No one is immune from the appearance of head lice. They don't care about your age, gender or social status. If conditions are favorable, lice will actively reproduce and you will have to make some efforts to get rid of them. Moreover, lice can get to you in different ways. Infection of people with head lice occurs directly through contact with a person infected with lice. This mainly occurs when hair touches. Infection can also occur indirectly through the use of items used by a person with lice, including combs, hats, bedding, and so on.
Where do lice come from and how are they transmitted?
The main way to become infected with lice is through close contact with another person. Children are especially at risk of infection because they spend a lot of time playing and doing activities together. Periodic outbreaks of the disease can occur in educational institutions: kindergartens and schools.
Lice cannot fly, but they move very quickly. Being at a close distance from another person, they instantly penetrate his scalp. Girls and women with long, flowing hair are at greater risk of becoming infected with lice.
There is also a risk of infection from blood-sucking insects when sharing combs, barrettes and hair ties. You can “catch” lice by lying on a pillow where an infected person was previously located.
Once on the scalp, the louse immediately begins its active activity. Insects reproduce very quickly: first, the female leaves eggs (nits) on the hair, and then larvae hatch from them. On average, one female lays up to 7 eggs per day.
Characteristics of the parasite
It is almost impossible to distinguish a body louse from a head louse with the naked eye: this is an insect with a characteristically elongated abdomen measuring 3-4 mm. Its chitinous body is grayish-yellow or whitish in color, almost transparent, therefore, when drinking blood, the parasite turns brown. Linen lice look abundantly saturated, almost like fleas, but, unlike the latter, they cannot jump.
With such an obvious similarity between the two varieties, if a linen louse accidentally lands on your head, it will not stay there for long. This is because the insect's legs are not designed to climb hair and lay eggs.
"Shelter" and food
The bed louse feeds on human blood. It feeds every three to four hours, but the insect does not need to constantly be on the body of the “owner”. Therefore, the parasite spends most of its life in the folds, seams and lint of clothing. Lice feel more comfortable in linen and cotton products. They avoid satin and silk: there is nothing to cling to.
The adaptability of parasites is amazing: pests almost never settle on woolen products, since people rarely wear such things on their naked bodies.
Life cycle
The lifespan of a male is a little less than a month, a female is about 45 days. During this time, she manages to lay approximately 100-140 nits (about four eggs per day). The life cycle of an insect can be roughly divided into five stages.
- Egg. The rudiment of a louse, covered with a special sticky substrate, is called a nit. This formation is attached to the fibers of clothing so firmly that it is problematic to remove it mechanically.
- Larva. After three days, a larva emerges from the nit, which outwardly looks like a small adult.
- Nymph of the first instar. The insect drinks blood, after which it immediately molts, changing its chitinous body - now it is a first-instar nymph.
- Nymph of the second age. After five days, the next molt occurs, and the parasite becomes a second instar nymph.
- Adult. After another eight days, the third molt occurs, after which the louse becomes a sexually mature organism capable of reproducing.
The body louse travels from an egg to a sexually mature insect in 16 days under favorable conditions.
Harm
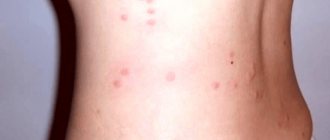
The body louse is a carrier of dangerous diseases: typhus (relapsing and typhus), Volyn fever. During the war, typhus, spread by pests, claimed thousands of lives. In the modern world, the likelihood of such infection is low. The main “trouble” caused by the parasite to humans is the bites of linen lice, the consequences of which are:
- unpleasant sensations - burning, itching;
- danger of infection - through the wound it is easier for pathogenic microorganisms to enter the blood;
- dermatological lesions - in advanced cases, scabs, suppurations, and pyoderma appear on the skin.
- when using someone else's bed linen and clothing;
- in a store fitting room;
- in places where large numbers of people gather;
- in kindergartens and schools.
On a social level, a person infested with lice also experiences inconvenience, feeling discomfort when interacting with other people. The dermatological symptoms that result from a lice infestation are called body lice.
Where do they come from?
A body louse cannot live without food for more than five to seven days, so if you do not wear clothes that have been “occupied” by insects for at least a week, the adult louse will die. Therefore, by and large, the “carriers” of parasites are representatives of asocial groups and people who neglect the rules of personal hygiene.
However, anyone can accidentally “catch” lice. Infection occurs only through close contact with the tissues on which the parasites live: they cannot fly or jump. The risk group consists of volunteers, medical and social workers, people who come into contact with representatives of antisocial segments of the population. Where else do linen lice come from? You can catch the pest:
Linen lice can be detected by two signs: the presence of bites on the body and the presence of the parasites themselves in clothing and bedding.
What is lice?
Pediculosis is a parasitic disease caused by small wingless insects called lice. The main symptom of the disease is itching. Interestingly, during the first infection, itching may not appear for up to 6 weeks. When reinfected, symptoms appear much more quickly. Before removing lice, it is necessary to “recognize the enemy by sight.” Despite the fact that science knows almost everything about lice, there are many myths associated with lice. Here are just a few of them:
- • Myth 1: Lice are caused by lack of hygiene. Personal hygiene and social status do not in any way affect the likelihood of getting head lice. Anyone can become infected with lice after contact with a sick person or their personal belongings.
