Nature presents us with various mysteries. We are accustomed to the fact that large species are usually higher in the food chain than small ones. And it seems that spider bugs feed on nectar or plant sap, birds feed on these spider bugs, birds are eaten by animals or stronger birds. And here, on you, is a tarantula spider, how can an arthropod defeat a bird!? Let's try to figure this out.
Tarantula spider: lifestyle, nutrition, breeding
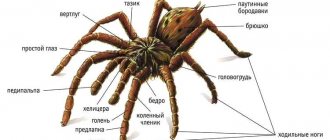
As always, at the beginning of the article we will give a brief description of the animal species, so that the reader can immediately imagine what we are actually talking about and who this tarantula spider is. It turns out that there is a whole family of tarantulas of various sizes and colors. These spiders are so interesting and varied that some people now enjoy keeping tarantulas as pets.
Spider Biology
These spiders got their name thanks to the engravings of the German artist and entomologist Maria Sibylla Merian. These engravings depicted huge spiders eating hummingbirds. This happened at the end of the seventeenth century, when this outstanding woman traveled around South America, in particular in the territory of modern Suriname.
Description
Tarantulas are huge spiders of the family of the same name, which includes many different species that have the following similar characteristics:
- The size of the animal is enormous for an arachnid, 20-30 centimeters in leg span.
- These spiders do not weave patina, but are ambush predators.
- All these arthropods have an exotic coloring that becomes more intense with each subsequent molt.
- Huge furry limbs.
- The body is covered with a dense exoskeleton made of chitin.
Help from Wikipedia. An exoskeleton is an external type of skeleton in some invertebrate animals. It forms protective armor like knightly armor and does not have a cellular structure. In terms of relative strength, the exoskeleton is one of the best fabrics in nature!
The body structure of tarantulas is similar to all representatives of arachnids: cephalothorax, abdomen and eight limbs:
- four legs;
- two are chelicerae for capturing prey, digging burrows, and so on;
- two pedipalps that perform the function of touch.
By the way! The hairs on the legs of spiders are organs of smell and hearing!
Nutrition
In fact, tarantulas rarely eat meat; their digestive system is so complex that it requires more tender and easily digestible (remember the miniature about rabbits?) food. But the diet of these spiders is exclusively carnivorous; they are also classified as so-called strict predators.
Our help! Strict, or obligate, carnivores are animals that feed exclusively on other animals without eating plant foods.
The diet of tarantula spiders may include the following species:
- birds;
- small rodents;
- insects;
- arachnids;
- amphibians;
- fish.
Lifestyle
Various tarantulas live at different levels of the biosphere. There are spiders that live in the crowns of trees, and there are individuals that live in the grass. Still other arthropods of this family prefer a burrow lifestyle. Biologists divide these spiders into three broad categories:
- woody;
- ground;
- burrows.
It is not difficult to guess about the lifestyle that individuals of each of these categories lead.
At the same time, in ordinary life, giant spiders are very sedentary. Even a hungry tarantula is capable of waiting for its prey in ambush for a long time, but there is nothing to say about a well-fed individual. Adult female spiders stay in one place for months without leaving their ambush.
Reproduction and development
Before mating begins, the body of the male tarantula changes slightly. On its limbs - the pedipalps - a so-called cymbium is formed - a growth containing seminal fluid. The chylicerae, on which grips grow to hold the female during mating, also undergo mutations; they are called tibal hooks.
Before mating, the male secretes part of the seminal fluid onto a web specially woven for the mating game. In addition, the man performs a mating dance, showing that the arthropods belong to the same species.
During mating, the male uses the tibal hooks to hold the partner, and uses the pedipalps to transfer the seed inside the female’s body. After this action, the male flees for his life, since the female, who is often hungry, can easily snack on her sexual partner.
After some time, it can last up to several months depending on the species, the female weaves a nest from the web in which she lays her eggs. Their number also differs by species: from 50 pieces to two thousand. Then the mother spider forms a ball-shaped cocoon around the clutch and stays close to it for protection and incubation. A caring female regulates the temperature inside the cocoon by dragging it from place to place or turning it over in different positions.
