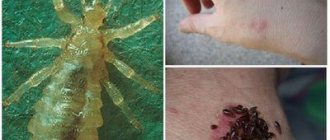
As soon as the first shoots appear in the spring or seedlings are planted, they are immediately occupied by insects, hungry over the winter. The cruciferous flea beetle is the most active in the garden. The little dirty trickster has nothing to do with true fleas. He received this name due to his jumping abilities. And cruciferous is called for its love for the crops of the same name. A large population of cruciferous flea beetles can destroy fragile young plants in a matter of days. Therefore, knowledge of what the pest looks like and what available methods can effectively combat it will not be superfluous.
Biological features of cruciferous flea beetle
Insects belong to the family of leaf beetles. Widely distributed in Europe, the Caucasus, Asia, and Western Siberia. All representatives are characterized by an elongated body, the dimensions of which do not exceed 3 mm. Color is determined by species. In the photo of the cruciferous flea beetle, attention is drawn to the long antennae, consisting of 11 segments.
Cruciferous flea beetles can be distinguished from other small pests by their characteristic jumps. “Jumpers” are able to migrate and cover long distances, thanks to which they rapidly spread to new territories.
Species diversity
There are several types of cruciferous pests in the world fauna. The most common ones include the following:
- Southern cruciferous, also known as black, is the most dangerous representative of its family in flea beetle habitats. Adults gnaw leaves, larvae damage the young root system. The main difference between fleas is the black color of the body with a metallic sheen. The head and elytra are covered with rough spots. The length of the body is from 2 to 3 mm.
- Light-footed is an inhabitant of the forest belt in the southern regions. Adults gnaw leaves, young individuals are harmed by mining leaf blades. A distinctive feature of the light-legged cruciferous flea beetle is the resin stripe on the elytra, which smoothly tapers in the front fragment, and the black color of the back and head with a bottle tint. Body length is from 2.5 to 3.5 mm. The paws are yellow.
- Notched is characterized by a black wide suture stripe in the middle part of the elytra or a yellow border with deep indentations. Dimensions do not exceed 2.5 mm. Notched cruciferous flea beetles are pests of crops in Yakutia, Primorye, and the Amur region. The adults skeletonize the leaves, and the larvae live in the ground and damage the roots.
- The wavy species lives in the northern part of Europe, the Urals, Siberia, and the Far East. Adult beetles, like their relatives, gnaw off foliage. The larvae prefer lateral roots. A characteristic feature is a wide black near-stitch stripe with bordering yellow and light brown stripes. Pronotum and head black.
On a note! Insects damage not only agricultural crops, but also ornamental and wild ones. Cruciferous flea beetles colonize mustard, shepherd's purse, rapeseed, rutabaga, spinach, lettuce, cabbage, radish, young horseradish leaves, turnips, rapeseed, alyssum, and matthiola.
Agrotechnical control measures
Agrotechnical methods are used to prevent and control insects. These include timely planting, weeding and watering. This also includes planting helper plants. As an emergency measure, sheltering seedlings is used.
Landing dates
In order to reduce the impact of parasites on the leaves of seedlings, it should be planted before or after the onset of the main stage of development and hatching of the larvae. The most favorable time for planting early varieties is April, for late varieties – July-August. By the time the fleas appear, the April seedlings have time to take root and gain a foothold in the area, and its leaves become coarser. Due to the peculiarities of the life cycle of insects, they do not have time to cause significant harm to July seedlings.
Weeding
Another agricultural control method is to deprive pests of a place to live. This is achieved through regular weeding and other means of removing weeds, which are favorite places to live. You also need to remove tops and weeds from the site in the fall after harvesting. Otherwise, insect larvae will certainly appear in it in the spring.
Watering
You can get rid of cabbage fleas by increasing the humidity. These pests love dry air most of all. Therefore, timely and frequent watering can curb the spread and reproduction of fleas. Helper plants
You can also use helper plants that naturally repel pests. This happens because these crops are rich in essential oils and have a strong odor that fleas do not like. Phytoncidal crops include:
- Calendula.
- Marigold.
- Nasturtium.
- Coriander.
- Caraway.
- Fennel.
- Dill.
The effect will be achieved only if these plants are planted around the entire perimeter of the vegetable garden or garden.
Shelter for young plantings
In places where summers are often hot, a good way to save plants is to use a covering material (this can be a special mesh fabric or non-woven fiber). Covering work is carried out immediately after planting the seedlings in the soil. This method will not only save plants from parasites, but also protect them from exposure to direct sunlight, which can burn the leaves.