- • Myth 2: Pets carry lice. Human lice do not live on animals. Therefore, there is no need to check the fur of pets for fear of infection.
- • Myth 3. Only children get lice. Outbreaks of head lice do often occur in children's educational institutions, as children are in close contact with each other. However, anyone can become infected, regardless of age.
- • Myth 4: Frequent hair washing prevents lice infestation. Washing your hair has no effect on the likelihood of lice. Water also does not help in getting rid of nits, since adult lice attach them to the hair using a special sticky secretion.
- • Myth 5. Lice can jump and swim. It is not true. Parasites crawl through your hair. Infection occurs through close contact with an infected person.
- • Myth 6. Lice are a purely aesthetic problem. Head lice are classified as a parasitic disease. Scratching bites leads to the appearance of wounds on the scalp, which can become infected.
If treatment doesn't help
Situations where folk remedies are not effective enough against lice are not uncommon. Therefore, until pediculosis begins to progress, professional medications should be used.
The most popular category includes special shampoos. They cleanse the hair and eliminate parasites at the same time. For shampoo to be beneficial, it should not be washed off immediately. The product should act on insects according to the principle of a mask - under a plastic cap. We will explain how to properly use anti-parasitic shampoos and tell you which ones are considered the most effective.
In the fight against lice, it is convenient to use sprays. Thanks to the presence of sprayers, these products are easily distributed throughout the hair. But this form of release also has disadvantages: you need to be especially careful to ensure that the contents of the bottle do not inadvertently get into your eyes or mouth. Compliance with safety rules will protect you from negative consequences such as poisoning and allergic reactions. You will find a description of popular sprays against bloodsuckers and their larvae, as well as detailed recommendations on the use of specific products in our thematic section.
Owners of short and medium hair can use special ointments and creams. Those who have thick and long curls often experience inconvenience when distributing paste-like products over their hair. Pharmacy ointments against pediculosis have earned a good reputation. They are considered effective drugs that help after the first procedure. To consolidate the result, it is allowed to re-treat the head, but only if this is provided for in the instructions. You will learn more about ointments against lice from our materials.
Main signs of pediculosis
The main signs of the disease are:
- 1. Itching. Occurs predominantly in the occipital region. It is noteworthy that itching is present in only 14-36% of infected people.
- 2. Insomnia. Lice feed at night, so the itching can intensify at this time, disturbing sleep.
- 3. Redness and sores. Most often appear on the back of the head and in the neck area.
- 4. Adult lice. They are not easy to see, as the insects move quickly along the hair, hiding from the light.
- 5. Nits. These are lice eggs. They are tiny, light brown in color, and oval in shape. Adults attach them to the hair closer to the scalp. Nits cannot be removed with a regular hair comb.
What happens if you don't remove lice?
The main symptom, sign and unpleasant factor when infected with lice is severe itching. It is impossible to live in peace when your head is constantly itching. Therefore, they try to remove lice as quickly as possible. However, in some cases, people do not pay attention to the itching. This may be due to decreased sensitivity of the scalp or other reasons. Some may feel that their itchy scalp is due to an allergy to shampoo, water, or hats. If itching does not interfere with your life, you should pay attention to other symptoms of lice infestation:
- the appearance of insects - they can be seen with the naked eye, since the female’s body length reaches 0.4 mm, insects move along the hair, so with a certain amount of observation they can be noticed; if the hair is thick, you can comb it - when combing, you can find parasites;
- the presence of nits - lice eggs: these are very small white balls at the roots of the hair, with a large accumulation they are visible;
- bloody bite marks - when piercing the skin, the louse injects a substance into the skin that prevents the blood from clotting, so that a drop of blood flows out and remains on the surface; tangled and glued hair that forms mats: they stick together due to waste products of lice;
- with severe damage and a large number of parasites, an unpleasant odor emanates from the hair.
If you do not remove lice, you can get the following complicated consequences of lice:
- severe scratching at the site of bites;
- allergic reactions;
- infection of scratched wounds;
- through wounds, the infection enters not only under the skin, but also into the blood, which is why it spreads throughout the body; in advanced cases, this can lead to dangerous diseases and even blood poisoning.
It's sad, but some parents believe that head lice in a child does not require treatment or is not treated at all. For children's health, infestation with lice and nits is especially harmful, since the psyche also suffers: the child becomes restless and irritable from constant discomfort. It is necessary to remove lice from everyone - both children and adults.
Features of the life of lice
During the life cycle of a lice, there are three stages: nit, nymph and adult.
- • Nits. They are laid by the adult female and attached at the base of the hair. The size of the nits is 0.8 mm by 0.3 mm. Lice are removed from the nits in about a week (6 to 9 days). Viable eggs are usually located close to the scalp (about half a centimeter away).
- • Nymphs. Nymphs hatch from the nits, after which their shell becomes more noticeable, lighter, but remains attached to the hair shaft. Externally, the nymph is no different from the adult head louse, except that it is smaller in size. The nymph matures after three molts and becomes an adult 7 days after birth.
- • Adults. About the size of a sesame seed. They have 6 legs with hooks at the ends, with which they cling to hair. Color varies from brown to grayish-white. It is noteworthy that in people with dark hair, the color of lice is also darker. Females are usually larger than males and can lay up to 8 nits per day. Adult lice can live on a person's head for up to 30 days. To survive, they need to feed on blood several times a day. Without a host, parasites die within 1-2 days.
