In this article we will find out where the name “earthworms” came from, what they eat and what their features are. We have all noticed more than once that after a good rain on the roads and in parks you can see creatures crawling out that have a reddish tint and risk being trampled by people or animals. They are not very pleasant in appearance; small children, as a rule, are afraid of them. But, besides fear, children and adults are still interested in learning what earthworms eat. We will try to answer this question in detail in our article.
What are these creatures?
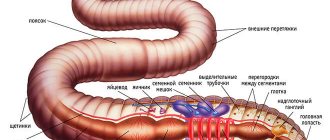
Biology classifies these representatives of the animal world as annelids. If you look closely at them, then on their thin body (50 mm in diameter, 15-30 cm in length) you can see rings, the number of which can sometimes reach 300. There are also very small worms about 2 cm. Few people know that There are giant worms that reach up to 2 meters in length. But they, like the others, are completely harmless and harmless to humans.
Features of earthworms and habitat
The body of an earthworm can reach three meters in length. However, on the territory of Russia there are mainly individuals whose body length does not exceed 30 centimeters. In order to move, the worm uses small bristles, which are located on different parts of the body. Depending on the variety, there can be from 100 to 300 segments. The circulatory system is closed and very well developed. It consists of one artery and one central vein.
The structure of an earthworm is very unusual. Breathing is realized with the help of special hypersensitive cells. The skin produces protective mucus with a sufficient amount of natural antiseptics. The structure of the brain is quite primitive and includes only two nerve nodes. Based on the results of laboratory experiments, earthworms have confirmed their outstanding regeneration abilities. The severed tail grows back after a short period of time.
The genital organs of the earthworm are also very unusual. Each individual is a hermaphrodite. She also has male organs. Based on biological factors, all such worms can be divided into several subgroups. Representatives of one of them search for food on the surface of the soil layer. Others use the soil itself for food and emerge from the ground extremely rarely.
The earthworm is a type of annelid. Under the skin layer there is a developed muscle system, consisting of muscles of various shapes. The mouth opening, from which food enters the esophagus through the pharynx, is located on the front of the body. From there it is transported to the area of the enlarged goiter and the small size of the muscular stomach.
Burrowing and bedding earthworms live in places with loose and moist soil. Preference is given to moist soils of the subtropics, marshy lands and the banks of various reservoirs. In steppe areas, soil varieties of worms are usually found. Litter species live in the taiga and forest-tundra. The coniferous broad-leaved strip can boast the highest concentration of individuals.
What kind of soil do worms like?
Why do earthworms love sandy loam and loam soils? Such soil is characterized by low acidity, which is best suited for their life. Acidity levels above pH 5.5 are detrimental to the organisms of these representatives of the ringed type. Moist soils are one of the prerequisites for population expansion. During dry and hot weather, worms go deep underground and lose the opportunity to reproduce.
What are the benefits?
First, let's find out what earthworms eat in nature, and what benefits these creatures provide. The role of these individuals in nature is very great - they process all kinds of organic waste, turning them into humus. They swallow particles of biomass along with the soil and thoroughly mix them during digestion.
Humus is the organic basis of the soil; by consuming it, plants acquire the necessary nutrients. 90% of all humus is food for the existence of worms.
What are earthworms?
Biological science classifies these representatives of the animal world as annelids. If you look closely, you will notice that their thin bodies (a little more than 50 mm in diameter) 15-30 cm long form rings, the number of which sometimes reaches 300. There are tiny two-centimeter earthworms. But few people know about the existence of giant worms that reach two meters in length. That's how scary earthworms can be. What these representatives of the fauna eat is also interesting.
Only when viewed from a very close distance can one notice that one end of the worm is thicker and darker. It's kind of like a head.
What do earthworms feed on in the soil?
I would like to immediately note that earthworms are omnivores. Since they feed on what is on the surface of the earth, at the same time they swallow a large amount of earth, which gives them the organic elements they need so much. In addition, the worms eat a large number of half-rotten leaves. It is important to note that earthworms do not have teeth directly in the mouth - they are located in the stomach. To receive food, the worm sucks it in with its special organ - the pharynx.