Female tarantula spider with cocoon
After some time, specific for each species, small nymph spiders emerge from the cocoon. They are almost transparent and do not feed from the external environment, using for life the supply of nutrients that nature put into them in the egg.
After some time and a couple of molts, the nymphs turn into larvae, which already look like spiders, but, however, do not feed for some time, continuing to use the food supply in their abdomens.
The larva molts and turns into an imago - an adult.
Shedding
Speaking about the development process of spiders, one cannot help but touch upon the topic of their molting. This is the most important process in their life, during which qualitative changes occur in animals. Young spiders molt every month; with age, the molt period extends to one year or more.
Molting is the process of replacing the exoskeleton in spiders. Shortly before the start of this process, animals stop eating to make it easier to free themselves from the chitinous coverings that have begun to burden their bodies. In most cases, spiders carry out the molting process by turning over on their back, this way it is easier for them to shed their outsized shell.
Reference! Often, when molting, spiders may lose chelicerae or pedipalps, which are usually restored the next time the shell is replaced.
After molting, the spider increases in size by almost one and a half times, while its color becomes brighter, as if it had purchased a new shell in a fashionable clothing store.
Age
Tarantulas hold the record for longest life expectancy among arachnids. Females of some species live to be over thirty years old. By the way, the age of spiders is sometimes measured by the number of molts. Males live much shorter lives, depending on who is lucky during mating.
Features of choosing a pet
In order to choose a healthy spider, you need to use a few simple tricks that will help protect yourself from wasting money:
the arthropod must be active and playful
In the case when the specimen you have chosen lies alone on the sidelines, is passive and constantly hides in the house, the animal is most likely sick, and you should not buy such a pet for home;
a healthy spider's abdomen should be even and smooth. If the abdomen is wrinkled or has other pathologies, the spider suffers from dehydration and may soon die; open wounds or ulcerative defects on the body of a tarantula are another reason to refuse to purchase such a spider;
It is best to purchase small spiderlings, since it is almost impossible to determine the age of a tarantula by appearance;
It is important to pay attention to the hairs that cover the abdomen. If they are not evenly distributed throughout the body or vary in size, the animal has health problems; the absence of paws in most cases is not a pathology, since they will instantly grow back after the next molt. This only means that the animal was not transported properly.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=HMmZyw4Xxro
Important! When choosing a tarantula, you need to pay attention especially to females, since males are not distinguished by longevity and live several times less
Defense mechanism
Tarantula spiders have three types of defense mechanisms against external enemies.
- Bites.
- Burning hairs from the abdomen.
- Attack with excrement.
Bites
The bite of a tarantula spider combines the painful sensations of piercing the skin with the action of the poison that spiders use to kill their victims and therefore you need to be doubly careful.
Many people are interested in what happens if a tarantula spider bites them? We answer that the reaction of each organism is individual: from mild itching to headache, fever and severe inflammation. However, no deaths from spider bites have been observed.
But if the tarantula spider is not dangerous to humans, this does not mean that there is no need to be afraid of it at all. Cases of cats dying after spider bites have been recorded.
Burning hairs
The hairs on the bellies of tarantulas can cause an allergic reaction when in contact with the skin of a person or animal. Therefore, spiders use them to protect the most valuable thing – egg laying. Females weave stinging hairs into their web and cocoon.
Excrement
Some types of spiders, when defending, shoot a stream of excrement in the direction of the enemy's eyes, trying to blind the enemy.
Breeding
Now let's talk about how to properly breed a tarantula spider at home. In order to properly maintain such an unusual animal from the point of view of the average person, you need to know several rules.
Terrarium
A terrarium for a tarantula spider needs to be selected and equipped depending on its belonging to one category or another. So, for example, for arboreal representatives, the height of the walls of the structure should be no lower than 35-50 centimeters. It’s a good idea for such a home to have an interesting tree branch that your animal could climb on as in natural conditions.
Ground spiders are given a terrarium that is elongated in length so that the pet can have somewhere to run and frolic.
For burrowing spiders, it is desirable to have an improvised burrow, similar to one made in nature. These could be objects such as:
- coconut shell;
- shell from a large mollusk;
- a piece of bamboo trunk;
- clay cup with a broken side.
