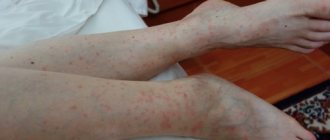
Only those who are lucky enough to avoid contact with fleas firmly believe in their harmlessness to humans. The opinion is erroneous, because blood-sucking animals have long been established in everyday life and parasitize not only domestic animals, but also their owners. Flea bites are quite painful, but this is not the biggest nuisance after an insect attack.
Armed with a special tool for piercing human skin, bloodsuckers are capable of infecting a dangerous disease and causing a serious allergic reaction. To protect yourself from possible complications, it is important to learn to recognize the consequences of a flea attack and learn the rules of first aid.
Who are fleas and how do they bite?
To date, more than 2 thousand species of fleas have been studied, divided into 200 genera and 15 families. Moreover, they all look the same, so the uninitiated are unlikely to distinguish representatives of different families by their appearance.
Translated from Latin (Siphonaptera), the name of the insect consists of two words: “wingless”, “pump”. The mouthparts of the brownish parasite actually resemble a pump equipped with a tool for piercing the skin of the victim. After the puncture, the insect sticks its head into the wound and releases a small amount of a special enzyme that prevents blood clotting. Since flea saliva does not contain painkillers, the insect bite is painful, reminiscent of a needle prick.
Due to the spines located on the chitinous shell, the flea easily clings and moves in the fur, feathers, and hair of the owner. Thanks to its developed limbs, the insect can move by jumping, up to 30 cm in height and up to half a meter in length. The length of the blood-sucking insect rarely exceeds 5 mm, so the insect, covered with a durable shell, is almost impossible to catch, and even more difficult to crush.
Interesting fact! The insect is distinguished by incredible jumping ability and endurance. A tiny flea can carry a load 160,000 times its own weight, jump 150,000 times its own height, more than 30,000 times in a row. Moreover, a year of living in low temperatures in no way affects the viability of the insect.
Can fleas bite humans?
In most cases, fleas parasitize at the expense of humans only when there are no animals nearby. And the point is not that the blood of a cat or dog is tastier - insects are unpretentious in this matter. It's all about the wool or feather cover, which provides the bloodsucking creatures with the most comfortable existence.
Often, flea bites appear in those people who simply got in their way first. And pet owners especially often find itchy, painful spots on their legs.
However, some varieties of fleas appear regardless of whether there is an animal in the house or not. The following types of fleas can be found especially often:
- Dog and cat. The animal can bring both of them from a walk. Insects jump on the floor and happily switch to human blood.
- Chicken ones - you can “pick them up” after going to the chicken coop. Poultry becomes infected after contact with wild birds.
- Ratidae, parasitic on rats and mice. It is believed that it was this type of flea that marked the beginning of the terrible plague epidemic that arose in the 14th century, killing more than 25 million people.
- Human - Domestic flea bites are characterized by very painful bites and can live on both humans and animals.
- Earthen (basement) - live in the upper layers of the soil. Once in a person’s home, they occupy carpets, furniture upholstery, and areas behind the baseboards. The bites of earthen (basement) fleas are localized under the nail plate, where the females lay their eggs. The bite site itches, swells, and festers.
- Sandy - live in the sand, mainly in coniferous forests. Unlike its relatives, the sand flea does not just bite, it penetrates the skin and lives there.
- Bed fleas live in bedding and furniture upholstery. Bed flea bites occur in the dark.
Having discovered flea bites on their body, many people let the situation take its course, without even thinking about the possible danger. It is important to understand that swollen areas of the body covered with red spots are just the tip of the iceberg. The main danger lies in the ability of insects to transmit deadly infections: typhoid, salmonellosis, encephalitis, etc.
Portrait of a bed flea
The bed (household) flea has a very small body size. It is very difficult to examine individual parts of an insect’s body with the naked eye; can this be done under a microscope? The body of the parasite is round, slightly compressed on the sides. The body cover is hard, chitinous, and performs a protective function; it is not easy to crush this shell with your fingers. The length of the flea is only 2-4 mm .