Thanks to the muscles of the body, food moves further, pushing first into the crop and then into the stomach. And already inside, food is ground into small particles by tooth-like protrusions. After this, the food is digested in the intestines by enzymes, useful substances are absorbed, and waste is excreted from the body. Since the worms have a small mouth, this explains why they eat rotten leaves and plant debris. Fresh sprouts can damage the delicate and small body of the worm. Usually such worms live under last year's leaves, where the soil is rich in humus. In such places they are provided with tasty food - pieces of plants, rotted organic matter.
How do worms move?
The worm moves due to the opposite ends of the body. The front end extends and clings to the rough surface of the soil. Then comes the turn of the back part, which, resting on the ground, is pulled up to the head. In this case, the body has to alternately stretch and contract, changing its length. Directly under the skin there is a well-developed muscle system, which has a two-layer structure. Changes in length spread along the body in waves, which is easy to notice.
The earthworm's respiratory organ is its entire skin. A prerequisite for the respiratory process is the presence of mucus on the surface of the body. Dry skin leads to the death of the animal. The worm can live in an aquatic environment for several weeks. “What do earthworms eat and how do they reproduce?” – this question is asked by many people.
The lack of hearing and vision is compensated by an excellent sense of touch, which helps the worm find food.
What is the process of eating?
Earthworms drag half-rotten or fresh leaves into their holes and eat them there. Usually they try to tear off small pieces, capturing the edge of the leaf between the protruding upper and lower lips. At such a moment, his throat, protruding, creates a support point for the upper lip. But if the worm encounters a wide flat leaf, it will behave a little differently. The front rings are slightly pulled into the others, thereby expanding the body. At this time, the pharynx is pressed against the plane of the leaf, then pulled back and made a little wider. As a result, a kind of “vacuum” is created in the dimple on the front of the body. The work of the pharynx at this moment is comparable to a piston, and the worm is very firmly attached to the leaf.
In addition to using leaves for food, these creatures cover the entrance to their burrow. To do this, they bring there pieces of stems, dried flowers, paper, feathers and whatever else they find. When a worm has swallowed soil for food or making burrows, it comes to the surface to empty its insides. The soil that the worm expels from the body contains a lot of secretions from the intestinal tract and therefore becomes viscous.
Worms' favorite treat
These animals prefer soil that contains large amounts of humus. The diet includes a variety of plant debris (for example, leaves fallen from trees and shrubs), including rotting ones. The worm takes them with it when it goes deeper into the lower layers of the soil. Many people are also interested in what earthworms eat on worm farms. There they are given humus and prepared food from old leaves and branches.
The obvious fact is that by “drilling” many tiny holes, the worms loosen the soil, making it possible for oxygen to enter it and enrich it with nutrients. Ultimately, this increases productivity. Experienced owners of summer cottages, taking into account the invaluable benefits of these tiny inhabitants of the soil, treat them with care and try to create conditions for reproduction and increasing numbers in gardens and vegetable gardens.
Earthworms in the garden or vegetable garden are the most desirable inhabitants. They bring many benefits to the soil, loosening and enriching it. Therefore, it is so important to know whether earthworms are useful, the characteristics of their life and methods of breeding in a summer cottage.
What to feed the worm at home?
If you are not aware of what earthworms eat at home and what diet they need, then the following information is just for you. After all, it is necessary not only to create optimal living conditions, but also to provide the necessary nutrition for these individuals. Consider the food that can be used for an earthworm:
- Food waste (shells, peelings).
- Horse or goat manure.
- Tea leaves, coffee grounds, leaves, grass.
It is worth paying attention to what earthworms feed on and what is unacceptable for them. You need to know that the manure for feeding should not be fresh, but rotted, otherwise the worm will simply die. All this is due to the large amount of ammonia, which is found in fresh manure and is very harmful to your pets. There is no oxygen in an ammonia environment, so sometimes individuals die.
Worm feeding schedule
Feed the worms as needed, once every 1-2 weeks. The substrate is introduced into the composter in layers, laying the fresh one on top of the already processed one (it is necessary to leave free space on the surface for air access). Until the pets have eaten the previous batch, a new one is not added - excess food acidifies the substrate and impedes gas exchange in the composter.
