Many people living in private homes are interested in the difference between a mouse and a rat. The point is not that both of them carry various infections, but that one should begin to fight rodents by determining their type. Thanks to this, it will be possible to choose an effective way to destroy them. To understand the differences between a mouse and a rat, you should know the structural features of the body of these similar animals.
Many people living in private homes are interested in the difference between a mouse and a rat.
Differences in appearance
Due to the external similarity, not every person can recognize the differences between a mouse and a rat. Both rodents have gray fur and a long tail. But there are also many differences in their appearance.
Dimensions
Size is the main difference by which these rodents can be distinguished. The average body length of a baby rat is 7–10 cm, the same as an adult mouse. And rats grow up to 25 cm.
The weight of rodents also differs significantly. Rats are larger and therefore heavier than mice. An adult weighs on average 220–250 g. Moreover, males are much larger than females. Their weight with proper nutrition can reach 450 g. An adult mouse weighs only 45–85 g.
Important! In rare cases, rats can grow to gigantic sizes. In nature, there were individuals whose weight exceeded 1 kg. The length of such a rodent can reach 40–50 cm.
Head and ears
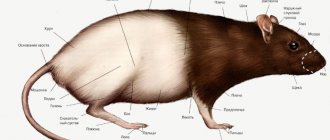
Mice differ from rats in the shape of their heads. In rats, the muzzle is strongly extended forward. And in mice it is slightly shorter and has a triangular shape. Rats have much smaller eyes.
Outwardly, they resemble black beads. Mice have large and mobile eyes. Rodents also rotate their heads differently. To do this, rats need to move their torso, and mice can twirl it without the participation of the body.
Mouse
Rats and mice differ from each other in the shape of their ears. In large rodents they are small, triangular and covered with sparse villi. In some subspecies their ends are blunted.
A mouse differs from a rat in having larger, movable ears that it can move. Rats can't do that. Mice have round ears and no hair on them.
Paws and tail
Due to their size, rats move primarily in horizontal places. To find food and escape from predators, they need to run fast and jump high. Therefore, their paws are powerful and muscular, and between the toes there are rough outgrowths of skin visible - these are rudimentary membranes.
Due to their light weight, mice can easily climb vertical surfaces. They are helped in this by small and flexible paws with tenacious claws.
Mouse
Rats have a short tail. It is thick and bristly, there is no hair on it. Its size is approximately half the length of the individual’s body. Mice have a thin tail. Its length is at least ¾ of the body size.
Rat
Wool
Rats have dark gray, dirty-colored fur. The hairs are thick and coarse, and the skin underneath is easily visible.
Important! Decorative individuals have softer wool. Its color depends on the species. Pet stores sell white, red, gray and black rodents. There are also individuals with a hood of a different color.
Decorative rats
The fur of mice is softer and silkier. These rodents have a smoky, grayish color. The hairs grow denser, so the skin is not visible through them.
Mice
What do the tracks look like?
What do rodent tracks look like?
The imprint of a rat's front paws on wet ground or snow is approximately 1.5 x 2 cm in size. You can see traces of 4 toes, which are widely spaced. The hind legs are larger (up to 4 cm), however, during movement, a small imprint remains - 2x2 cm, i.e. the mark is only partially visible. If the animal moves slowly, a thin chain of prints will remain on the surface. During the jump, the rat leaves rare traces - at a distance of up to 1.5 m.
The paw prints of mice during a jump are characterized by a smaller step (up to 30 cm). The tracks form a kind of trapezoid: when moving, the mouse places its hind legs wider, pushing off with its front, closely spaced legs. As a result, the tracks of the hind paws remain in front, and the tracks of the front paws remain behind. In addition, a thin line is visible behind - from the tail.
Intelligence difference
If we compare the intelligence of two types of rodents, then mice are much inferior to rats, which are more intelligent. Scientists equate their intelligence to that of cats and even dogs. These are careful animals.
