The sand flea, also known as the Brazilian ground and penetrating flea, belongs to the Tunga family of blood-sucking insects.
Just like its other brothers, it is a blood-sucking parasite, and at the same time a carrier of dangerous infectious diseases.
- 10.1 Chemical control agents
Natural habitat
The largest populations of the parasite are observed in countries with warm climates. Optimal conditions for the development of sand fleas are in Vietnam, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Africa. Rare individuals can be found on European territory. The insect population grows very quickly on neglected beaches, landfills, quarries and other places where there is sand and water.
sand flea
Another place where a high concentration of the parasite has been observed is in Cuba. There, ideal conditions have been created for her: countless beaches, an abundance of sand, water and an optimal climate. A flea can choose almost any warm-blooded animal, including humans, as a carrier.
Harmless amphipod
Let's start with the “enemy”. He is “neither a friend nor an enemy, but so,” he is a crustacean, an amphipod ( Amphipoda
,
Talitridae
). Among the representatives of this order there are species that do not live in water, like most crustaceans, but in the surf zone on wet sand, where they feed on algae washed ashore. Why is a harmless vegetarian slandered on the Internet? The fact is that amphipods are the favorite food of sandpipers. Many people have probably seen sandpipers on the shores of cold and warm seas. A flock of them moves along the shore in a sinusoid, running away from incoming waves and catching up with outgoing ones (Fig. 2). From such a life, amphipods learned to jump, sharply unbending their abdomen, which was tucked under the body. Amphipods are poorly able to regulate the direction of a jump, but, apparently, the jump already complicates the hunting of sandpipers. For these jumps, the amphipods of the surf zone of the northeastern Atlantic received the name sand fleas, and their relatives on warm beaches also began to be called “sand fleas.”
Rice. 2.
A flock of sandpipers hunts amphipods. Photo by Grigory Smekalov (Sakhalin)
The English language is not rich in word-formation tools: starfish - starfish, jellyfish - jellyfish. The name sand flea is used twice - for surf amphipods and for a really nasty flea, which we will move on to after rehabilitating the amphipods.
Appearance of an insect
The sand flea looks like an oval disk. The insect's body is flattened and divided into three unequal parts: the head, the oblong belly and the sternum. The cover is smooth with a slight mirror effect. Mature individuals reach a length of 2 mm with a width of 1 mm.
A durable chitinous shell protects the pest from physical impact. There are three pairs of legs on the body, the hind ones are jumping: they are more developed and allow you to cover a distance of 3-5 cm in one jump. Depending on its habitat, the color of the parasite can vary from black to dark red. The family does not have wings.
Anatomy and life cycle of the sand flea
On the disproportionately small head of the insect there is a tiny pair of eyes. They also act as a sensor, allowing not only to navigate in space, but also to find a suitable place to get food.
The similarity of mandibles on the oral apparatus allows you to easily bite through thick skin, and thin tubes easily reach the capillaries, organizing a continuous supply of nutritious blood for the parasite. The food enters the insect's stomach and, after processing, is released as excrement.
For reference! Sand fleas have a special buffer where excess food is stored. At the same time, the insect inflates and increases in size, noticeably exceeding its original dimensions.
Life cycle of a flea:
- Egg . A grain of sand seemingly invisible to the naked eye. This period takes the insect about 2 weeks. One female can lay up to 300 eggs.
- Larva . White worm 2-4 mm long. It feeds on any organic matter: hair, dandruff, excrement, etc. Moves to the next period after 2-3 weeks.
- Doll . It is distinguished by its robust construction and the ability to fall into suspended animation for up to a year upon the onset of unfavorable conditions. The average development time is 3 weeks.
- Imago . A sexually mature insect capable of feeding and reproducing.
Reproduction
Adults live for about 6 months, the lifespan depends on climatic conditions and the abundance of food. The optimal temperature for the development of the parasite is from +25 to +30⁰С with a humidity of 40-60%.
What are sand fleas most often confused with?
Many people confuse the bite of a sand flea with the activities of other blood-sucking and parasitic insects. Therefore, many, in the fight against supposedly one pest, ignore the weaknesses of another, and sometimes contribute to its active development.
Similar activities are observed in the following insects:
- midges and mosquitoes;
- mites;
- ants;
- bedbugs.
Important! If you have a pronounced allergic reaction to insect bites, it is advisable to consult a doctor rather than engage in self-diagnosis. The course of treatment depends on the type of parasite, so specificity is extremely important here.