The worm consumes a volume of food per day equal to its own weight. The feeding rate is calculated from this indicator. Worms process layers of substrate, moving from the lower tier to the upper, “edible” one. When resettling the livestock, the breeder removes the inhabited layer of compost along with the worms and transfers them to prepared worm pits. The lower layer is the waste of pets, for the sake of which people engage in vermicultivation.
The feeding of the worms stops with the onset of cold weather (below +4°C). Invertebrates go into the ground and hibernate. If vermicomposters are located in a heated room or are reliably insulated, then feeding does not stop all year round.
What not to do?
Also, when breeding pets at home, it is not recommended to feed them with fish, meat and dairy products. Also eliminate salty foods from your diet. In addition, neither canned cucumbers, nor tomatoes, nor cabbage will bring any benefit. You need to remember that feeding the worm once a week is enough. To do this, you need to crush the food and put it on the ground. The feed layer is allowed up to 10 cm.
When it comes to what earthworms eat, you need to know that they usually get used to the same food, and it will take them some time to switch to a different diet. If you decide to change their diet, then you need to do this gradually, adding new food to the usual in small portions.
As a rule, the feed mass is placed in boxes 5-7 cm thick once every 3 weeks, depending on the number, size and appetite of the worms. When they process one layer, they soon leave it and rise higher to a new one. After processing, humus remains in the lower layer, which can be used as fertilizer.
Not only is it important for us to know what earthworms eat, but we should also remember that these individuals are inconspicuous, quiet workers who make the soil fertile. They are the most important friends and helpers for gardeners and gardeners. They need to be protected and helped in every possible way.
Population and species status
If the soil is not contaminated, then you can count from several hundred thousand to 1 million earthworms, with their weight from 100 to 1 thousand kilograms per 1 hectare of arable land. Farmers who practice vermicultivation are interested in having as many worms as possible, so they breed worms themselves, ensuring maximum fertility of their lands.
With the help of worms, the process of processing organic waste into vermicompost, which is a high-quality fertilizer, occurs. Some farmers raise invertebrates to feed their animals and poultry. To do this, they prepare composts consisting of organic waste. As far as we know, fishermen actively use worms when fishing.
Experts, having examined ordinary chernozem, found 3 varieties of earthworms in it, and one species turned out to be 42 units per square meter of uncultivated land and only 13 units on arable land. No other species was found on virgin lands, and only one specimen was found on arable lands.
The number of earthworms depends on living conditions and can vary significantly from several hundred pieces to several hundred thousand pieces per square meter.
Internal structure
The internal structure of earthworms is quite complex.
The circulatory system is closed and consists of two main vessels:
- abdominal (blood moves from the front of the body to the back);
- dorsal (blood moves from the back of the body to the front).
The main vessels are connected by ring vessels located in each segment of the body and passing into smaller capillaries. Some annular vessels are thickened and can contract, moving blood from the dorsal to the ventral vessel.
Respiration of earthworms occurs through the surface of the body.
The digestive system is connected in series:
- mouth opening;
- pharynx;
- esophagus;
- muscular belly.
From the stomach and almost to the end of the body runs the middle intestine, where food is digested and absorbed. Undigested residues enter the hind intestine and are then eliminated through the anus.
The excretory system is a set of thin ring-shaped tubes, one end of which enters the body cavity and the other exits. In addition, the worm has special excretory pores.
The nervous system consists of the brain (a large collection of nerve cells) and the abdominal brain with nerve ganglia in each segment, from which we can conclude that each segment is independent, but the work of all organs is coordinated.
Life cycle of an earthworm
The life cycle of an earthworm is the same as that of other oligochaetes. These representatives are also hermaphrodites. When mating, two individuals unite and exchange sperm, thus cross-fertilization occurs. They find each other by smell. Fertilized eggs are collected in a special cocoon, wrapped in a shell of mucus. This is the same belt visible on the body of the worm. It occupies several segments in the front of the animal's body.