They assess the area they intend to settle in, study it for potential dangers, and leave if they see a serious threat. Other amenities are also important to them: they know how to assess the temperature of the room and the quality of food. If the food seems dangerous to them, they will not take risks.
Rat
Mice are not capable of such actions. They assess the territory worse and easily eat poison. Small rodents are more likely to become victims of predators because they leave behind many traces and cannot identify potential danger.
The difference in intelligence is also noticeable in the fact that mice gather in packs less often, they do not have a clear hierarchy and defined roles. Rats always live together. Each individual in the pack has its own responsibilities. For example, before settling into a new territory, a small group of rodents must explore it. If she seems safe to them, then the rest of the pack will follow.
Rats
Important! Rats are very aggressive. They often attack mice and kill their relatives if they feel threatened by them. Sometimes they attack weakened individuals if the flock lacks food.
Rats easily recognize danger and try in every possible way to avoid it. When they see a predator, they run away to a previously found shelter. Mice act chaotically, rushing around in circles, so they get caught more often.
Similarities and differences between rats and mice
At first glance, the difference between these rodents is only in size: rats, as a rule, are somewhat larger and larger than mice. However, in reality, there are much more differences. Very often people confuse these animals, considering them almost identical animals.
Mice and rats: general features of life
Both species of rodents live on almost every continent, with the exception of the most northern latitudes - Antarctica and the North Pole. In addition, these animals are almost never found high in the mountains, preferring to live on the plains.
In warmer regions, these animals live separately from humans, finding food on their own without any problems.
Such animals are predominantly nocturnal, but domestic mice easily adapt to human routines, staying awake during the day and resting at night.
This type of mammal is distinguished by its great mobility, running quickly, swimming and jumping high, as well as its body plasticity: rats, like mice, can easily crawl into the smallest hole.
In the wild, this type of animal forms entire colonies with a leader and a clear hierarchical system.
Despite existing stereotypes, rats and mice are very clean animals. They are very careful about the cleanliness of their home, leaving pieces of dust or droppings only as special identification marks.
Both animals have sharp incisors
Similarities and differences in appearance
At first glance, you can distinguish a rat from a mouse by the size of the body, because the mouse seems to be a miniature copy of a rat. Indeed, there really are similarities between these types of rodents.
Similarities in appearance:
- both species of these mammals have fairly long tails, which are covered with small sparse hairs and scales;
- both rats and mice have a specific muzzle: slightly pointed, with small rounded ears, black or red eyes and whiskers;
- A distinctive feature that unites this type of rodent is the presence of sharp incisors, as well as the absence of fangs. The teeth of these animals grow throughout their lives, so the animals constantly need hard objects on which to sharpen their teeth.
Differences in external features:
- size. Rats usually reach about 30 cm in length, not including the length of the tail. Mice grow about 9-10 cm in length;
- weight. Rats weigh much more than their smaller counterparts: the weight of a rat, as a rule, fluctuates around 600-650 grams, and the weight of mice does not exceed 30 grams;
- rhythm and way of life. Mice usually sleep in fits and starts, 30-45 minutes at a time, falling asleep about 20 times a day. Rats prefer to sleep for a long time, but only once a day.
Behavior of rats and mice: similarities and differences
A big difference between these animals can be seen by observing the behavior of the animals. As a rule, rats are more aggressive than mice and in some cases are able to attack first.
Behavioral Similarities:
both types of rodents, living in the wild, can prey on other mammals or insects; in natural conditions they live in burrows with complex passages and labyrinths; caution and attentiveness are a characteristic feature of the behavior of these animals. Differences in behavior:
Differences in behavior:
- rats prefer to hunt in packs, while mice usually do it alone;
- Mammals are often the prey of rats. Mice typically hunt insects;
- mice are considered more timid animals;
- Mice move at a run, leaving behind many traces. Rats move by jumping, trying not to make tracks.
In addition, there is a difference in the diet of these types of mammals: rats have a predatory instinct to a much greater extent than their smaller counterparts. These animals love meat, while mouse colonies feed mainly on plant foods.