Regardless of the type of spider, the bottom of the terrarium should be covered with loose substrate. Coconut shavings are best suited for this, although clean, dry soil can also be used.
Climatic conditions
For residents of warm tarantula countries, temperature means a lot. When kept at home, you need to maintain it at a level of 25 degrees Celsius. This can be achieved by using special heat lamps or heating mats on the bottom of the terrarium.
Humidity also plays a big role for the inhabitants of the subtropics. It should be at a level of 80-90 percent. To do this, spray the substrate 2-3 times a day or place a bowl of water, which humidifies the air as it evaporates.
Attention! It is necessary to moisten the substrate only in one corner of the terrarium; the rest of the litter should be dry.
Feeding
The domestic tarantula spider is unpretentious in food, the main thing is that it is of animal origin and larger in size than your pet’s body.
The choice of what to feed the tarantula spider at home is varied, it can be:
- locusts and grasshoppers;
- large insects;
- little mice;
- baby frogs;
- worms;
- bloodworms and maggots.
Attention! It is very important that your pet's prey is alive. This is how the spider feeds and develops at the same time.
Arrangement of the terrarium
A terrarium is a kind of “splinter of nature” in which your spider will live. Proper arrangement is the key to the health and well-being of the spider
Speaking about arranging a terrarium, you can write a separate article, so we will list the most important
The terrarium should contain several levels for living and hunting. This can be organized by placing a couple of driftwood or branches inside. The “ground” is usually laid out with a neutral coating, in the form of pine sawdust or a special substrate. The thickness of such a substrate should be at least 5 cm. Due to the fact that some spiders cannot tolerate bright light and are nocturnal, it is necessary to create several shaded areas using pieces of thick paper or twigs with leaves. It is also worth leaving small pieces of bark, they will serve as a “shelter” for the spider: under them they build peculiar burrows.
Juveniles, depending on the species, are best kept in a container with minimal equipment in the form of a bedding of shelter substrate and a few small branches for hunting. Large snags to form “high” hunting points for spiders under one year of age should not be placed at all, since young spiders can be injured by falling from them.
Substrate
To keep a tarantula at home, soil (substrate) must be present in the terrarium in order to bring the conditions of its keeping closer to its natural habitat. Naturally occurring substrate can be used as bedding for the spider. The simplest and most common option is a mixture of soil, peat and sand. You can also try other naturally occurring materials: gravel, pebbles or vermiculite.
The substrate in the terrarium should be completely replaced every six months.
Temperature
The temperature inside the terrarium should be kept between 23-28 degrees. At low temperatures, the tarantula may experience problems with the digestive system, putrefactive processes may begin in it, which will lead to the death of the animal. At temperatures below 15 degrees the spider will hibernate.
Humidity
Humidity should be between 75-80 percent. It is worth raising it higher only during molting, so that the spider’s body does not suffer from dehydration. If the humidity is below 75%, the spider will hibernate, and if exposed to a dry climate for a long time, it will die.
Types of spiders
Now we will list several of the most popular species of tarantula spiders, which are mostly kept at home by lovers of these exotic animals.
Goliath
The goliath tarantula is perhaps the most famous of the family. This spider is the largest of the tarantulas. The Guinness Book of Records mentions a female whose limb span was 28 centimeters. And body sizes are ten.
Many spider lovers are trying to get it into their collection, but thanks to the bans of the authorities of the South American countries where it is found, the goliath is still very rare.
Chilean pink
The Chilean pink tarantula, on the contrary, is one of the most common inhabitants of home terrariums. He is very handsome and a little aggressive. In nature, it is distributed throughout almost the entire American continent: from the United States to Chile.
The dimensions of the “Chilean” do not exceed one and a half tens of centimeters in leg span.
Lifespan in the wild
In the wild, not every spider is able to live to old age. There is a huge list of factors that influence the life expectancy of an arthropod:
- humidity level;
- presence of predators nearby;
- availability of food;
- air temperature;
Very often, males die after mating, being eaten by their partners. Cannibalism in the life of arthropods is quite common. On average, the lifespan of a female tarantula spider is 8 years, and a male one is 3 years.