The color of juveniles is black; in adults it varies from yellow to dark brown. There are no wings. There are three pairs of paws. The hind ones are more powerful - with their help the flea pushes off, making a jump. The flea jumps high ( about half a meter ) and far ( a meter or one and a half ). This method of movement is very convenient for finding a victim on which the bloodsucker can easily jump. The bristles that densely cover their small bodies help fleas stay on any surface while they eat.
The insect navigates in space with the help of antennae, capturing all kinds of sounds and smells. The flea's oral apparatus is of the piercing-sucking type and is a proboscis. There is no anesthetic enzyme in flea saliva, which is why their bites are very painful compared to mosquitoes or bedbugs.
Why do fleas appear in an apartment?
A flea, first noticed in a clean, tidy house, causes extreme bewilderment and displeasure of the owners. This reaction is explained by people’s confidence that parasites appear only in unsanitary conditions. And yet, if you have a pet, you can suspect that the parasites were brought from a walk.
The situation becomes especially unclear when there are no pets in the apartment, but fleas appear. However, experts say that in most cases, a flea is a causeless, random and unexpected phenomenon.
Very often, if we are talking about a private house or an apartment located on the ground floor, insects enter through basements or directly from the street. A little less often, fleas enter an apartment through windows, doors, ventilation, cracks in the walls, and joints of water pipes.
So, let's look at the main ways parasites get into your home:
- from neighboring apartments: through loggias, balconies, thresholds when the door is open;
- from basements (the damp warmth of basements is the best environment for flea breeding);
- from attics or technical floors;
- with dirty shoes;
- from adjacent non-residential premises: supermarkets, warehouses;
- on the fur of a pet after a walk;
- on the fur of rodents that enter a person’s home with the onset of cold weather (especially important for private homes).
Attention! Even one flea found in an apartment is a reason to contact an exterminator. A person sees only 1 flea out of 100 living ones, because for each adult there are many pupae, larvae and eggs.
Precautions when getting rid of fleas
When dealing with domestic parasites, it is necessary to strictly adhere to precautionary measures. This will help optimize work and reduce the risks of negative consequences. By ignoring strict rules, you can cause enormous harm to your body, as well as expose your loved ones, especially children and pets, to the risk of infection.
Personal safety measures
If you are planning independent actions to combat insects, you need to pay attention to the following aspects:
- take care of protective clothing. This is especially true for chemical control methods. It is necessary to have gloves, a respirator, shoes and clothing made of thick fabrics or polyethylene;
- provide for the presence of a vacuum cleaner, broom, iron, brush, rag, bags, etc. This is necessary so that during the work everything is at hand, since leaving the room or searching for the right thing will be inconvenient;
- make sure there is adequate ventilation. This is especially necessary after chemical treatment. You should immediately check how easily the windows and doors open.
- Chemical processing agents are highly flammable. It is recommended to keep this in mind and avoid open flames. When using electrical appliances, it is necessary to check the serviceability of sockets and wires to avoid sparks.
General safety measures when there are children and animals
Particular attention should be paid to the points below if you have children and pets. Elderly people also need help and need to be taken care of:
- Decide on the choice of means. To do this, you need to familiarize yourself with the necessary information and instructions for use. It is recommended to pay attention to the timing of the procedure and assess the situation. You will have to leave the premises for some time, so you should take care in advance about who will be there and where. You may have to set up a crib and pet house in another room, since chemical disinfection takes a long time.
- At the end of processing and keeping for a certain time, it is necessary to thoroughly ventilate the room. Even if there is a slight odor, the return to the premises should be cancelled. Children's bodies and animals' bodies are particularly sensitive to toxic substances.
- Thoroughly treat with a soapy solution and soda those places that the child will come into contact with or that the animal can reach.
- When using the powder, you must make sure that neither a child nor a pet can get it.
- If there are any unspent funds left for disinfestation, they must be hidden in places inaccessible to children and animals.
Video: flea trap
Signs and symptoms of flea bites
Flea bites are always accompanied by pain, which the affected person characterizes as a needle prick. An enzyme injected into the wound by insects causes itching, swelling and redness of the affected area. As a rule, flea bites are accompanied by local reactions noticeable on the human body:
- The attack is accompanied by sharp pain, because unlike other parasites, during the bite the insect does not release an anesthetic substance.