Symptoms of lice and nits in children
Lice infestation has a special medical name - pediculosis.
This term comes from the Latin "pediculus" - louse. With pediculosis, bloodsuckers - lice - appear in a person's hair. They feel at ease on human skin: they feed on blood, reproduce, and lay up to 15 eggs a day. A couple of lice will quickly create a whole colony, and then the symptoms of the problem will not be long in coming. The main symptom of lice in children is the presence of nits - small white eggs - in the hair. Nits are very similar to dandruff, but they are very difficult to comb out and practically cannot be washed off. You can also see lice in your hair, but these bloodsuckers are quite mobile, so they only catch the eye of a meticulous searcher.
The second clear sign of pediculosis is itching of the skin under the hair at the sites of lice bites. In addition, small wounds may appear on the skin from constant scratching of the bite sites.
— Very often, symptoms of lice do not appear immediately after infection, but after several days, and sometimes weeks. The fact is that in most cases, pediculosis is transmitted by getting nits on the hair, not lice, which turn into adults only after two weeks, explains general practitioner Aigul Kharisova . — Children with lice become restless, restless, and constantly scratch their heads. They feel discomfort, but do not understand what it is connected with.
Since children cannot diagnose themselves, parents should take a closer look at their behavior. If your child begins to scratch his head frequently, fidget a lot, and whine, examine his scalp. It is easier to get rid of lice in children before there are too many of them.
Main transmission methods
A person can become infected with lice in several ways. The main route of transmission is contact with an infected person. Children are more susceptible to head lice because they often come into close contact with each other in kindergarten, school, sports, or camp. Infection can also occur through clothing or personal hygiene items (towels, combs). However, the likelihood of infection in this case is extremely low. Children who come into contact with bedding on which an infected person has previously slept are at greater risk.
How to remove lice
- • Home remedies. There are many recipes for treating head lice at home. These include: kerosene, vinegar, essential oils, etc. If you choose this treatment method, you must be prepared for the fact that the fight against parasites will take some time.
- • Pharmacy drugs With the development of medicine, a large number of effective anti-pediculosis drugs have appeared. Their only drawback is that lice develop resistance (become resistant) to insecticide-based preparations
- • Mechanical method. Probably the oldest way to fight head lice. It consists of regularly combing adults and removing nits.
Efficiency of funds
Traditional medicine is an experience accumulated over several generations. That is why the use of many options from “grandmother’s” piggy bank gives positive results in the fight against various diseases. The effectiveness of home recipes against nits and lice is influenced by several factors:
- how long have insects been on your head?
- what drug is used to eliminate head lice - toxic or not;
- how often and with what frequency this or that remedy is used, etc.
Some recipes give noticeable results after the first procedure. Others work slowly, but also effectively. There are also those that are recommended only for prevention or in addition to medicinal ointments and shampoos. It is believed that many home methods are more designed for the initial stage of infection, when lice have not had time to acquire extensive offspring and take a strong position on the head.
Attention! Folk remedies have health contraindications and age restrictions.
We discussed the treatment of head lice in children separately in the following articles:
The best remedies for lice and nits for children
Prevention of lice in children, causes of lice infection
Vinegar
The main disadvantage of this method is that vinegar does not kill adult lice. It simply lacks the properties to do this. However, the acid in vinegar can kill nymphs, young fish that are not yet able to lay eggs. Therefore, the anti-pediculosis effectiveness of vinegar is a controversial issue. However, vinegar does help in the fight against nits. Acetic acid does not dissolve the exoskeleton (the protective shell of nits), and therefore does not kill them. However, it weakens the glue that holds nits on the hair shaft and makes them easier to remove mechanically. To treat with 9% vinegar, it must be mixed with water in a ratio of 1:2, applied to hair, covered with film and left for 30 minutes.
What is dichlorvos
Dichlorvos is a broad-spectrum insecticide. Relatively safe for humans, but harmful to insects. Has a neuroparalytic effect. It is used in everyday life and at work to kill flies, mosquitoes, cockroaches, moths and other pests.
Dichlorvos affects lice in the same way as other insects. Parasites do not have a powerful chitinous covering, like cockroaches, so the toxin effectively paralyzes and kills them. However, the product does not cope with nits - the eggs of parasites have a strong protective shell.
Kerosene
This remedy has been used for a long time and, indeed, has a pronounced anti-pediculosis effect. Kerosene is mixed with vegetable oil in a ratio of 1:10. For this purpose, you can use olive, sunflower or corn oil. The resulting mixture is evenly applied to the hair using a cotton swab, the head is covered with film and the product is left for 15 minutes. Before removing lice from a child using this method, keep in mind that kerosene is a toxic and flammable substance. Therefore, this recipe cannot be called safe.
Essential oils
Lice are sensitive to certain odors. For example, they do not like the smell of eucalyptus. But the effect can only be achieved through direct contact with parasites. To do this, you need to prepare a special infusion. Eucalyptus leaves are dipped in boiling water and then infused for about 15 minutes. The infusion is applied to the scalp and hair, after which the lice and nits are combed out using a fine-tooth comb. Essential oil blends work similarly. For example, you can mix coconut, jasmine, anise and geranium oils in equal proportions. Their smell also repels lice. The mixture should be left on the head for at least half an hour.
