.
- Red bird mite is one of the most dangerous mites on pigeons. The parasite is small in size - up to 0.7 mm. Red bird mites do not like sunlight, so they hide inside the dovecote, waiting for the right moment. Having drunk blood, the parasites swell, and red dots remain at the site of the bites, by which the owner can identify the infection. In this case, pigeons often experience inflammation of the mucous membrane, and the chicks stop developing. A clear sign indicating the defeat of pigeons is twitching of the head and paws.
- Scabies mites are insects with a body length of up to 0.5 mm that feed on the upper layer of the skin, in which they make numerous exits and holes. When infected with scabies mites, pigeons experience severe itching and pain, turn away from food and frantically pull out their plumage to get to the source of the discomfort.
Red bird
Pigeon mite
Scabies mite
Bedbugs
Pigeon bugs have a characteristically flat body and feed on the blood of birds. The danger of infection by these insects is very high, since bedbugs are hardy and can live without food for 6 months.
These parasites attack pigeons at any time of the day and have an exorbitant appetite. Females lay up to 500 eggs, and after a week, larvae emerge from them, which are very fond of the blood of young chicks. Symptoms of pigeon infestation with bedbugs are as follows:
- anemia and weakness;
- exhaustion of the body;
- excited state - the birds itch and behave restlessly.
Bedbug bites cause severe itching. In addition, insects are considered carriers of pigeon pox, which is recognized as one of the most dangerous diseases of poultry.
Worms
By contacting their wild counterparts, tamed pigeons can become infected with different types of helminths. The most common are roundworms that live in the intestines of birds. Frequent routes of infection are food, drink and earthworms, which are carriers.
Symptoms of bird infestation with worms:
- lethargy and loss of appetite;
- diarrhea and vomiting;
- developmental delay, weight loss;
- dulling of feathers.
It is important to note that worm eggs can be carried by the wind, so birds cannot be completely protected. Regular disinfection and cleaning of the poultry house will help reduce the chance of infection.
What are the dangers and what diseases do they carry?
Fleas are not only blood-sucking insects. They carry many diseases on their legs and bodies. Eggs of scabies mites, lice-eaters, and helminthic infestations were no exception. It is impossible to immediately notice an infection with these parasites. And only after 3-6 months the signs will become obvious, but treatment will not provide a complete guarantee.
Fleas also actively spread tularemia on the body. The infection is dangerous, in 65% of cases it ends in death, even with the parrot treated. The most harmless consequence will be pediculosis or skin irritation. Due to constant itching, the bird tears the thin skin with its claws and tears off feathers.
If fleas are not diagnosed in a timely manner in budgerigars or pigeons, in addition to the problems already mentioned, anemia occurs, and then weakened immunity. Complete or partial exhaustion occurs. The result will be, if not the death of the pet, then a nervous breakdown.
Why are fleas on pigeons dangerous for humans?
Pigeon flea bites pose a serious danger to humans. This is due to the fact that parasites feed on the blood of birds, which are carriers of many diseases and infections.
By interacting with infected birds, a person risks getting the following diseases:
- encephalitis.
- Hepatitis.
- Typhus.
- Brucellosis.
You can tell if fleas bite by looking at the following characteristic signs:
- severe pain.
- Suppuration of the bite site, appearance of a bluish tint.
- Allergic reaction.
The latter is manifested by the following symptoms:
- severe itching.
- Inflammatory process in the lymph nodes, increasing their size.
- Fever, chills.
- Increase in body temperature.
The presence of bites, especially those with signs of allergy, requires immediate consultation with a doctor, since such a strong reaction of the body often signals a serious problem.
How to understand that a bird is infected
Parrots don't have to be outside to become infected with fleas. Therefore, if one or more symptoms appear, you should immediately conduct an independent examination of the bird, or go to a veterinary clinic for diagnosis. The second option will be more beneficial, since the veterinarian will give a full assessment of the condition of the feathered friend, and the treatment will be qualified and comprehensive.
Diagnostics in a veterinary clinic
It is difficult to recognize flea infestation in a parrot in the early stages, even in a clinical setting. But with regular visits to the clinic, doctors always conduct a thorough examination. Moreover, they treat patients carefully and notice changes in behavior faster than the bird’s owner himself.
In the veterinary clinic, special devices are used to examine the health of the parrot.
We carry out an independent inspection
In the initial stages of infection, the bird behaves as it always does. Parrots in captivity clean their feathers very often, and it is difficult to notice any changes. At the second and third stages of infection, the symptoms intensify, the signs become obvious:
- the bird may be disheveled or tufted all the time;
- there are more feathers on the floor of the cage;
- The parrot is nervous and itchy. For carding, he uses not only the paws, but also the bars of the cage, a perch, and a mirror;
- During severe itching, the bird screams loudly.
At the last stage, the parrot begins to look very plucked and tired. This phenomenon is an indicator of severe exhaustion, anemia and a weakened immune system.