- Immediately after an insect bite, a swollen red spot remains on the body.
- For several hours, the victim experiences serious discomfort due to the itching and burning sensation.
- The puncture point is not visible, but a speck of blood appears at the site of the bite. If there are many bites, extensive hemorrhages (bruises) form around the wounds.
- Flea bite marks are located in groups of 2–3 spots with a distance of 1–2 cm between them.
- To a greater extent, insects live on the floor or baseboards, so in most cases the legs are affected: legs, feet.
Attention! Scratching the wound can lead to infection.
For allergy sufferers, blood-sucking saliva can cause a noticeable deterioration in well-being: difficulty breathing, increased body temperature, gastrointestinal upset, swelling of the lips. Without timely medical care, swelling of the larynx, suffocation, and death can occur. But even an absolutely healthy person can develop a condition resembling an allergic reaction - pulicosis. It manifests itself:
- continuous rash;
- inflammation, suppuration of wounds;
- ulcerations in the oral cavity;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- increased temperature;
- headache.
Having discovered characteristic signs of a flea attack on your body, you need to carefully inspect your home, paying special attention to baseboards, carpets, and animal bedding (if any). If your fears are confirmed, you should see a specialist and find out what to apply to flea bites.
Allergic reaction
For allergy sufferers, even a few flea bites are extremely dangerous. If you do not seek medical help in time, the consequences will be severe. Insect saliva causes serious deterioration in health, accompanied by fever, difficulty breathing, and damage to the gastrointestinal tract. Bites can lead to inflammation of the larynx, angioedema and suffocation. In some cases, death is possible.
Even a healthy person is not immune from an allergic reaction. A purulent rash, fever and headache are signs of pulicosis. Its causative agent is the human flea. These insects can infect the victim with worms, salmonellosis, and plague.
What infections can fleas carry?
The insects themselves cause severe skin lesions - sarcopsillosis and pulicosis. However, by feeding on the blood of an infected victim, fleas become carriers of more than 25 dangerous infections (and the viability of pathogenic microbes in the parasite’s body remains for a year).
The 10 most dangerous include:
- tularemia;
- encephalitis;
- anthrax;
- plague;
- typhus;
- salmonellosis;
- listeriosis;
- hepatitis;
- brucellosis.
Relieving inflammation after a flea bite
While for some people a flea bite remains almost unnoticeable, for others it can turn into an inflammatory process.
To relieve inflammation use:
- Sulfur ointment (available without a prescription). The product is applied to the affected areas in a small amount. The ointment has an unpleasant odor, but the effect is noticeable after three applications.
- Infusion of celandine, wormwood, calendula, dandelion. To prepare, pour 15 g of dry herb with a glass of boiling water and let it brew for half an hour. Dip a cotton pad in the solution and lubricate the wounds.
- Calamine solution. The product contains zinc, which has healing properties. The drug is applied in a thin layer to the bites up to four times a day. There is no need to rinse the product off the skin.
Traditional medicine methods are used as additional therapy.
Why are flea attacks dangerous?
A single flea bite does not pose a serious threat to human health. But with systematic attacks by “bloodsuckers”, the following complications can develop:
- Unbearable itching and burning of the affected areas of the skin. This in itself is not a complication. The danger of infection lies only in those who furiously scratch the bite sites.
- Mental or neurological disorders (a person is constantly attacked by imaginary insects).
- Acute allergic reactions, dangerous in their rapidity, which can be complicated by Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock.
- Infection of the body with helminths.
- Damage to the body by toxic substances from flea saliva.
In addition, fleas living on sick or dead animals can carry parasitic worms and fungal infections. Zoonotic infections (tularemia, listeriosis, brucellosis) “borrowed” by insects from animals pose a significant danger. Such diseases are difficult to diagnose and almost impossible to cure.
What to do if bitten by a flea?
