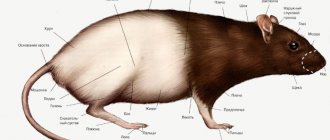
External differences
The main signs of differences between rats and mice can be observed in external characteristics. First of all, they are clearly visible in the mass of animals, as well as in the structure of the body. Based on them, you can easily determine which representative of the rodent family is in front of you.
Dimensions
The most significant difference between rodents is determined by size. Rats have significantly larger dimensions and a stocky body. The length of an adult can reach 30 cm, not counting the tail. At the same time, weight indicators fluctuate between 600–700 g. A mouse is a smaller rodent. It rarely grows more than 10 cm in length, and its weight does not exceed 30 g.
Tail
It is also not difficult to distinguish animals by the characteristics of the tail. In rats, it looks more massive, thick, has an impressive length, which is sometimes not inferior to the length of the main body, and sometimes exceeds it, reaching up to 35 cm. The tail is bald or bristly, depending on the species. In small rodents, the length of the tail ranges from 4 to 6 cm, almost all over it is covered with small hairs.
Find out also what to feed and how to care for a decorative rat.
Head
The shape of the head of a rat and a mouse also has significant differences. The former has a more elongated, pointed muzzle. The organs of vision are poorly developed. Small black or red eyes are deep-set and have a small viewing angle, so the animals have to constantly turn their heads to examine their surroundings. It is interesting that they see it in gray tones, and red objects are transformed into black.
In mice, the shape of the head is more rounded, flattened, and its size is much smaller. But the eyes, compared to the size of the muzzle, are large, convex, and expressive. The animal has developed farsightedness.
Important! Both types of rodents have teeth that grow throughout their lives, so they need to be given hard objects to chew on that can wear down their incisors.
Paws
There are practically no calluses on the rat's paws, which are necessary for climbing. But there are movable fingers with sharp claws. Thanks to this property, rodents can move freely through trees. Sometimes they make homes for themselves in abandoned hollows. The excellent muscularity of the paws allows rodents to jump long distances. Another advantage of the limbs is the presence of membranes between the fingers, which are similar in appearance to folds of skin.
They make rats excellent swimmers, capable of obtaining food in a body of water. When moving along a horizontal surface, the paws of rodents are widely spread. If you manage to examine the footprint, you will notice that the angle between the outer phalanges is about 180°. Since the predator often moves by jumping, the distance between the tracks can also be impressive.
You may find it useful to know what types of domestic rodents there are.
The legs of mice are short. Each of them has 5 tenacious fingers, so these small rodents are able to move through trees. However, their limbs are not as powerful as those of rats. They move mainly in mincing steps, with the toes spread minimally, and the distance between the tracks is about 1 cm.
Wool
Mice have softer, more delicate fur. In nature, its predominant color is brownish-gray or ash-gray, but it can vary depending on the environment. For example, desert mice have a yellow-sandy coat color, and among decorative species there are white, black, gray-blue, and variegated tones.
Did you know? Mice keep their homes clean and tidy, and with droppings they mark routes to food sources.
Rats have thicker, longer, and coarser fur. The most common colors are gray and dark brown. In individuals bred as decorative domesticated animals, many other shades are found: white, gray, reddish, spotted, etc.
Ears
The rat's ears are straight, even, pointed towards the top.] Hearing is very well developed - the animal perceives sounds with a frequency of up to 40 kHz, while humans - up to 20 kHz. In mice, this figure is even higher - animals perceive sounds with a frequency of up to 100 kHz, although the hearing organs themselves are small, rounded, rolled up.
Paws
In mice, they are small and have tenacious claws, thanks to which the pest can easily run along vertical surfaces.
Rats have strong and muscular limbs. The hind legs are longer than the front ones, which allows the animals to move by jumping. The fingers have membranes called leathery folds.
Head
Rats' ears are small and triangular. They are pressed to the head. Mice have large pink ears that are wide at the base.
The eyeballs of rats are small. Norushkas have large and expressive eyes.
Wool
The mouse feels silky and pleasant to the touch. And her relative has hard and coarse “hair”. The cover of an adult resembles a hard pile. Fur does not cover a rat's tail. Rat and mouse
Differences in behavior
Both rodents are capable of causing enormous harm to humans. Not only do they brazenly eat food supplies, they also bite a lot of things on their way, rendering not only food unusable, but also household items, clothes, and shoes. They are carriers of serious diseases and infections dangerous to humans. It is difficult to get rid of mice and rats, since both types of rodents are unpretentious and can live in various conditions - in cold basements, hot boiler rooms, etc.
Did you know? It has long been believed that of all the creatures on the planet, only humans can laugh, but American scientists have proven that rats, who also have a sense of humor, also have this ability.
The speed that running animals are capable of developing is quite high in relation to their size. Mice move faster, moving at speeds of up to 13 km/h. Rats are slightly inferior to them in “sprinting”. The maximum speed developed by gray “robbers” is 10 km/h, but at the same time they are able to jump over obstacles up to 80 cm high and make long flight jumps at a distance of up to 1 m. Both mice and rats are able to fit into very small holes and hold on perfectly on the water.
There are some differences in the lifestyle of these two types of rodents. Mice in nature live in colonies with a clearly expressed hierarchical structure. However, they obtain food individually, and therefore feed mainly on “harmless” food, rarely attacking insects that they are able to overcome on their own. The animals are quite shy and cautious.