Side effects
Neglecting the recommended rules when using Dichlorvos can lead to allergic reactions of the skin or even poisoning of the body as a whole. The procedure should be stopped if the following symptoms appear:
- an undesirable reaction on the scalp (or face) looks like the appearance of rashes in the form of red spots or swelling, sometimes burns are possible.
- signs of Dichlorvos poisoning also include itching, burning, tingling or numbness of the skin.
Undesirable side effects of this drug may occur through inhalation or direct exposure to the throat and stomach during nebulization. In this case, the following are observed:
- reaction in the form of cough;
- dizziness, spasm of blood vessels in the head;
- a sharp rise in temperature is possible.
Important! Particular attention should be paid to eye protection. If, however, Dichlorvos gets ingested during the procedure, you should immediately take action: rinse thoroughly with water. Otherwise, it may lead to the development of conjunctivitis.
If the drug gets into the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract , it is recommended to begin removing toxins from the body without wasting time. To do this you need:
- perform gastric lavage or induce vomiting;
- take an adsorbent drug (for example, activated carbon);
- After some time, you can use a laxative.
- Throughout this period, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids, preferably clean water.
All these measures are aimed at intoxicating the body, so it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the possible consequences in advance and stock up on the necessary medications.
Mechanical method - combing
The number one enemy of lice and nits is the fine-tooth comb. It is almost impossible to successfully get rid of lice without this assistant. Studies have shown that mechanical combing is even more effective than pediculicide treatment. First of all, a fine-tooth comb is the easiest way to diagnose lice. Dermatologists say that diagnosing head lice using a comb is four times more effective and twice as fast as direct visual examination.
Treating lice with a comb is not an easy process, but it is very effective if done correctly. Apply a thick conditioner mixed with a pinch of baking soda to your hair. It will make combing easier. Separate your hair into sections and comb out, starting straight from the scalp. After each stroke, clean the comb with a napkin or paper towel. The procedure must be repeated daily for two weeks until the parasites completely disappear.
Pediculosis - symptoms and treatment
Hospitalization for pediculosis is not carried out except in cases where there are special indications: unfavorable sanitary and hygienic living conditions, inability to independently provide the necessary therapy. Treatment is carried out at home. Isolation of the patient is necessary, as well as anti-epidemic and pest control measures.
Treatment of pediculosis is aimed at destroying the pathogen at all stages of the life cycle. When prescribing treatment, the patient must be explained how to use the drug (method of application, exposure time, frequency of treatments). If the recommendations are not followed, there is a high risk of treatment failure, as well as the development of lice insensitivity to drug therapy. In case of body lice, treatment of patients and their belongings must be carried out by special licensed disinfection organizations. To disinfect premises, furniture, as well as linen, clothing and bedding, pediculicidal agents are used in an aerosol.
Three methods are used in therapy: mechanical, physical and chemical. Additional treatment methods are required if complications develop.
The mechanical method of lice removal is suitable for single individuals. In this case, a special comb with fine teeth is used (the distance between the teeth is 0.2-0.3 mm). How to use:
- Wet and comb your hair to prevent tangling (you can use hair balm or conditioner before doing this).
- Place the comb so that its teeth touch the scalp. Comb all hair at least twice. After each combing, you need to inspect the comb and be sure to treat it with boiling water or a 70% alcohol solution [16].
To make it easier to comb out nits the day before, it is recommended to apply Vaseline oil or a combination preparation containing coconut, anise and ylang-ylang oils to your hair [17].
Evidence evaluating mechanical removal as an alternative to pediculicidal therapy is limited and conflicting.
The physical method involves killing lice using high or low temperatures. To remove nits from clothes and hats, people use boiling laundry and ironing clothes with a hot iron. Items that cannot be washed can be processed in steam-air-formalin, steam and combined disinfection chambers and in air disinfection chambers. These methods are considered quite effective.
The chemical method, or drug treatment of lice, is based on the use of pediculicides - drugs designed to kill lice. There are products in the form of lotions, shampoos, soaps, emulsion concentrates, aerosol products, etc.
Remedies for pediculosis:
1. Pyrethroids:
- Permethrin 1% cream rinse or 5% cream. Sold without a prescription, it is a reasonable first choice drug for the treatment of head lice unless resistance to it has been proven. Apply the product to towel-dried hair and rinse with warm water after 10 minutes. Approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) for the treatment of lice in adults and children over 2 months of age. The drug does not act on nits, therefore, after 7-10 days, repeated treatment is recommended to destroy lice that have not yet hatched at the time of the first treatment. A third treatment on days 13-15 may be required to remove surviving and hatched lice nymphs.
- Pyrethrins/piperonyl butoxide (gel, shampoo, solution for external use) applied to dry hair for 10 minutes may be effective, but there is emerging evidence that lice are resistant to these drugs [18]. In this case, it is recommended to use alternative agents with a different mechanism of action.
2. Organophosphorus compounds (OPS):
- Malathion 0.5% solution. More effective than permethrin. Apply to dry hair and wash off with shampoo after 8-12 hours. Approved by the FDA for the topical treatment of head lice in adults and children over 16-18 years of age. May be recommended if permethrin resistance is suspected. Kills 88% of lice in 10 minutes and 100% of lice in 20 minutes [19].
- Fention. As an active ingredient, it is included in preparations either alone (20%, 24%) or in combination with permethrin (total concentration - 10%, 20%); According to the manufacturers' instructions, the concentration of the working emulsion ranges from 0.1% to 0.25% [20].