If you find flea bites on your body, do not scratch the affected areas of the body under any circumstances, but immediately wash them with running water and antiseptic soap. It is recommended to treat the bite site with calamine soothing lotion, but if this is not available, use alternative treatment methods.
You can treat the affected area of the body with water and apple cider vinegar. Mix the necessary ingredients in a 1:2 ratio and refrigerate. Soak a thin cloth in the cooled liquid and apply it to the bitten area.
A paste made from sodium bicarbonate and water relieves itching well. The resulting paste is applied to the bite site for 15 minutes. You can also prepare a liquid from 250 ml of water and lemon peel. The infused mixture is used to treat itchy areas.
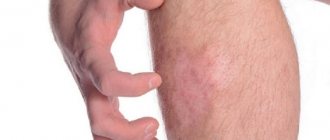
What does a flea bite look like?
By examining the mark of a flea bite, you can guess what type of insect attacked. Rat or cat fleas leave tiny sores that resemble allergic rashes. Inhabitants of large animals leave painful swellings that resemble bee stings.
Regardless of the type of parasite that bites, the affected area appears as a tiny red dot, around which a halo of reddened skin forms. Redness lasts from 2 to 48 hours . If an allergy develops, the local reaction does not disappear for several weeks.
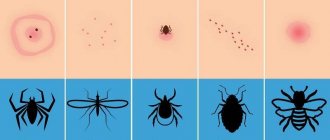
What is the difference between a flea bite and other bloodsuckers?
Mosquitoes, linen lice or bedbugs can attack a person right in his home. Moreover, the bites left by bloodsuckers are easily confused, which means that the likelihood of erroneously identifying the pest is quite high. But, although flea marks on the human body resemble wounds left by other parasites, they have characteristic differences:
- a flea attack is always accompanied by sharp pain (insect saliva does not contain an anesthetic);
- the presence of subcutaneous hemorrhages;
- the wounds are located randomly, with 2–3 spots next to each other;
- the main affected area is the lower limbs (fleas rarely attack open areas of the body).
This is interesting! To identify the elusive "criminals", you can take a sheet of white paper and place it in the place where someone is biting. After some time, black dots will appear on a white background, disappearing at the slightest vibration of the sheet. These are fleas.
Comparison of flea and bedbug bites
There are several signs that allow you to distinguish a flea bite from a bug bite:
- Fleas bite the lower limbs, and bedbugs bite the entire body.
- Fleas bite randomly, and bedbugs make paths.
- Fleas attack at any time of the day, and bedbugs attack at night.
- A flea bite resembles a needle prick, and the bug attacks painlessly.
Can fleas bite humans?
Among the huge species diversity, there are only a few species that “do not change” their host. These faithful companions include fleas that parasitize bats. All other dog, bird, and cat fleas can easily change their food source and migrate to other types of warm-blooded animals. Human blood is slightly different in composition and temperature, but this does not make it unsuitable for parasites to feed on, so people can be attacked by jumping vampires.
Separately, it is worth noting the human flea, which prefers to feed on human blood. Like other relatives of the flea family, these parasites do not live on the human body and use it only as a source of food.
If you look at what fleas look like on humans, this species has no striking differences from other representatives, with the exception of larger sizes. The difference can only be seen under a microscope. It is impossible to examine an insect while moving - a person’s gaze only has time to note the presence of the parasite and its disappearance in the next moment. It is worth noting that a flea can make up to 30,000 jumps without stopping.
Use of medications
After a flea attack, you need to provide first aid to the victim:
- Using warm water and laundry soap, wash off the remaining insect saliva and feces;
- treat the wound with brilliant green, hydrogen peroxide, alcohol or vodka;
- apply a cold compress to prevent swelling of the skin, relieve itching and pain;
- lubricate the affected area with anti-bite cream/ointment;
- Give the victim any antihistamine to promptly stop the development of an allergic reaction.
After providing first aid, you need to act according to the situation: if up to 6 bites are noticeable on the skin, and the person does not suffer from allergies, medical attention may not be needed. In all other cases, the victim must be shown to a doctor. A specialist will conduct an examination and tell you how to treat flea bites correctly.