Rats hunt more often in packs and are more aggressive. In a group, they may well attack a mammal that is larger than them. When danger approaches, they show incredible courage, and in self-defense they can even attack a person. There is also a difference in the activity of the animals. Mice sleep much more often, plunging into the “kingdom of Morpheus” about 15 times a day. Moreover, their sleep is short, and each period of activity lasts 30–60 minutes. Rats, as a rule, sleep once a day.
Familiarize yourself with the behavior, care and nutrition of rats at home.
Who's smarter
The rat is one of the smartest animals. She has a highly developed intellect, thanks to which, according to scientists, she is able to analyze information. Animals easily adopt the experience of their ancestors and, as far as possible, do not repeat their mistakes. If a rodent falls into a trap, it will signal danger to other members of the pack, who will try to leave the area. Rats are trainable and can be taught to perform a lot of tricks.
Mice are not inferior in brain size to body size, but in an intellectual battle they will definitely lose to rats. They are extremely difficult to train, although sometimes they get used to their name and respond to it. They remember routes leading to food sources and are able to stock up based on their instincts. Otherwise, their mental abilities are much weaker.
How to determine the type of spoiled food
You can also distinguish a mouse from a mouse by the type of spoiled food.
If rodents are indoors, their species can be determined by the following behavioral characteristics:
- Flakes. When eating grains, rats eat the grains without leaving any traces. Mice leave husks and spoiled grains.
- Small family members prefer to eat in only one place, while large ones cause great harm to the family and food supplies, each time choosing new food sources.
If rodents have settled indoors, it is important to be able to identify their species, since methods of dealing with them are different. To kill mice, you need to collect a trap or insecticide; To get rid of large rodents, you need to call professional pest controllers, as these animals are extremely careful, cunning and witty.
Life expectancy difference
Mice live very little in the wild and at home - their average lifespan is 1.5–2 years. Despite this, the colonies of these animals grow quite quickly, since rodents are able to give birth to offspring already at the age of 8–9 weeks. Moreover, additions to the family can occur up to 10 times a year.
You will be interested to know how many years decorative house mice live.
The lifespan of rats is longer - up to 3 years. They also become “parents” quite early, reproducing up to 12 members of the offspring at a time.
Life cycle
On average, ordinary gray rats live about 3-5 years. Larger black individuals are 4-6 years old. The lifespan of mice is 3 years. Both are extremely fertile, and the family is growing by leaps and bounds.
Pregnancy in rats proceeds very quickly - about 24 days, and in mice about 18. There are more than 10 individuals in one litter. There may be 7-10 cases of pregnancy per year. So they gain numbers with amazing speed, especially in favorable conditions: a good climate and constant access to food.
Differences in nutrition
In the warm spring-summer period in the natural environment, the mouse prefers to eat plant seeds and cereals. Field animals feast on wheat, buckwheat, and oats. Rodents living in forests prefer hazel nuts, acorns, and can even feed on small insects. Near reservoirs they find roots and stems of plants, berries, and larvae.
With the arrival of autumn cold weather, the mouse begins to actively look for warm places to eat, moving closer to humans. Penetrating into a home, it becomes omnivorous. In addition to any edible food, she will not disdain such products as soap or candles. Animals cause particular harm to stocks of vegetables stored in the basement, to cereals in bags, they can chew wires, and inhabit shelves with linen and clothes.
Important! Ornamental rodents should not be given raw meat, lard and smoked meats.
Rats bring even more trouble. These rodents are capable of causing damage to anything in their path, including wires and structures. Everything that humans eat suits them perfectly. Under natural conditions, rats need food high in protein, feeding on fish, amphibians, and insectivores. By nature they are predators, they destroy bird nests, and can eat small rodents, including mice.
At home, a large rodent eats any food products and waste, and does not disdain feed intended for livestock and poultry. The rat does not store supplies, but without food it dies quite quickly, after 3–4 days. Her diet must contain water or food containing a lot of moisture. Without receiving it, the rats die within a few days. As for domesticated ornamental species of rodents, it is recommended to feed them with grain feed and vegetables. Protein foods are served in the form of boiled chicken, egg whites, and cottage cheese.
Read how to properly bathe a rat at home.
Intelligence of Rats and Mice: Key Differences
Rats have more developed intelligence than mice (this also applies to domesticated rats and mice). But this does not mean at all that a mouse is a bad pet. Decorative rats are very smart animals that quickly make contact, and they also quickly become attached to their owner. They are trainable and can express their affection and love. In addition, the decorative domesticated rat knows and responds to its name when it is called to itself, especially if the owner offers some kind of delicacy or fun activity.
Essentially, the intelligence of a pet rat can be compared to that of other pets (cats and dogs). Rats are sociable animals that respond well to people, as evidenced by their love of games. According to many owners of pet rodents, the latter can even come up with their own entertainment and games, subsequently willingly demonstrating them to their owners, inviting them to join in the fun.
What do newborn rats and mice look like?
Like all cubs, pups and mice have an attractive, funny appearance. Watching these harmless little lumps is pure tenderness. At first glance, they seem very similar, but upon closer examination, significant differences in appearance are clearly visible. First of all, you need to know that a newborn rat has a body length of about 3 cm, while it is completely naked, without any signs of fur. A mouse that has reached this length already has a fluffy coat.
Differences that are mostly similar to those present in adults:
- the mouse's body is more rounded. The animal prefers to sit huddled into a ball. Rats have a more elongated body, and they often like to rest stretched out, like cats;
- the tail of a large rodent is more powerful, occupying about 80% of the body length, while that of a small rodent is thin, barely more than 50%;
- The baby rat's muzzle is pointed and oblong. The hearing organs also have the same features. Mice have shorter and rounder heads, thin, rounded ears.