3. Benzyl benzoate 20% is included in anti-lice preparations in the form of a spray (exposure time - 30 minutes, single treatment) and in the form of lotion (exposure time - 10 minutes, single treatment). Benzyl alcohol 5% is effective in eliminating live lice. Apply to dry hair for 10 minutes once a week for 2 weeks. FDA approved for the treatment of lice. The most common adverse reactions include itching, erythema (limited redness of the skin) and eye irritation [21].
4. Polydimethylsiloxanes (dimethicones) are synthetic silicone oils that are highly safe and effective against lice. Available in lotion and spray form. Dimethicone blocks the respiratory system of lice, causing them to die. There is evidence that dimethicones are also effective against nits [28]. It is necessary to apply the lotion to dry hair from base to ends and to the scalp, let the hair dry naturally, leave for 8 hours (or overnight), then rinse with regular shampoo. Repeat the course of treatment after 7-10 days. Dimethicones are also used in the form of shampoo containing clearol mineral oil (69.25%). The shampoo is kept for 10 minutes, re-treatment is carried out after 7–10 days [22].
5. Isopropyl myristate (isopropyl myristate) is used in the form of a liquid that contains a mixture of isopropyl myristate (50%) and cyclomethicone (50%). The drug is applied for 10 minutes, after 7-10 days the treatment is repeated [23].
6. Anise and clove essential oils are considered a fairly effective method of treating head lice. They are used in the form of an alcohol lotion and left for 30 minutes. A single treatment is sufficient [24].
Treatment of pregnant and lactating women
For this group of patients, in the case of head lice, it is allowed to prescribe a permethrin solution prepared from a 5% emulsion concentrate in ethanol, or a lotion containing 4% dimethicones.
Treatment of pediculosis in children
Most anti-lice medications are approved for use from 5 years of age. Exception:
- 1% permethrin-based gel is approved for use in children from 1 year of age. The gel is kept for 40 minutes, a single use is enough.
- A drug containing a mixture of malathion and permethrin (0.5% and 1%, respectively) and the synergist piperonyl butoxide (4%) is approved for use from 2.5 years. The drug must be kept for 10 minutes, a single treatment is required.
If you have a concomitant allergic disease (atopic dermatitis), it is recommended to consult a dermatologist for individual selection of the drug.
If eyelashes are damaged, lubricate them with Vaseline 2 times a day for 7-8 days or use eye ointment with physostigmine 2 times a day for 1-2 days.
Treatment of pediculosis complicated by secondary bacterial infection
External therapy is used: drying with any antiseptics (solutions of aniline dyes, povidone-iodine, etc.). Local or systemic antibacterial therapy is administered as prescribed by the doctor.
Oral medications are not FDA approved for the treatment of head lice, but are sometimes used to treat difficult to remove head lice:
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 5 mg/kg twice daily in combination with permethrin may increase the cure rate.
- Oral ivermectin 400 mcg/kg, repeat dose after 7 days
It is not recommended for treatment:
- Use Vaseline, vinegar, mayonnaise, butter or margarine, and vegetable oils. Lice are able to close their airways, preventing oily substances from entering them, and open them again when the substance is washed away. Treatment with these substances is not able to kill a significant number of lice [25].
- Blow-drying your hair using hot air can cause lice to become airborne and spread to other people.
- Shaving your head (effective, but not practical)
- Use flammable or toxic substances such as gasoline or kerosene [26].
- Use vinegar, acetone, bleach, vodka and WD-40. These substances negatively affect the hair and scalp and inhibit the therapeutic activity of permethrin.
- Use dye sprays that color insects and nits in bright neon colors. Such products do not kill lice; in addition, they reduce the effectiveness of permethrin. Not recommended by the National Lice Association due to lack of research on safety and effectiveness.
Hygiene in the treatment of lice: daily cleaning of premises, boiling laundry, ironing clothes with a hot iron, disinfecting combs and brushes.
Mayonnaise
Mayonnaise is an excellent sauce that is found in almost every kitchen. However, few people know that it can be used to treat head lice. The technique is that viscous mayonnaise closes the respiratory channels of parasites, as a result of which they die from suffocation. People who have tried this product recommend using thick, high-fat mayonnaise. It is applied generously to the hair and the head is covered with film. The sauce is left on the hair for half an hour, after which it is washed off with shampoo. Some people recommend leaving mayonnaise on your hair overnight to increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Duration of treatment
The timing of treatment for pediculosis depends on which folk remedy is chosen for this purpose. Aggressive drugs - alcohol, kerosene, etc. - help the first time. More gentle ones, for example, mustard, cranberry juice, give positive results after 3-8 applications. However, no folk remedy can guarantee a 100% positive result. Especially when it comes to advanced cases.
Such therapy is more effective for the initial stage of pediculosis. Folk remedies are best used as additional measures. Less aggressive ones are also suitable for children. In any case, it is important not to start lice, hoping to get rid of it with vinegar or laundry soap.
Herbs for lice
Among the various ways to get rid of lice, there are recipes based on medicinal herbs. Decoctions or infusions are prepared from them for washing or rinsing hair. Many people consider them safer, although in some cases herbs can cause allergic reactions.