Signs of illness
Signs of the disease do not develop immediately. It takes from a week to 12 days before the first symptoms appear. This is due to the fact that all this time the female is growing under the skin.
Most often affected:
- feet;
- nails;
- wrists;
- elbows;
- legs to knees;
- groin and buttocks area;
- stomach;
- back.
There have been cases where the female was found even in the area of the back of the head, pubis, penis, lips, eyelids. Depending on the degree of damage, mild and severe forms of the disease are distinguished.
The death of a female in human skin causes a number of unpleasant symptoms:
- severe itching;
- pain;
- inflammation.
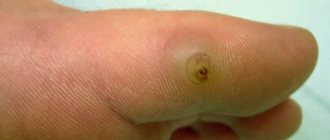
In response to the presence of the parasite in the skin tissue, the body triggers an allergic reaction. The skin turns red. Then the tissues around the parasite swell and begin to become inflamed. As a result, an abscess that resembles a boil forms. Once opened, it turns into an ulcer. If an infection gets into the wound, severe inflammation is possible, which can result in gangrene and sepsis.
Fleas tend to bite humans in certain places. These are, most often, places where the skin is thinnest - the popliteal and armpit hollows, waist, legs (bites especially often appear on the top of the foot and on the sides of the heel bone)
As the eggs develop, the entire time the female is in the skin, fluid may be released from the wound.
Pain and itching can become so severe that a person can hardly move. Unpleasant sensations may intensify at night.
Itching leads to scratching, which can lead to infection in the wound. Microbes that get into the wound cause suppuration and an abscess. Complications of this can include tetanus and gangrene.
But even if it doesn’t come to this, the consequences of infection can be very sad. Tungiasis causes:
- deformation of fingers;
- finger amputation;
- necrosis;
- thrombophlebitis;
- elephantiasis;
- pneumonia.
Routes of infection by sand fleas
The parasite lives not only in sand near water, but also in other places. The flea waits for a suitable host in bushes, grass and farmland. The insect can also be found in swampy areas, but its main carriers are animals. Even fleeting contact with an infected dog or cat is enough for a person to become infected with a dozen parasites.
Beach fleas attack the feet of tourists and the paws of animals. Subsequently, the insect moves higher - to the legs, groin and back. Very often the pest gets under the nails, where there are a lot of capillaries, as well as food.
Important! When visiting a foreign resort, you should avoid wild beaches. The authorities of Thailand or Vietnam are very reluctant to carry out preventive measures in such places or do not treat them at all. The parasite bites tourists especially actively in September.
The many faces of sandfly
It’s worth changing the sand flea a little to sandfly - and the solution will come closer.
In non-American English, sandfly is translated as "mosquito" (family Phlebotomidae
).
Mosquitoes should not be confused with the mosquitoes that pester us in the forest (family Culicidae
); Few people have seen mosquitoes, like fleas; they live in arid regions, for example in Central Asia (and therefore the name sandfly in relation to them is quite justified). If someone still wants to get acquainted with mosquitoes in person, then I can recommend Turkey as a resort area, where they are present, albeit only a little, on the vast sand dunes around the ruins of ancient Side. To a non-specialist, mosquitoes look like ordinary blood-sucking mosquitoes, only clearly small. However, during the day they sit in shelters, most often in rodent burrows, and fly to bite at night. That's why it wasn't mosquitoes that bit my friend on the beach on Koh Chang.
In American English sandfly means or horsefly ( Tabanidae
), or the smallest mosquitoes from the family
Ceratopogonidae
, which in Russian are called “mokretsy”. (I can’t even imagine why horseflies and biting midges are called “sand flies”: horseflies have nothing to do with sand; midges are not only not sand flies, but not even flies, but mosquitoes. For clarification, please contact the Americans.) Horseflies in Thailand there are, but even cows and horses, when they are bitten by a horsefly, notice it well and react adequately. It was clearly not them who offended my friend. But biting midges are the correct answer. These small (usually 1.0–1.5 mm) creatures (Fig. 4) have earned their own word in the Russian language for a reason.
Rice. 4.
Female
Culicoides
bites a human (photo from diptera.info)
Symptoms of a sand flea bite
The human body reacts to a sand flea bite almost instantly. Clear signs of infection begin to appear within 2-3 minutes after contact with the parasite.