Lifestyle
Regardless of species, cruciferous flea beetles spend the winter as adults in the surface layers of the earth, under plant debris. With the onset of warmth, they leave their shelters and migrate to weeds, which serve as intermediate nutrition. When the first shoots of horseradish and radish appear, cruciferous flea beetles move onto them. Insects are not particularly picky eaters, but pests still show special love for cabbage seedlings and their young leaves during the period of rosette formation. Farmers also note the appearance of cruciferous flea beetle on rapeseed in the first and second ten days of May.
Adults scrape the skin off the leaves and absorb the succulent nutritional tissue, leaving behind specific holes. At temperatures above +15°C, fleas begin to actively reproduce. Females lay tiny elongated yellowish eggs in the soil, where larvae subsequently develop, feeding on plant roots. The eggs are only about 3-0.4 mm in length. The larvae have a thin caramel-colored body on 3 pairs of legs.
The exception is light-legged cruciferous flea beetles, which lay eggs on the leaves of radishes and radishes. The development of the larvae takes place inside the leaf mass, where they make mines. Egg laying begins at the end of June and continues until the end of July. There may be deviations in timing depending on geographic location.
The larvae hatch in 4-14 days. The final stage of development - pupation occurs in the soil in early August. The young beetles that emerge to the surface continue to cause damage in vegetable gardens, and in the fall they go into the ground for the winter.
On a note! The increased activity of cruciferous flea beetles occurs in hot weather. Significant population growth is recorded during periods of drought. Rainy weather keeps pest numbers down.
Signs of appearance
To recognize the pest in time allows you to be savvy in determining the appearance of an insect by the first signs. The signs are:
- Detection of ulcerative gnawing marks on the leaf parts of plants.
- The appearance of damage on the leaves in the form of skeletonization.
- Detection of interveinal gnawing.
- Detection of the insect itself.
Damaged foliage begins to dry out, which leads to the death of the young plant. The cruciferous flea beetle damages the leaves and stems of young seedlings, which subsequently turn yellow and die.
How to get rid of a pest
How to deal with cruciferous flea beetle is determined by the size of the population and the phase of plant development. It is worth noting that manual collection is an ineffective exercise, given the miniature dimensions of the bug and its jumping ability.
Agrotechnical measures to combat cruciferous flea beetle:
- Insects spend the winter period in the soil or in plant litter. Therefore, timely removal of all plant debris from the garden will significantly reduce the number of fleas and other pests.
- For the same purpose, deep plowing of the land is carried out in the autumn. Once on the surface, the wintering beetles will die from frost.
- Constant cleaning of weeds, especially cruciferous ones. It is also important to ensure that no weed seeds fall off during disposal. Having lost the food source that individuals use after wintering, pests will have no choice but to migrate to other areas in search of food supply.
- Feeding plants with fertilizers will help reduce the harmfulness of cruciferous beetles.
The fight against cruciferous flea beetle on cabbage begins at the stage of planting seedlings. It is recommended to plant as early as possible or plant seeds in early spring under film, in greenhouses. So, by the time the beetle population appears, the plant will have time to get stronger, the leaves will become coarser and insects will not be attracted to the seedlings.
Plants such as turnips and turnips are often planted, on the contrary, very late. As a result, seedlings appear when the peak of cruciferous flea beetles has already passed.
Holes with planted seedlings are mulched with tomato shoots or tansy. On hot days, the beds are shaded or covered with agrofibre. The edges should be secured and wood ash or hot pepper should be sprinkled around the perimeter. To repel the cruciferous flea beetle, agricultural or ornamental crops are watered with water with the addition of vinegar, chopped garlic cloves, wormwood or dandelion leaves, dill, and cumin.
Reasons for appearance
Cruciferous flea beetles live in the winter in the upper layers of soil or under plant debris. When spring comes and the ambient temperature rises above 15 °C, flea beetles come out of their wintering shelters. If the time of planting the crop coincides with the time of leaving hibernation, the insect will feed on young foliage.
Another reason for the appearance of insects on seedlings can be considered a large number of weeds and cruciferous plants. Their abundance near the future location of the seedlings influences the fact that the cruciferous flea beetle has a source of food and they can develop.
The appearance of leaf beetle insects is influenced by soil moisture levels. The cruciferous flea beetle is an insect that does not tolerate moisture well. In dry and hot weather, the flea beetle grows actively. If you water lightly or plant crops in soil with low moisture, you may find an increase in flea beetle infestation.