Among the herbs for lice used in traditional medicine, we highlight:
- • wormwood – the effectiveness of the plant is achieved thanks to its composition, which contains amino acids, tannins, and essential oils;
- • hellebore - an alcohol tincture is prepared from its root for hair treatment;
- • tansy – the herb of the plant is boiled in a water bath and applied to the hair;
- • larkspur – a decoction for treating the head is prepared from grass or plant seeds;
- • burdock – the plant is used in dry or fresh form; a decoction prepared from burdock is used to wash hair.
The list of herbs with insecticidal properties also includes mint, elecampane, geranium, and black cumin.
Most often, decoctions are prepared from crushed herbs in a water bath. The prepared herb is poured with boiling water and kept over low heat for 15-20 minutes. After this, you can wash or rinse your hair with the broth. Infusions are also prepared on its basis.
Compresses are prepared from decoctions and infusions and applied to the hair and scalp. After an hour, wash off the compress with warm water and wash your hair with shampoo.
The effectiveness of herbs in eliminating lice and nits will be achieved only after repeated use, at intervals of 2-3 days.
Anti-lice herbs are not recommended for pregnant and lactating women, as well as persons with individual intolerance to the active substances of plants.
It should be borne in mind that some herbs can be poisonous, so before using them to combat lice, it is necessary to study the properties of the plants.
If nausea, vomiting, dizziness and deterioration in general health occur while treating the head with herbal decoctions, the procedure should be stopped.
Precautionary measures
Due to the non-zero toxicity of dichlorvos to humans, it is important to take precautions when treating hair for lice. They are quite simple, follow the recommendations:
- • wear rubber gloves;
- • protect your eyes with special glasses;
- • use a respirator;
- • do not touch your face with your hands;
- • refrain from eating during treatment
- • work in a ventilated room;
- • hide food from the aerosol.
When finished, remove gloves and wash your hands and face with soap. Be especially vigilant if the procedure involves a child. Children are more susceptible to poison, since a lower concentration is needed to poison them. If possible, carry out the procedure outside or on the balcony.
How to quickly remove lice?
The main mistake that parents make when treating lice is the incorrect use of pharmaceutical products. When treating, be sure to take into account the life cycle of parasites. Most pediculicides do not penetrate the well-protected shell of nits, so treatment must be repeated after 7-10 days, when nymphs hatch from the nits.
Many parents, desperate to cope with lice, spend a lot of effort cleaning the house, suspecting that the child is re-infected with lice through household items. Meanwhile, parasitologists say the fight should be focused on the baby's head, not the environment
A 2010 study published in the journal Open Dermatology found that the risk of transmission from combs, hats and toys is very low. Scientists tested students who had a total of more than 5,500 head lice. However, no parasites were found on their hats. The same goes for floors: When researchers checked the floors of 118 classrooms in a school with a head lice outbreak, no lice were found on them.
Is it possible to remove lice in 1 day?
Unfortunately, you can only get rid of lice in 1 day using a very radical method - shaving your head. However, before resorting to it, consider the following points:
- • You cannot bring a child with lice to the hairdresser. And shaving your head yourself can lead to cuts and infection.
- • Shaving can upset the child and mean temporary isolation. Many children are very embarrassed by such a radical hairstyle, as well as the reason why their parents resort to it.
- • For girls, a shaved head remains a social taboo.
- • In order to be sure to get rid of lice, you will need to completely shave your hair. Parasites cling to even the shortest hairs, so cutting with a clipper will not be enough
How to get rid of linen lice: effective methods
Linen or, in other words, body lice are a tiny insect (but unlike the species that prefers to live in hair, they are larger) that have good survival in an aggressive environment. It is difficult to remove such “uninvited guests”. Insects prefer to hide in warehouses of cotton linen, seams of wardrobe items (dresses, shirts), blankets, mattresses. If you have established that there is a linen lice in the room, how to get rid of it is a logical question that should arise first of all. Why? These insects pose a serious danger to human health.
How to protect yourself from lice infestation?
The main method of prevention is to avoid close contact with the head of an infected person. This is difficult to explain to a small child. But teenagers need to understand this simple rule, especially since recent head lice outbreaks around the world have been linked to the habit of taking selfies with children's heads touching. You should also teach your child not to use other people's combs, even though the likelihood of lice being transmitted this way is extremely low.
As a preventive measure, you can use essential oils, especially geranium oil, the smell of which repels lice. You can add a few drops of this oil to your shampoo. Girls with long hair can apply a few drops of oil directly to their hair.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of folk remedies against blood-sucking insects and their larvae:
- ease of use;
- efficiency;
- availability;
- low cost;
- a large selection of various options;
- Ease of use.
Disadvantages of products prepared according to traditional recipes:
- toxicity of many drugs;
- risk of developing allergic reactions;
- often - deterioration of the condition of the skin and hair associated with the aggressive effects of certain components;
- presence of restrictions, contraindications;
- duration of treatment;
- low effectiveness in advanced cases.
Is reinfection possible?
The likelihood of re-infection with lice at home is very low. However, it is worth washing your child’s bedding at a high temperature. Soft toys can be placed in a sealed plastic bag and left for two days. Contrary to popular myth, lice don't care whether a child's hair is clean or dirty. Therefore, frequent washing does not protect you from lice. The best advice is to avoid direct contact with other people. It is better to wear long hair in a ponytail or braid.
What else must be done when removing lice?