Bite
Bite symptoms:
- redness;
- swelling;
- itching;
- an increase in the size of the problem area;
- painful sensations when touching the bite site;
- peeling of the skin;
- visibility of the parasite.
Important! If symptoms develop for more than two days, consult a doctor immediately. It is extremely difficult to remove a tiny flea on your own, because the parasite is securely attached under the skin by means of tenacious legs.
Reproduction
Unusual sexual behavior of adults depends on the special structure of their organs
reproduction. These organs are the most complex in the entire animal kingdom. The female, climbing onto the male, pulls his genitals into herself. The male reproductive system consists of one pair of testes, vas deferens, two pairs of accessory glands and the copulatory apparatus. The size of the genital organ in an inactive state is equal to a third of the length of the body. It has a beard and spines. The female reproductive system consists of paired ovaries flowing into paired oviducts. They merge into a single oviduct, which passes into the ectodermal vagina, which opens outward into the vulva.
The entire penetration process takes more than ten minutes, and the duration of sexual intercourse is almost ten hours.
Females lay eggs that are less than a millimeter long. Their development lasts about two weeks.
How are bites treated in Thailand and Vietnam?
Insect bites at resorts are treated with local antihistamines. However, in difficult cases, this approach can be called rather preventive: if the parasite has penetrated the skin, then it is impossible to do without the intervention of a specialist. Local doctors constantly encounter such problems and know exactly how and with what to treat the consequences of the activities of beach insects.
Popular remedies for bites in Thailand and Vietnam:
- Yellow Balm;
- Compound Dexamethasone.
Pest development cycle
The development cycle of the parasite has 4 stages:
- egg;
- larva;
- chrysalis;
- adult.
2 days after conception, the female is ready to lay eggs. Most often, insects do this on the body of an animal, less often on a person. A flea can lay from 30 to 50 eggs per day in batches of several pieces. Along with the eggs, the female lays out a certain amount of feces - digested blood, which has a brown color.
After a few days, the eggs hatch into larvae.
Outside the host organism, the larva penetrates the sand and feeds on organic debris. On the body of an animal or person, the larva absorbs the remains of feces.
The body grows within a week. During this period, the larva molts using the fibers of its scales, wraps itself in a cocoon - a pupa appears. The cocoon is wet, sticky and within 7 days it grows an adult inside it.
The life cycle of an insect lasts about 15 days. The pupa may not develop into an adult in the absence of appropriate conditions and may prolong the cycle up to 12 months.
Consequences
If you do not see a doctor in time, there may be serious consequences. In some cases, after an insect bite, an allergic reaction occurs, which sometimes leads to the development of asthma or even anaphylactic shock. The problem gets worse when combing the problem area.
For reference! The bite of a female sand parasite is considered the most dangerous. She dives into the skin and lays eggs there. The process is accompanied by severe itching, burning and pain. If measures are not taken, the inflammation will develop into tungiasis, which can deprive a person of a limb.
Other possible names for the Brazilian flea
The scientific name of the parasite is Tunga penetrans. Perhaps this flea lived in other tropical areas on the American continents, but it was first described in Brazil. Hence the first name – “Brazilian earthen”. The second name is a direct translation of Latin and means “penetrating flea.” Reflects the conditions under which the female lays eggs.
In English, in addition to Sand flea, there is a second name for this dangerous parasite - jigger. In each language this insect is called differently, so it is usually enough for a tourist to know the English name of the flea. And remember that "Sand flea" can cause confusion, while jigger indicates a specific type of insect.
Important!
Do not confuse the colloquial name of the parasite jigger (jigger) with chigger (chigger) - a parasitic mite.
Prevention and precautions
If you follow simple rules, the risk of infection with the parasite is significantly reduced. First of all, avoid wild beaches. The latter are a real breeding ground for sand fleas and other equally dangerous pests.
How to protect yourself from the parasite:
- Avoid going to the beach in the early hours and at sunset.
- Treat your skin with protective insect repellent creams after each bath.
- Wear socks and closed shoes.
- Maintain cleanliness and change bed linen regularly.
- After walking, wash your feet in soapy water.
Washing feet
Important! Before traveling to an exotic resort, you must get a series of vaccinations. Depending on the country, their list may vary. The doctor and tour operator should be aware of this.
Harm
Fleas cause a disease called tungiasis. It most often affects people from poor areas who rarely wear shoes. Also, the disease has recently affected tourists who do not follow the safety rules for staying in southern countries. Men become infected more often.