Catching beetles
Traps are an effective, safe remedy for cruciferous flea beetles. Making devices will not take much time and does not require significant financial costs. How to make your own trap:
- Build something like flags from available materials. These can be pegs with canvas attached or plywood or cardboard blanks. Lubricate one side of the panel with any adhesive (glue, honey, garden pitch, grease). Take the received attribute in your hands and walk with it along the beds, running the lower part over the plants. Fleas are very shy and will begin to actively jump and stick to the sticky fragment. When a fair amount of insects stick, remove them and repeat the process. Exercise with a flag is most effective during hot hours and dry weather.
- Make a cone out of cardboard so that it can completely cover the plant. Also coat the inside with glue and cover the seedlings one by one. A certain part of the fleas will stick to the cap.
- A less labor-intensive option is to lay plywood with glue applied along the beds. When moving along the ground, between plants, insects will stick to simple structures. You can also use a rag dampened with used automobile oil.
- A similar effect is achieved by low, flat containers of water, into which a little kerosene or vegetable oil must be added so that the captives cannot escape from the trap.
Important! Traps with glue, kerosene, and diesel fuel should be removed during rainy periods so that harmful components are not absorbed into the soil.
Proven folk recipes
Folk remedies against cruciferous flea beetle have been accumulated for decades. The most effective and well-proven among gardeners are the following:
- Dusting plants with wood ash or tobacco dust, lime, shag, and ground pepper. It has been noticed that the beetles are unusually “clean” and do not attack dirty leaves. The most inventive gardeners sprinkle young shoots with stove soot. After precipitation, the procedure is repeated.
- Planting plants along the beds that will repel cruciferous flea beetles with their aroma. These include garlic, dill, calendula, coriander, and marigolds.
- Fresh or dried wormwood grass is laid out near the holes.
Plants can be treated against cruciferous flea beetle with the following decoctions and tinctures:
- a bucket of water, 2 cups of ash and 50 g of crushed tar or green soap;
- to spray the leaves, mix a liter of water and a glass of vinegar;
- Chop 250 g of freshly cut dandelions along with rhizomes and add 5 liters of warm water, let it brew, add a bar of soap to improve adhesion;
- prepare a mixture of tomato tops (1 cup) and a cup of garlic in the same way;
- an infusion of chicken manure (1:20) is infused for several days, after which the foliage is sprayed with it.
On a note! It is advisable to spray plants in the morning or evening hours.
Preventive actions
Digging up the soil on the site
To prevent the flea from invading the site, the following measures are used:
- destroy weeds in a timely manner, especially those belonging to the cruciferous family, dig up the soil;
- if there is already a flea beetle in the beds, then cruciferous green manures are not planted;
- be sure to dig up the soil in the fall;
- water the soil abundantly, as the insect cannot tolerate moisture;
- If possible, plants are planted either early, before the flea flea wakes up, then they have time to get stronger, or at the end of June. In this case, the pest will cause less harm;
- Fragrant plants are planted next to the crops.
Despite its small size, the cruciferous flea beetle has an excellent appetite. Preventative measures help reduce the risk of pest occurrence. If insects do settle on plants, you need to take immediate action. Timely control is always effective and saves most of the harvest.
Source
Chemicals
If folk remedies fail to stop the aggressor, then insecticides for cruciferous flea beetles will help. More than 5 beetles on one plant is a serious reason to think about using chemicals. It is recommended to initially test the product on one object. If after 24 hours its condition has not worsened, then the remaining plants can be processed.
On a note! If it suddenly rains after treatment, the procedure is repeated again.
Preparations for cruciferous flea beetles for cabbage are available in specialized stores in a large assortment. Here are just a few of them: Decis, Intavir, Karate, Aktaru, Aktellik, Bassoon, Tsapellin, Tabazol, Fitoverm, Actofit. Before using the products, you should carefully read the instructions and avoid overdosing when diluting the working mixture.
Radish varieties resistant to diseases
In official documents describing the properties of various radish varieties, there is practically no information about their resistance to diseases. Fragmentary information on this issue can only be gleaned from descriptions of varieties compiled by the companies that bred them and seed producers. If you trust this information, then the following varieties are more or less disease-resistant:
- Würzburg 59;
- Hussar;
- Diego F1;
- Duro;
- Rebel;
- Rondar.
It seems that with poor care, these varieties can also contract, for example, blackleg, but with proper agricultural technology, producers guarantee their health.