Origin of the species and description
Photo: Earthworm
Lumbricina belong to the suborder of oligochaete worms and belong to the order Haplotaxida. The most famous European species belong to the family Lumbricidae, which contains about 200 species. The benefits of earthworms were first noted by the English naturalist Charles Darwin in 1882.
When it rains, the burrows of earthworms fill with water and they are forced to crawl to the surface due to lack of air. This is where the name of the animals comes from. They occupy a very important place in the structure of the soil, enriching the soil with humus, saturating it with oxygen, and significantly increasing productivity.
Video: Earthworm
In Western Europe, dried worms were processed into powder and applied to wounds to promote healing. The tincture was used to treat cancer and tuberculosis. The decoction was believed to help with ear pain. Spineless, boiled in wine, treated jaundice, and with the help of oil infused with invertebrates, they fought against rheumatism.
In the 18th century, the German doctor Stahl treated patients with epilepsy with a powder made from washed and ground worms. In Chinese folk medicine, the drug was used to combat atherosclerosis. Russian folk medicine practiced the treatment of cataracts using the liquid dripping from salted fried worms. It was dropped into the eyes.
Interesting fact: Australian Aborigines still eat large types of worms, and in Japan they believe that if you urinate on an earthworm, the causative area will swell.
Invertebrates can be divided into 3 ecological types, depending on their behavior in the natural environment:
- epigeic - do not dig holes, live in the top layer of soil;
- endogeic - live in branched horizontal burrows;
- anecic - feed on fermented organic matter and dig vertical burrows.
What is the difference between a compost worm and an earthworm?
In addition to earthworms, there is the compost worm, also known as the dung worm (Eisenia foedita). It is reddish in color. It is a kind of domesticated worm, specially used by humans for composting. It does not build tunnels, but rather creates fine, crumbly soil.
Composting with these worms brings primarily one advantage: composting occurs at a low temperature of the substrate, which suppresses the processes of decay. This reduces energy loss compared to traditional composting.
Spring Solstice (March 21): In the old days, people took knives to drive away troubles
5 things predicted in 2010 by writer Gary Shteyngart that came true
How to celebrate the Larks holiday (March 22) so as not to attract misfortune
Earthworms: feeding method
An earthworm can safely be called an omnivore. He is capable of consuming huge amounts of food. Earthworms often drag food underground and then eat it or store it in special burrows. There they stack the leaves, compacting them and lubricating the spaces between them with soil from their intestines.
These animals are nocturnal. The earthworm's feeding method is very peculiar. Climbing to the surface of the ground in the dark, it tears off a small piece of food, holding it between its protruding upper and lower lips. Meanwhile, the powerful pharynx protrudes forward, creating a fulcrum for the upper lip. Food is first ground in the pharynx, after which it enters the intestines, where it is exposed to special enzymes. Some of the nutrients are absorbed and provide the body with the necessary energy, while the remaining components are released along with the soil and enrich the soil.
The famous scientist Charles Darwin devoted a lot of time to studying the life of earthworms. In his work, he described how these animals consumed the meat that was left to them in advance. In addition, they even ate pieces of their dead brothers. For which the scientist called them cannibals.
Eating worms in nature
Many people are interested in what do earthworms eat in nature? Under natural conditions, these animals consume mainly plant foods, so during artificial breeding it is not recommended to feed them with animal protein.
Favorite food of an earthworm:
- fresh leaves, except very hard veins;
- fallen leaves, which they actively store in burrows;
- rotten parts of stems;
- fallen flowers.
They settle in soil that is rich in humus. They eat leaves, biting off small pieces.
Lifestyle of worms
Earthworms are nocturnal. At night they can be found swarming in large numbers in various places.
At the same time, they leave their tails in the burrows, and stretch out their bodies and explore the surrounding space, grabbing fallen leaves with their mouths and dragging them into the burrows. While feeding, the earthworm's pharynx turns outward slightly and then retracts back.
In earthworms, the body stretches well, and it is also covered with small bristles curved back, thanks to which the worm can hold so tightly in the burrow that it is difficult to remove it from it without tearing the body. Worms spend most of their time in their burrows. The only exceptions are worms, whose bodies are parasitized by fly larvae; they crawl along the surface of the soil during the daytime and do not die in burrows.