The sand flea can lead to the appearance of festering ulcers on the human body
In addition to people, fleas also infect domestic animals - goats, pigs, dogs, causing approximately similar symptoms in them.
Ways to get rid of sand fleas
At the first signs of the appearance of a parasite, no matter where: on the human body, on a pet or on interior items, disinfection should be carried out urgently. Otherwise, after a short period of time, there will be many more insects.
Chemical control agents
Not only interior items need to be treated, but the entire room: floors, walls, baseboards and crevices where the parasite can hide.
Effective preparations for sand fleas:
- Tick Lawn Spray;
- T Room Fogger;
- Get;
- Tick Carpet Spray.
Traditional methods
The clear advantage of this approach is accessibility and a much lower likelihood of developing allergies. However, in difficult cases, such remedies against fleas are ineffective.
Traditional methods:
- Treat all items with a mixture of baking soda and salt.
- Place bunches of wormwood and/or tansy around the room.
- Ventilate the room as often as possible when the temperature outside is low.
- Place pine shavings in areas where fleas are concentrated.
Treatment
Tungiasis can only be cured through surgery. As soon as a diagnosis is made and fleas are found in the skin, they need to be removed.
Getting rid of a sand flea that has penetrated the skin is extremely difficult. Many people try to pull out the parasite on their own with a knife or needle, but it is still better not to do this, but to seek help from doctors
The flea is removed with tweezers or using a sterile needle, being careful not to damage it. After removing the parasite, the wound is disinfected and bandaged.
Types of fleas and structural features
Often found: chicken, cat, dog, human, rat, sand fleas. This classification is based on the principle of connection with the victim. But these are not all the characteristics of fleas: bloodsuckers of the same species are not present on the body of the same victim. They can attack representatives of different species, feed on them, and then rest or mate outside the victim's body. The structure of a flea can be examined in more detail under an ultramicroscope.
Human flea
In principle, they are no different from other adherents of this species. When observed under a microscope, one can notice the absence of the cephalic and thoracic teeth. Body length up to 3 mm. The victims are not only people, but also cats, dogs, horses, and wild animals. The danger is that fleas carry plague, pulicosis, and some helminths.
Earth flea
Externally, this type of flea is practically no different from other species. Individuals feed on the blood of mammals. Most often, residents of the first floors, as well as those who have high levels of humidity in the room, suffer from them.
Habitats: basements, baseboards, furniture, soil.
House flea
This flea can be of several species that can live in a warm room. They can be found in animal bedding, on animals, under baseboards, in furniture, carpets, and bedding. As a rule, they feed on the blood of cats and dogs, and in rare cases, human blood.
Penetrating flea
She is also the sand flea or the Brazilian ground flea. Originally from Brazil and Haiti, this flea was eventually introduced to Africa, India and Pakistan, where it successfully took root. It has an oval-shaped body and a red-brown color with a white spot in the middle. The average body length of this flea species is 1 mm, and it is capable of jumping to heights of up to 30 mm. Usually lives in the grass, from where it jumps on animals, birds and humans. Penetrates under the skin of animals' feet. A person can penetrate under the nails of his toes and fingers, and lead to inflammation, tetanus, and in especially difficult cases, gangrene and amputation of limbs.
cat flea
This order of fleas develops in nests and burrows. In apartments, houses and other premises where a person directly lives or appears from time to time. It mainly affects the legs, feet, arms, abdomen, and back. Body length up to 5 mm. They are carriers of brucellosis, plague and other dangerous disorders.
Dog flea
The insect can be found not only in dogs, but also in others, even in humans. This variety is less common than cat fleas. Spends most of his time outside the victim. Body length is about 5 mm. The danger lies in the fact that during a bite it can transmit plague and trypanosomiasis. But do fleas have wings, no, but they can jump up to 1 meter in height, this also applies to other representatives of blood-sucking fleas.
Southern rat flea
This is the most dangerous order of fleas; it carries typhus, plague, encephalitis, and parasitic worms. Widely distributed in countries with subtropical and tropical climatological conditions. The body size is about 3 mm.
sand flea
The main difference is the size of the body, no more than 1 mm. Sand flea - habitat - subtropical areas. Those who like to vacation in India, Vietnam, Cuba, and the Dominican Republic should be the most attentive. These bloodsuckers not only bite painfully, but are also often the cause of such a peculiar disease as sarcopsillosis.