At home, such a rodent should be fed grains, vegetables and fruits. You can give boiled chicken breast, cottage cheese and hard-boiled egg white. It is prohibited to feed the animal raw meat, cheese, as well as spicy, fatty or smoked foods.
Which would you have - a mouse or a rat? Poll Options are limited because JavaScript is disabled in your browser.
Mice adapt easily in captivity
Differences in nutrition
Both species are omnivores, but rats and mice can be distinguished by their feeding habits. Both of them are predators. They can attack other animals and insects and eat their meat.
Rats are more aggressive. Wild individuals hunt more often and mainly in packs. But they can attack alone. Small and weakened animals, including mice, often become victims of rats. When there is a shortage of food, rodents also attack each other. More often than mice, they feed on human household waste, so entire flocks often live in landfills.
Rats
Mice eat meat less often. These rodents prefer plant foods. They regularly replenish their supplies with leftover vegetables, seeds, and cereals. But this does not mean that mice will refuse meat. They will eat it with pleasure, but they will not hunt for it.
Mouse
Difference in tracks
Rats eat meat, cookies, bread, smoked meats, lard, and sausage.
They sharpen their teeth on wood or other hard objects, including concrete. They can chew through electrical wires. The habitat is located near waste storage areas. They move with long strides and can jump up to 2 m in length and 1.5 m in height. The tracks are long. The angle between the extreme phalanges is almost turned around. Mice prefer grain and flour products, sugar, and very rarely eat meat. They damage paper, polyethylene and leather products. They move in small steps, jumping is generally unusual, they are characterized by climbing on horizontal surfaces located above the floor. The tracks are round. The distance between them is about 1 cm.
How to distinguish a mouse from a rat
Baby rats and mice are visually similar, so it’s not easy to tell them apart, but it’s possible:
- The little rat's tail is much longer and thicker. The mouse's is short, thin and flexible.
- The mouse has a more rounded muzzle, and the pups have an elongated head, like adults.
- The body shape of a mouse is round, while that of a rat is elongated.
- Little mice curl up into a ball in their sleep. Baby rats often lie on their backs and stretch out their paws.
It is much more difficult to distinguish between baby mice and hamsters. Representatives of both species are small in size. Their fur is soft and their ears are round in shape. A hamster differs from a mouse in color and the presence of cheek pouches, where these animals love to store food supplies.
Baby rats
Little mice
Despite the similarities in appearance, there are still more differences between rats and mice. But they are united by sociability, they get along well with people. Because of these qualities, both types of rodents can make excellent pets.
Character and behavior
Little Rat
Mice and rats, especially decorative ones, are peaceful animals that are not prone to unreasonable aggression. The only exception is that during sexual activity and during hunting, rats can be very militant.
When it comes to relationships with people, mice are more timid. Seeing a person or hearing his approaching steps, the mouse will immediately hide so as not to become noticed.
Rats are calmer and more sociable. They are much easier to tame. In addition, decorative rats interact well with other pets. The main thing is to carefully monitor the interaction of pets in order to come to the rodent’s aid if a large animal (cat or dog) suddenly awakens its hunting instinct.
What is the difference between a rat and a mouse
Despite the similarities between these rodents, they differ greatly from each other:
The main differences are due to the different number of chromosomes. In rats there are 22 of them, and in mice 20. Therefore, it is impossible to cross these mammals in order to produce offspring. Decorative rats reach 30 centimeters in length excluding the tail. Mice do not grow more than 9 and a half centimeters. Large rodents weigh up to 650 grams. A mouse cannot be heavier than 30 grams. Despite the fact that the number of newborn rat and mouse pups per female varies from 5 to 12, the number of nipples in rodents varies. A rat has 12 of them, while a mouse has fewer nipples - only 10. Due to their fast metabolism, the activity of mice differs from rats in being polyphasic. The animal falls asleep 15-20 times per day. Each activity phase lasts from 25 minutes to one and a half hours. The rat lives more “slowly”: it sleeps once a day if it is not disturbed. There is a difference between them in nutrition. Although both of these species are omnivores and can attack and eat other living creatures, the rat’s predatory instinct is more developed. Mice are seed eaters. Predatory instincts appear only when absolutely necessary, which is why they are even considered vegetarians.