Pharmacy drugs
The doctor prescribes pharmaceuticals depending on the severity of symptoms, the person’s age, and the extent of the lesion. Most often, flea bites on humans are treated with the following medications:
Fenistil gel
A unique product that allows you to quickly and effectively relieve itching, redness and swelling. Often prescribed to treat allergic rashes. Used 2–4 times a day. Contraindicated for infants, as well as for the treatment of large areas of skin for young children.
Hydrocortisone ointment
A potent hormonal drug that has many side effects, therefore it is prescribed only in emergency cases. The ointment is indispensable for severe consequences of a flea attack, when “softer” medications have proven to be ineffective.
The drug quickly eliminates all symptoms of the bite. It is not used for pregnant women and children of the first year of life.
Balm “Star”
A time-tested product with a sharp menthol-eucalyptus aroma that perfectly relieves pain and swelling. It is enough to rub the balm into the area affected by insects every 20 minutes until the discomfort completely disappears.
Balm “Star”
Attention! If the bites become inflamed due to scratching or ulcers form on the wounds, the caustic composition of the star can only cause harm. The balm is contraindicated for children under 2 years of age and pregnant women. Since the product can cause an allergic reaction, a sensitivity test must be performed before using it.
Miramistin
An antiseptic prescribed for flea bites has a wide range of antimicrobial effects. Kills gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and fungi, which the flea generously shares.
With regular irrigation of the affected areas of the skin (2-3 times a day), the pharmaceutical preparation starts regeneration processes, relieves inflammation, without being absorbed into the bloodstream. Suitable for patients of all ages.
Flucinar
A powerful hormonal agent is available in the form of an ointment or gel. Like Hydrocortisone ointment, it is prescribed in the most serious cases. Relieves allergy symptoms and inflammation, relieves pain.
Apply a thin layer to flea bites at least once a day. It is not prescribed for the slightest suspicion of a bacterial, viral or fungal infection. Contraindicated: in the first trimester of pregnancy, children under 2 years of age and immediately after vaccination.
Sulfuric ointment
Due to its high sulfur content, the antiseptic disinfects and kills germs and parasites. Not used to treat children under 3 years of age or during pregnancy. Apply to affected areas 2-3 times a day.
Important! In combination with hydrogen peroxide or other pharmaceuticals, it can cause severe chemical burns. Therefore, it can only be applied to clean skin and it is advisable not to combine it with other external products.
Transmitted diseases
A flea bite on a person, a photo of which clearly shows the visible consequences of an insect attack, is dangerous not only for its external signs and discomfort.
Fleas are carriers of various diseases, including those fatal to humans. Thus, rat fleas are considered one of the reasons for the spread of plague epidemics that destroyed medieval settlements and entire cities.
| Types of diseases | Classification | Incubation period, days | Carriers of the pathogen | Brief description, symptoms |
| Diseases of the musculoskeletal system | Brucellosis | 7 – 14 | Cattle and small cattle, pigs. | Characterized by joint pain, weakness, sweating and sudden increases in body temperature. Over time, the disease spreads to other organs, covering the nervous, respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and genitourinary systems. |
| Diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular systems | Typhus | 6 – 14 | Small rodents. | Severe headaches, confusion, pink rash, fever, chills, back pain, high temperature. Possible death. |
| Encephalitis | 4 – 21 | Livestock, small rodents, birds. | The virus infects nerve cells, spreading to the brain. May be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, headaches, fever, convulsions, impaired consciousness, loss of sensation in the limbs, and hallucinations. | |
| Listeriosis | 7 – 30 | Pets. | Weakness, fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes, headaches, conjunctivitis, sore throat, rash. The disease can take the form of encephalitis, meningitis. Possible death. | |
| Skin diseases | anthrax | 2 – 4 | Livestock. | The formation of a carbuncle (most often a single one) followed by ulceration and the appearance of a scab, accompanied by an increase in body temperature, fever, weakness, itching and swelling. In the intestinal or pulmonary form, death is possible. |
| Tularemia | From a few hours to 21 days | Small rodents, hares, rabbits. | The infection affects the skin, lymph nodes, sometimes affecting the mucous membranes. Accompanied by headaches, fever, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes, sweating, and pinpoint lesions of the mucous membranes. | |
| Bubonic plague | 2 – 12 | Small rodents, wild and domestic animals. | It is characterized by the presence of a specific bubo (pronounced skin neoplasm, most often in the groin), fever, high temperature, pain in the groin area, and weakness. | |
| Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract | Pseudotuberculosis | 3 – 21 | Small rodents. | It affects the intestines, spreading to the liver, and sometimes affects the joints. The disease is characterized by fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, headaches, conjunctivitis, and a white coating on the tongue. |
| Salmonellosis | From 6 hours to 2 days | Wild and domestic animals, humans. | Acute intestinal infection, accompanied by symptoms: vomiting, weakness, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, dehydration. |
A flea bite on a person can transmit bubonic plague!