Regardless of the flea species, a fertile female can lay up to 50 eggs daily.
Safety measures: what to do to prevent fleas from biting you on the beach?
On the well-groomed and clean beaches of hotels in Vietnam and Thailand, there is no need to be especially afraid of fleas - here they are actively fighting against them.
But if you want to tickle your nerves (and legs) on a wild beach or in the forest, but not become a victim of fleas and other parasites, you should:
- Get dressed. Preferably in pants, a long-sleeved shirt and socks. It is good to tie a scarf around your neck.
- Spray your feet, hands and neck with a repellent containing more DEET.
- Avoid moving through areas with tall grass.
- Try not to step in puddles.
When sunbathing on the beach, at the first bite you should move to a sunny place. Fleas, and other parasites, prefer to be in the shade of trees and usually do not come out into the sun. They are also untouched in sea water.
Enjoy your holiday!
The video shows sand flea (or Chigoe Flea) bites. The footage is not for the faint of heart
Tips on how to protect yourself
In an exotic country where there is a risk of encountering a sand flea, it is worth taking precautions in advance:
- wear rubber slippers when walking along the coastal sand;
- avoid getting sand on your skin;
- sunbathe only on a sunbed or mat;
- Treat your feet with repellent. It is effective for up to 5 hours;
- after visiting the beach, wash the sand off your feet;
- when visiting places with dense vegetation, wear closed clothing with long sleeves;
- do not step on puddles.
Note. Careful daily inspection of the area between the toes will help prevent the disease at an early stage.
Sand fleas settle in places that are not disinfected. With proper prevention of the territory, premises and the beach, the parasite ceases to exist. The bite of this flea is painful and can lead to serious illness. Timely contact with a specialist, removal of the female flea and a prescribed course of antibiotics completely cures and restores the body.
Source
Fleas - description, characteristics, structure. What do fleas look like?
The flea's body length is only 1-5 mm, but females of certain species, after intensive feeding, reach a length of more than 1 cm due to their hypertrophied abdomen. The length of a fertilized female can be 1.5 cm. The largest fleas that parasitize moose have a body length of up to 1 cm.
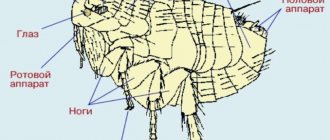
The flea's body consists of a small head and abdomen, covered with a durable chitinous covering. If you look at a flea under a microscope, you can see how the insect’s body is flattened laterally, somewhat reminiscent of a shrimp. But this body shape is evolutionarily justified and allows the parasite to move unhindered in the feathers, thick fur of the host, in the substrate of burrows and nests, or in the folds of clothing.
SEM image of a flea in artificial flowers
The color of a flea can be yellowish, reddish, dark brown and even almost black.
The flea does not have wings, and this is no coincidence: a winged parasite is easier to crush, and the presence of adaptations for flight could complicate motor activity.
Thanks to 3 pairs of long, strong limbs, fleas often move by jumping, which is ensured by powerful pushes of the second and third pair of legs. Some types of fleas have relatively short legs and practically never leave the host's body. Each limb consists of 5 segments and ends in sharp forked claws.
The easy movement of the flea is also facilitated by numerous spines and bristles scattered throughout the body, as well as jagged combs and ctenidia located on the head. This structure of the flea is a kind of protection for the insect: all attempts to comb, pull out or bite the flea will end in failure. The only way to destroy a parasite is to crush it with a fingernail on a hard surface.
There are simple eyes on the head of the flea, and antennae grow behind them, with the help of which males hold females during mating. In a calm state, the flea's antennae are immersed in small antennal fossae.
Fleas have a piercing-sucking type of oral apparatus, which is characterized by the transformation into stylets of epipharynges (unpaired stylet) and lacinia (paired stylets), articulated with maxillary lobes. The parasite bites through the host's skin, widens the wound and releases saliva, which prevents blood clotting. The flea then plunges its body into the wound to reach the blood vessel. When feeding, fleas fill their stomachs with blood, which can become very swollen.
A distinctive feature of the structure of fleas is the presence of a pygidium, a special sensory organ located in the back of the abdomen. Tactile hairs covering the pygidium sensitively detect the slightest vibrations in the air and signal danger.
The reproductive organs of a female flea consist of oviducts, ovaries and a spermatic receptacle, which resembles a curved flask. Males are endowed with a copulatory organ - the genital claw.