Pediculosis is a contagious disease. This means that if lice appear on one of the family members, it is necessary to examine all the others and take preventive measures.
It is better to use any anti-lice products in the bathroom so that the lice removed from the hair do not spread throughout the apartment. During treatment, the person who helps with the application and rinsing of medications, who combs hair and monitors the progress of treatment, must carefully protect themselves. When combing, cover your shoulders and back with a white towel so that you can see the falling insects. The room and everything in it must be washed thoroughly after manipulation. For disinfection, you need to use the same pediculicidal agents, for example, MediLis-Permifen.
Important! Lice and nits can be found not only in the hair, but also in the patient’s personal belongings. All clothing, bed linen, and towels should be washed at high temperatures. You can use a pediculicide solution for soaking. Things that cannot be washed can be treated with a steam cleaner, ironed or exposed to frost - at very high or low temperatures the pests die. It is also better to treat upholstered furniture, mattresses, blankets and pillows with a steam generator or dry cleaning. Head lice do not live in furniture, but they can wait out “difficult times” in it and then continue to parasitize people.
For difficult-to-handle items that cannot be dry cleaned, washed or ironed, you can use this method. Pack them as tightly as possible in a thick plastic bag and leave them in this form for 2 – 4 weeks. During this time, all adults and even nits will die of hunger and will not produce offspring. This method is suitable, for example, for outerwear.
It is also better to rinse the entire apartment with a solution of anti-lice or insecticide. In case of severe damage, you can call special services. The main thing is that the fight must be comprehensive so that not a single individual or egg remains viable. This is the only way to remove these parasites.
Effective method
Currently, there are many pharmaceutical preparations for lice. However, not everything is so simple with them. Although pediculicides have been approved for use by regulatory authorities and are approved by many pediatricians, there are studies that show they are unsafe. Scientists have found a link between the effects of pyrethrins and pyrethroids and increased levels of estrogen (which can increase the risk of cancer), as well as hyperactivity and other behavioral problems in children.
In addition, insecticidal shampoos often do not work because lice develop resistance to them. As an alternative, you can use the anti-pediculosis drug “Paranite”, which has a completely different principle of action. The dimethicone and mineral oil it contains irreversibly block the respiratory tract of lice, leading to their death. Therefore, the drug does not lose its effectiveness even with repeated use. “Paranit” is a low-hazard compound, so it can be used to treat all family members, including children over 1 year old and pregnant women.
To achieve the effectiveness of treatment with “Paranite”, the drug must be applied generously to each strand of hair, starting from the roots to the very ends. The kit includes a fine-tooth comb, which is very effective both in diagnosing head lice and in combing out lice and nits. The new generation product “Paranit” helps to quickly and safely cope with head lice.
Popular recipes
If not one drug is used to treat head lice, but a composition of several components, this mixture is used immediately after preparation. Otherwise it will lose its properties. Before starting the procedure, the hair is thoroughly combed, and if necessary, a plastic bag or rubber cap is prepared to cover the head (if required by the folk medicine recipe). The frequency and number of procedures depend on what particular product is used to eliminate blood-sucking insects.
Lemon acid
White crystalline powder costs little, but is effective in treating head lice. Citric acid affects both adults and their offspring. Because of this folk remedy, lice become lethargic, so it is easier to comb them out of the head.
Insects also lose their ability to lay larvae. This slows down the increase in the population of bloodsuckers. In addition, the acid corrodes the adhesive substance with which the nits cling to the hair, so after treatment the larvae fall off the strands on their own.
Citric acid is generally well tolerated. Contraindications include individual intolerance, high sensitivity of the skin. In these cases, as well as in case of overdose during the manufacture of the folk remedy, itching, redness of the skin, and allergic reactions are possible.
Please note that con slightly lightens the hair.
Famous folk recipes based on citric acid:
- Hair rinse. Dilute half a teaspoon of crystals in 2 liters of water and rinse your hair. After this, carefully comb out the insects with a thick-toothed comb.
- Dilute the acid with water in a 1:1 ratio. Distribute selectively throughout the strands. Wrap your head in plastic or foil. After an hour, rinse your hair.
- Prepare an infusion of 10 g of comfrey, 5 g of citric acid and a glass of boiling water. After cooling, spread over the scalp. Use daily. The minimum course of treatment is 6 days, the maximum is 10.
- Make a decoction by combining a glass of water, 5 g of acid crystals and 15 g of an herb called larkspur. Boil all this and keep on fire for another 10 minutes. Filter, let it brew and rub it warm into the root zone for 10 days.
- Another tincture is prepared from St. John's wort and tansy. Take 1 tbsp. l. each herb, pour boiling water and leave in a thermos for at least 6 hours. Then add 5 g of acid crystals. Rub the infusion into your scalp.
As a folk remedy against lice, citric acid is effective at the initial stage of pediculosis and with a small number of insects.
Laundry soap
The drug is used in many folk recipes not only to combat lice, but also against helminthic infestations, fungal diseases, etc. The high effectiveness of soap is due to the large amount of alkali, which also has a drying effect on the hair.
In order not to spoil your hair, you need to strictly follow the instructions for using this folk remedy. It is not prohibited to use laundry soap to eliminate the symptoms of head lice in children and expectant mothers. Find out what will help increase the effectiveness of the drug and how long the course of treatment lasts.