Any infectious diseases transmitted by blood-sucking parasites are called vector-borne diseases. Infection can enter the human body not only through the saliva of an insect, but also when scratching an existing bite wound.
However, flea bites can lead not only to infection by a virus or bacteria, but also cause the body to respond to saliva containing substances that prevent the victim’s blood from clotting.
They can cause an allergic reaction and contribute to the development of dermatitis, eczema, urticaria, and Quincke's edema. Children and people prone to allergies are especially susceptible to this phenomenon.
Flea bites in children
Children have thinner skin than adults, and the immune system is not fully developed, so flea bites cause a more severe reaction in the body. Even one insect bite can cause hives. This symptom makes it very difficult to identify the “aggressor,” especially in children of the first year of life.
More often than adults, children develop an allergic reaction, manifested by a clear clinical picture:
- a sharp increase in temperature to abnormal levels;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- difficulty breathing;
- chills;
- anxiety;
- subcutaneous hemorrhages (occur much less frequently than in adults).
Moreover, children scratch itchy bites until they bleed, which is why they are at risk for secondary skin infections. Due to constant discomfort, some babies develop nervous disorders.
When to see a doctor
A flea bite on a person, a photo of which demonstrates possible variations in its manifestation, may be a reason to contact a medical facility if the following symptoms are present:
- long-lasting spots and regular itching;
- an increase in the area of irritation and the growth of spots into ulcers;
- the appearance of pus on the wounds;
- the occurrence of ulcerations on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- the appearance of weakness in the body, dizziness;
- fever, chills and increased temperature;
- severe swelling at the bite site;
- the occurrence of attacks of suffocation, a feeling of laryngeal congestion;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
The initial examination is carried out by a therapist, who, based on the results of the examination, will prescribe diagnostic measures and, if necessary, give a referral to another doctor: a dermatologist, otolaryngologist, surgeon, gastroenterologist, neurologist.
Actions for allergies to flea bites and the development of irritations
If the development of an allergic reaction is not stopped in a timely manner, parasite bites can provoke severe and life-threatening conditions. The following symptoms should be a cause for concern:
- difficulty breathing, sometimes barking cough;
- rapid swelling of the ears, lips, tongue;
- pallor;
- tachycardia.
Having noticed the listed symptoms, the victim needs to be given an antihistamine: “Suprastin”, “Diazolin”, “Eden” and call an ambulance. Without timely assistance, these symptoms develop into angioedema and anaphylactic shock. Life-threatening complications require highly qualified medical care and specialist supervision, even after the patient’s condition has been stabilized.
Features of bedbug bites
Some features of bedbug bites:
- Bed bug bites are flat and red.
- Bites often appear in tracks of 3 to 5 bites in a row.
- Bites take a long time to heal.
- Itching appears gradually.
- If an adult bites, it injects an anesthetic, so the insect is difficult to notice after the bite.
- If small bugs bite, the bite is felt immediately.
- They bite at night.
Details about bedbug bites
This is what bedbug bites look like
Bedbug bites
Prevention measures
To protect your home from the penetration of dangerous insects, it is enough to adhere to preventive measures:
- Keep your home clean, paying due attention to hard-to-reach areas.
- Seal cracks in baseboards, window sills, and trim.
- Buy flea collars for your pets.
- After each walk, thoroughly wash and dry your pet's paws.