How to determine the presence of fleas?
Several characteristic symptoms indicate that a bird is infected with parasites:
- ruffled plumage;
- behavior is dominated by anxiety, restlessness, aggression, nervousness;
- severe loss of feathers and down;
- the bird often cleans its feathers with its beak;
- the bird often takes dust baths.
Flea control products
The problem must be resolved in a comprehensive manner. It is not enough to treat the bird. You will need to disinfect the room and cage. If the infection is severe, the cell is discarded. After careful processing of the apartments, a new home for the parrot is purchased. The complex of procedures, in addition to insecticides, should include vitamins, minerals, and drugs that will increase immunity. When diagnosing anemia, iron-containing agents are added. Only a veterinarian can tell you how to properly treat a parrot or pigeon.
Chemicals
Timely and correct treatment is the key to a quick recovery of your feathered friend. To get rid of parasites, two drugs are recommended in 80% of cases: Frontline or Ivermec. Common and serious remedies are Piren-D and Anostomazan. The products are used exclusively in veterinary procedures.
Important! It must be remembered that it is necessary to use chemical drugs after thoroughly studying the instructions for their use. If the bird is tired due to fleas or infected with other infections (ticks, worms, etc.), then chemicals may not give the desired result.
Attention! Chemical substances are not applied to the plumage. Only on the body. After all, fleas can only bite the body, not the feather.
Insecticides
Neostomozan is widely used to kill parasites. The insecticide is the most harmless for parrots and pigeons at all stages of infection. Application is simple. There are two options for processing birds:
- Spray your pet with a spray bottle and treat according to the instructions.
- Bath in the prepared solution. In this case, contact of the insecticide with the eyes and head is prohibited.
Neostomazan solution is prepared as follows: diluted in warm water immediately before use. The dosage of the drug should take into account the body weight of the bird and its size. This substance is used as a means to disinfect cells. But it is better to choose an additional substance for disinfection.
Folk remedies and medicinal herbs
Medicinal herbs such as eucalyptus, rosemary, thyme, wormwood and mint effectively protect against fleas. These plants will help rid your parrot of fleas. Decoctions are made in which the feathered friend is bathed.
How quickly medicinal plants eliminate the problem can only be said after practical use at the infection stage. More herbal infusions and solutions are suitable for prevention, treatment of cells and premises. It is also impossible to determine the best from the list. They all have fungicidal properties.
Need to know! It is advisable to use medicinal herbs for prevention. It is enough to hang them in bunches in the corners and place them near the cage with the parrot. The strong smell does not harm the bird, but repels fleas.
Bird handling rules
Regardless of the product you choose to treat your feathered pet, you should remember the safety rules for the life of the bird. When using strong chemicals, the bird is carefully handled. Only the skin is processed. To prevent the product from getting on the head and eyes, make caps.
Baths are made warm, not hot. The bird's head is also supported so as not to get wet. If a parrot is treated with a herbal solution or medicinal liquid through a spray bottle, it is recommended to put a cap on the head. This will help prevent the medication from getting into your eyes.
Habitat disinfestation
When infested with fleas, both the bird and the habitat (cage) are treated. For this purpose, they choose the same drugs that were used to treat the bird. Completely wash all elements of the cage, food and drinking containers. After this, you will need to take everything out into the fresh air for ventilation (from 3 to 6 hours). Toys and mirrors are thrown away.
During the treatment, the parrot is sent to another home, but pre-treated with soda, manganese or another flea remedy. When treating pigeons, birds are allowed into the dovecote only after 6-8 hours. All bedding, hay and other things are taken out and burned.
Prevention is the key to bird health
Preventive measures will help avoid repeated or primary flea infestation if you use:
- baking soda. Add 1 tsp to 200 ml of boiling water. soda Steaming helps chemical reactions take place. Regularity of processing the parrot's cage, bedding, and dishes - once a week;
- weak manganese solution or turpentine liquid. The second option is more effective. Manganese is used to disinfect the bird's home during hatching.
In addition to treating the cage, drinking containers, and food, the entire apartment is disinfected. Potassium permanganate or turpentine is also suitable. Medicinal herbs are called an excellent preventive remedy.
Where is the risk of infection high?
For a person, the risk of becoming infected with fleas becomes higher if he lives in an apartment located on the top floor of the house. In this case, fleas can enter houses through ventilation shafts. The risk increases if pigeons have settled in the attic of the house and there are many nests there. In this case, you need to fight not only fleas, but also pigeons, trying to remove them from the attic.
You can suspect the presence of pigeon fleas if down and feathers begin to fall out.
You can also catch pigeon fleas if a person has hobbies of traveling. When visiting various caves, grottoes, and places where birds have settled, the risk of infection increases sharply.
Pigeon parasites rarely attack humans and rarely appear in apartments. This distinguishes them from other fleas. But there is still a risk for a person, and if they appear, they must be fought and gotten rid of by any means.