Rodent hunters
A rat differs from a mouse in being more aggressive. When danger approaches, they show miracles of courage and can even attack a person in defense. In nature, rats often hunt in packs. Animals in groups can even attack mammals larger than themselves.
Mice prefer to hunt alone. Therefore, only insects and smaller animals become their victims. These animals are shy and extremely careful.
Due to such character traits, these animals are natural enemies. Large rodents attack small ones, kill them, and may even eat them. Therefore, the instinct of self-preservation dictates that mice beware of their larger relatives. Smelling the smell of a rat, small rodents leave their habitat.
For the same reason, individuals of these two species cannot be kept together. It is not even recommended to place cages with them in the same room.
Comparison of rodent intelligence
Rats are smarter and smarter than their smaller counterparts. Catching a wild specimen is a troublesome task. They are careful, attentive, cunning. If the loser suddenly falls into a trap, she lets the rest of the colony know about the danger. Never again will any animal appear here.
There are many stories about how these clever thieves opened bottles of wine, closed with plastic caps, one of them put the tail into the neck, pulled it out, and others licked the delicacy from it.
Or how rodents, climbing over a wide crevice, stuck together in a path, biting the tail of the animal in front with their teeth. Using such a living bridge, the entire colony easily crossed the obstacle.
Companion rats, living next to humans, also show their remarkable abilities. They are easy to train, respond to names, and even come up with their own games, inviting the owner to join.
There are no similar stories about mice. However, these sweetest creatures can give their owners a lot of pleasant moments of communication. They also become attached to a person and touch those who watch their lives with their habits.
Who grows faster: a mouse or a rat?
The metabolism of mice is higher than that of rats, so their lifespan is shorter. The average lifespan of small rodents when kept at home is 1.5-2 years, while their large relatives live up to 2-3 years.
Rats and mice grow the same way. At the age of 1-1.5 months, young rodents are capable of reproducing their own offspring.
Rat tails are longer than mice's. They are equal in size to 70-110% of the body. Mouse tails are shorter. They can reach no more than 60% of the body; the tails of large rodents are thicker than those of mice and more powerful (with the exception of the tailless rat); rats' faces are sharper and more elongated. Mouse heads are rounder and less pointed; The body of small rodents is more round. The animals rarely straighten up, preferring to sit huddled together in a ball. And their species relatives can rest, lying on their tummy, with their hind legs stretched out, like cats; mouse fur is soft and silky, while rat hair resembles coarse hair; The hearing organs of rodents are structured differently. Mouse ears are thinner and rounded. They resemble petals rolled up into a ball. Rat ears are thicker, sharper, and not curled.
Mouse poop
They are quite small, similar to black grains of rice. Mice leave up to 80 pieces of excrement per day. The droppings of these rodents range in size from 1 to 5 mm. Granules with pointed ends, black when fresh. After a short period of time they acquire a grayish or brown color. The feces usually dry out within 24 hours and become very hard. The detection of such “grains” is a signal to begin the fight against rodents. The condition of the excrement can determine how long mice have been in your home.
Typically, these rodents prefer to move along walls. Therefore, this is where the largest amount of excrement is found.
Damage that rodents can cause
Both rats and mice cause many problems for the home owner.
- The first problem is damaged things, furniture, food, damaged electrical appliances due to chewed wires, an unpleasant odor, and droppings.
- The second problem is possible attacks by rats on household members.
- The third problem is the high birth rate of rodents, which makes them difficult to get rid of.
- And the fourth, most serious problem associated with the presence of rodents in the house is the infections that they carry. They are carriers of many infections, such as plague, tuberculosis, hepatitis, rabies and many others. When an animal bites, it can infect a person.