- Wash the rug lying by the front door and the dog or cat bedding as often as possible.
- Keep bouquets of plants that repel fleas in the house: wormwood, mint, tansy, calamus, etc.
- Once a month, wipe all surfaces in the house with a soda-soap solution.
- When going to places where parasites may accumulate, you need to dress in such a way as to block access to your body.
Having discovered at least one parasite in your home, you should not let the situation take its course. It is important to remember that fleas multiply very quickly and in just a week, hungry hordes of insects will literally “gnaw” the inhabitants of the apartment.
So, if bloodsuckers do appear, you need to call specialists from sanitary and epidemiological services to combat them.
Methods of disposal
If the number of fleas in a residential area is small, you can fight them with chemical insecticides. There are many effective means that can be used to poison these insects, but when using them, some precautions should be taken to avoid poisoning. If this option is undesirable, you can use folk remedies to kill fleas.
In apartments on the first floors, even with the use of folk and chemical remedies, fleas appear again after a short time. This indicates that the basement is infested with them. In this case, fighting with simple methods will not help and you should turn to professionals to thoroughly disinfect not only the apartment, but also the areas underneath it.
Professional pest control
Professional pest control is the most effective. Experts agree to poison insects even in large rooms. They use special equipment and potent insecticides that can destroy not only adults, but also eggs, larvae and pupae. Many companies provide a guarantee for their services and, if necessary, carry out repeated disinfestation free of charge.
Chemicals
The most common method of killing fleas is to treat the premises with chemical insecticides. They are available in the form of powders, concentrates, aerosols, drops, and emulsions.
Option for a remedy for earthen fleas.
Insect control can be carried out with the following drugs:
- "Clean house".
- “Butox 50”.
- "Raptor".
- “Ecokiller”.
- "Phenaxin".
- “Nats.”
- "Raid".
- "Combat".
- "Dichlorvos".
It is difficult to determine which product is the best. One treatment with any of these drugs does not always give a good result, because... they are unable to destroy flea eggs. To achieve a positive effect, it is advisable to carry out 2-3 procedures with an interval of 5 days.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies that help repel fleas are recommended to be used when the number of insects in the house is small. To poison parasites, you can prepare a mixture of soda and salt. The components are taken in equal proportions. The composition should be thoroughly treated with all carpets and sprinkled in corners and on the floor in the basement. Turpentine can be used to treat outbuildings.
Herbal products are also effective in controlling fleas. A decoction of wormwood and tansy helps to quickly eliminate parasites. To prepare it, 2 cups of wormwood are mixed with 1 cup of tansy and 1 cup of eucalyptus.
The composition must be filled with 10 liters of hot water. The mixture is boiled for 3-5 minutes. After this, the container with it is removed from the heat, wrapped in a blanket and left to infuse for a day. The finished product should be filtered, poured into a spray bottle and used to treat the room.
To repel fleas, it is recommended to place spruce and pine branches in the corners of the living room. These insects cannot tolerate the smell of pine needles. To treat the room, brewer's yeast and garlic are used, mixed in equal proportions. The mixture should be rubbed onto all places where fleas can enter the house.
Folk remedies for fleas.
Preventive measures
To prevent the appearance of parasites in the apartment, preventive methods are used:
- After baiting parasites, use insecticides once a week.
- Keep the house clean.
- Do not allow old things to lie around.
- Pets and indoor plants are treated with insecticides.
- Check your pet's fur regularly.
- Limit the contact of domestic cats and dogs with their street “brethren”.
- Fresh mint, tansy, and wormwood are laid out around the house.
- Use an ultrasonic repeller. The device is absolutely safe for pets, but effectively eliminates fleas.
If you cannot cope with the parasites on your own, seek professional help. The procedure is expensive, but your own health and the health of loved ones is more expensive.
Bedbugs or fleas
When declaring war on parasites in order to protect yourself, your children and pets from their attacks, do not forget the main thing - to correctly determine the source of the attacks. When a person begins to be bothered by bites, he is often inclined to act based on premature conclusions. Here's why fleas can be confused with bedbugs: