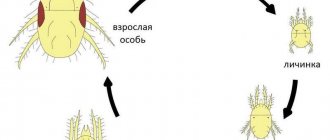
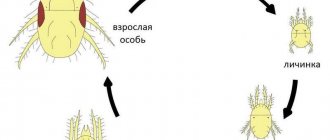
Description of the disease and pathogen
Clubroot is one of the most dangerous and common diseases. Almost every farmer is familiar with “disfigured” plant roots. The causative agent is the lower fungus Plasmodiophora brassicae.
It develops only inside living crops and is stored in the form of spores in the soil for the winter. In the spring, zoospores are formed from them - this is a stage in the life cycle of algae and a number of lower fungi. With the help of flagella, the zoospore moves in a liquid medium into the plant through the hair roots. Infected cells increase in volume and proliferate very quickly.
A plant can become sick with clubroot at any time during the growing season.
Signs of the disease
In some cases, at the initial stage, the disease does not affect the appearance of cabbage in any way. The gardener, caring for the plantings, may not even realize that the crop has been infected. However, inspection of the root system puts everything in its place.
On the roots of young bushes you can see various growths and swellings with the naked eye. They block the absorption ability of the roots, so the absorption of water and minerals by plants is disrupted. On the roots of healthy seedlings, growths appear on the lateral roots in the form of icicles and small beads.
With severe and early infection with clubroot, cabbage seedlings are stunted in growth and their leaves turn yellow. Sick plants are unsuitable for further cultivation, since they take root poorly, the head does not form at all or is not fully formed, that is, it is impossible to obtain a good harvest suitable for further long-term storage.
One of the main signs of cabbage being affected by clubroot is the wilting of the lower leaves in hot weather.
The appearance of the disease
If wilting appears in the cabbage bed, despite proper care, you need to dig up the seedling and carefully examine it. The presence of characteristic formations on the roots indicates the presence of a disease. The root system affected by growths cannot fully develop and nourish the vegetable.
Diseased specimens stop contacting the soil and are easily removed from the ground. The resulting growths begin to rot. This is how cysts appear in the soil. Cabbage is affected by this parasite at any stage of development. Young plants are often susceptible to the disease. An acidic environment gives impetus to development.
At the initial stage, the foliage has a slightly purple tint, after which it becomes yellowish and the plant looks lethargic.
Factors provoking the disease
The source of infection is usually the soil in which the fungal spores live. They can maintain their viability for a very long time - 6 or more years. In addition, spores are well preserved in compost, so putting plants infected with a parasitic fungus into it is strictly prohibited.
The pathogen, which entered the soil from decomposed plants, can be spread throughout the entire area with the help of water, soil insects and earthworms. Clubroot is introduced into uninfected areas mainly with diseased seedlings. Weeds can also be a source of infection.
The development of clubroot is favored by the following climatic conditions:
- air temperature 18-25°C heat;
- ambient humidity 75-90%;
- soil acidity is 5.6-6.5, that is, acidic and slightly acidic soils; in a neutral environment, the activity of the pathogen decreases, and in an alkaline environment (pH greater than 7.0) it dies.
Most often, this disease is recorded in the Non-Black Earth Region, the soils of which are characterized by high humidity and acidity. It is a frequent visitor to heavy and wet soils.
However, overdried soil also contributes to the awakening of microorganisms, as well as depleted soil, which has a lack of calcium and potassium, as well as microelements - boron, zinc and chlorine, humus.
As soon as soil infestation with clubroot is detected, the area is “sent” to quarantine, which can last for several years.
Resistant varieties
Modern breeding methods have made it possible to obtain pathogen-resistant hybrids. Varietal cabbage is planted immediately after soil treatment. The hybrids were named “Kilagerb”, “Nadezhda”, “Tequila F1”. In addition to them, strong and infection-resistant varieties of white cabbage have been bred:
- "Ladozhskaya";
- "Losinoostrovskaya"
- "Gribovskaya";
- "Harvest";
- "Present";
- "Late Moscow".
Chinese cabbage is known to be resistant to fungi. We can distinguish such popular types as Clarifry, Clapton F1. The weight of a head of early cabbage ranges from 1.7 to 2.5 kg. Mid-season heads of cabbage are larger: they weigh from 2.2 to 3.3 kg. A head of cabbage of late varieties reaches 2.0-2.9 kg. Late varieties are recommended to be planted in the Central and North-Western regions of the country, while early experts advise planting in the Urals, Central Black Earth Region and the Caucasus.
Fighting methods
Dormant spores of the parasitic fungus live in the soil for up to 7 years, but if host plants are not planted on the site, their viability decreases every year. Therefore, one of the effective methods of combating this disease is crop rotation, but folk remedies, as well as chemicals, are also used.
Crop rotation
Plants are planted in the area with clubroot that are not only resistant to it, but also accelerate the death of the fungus.
“Pills” for clubroot are:
- All plants of the nightshade family - tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, peppers, aromatic tobacco, hybrid petunias and others. They will cure the earth of a pathogenic microorganism in 3 years.
- Crops of the goosefoot family - beets, spinach, chard. The last two families will help clear the land of spores even faster - in 2 years.
- Representatives of the lily family include onions, garlic, lilies, hyacinths and others.
The best therapeutic effect was shown by mixed plantings of tomato and spring garlic. In this case, the soil becomes healthier in 1 season. Next spring, to be on the safe side, beets are planted in this bed.
Folk remedies
If cabbage gets sick in adulthood, you can try to save the crop using folk remedies. But, it should be remembered that it will not be possible to completely cure clubroot this season. Apply:
- Infusion of wood ash. At the first signs, all withered, yellowed leaves are torn off, and the bush is watered with an infusion of wood ash - 10 glasses of the substance are poured into 10 liters of water and left for 2 days. Then 1 liter of infusion is poured into a bucket of water, stirred and 500 ml is poured under each bush. Water the plants after the main watering. Next, the cabbage is hilled higher - this promotes additional root growth in the upper part of the stem.
- Organic. Once every 7 days, organic fertilizers are applied to the plants - mullein, vermicompost, compost, yeast. They help curb the activity of the fungus and its spread.
- Tops. After harvesting, crushed beet and quinoa tops are spread on the site, a large amount of organic matter is added and the soil is dug up.
- Mortar. Infected beds are also watered with lime mortar - 150 g of lime is dissolved in 5 liters of water. 500 ml of the prepared solution is poured under each bush. After this procedure, the pH of the soil will increase and it will become alkaline.
If clubroot manifests itself at the last stage of development, then all heads of cabbage are removed and the soil is immediately treated.
Chemical and biological drugs
This pathogen is resistant to most antifungal drugs. But experimentally, several drugs have been found that really help inhibit the growth and development of the fungus. This:
- Trichodermin;
- Previkur;
- Glyocladin;
- Topaz;
- Fitosporin-M;
- Alirin B;
- Fundazol.
However, no drug can destroy the parasitic fungus and cure cabbage; they only inhibit the development of the fungus and prevent its reproduction.
Site testing
The results of the preventive and health measures taken need to be checked in order to return cruciferous plants to such beds where there really will be no pathogenic microorganisms. To do this, they first plant Chinese cabbage, which grows the fastest. During the entire growing season, several plants are dug up and their root system is checked.
Checking for clubroot should begin at the stage of the appearance of the first true leaves and continue until full-fledged forks are formed. If there are no pathological changes, then you can begin to grow any cruciferous crops on the site. The appearance of even a small growth can be considered evidence that spores remain in the ground. In this case, you need to carry out treatment measures for another year.
Clubroot spore test
Experts recommend testing for the presence of fungal spores before returning cabbage to the beds. To do this, in the spring the area is sown with fast-growing Chinese cabbage. Throughout the growing season, it is gradually dug up along with the root system, and all roots are carefully examined.
Young plants that have grown their first true leaves begin to be dug up until heads form. If there are no thickenings or growths on any of the roots, then the soil has been successfully treated and cruciferous plants can be planted on it without fear.
The appearance of even one “icicle” on the roots signals the presence of spores in the soil; treatment must be extended for another year.
How to understand that cabbage has been affected by clubroot
Most often, clubroot affects young plants or seedlings. It is very difficult to see the signs of the disease by eye: the growths on the roots of the seedlings resemble ordinary lumps of soil. You can only pay attention to the unnatural lethargy of the seedlings, despite all the feeding and regular watering.
Pronounced signs of clubroot appear already in grown cabbage:
- cessation or slowing of growth;
- general withering;
- yellowing and drying of leaf edges;
- turning the head of cabbage on its side.