No owner will be happy with such a neighborhood. As soon as traces of rodents in the house are noticed, you must immediately begin an active fight against them, otherwise in a couple of months there will be many more of them and it will be very difficult to remove them from the house.
How to get rid of rodents
It may be difficult to get rid of rats and mice, but it is possible and necessary! There are traditional ways to control rodents:
If you are unable to get rid of the rodents on your own, then you should resort to poison. You can call a special service that deals with rodent baiting, or you can purchase chemicals yourself at a hardware store and disinfect your home.
Both mice and rats are very resilient animals that have lived side by side with humans since ancient times. They cause a lot of trouble for home owners, and it is important to get rid of them at the very beginning of their move in, since over time their flock will increase significantly.
Litter
When solving the problem of how to distinguish a house mouse from a rat, you need to pay attention to the products of their vital activity, since this is often the only thing that reminds you of rodents. The differences between rat and mouse droppings are the shape, size and location. Rodents of different species leave waste products that differ in color and size. Thus, black rat droppings are large formations up to 12 mm in length, dark in color.
The red counterparts leave behind droppings that resemble oat grains in shape and are brown in color. Mouse feces are small, outwardly similar to pointed granules no larger than 6 mm in size. In addition, mice defecate chaotically, and rats usually leave droppings in one place.
Interesting video: Smart Rats
Determining the type of rodent by the type of spoiled food
Preferred foods are affected first. For mice these are cereals. Moreover, they leave behind a large amount of litter and husks, but the rat eats the whole grain. In addition, large rodents do not feed in one place for several days, so the damage they cause is always greater. If the mouse returns to the same place every time to eat (for example, a bag or bag of cereal), then traces of the rat’s teeth remain everywhere: on furniture, food: cereals, fruits, etc.
You need to know what a rat and a mouse look like in order to choose effective control methods. Because the behavior of outwardly similar animals is somewhat different. Rodents differ in size, mentality, and food preferences.
Rat breeding
Determining the sex of a rat is quite simple: males are larger and heavier than females, and by the age of 1.5-2 months, large testicles grow at the base of the animal’s tail.
The age of a rat can be determined by weighing the animal:
- At 2 months, males weigh 160-220 g, females 150-200 g;
- At 3 months, males weigh 250-310 g, females 210-250 g;
- At 4 months, males weigh 350-410 g, females 250-290 g;
- At 5 months, males weigh 450-490 g, females 290-340 g.
When a rat is six months old, its weight remains unchanged
To understand that this is an old specimen, pay attention to the following signs:
- the animal's fur becomes sparse, dull, and sticks out in places;
- the skin on the tail becomes rough, rough, with many flaking keratinized particles;
- the incisors become significantly longer. Their back part is ground down, and the teeth take on the shape of a chisel.
Rodents living in their natural habitat breed mainly in the warm season, mainly in spring and autumn. Rats living close to human habitation, or decorative individuals, can reproduce regardless of the time of year.
The female's pregnancy lasts 22-24 days, after which 8-10 cubs are born. Rats are born naked, blind and helpless, so they need extra care. The problem is that babies cannot pass feces and urine on their own. The owner can help them along with the mother rat by massaging their bellies from time to time. This helps stimulate excretory processes.
Reasons for incompatibility
As mentioned above, these rodents do not interbreed. In addition, these animals are natural enemies. It's no secret that a rat destroys caught prey (a mouse), but can also eat it if there is no danger. If an adult rat gets into a place inhabited by mice, then, most likely, the latter will be killed or expelled in a fairly short period of time. Note that the very presence of rats in a place where there is a concentration of mice leads to great concern for them.
This is explained by the fact that, according to some data, mice can detect the smell of rats, which for them is the smell of danger. It is for this reason that pets of different species should not be in the same cage.
Therefore, it is important to know how mice differ from rats; the signs are extremely significant. After all, if you decide to have such pets, then it is better to keep them away from each other, in separate cages located in different rooms