Does laundry soap help against lice and nits, how to use it effectively
Dust soap
This remedy is a well-known insecticide, also used in folk medicine. The dust would not be able to effectively cope with insects if it did not contain a pesticide, albeit in a small volume - only 5%. Because of this feature, dust soap, unlike laundry soap, has many contraindications for use.
Among the complications associated with the accumulation of toxic substances in the body are deterioration of immunity, nervous and other disorders. After reading our article, you can decide for yourself: is it worth using dust to fight parasites, or is it better to choose a slightly less effective, but safer folk remedy.
Rules for using dust soap against lice and nits
Hydrogen peroxide
It is considered one of the most effective drugs for removing lice and eliminating nits. Positive changes are noticeable after the first procedure. Even if peroxide does not destroy insects instantly, it will still disrupt their life cycle, deprive them of the ability to feed and increase their population on a person’s head.
The product is not used in its pure form, despite the fact that it is non-toxic. We will tell you how to properly dilute and use peroxide so that it helps get rid of lice, but does not dry out or burn your hair.
Is hydrogen peroxide effective against lice and nits, how to use it correctly
Vodka
Popular rumor gives alcoholic drinks antiparasitic properties, while noting the high effectiveness of the products. It is believed that pure alcohol or vodka can eliminate blood-sucking insects in just 1-2 applications. At the same time, opponents of such treatment methods cite other compelling arguments: alcohol solutions harm hair, dry out the skin, which is why they are not suitable for everyone.
Find out the specifics of using vodka masks to get rid of lice, as well as precautions for using this folk remedy against lice.
Does vodka help against lice and nits, secrets of proper use
Vinegar
A pungent odor and associated dizziness, skin burns, deterioration of the structure of curls is an incomplete list of side effects from the use of vinegar. Nevertheless, the method is popular. The secret to the popularity of this folk remedy is simple: it is suitable for adults and children over 3 years old, quickly destroys lice and their larvae in a couple of sessions, and is very cheap.
Vinegar is not used in its pure form, supplementing it with other components. In addition, step-by-step instructions will help you avoid negative consequences from using the essence, which, together with recipes against lice, are described in detail in our thematic material.
Does vinegar help against lice and nits, a recipe for an effective solution
Mustard
The folk remedy fights various insects in the garden: Colorado beetles, wireworms, aphids, as well as parasites that attack the human body - worms, demodex, lice. Each type of insect has its own recipes to combat. All of them are united by the powerful antiparasitic effect of mustard, which is often called a natural antibiotic. When used correctly, the drug heals the skin and has a beneficial effect on the hair.
For those who want to remove lice and nits using mustard, the most popular folk recipe will help. The multicomponent product is prepared as follows:
- A 3% solution is made from a 9% bite. To do this, 1 part of the essence is diluted with 3 parts of boiled cooled water.
- Measure out 200 milliliters of the resulting liquid.
- Add 2 tablespoons of dry mustard powder to it.
- Drive in 2 chicken eggs.
- Mix everything thoroughly. You can add an ampoule of vitamin E to this folk remedy.
- The resulting mixture is distributed over the hair, which is then covered with a plastic cap.
- After 3 hours, the mustard-vinegar mask is washed off, and each curl is thoroughly combed.
Frequency of use: 3–4 days in a row. After a week, the course of treatment with a folk remedy can be repeated.
Tar soap
Another remedy actively used against pediculosis. Tar soap contains birch tar, which has a negative effect on the nervous system of insects. Additional components - citric acid, phenols, alkali, etc. - repel bloodsuckers, cause burns to them and reduce the productivity of lice.
The soap also contains fragrances, softening ingredients (bar form) or esters, herbal extracts (liquid consistency). All this will allow you to fight lice at home, without damaging your scalp and hair.
You will learn about folk methods of using tar soap against pediculosis from our article.
How to get rid of lice and nits using tar soap
Dichlorvos
The updated and improved product traditionally copes with various insects: ants, fleas, cockroaches, bedbugs, and lice. Today, several varieties of dichlorvos are produced. They are less toxic than those produced in the Soviet era, but still require compliance with safety precautions. You need to wear a mask and rubber gloves when working with the drug. Do not allow it to get into your eyes, mouth, or nose.
We will tell you about other rules for using the product, as well as how different types of modern dichlorvos differ from each other.
Is it possible to remove lice and nits with dichlorvos and how to do it
Kerosene
Technical fluid is not only fuel, but also an effective remedy against parasites, popular in folk recipes. Kerosene literally cuts off oxygen to insects, which inevitably leads to their death. The effectiveness of such processing reaches 90%. To eliminate lice, use pure technical kerosene or mix it with other ingredients: milk, water, honey, shampoo. The second option reduces the toxicity of the drug.
In our article you will find folk recipes based on kerosene that will help get rid of bloodsuckers on your head.
How to use kerosene for lice and nits without harming your health
Cranberry
Due to its rich acid content, this wild berry acts on nits in much the same way as vinegar. Cranberries corrode the sticky substance with which insect larvae attach to hair. For this, concentrated cranberry juice is used. This folk remedy is considered one of the safest for humans. However, it can also cause skin irritation (all due to the same acids).
Find out how to properly use the berry, and whether cranberries can rid your hair of adult parasites.
Does cranberry help against lice and nits on the head, how to use it correctly
Folk remedies that help eliminate lice and nits also include mayonnaise, henna, hellebore water, etc.