If you pull a head of cabbage out of the ground, then instead of a thin root system you will see spherical and oblong growths with open rotting wounds - this is a sign of the maturation of new spores.
Preventive actions
In order not to waste time and effort on treating this dangerous disease, they adhere to some preventive rules.
Kill-resistant varieties of white cabbage
Cabbage varieties resistant to the disease are presented in the table:
| Name | Ripening period | Growing region | Head weight, kg |
| Kilagherb | mid-season | Northwestern, Central | 2,4-3,0 |
| Kilagreg | early ripening | Northwestern, Central, Volga-Vyatka, Central Black Earth, Ural, West Siberian | 1,7-2,5 |
| Kilaton | late-ripening | Northwestern, Central, Volgo-Vyatka | 1,9-3,0 |
| Hope | mid-season | all except the Northern and North Caucasian districts | 2,4-3,4 |
| Ramkila | late-ripening | Central | 2,0-2,7 |
| Tequila | mid-season | Northern, Central, Volga-Vyatka, North Caucasus, Ural, West Siberian, Far Eastern | 2,3-3,0 |
Cabbage Kilagherb
Cabbage Kilagreg
Cabbage Kilaton
Cabbage Nadezhda
Ramkila cabbage
Cabbage Tequila
Pre-sowing preparation of seeds and soil and what to add to the hole before planting
Before sowing, seeds are treated in several ways:
- soak them in hot water (50°C) for 20 minutes, the water should not cool; then the seed material is cooled and well dried;
- or leave the seeds in a 1.5% mustard solution for 6 hours.
A week before planting seedlings in a permanent place, the soil is treated with a solution prepared from 300 g of copper sulfate, 300 g of slaked lime and 8 liters of water or treated with a 0.1% solution of Fundazol.
The roots of seedlings, before transplanting to a permanent place, are kept for 2 hours in a solution of Fitosporin-M or treated in a suspension of sulfur-containing preparations - colloidal sulfur, Thiovit Jet, Cumulus DF.
When planting without an earthen ball, the roots of the seedlings are rolled in lime flour or dipped in lime-clay mash. The second option is preferable, since lime attaches well to the roots.
Weeds are removed in a timely manner, especially representatives of the cruciferous family - shepherd's purse, rapeseed, spring grass, and field mustard. The roots of these plants are an excellent refuge for spores in winter.
It is recommended to add 1 handful of wood ash or ash to the hole before planting cabbage.
How to prevent contamination of entire soil
Seed treatment before planting is mandatory. At the same time, the experience of gardeners allows us to understand how best to process the seeds before further planting:
- It is recommended to treat the seeds with an immunostimulant, which will increase resistance to external factors.
- Seeds can be poured with hot water (optimum temperature - 50 degrees Celsius) for about 20 minutes. The water must remain hot to achieve the desired result.
- The seeds are kept in a weak mustard-based solution for six hours.
- The seed is treated with ascorbic acid for 16 hours. The solution is prepared according to the following scheme: 0.1 grams of ascorbic acid per liter of water. It is recommended to stir the solution with the seeds every hour, and then rinse the seed.
- Dry seeds can be placed in the refrigerator for a day. This seed treatment allows you to count on obtaining high-quality seed material that will be resistant to fungal infections.
Soil preparation
Proper soil treatment becomes mandatory. Only after this is it recommended to plant cabbage seeds.
In autumn, lime mortar is used to treat the soil. In early spring, the soil is dug up and organic fertilizers are added to it.
To obtain a healthy and rich harvest, you can plant healthy vegetable crops for three years. In addition, it is recommended to remove weeds and disinfect the soil before planting vegetables and harvesting. After time, you can successfully plant and grow cabbage.
Crop rotation
Proper crop rotation regulates the condition of the soil. It is recommended to use the following plants to successfully grow cabbage:
- Solanaceae - land clearing occurs within 3 years;
- lily and goosefoot - parasitic fungi are killed in about a couple of years.
Measures to combat sauerkraut largely determine the possibility of successfully growing cabbage. Features of agricultural technology that lead to a reduction in the risk of developing fungal infections are as follows:
- eliminating the lack of calcium and potassium in the soil;
- possibility of replenishing zinc, boron and chlorine;
- increasing the humus content in the soil;
- compliance with the optimal watering regime;
- acidic soil needs to normalize the pH level.
Folk remedies will help to successfully eliminate clubroot on cabbage:
- 150 grams of lime are stirred in 5 liters of water. Water the cabbage bushes with the prepared solution. Each cabbage requires up to 500 milliliters of solution.
- Slurry or mullein solution is recommended for feeding cabbage.
It should already be clear that after identifying the disease, at least one season must be skipped and cabbage should not be planted. But with the onset of the next season, there is no rush to plant. The best thing to do is test. After all, using laboratory methods for ordinary summer residents is unprofitable and expensive.
Testing is carried out in the area where the cabbage was sick the year before. So:
- plant several bushes of Chinese cabbage;
- The first examination should be carried out if the seedlings wither or after the formation of new leaves;
- Carry out the next check at the moment when the heads of cabbage begin to form.
If the plant withers and growths appear on the roots, then the soil is not neutralized. We will have to devote another couple of years to this event.
If the tested plant did not suffer throughout the season, the roots remained clean throughout the growing season, then you have managed to defeat the disease. Even a small growth, the size of a pea, indicates the presence of a disease in the soil. When planting cabbage, the disease will quickly spread, infecting the plant and soil.
Advice from gardeners
Experienced gardeners know how to fight fungal disease and protect their crops from it forever:
- for preventive purposes, marigolds, spinach and calendula are planted next to cabbage;
- water the seedlings with lime milk (80 g of the substance is stirred in 1 liter of water) 2-3 days before transplanting them into open ground;
- Before planting seedlings, add 1 dessert spoon of calcium nitrate to each hole and mix it with the soil;
- Cabbage is grown in narrow beds, which makes it possible to localize the disease if necessary and quickly clear the soil of the pathogen.
Clubroot is a dangerous fungal disease that can completely leave a gardener without a vegetable harvest. Timely fight against the disease and compliance with preventive measures will help you cope with it and forget about its existence forever.
0
0
Copy link
How to prevent contamination of entire soil
If clubroot is discovered in the middle of the season, then it is already difficult to do anything for treatment.
It is important not to spread the infection further around the area. It is not advisable to use contaminated soil for growing cabbage, as this will cause re-infection with clubroot.
Weeding
To localize the source of infection, thoroughly clean the beds where clubroot is found and the passages near them of weeds from the cabbage family. Where clubroot was discovered only once, it remains for a long time. Therefore, carry out all work on caring for an infected bed with specially designated equipment so that the spores are not spread throughout the garden. In the fall, when the cabbage roots are removed from the garden bed, dig up the soil with beet tops. All plant residues from the soil must be selected very carefully - do not leave even minimal seedlings.
Before you start fighting clubroot, remove all affected plants from the beds, dry them and burn them. It is better to burn it in the same place where this cabbage grew. Place the infected heads of cabbage with clubroot on an iron sheet, pour gasoline on them and set them on fire.
It is important that the fire be strong, as a smoldering and smoking fire can spread spores throughout the garden. Hill up the remaining healthy seedlings higher and water more abundantly
Soil liming
In an infected area, it is necessary to liming the soil, intensive watering and high hilling of planted plants. After harvesting, fluff lime is added to the beds where cabbage grew at the rate of 600 g of powder per 1 square meter. Liming is repeated a year later with the same amount of lime. When planting cabbage seedlings in a different place, fill each hole with 250 ml of lime milk solution. To prepare it, pour 800 g of fluff lime into 10 liters of water. This will prevent clubroot from appearing in another bed.
Sometimes the entire area is infected with clubroot. In this case, the question of what clubroot is on cabbage and how to deal with it becomes a real headache for the gardener. It can be very difficult to clear such an infected garden of the pathogen. Treatment of the land should be carried out in stages.
Health activities
First of all, the entire area must be cleared of cabbage crops, including weeds belonging to this family. It can be divided into two parts: potatoes can be planted on one, and garden crops on the other, but not from the cruciferous family. Replace plantings within three years.
At the end of treatment, test the soil for the presence of clubroot and in the future use the recommended therapeutic and preventive crop rotation and agricultural practices. As a test, plant seedlings of early ripening cabbage on the plot and monitor its condition throughout the season. If no growths form on the roots, then the area is cured.
I recommend watching the video where Oktyabrina Ganichkina talks about how she fights clubroot on cabbage.
Sources of material: https://www.syl.ru, https://sveklon.ru, https://good-tips.pro, https://ranchomoe.ru