Types of fleas
| Dog flea | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Type: | Arthropods |
| Class: | Insect |
| Order: | Siphonaptera |
| Family: | Pulicides |
| Genus: | Ctenocephalids |
| Variety: | C. canis |
| Binomial name | |
| Ctenocephalides canis (Curtis, 1826) | |
The dog flea
(
Ctenocephalides canis
) is a species of flea that lives as an ectoparasite on a wide variety of mammals, especially the domestic dog and cat.
It is very similar to the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis
, which can feed on a wider range of animals and is generally more common worldwide.[1]
The dog flea is a concern because it can spread Dipylidium caninum
.
Although they feed on the blood of dogs and cats, they sometimes bite people. They can live without food for several months, but females must have blood food before they can produce eggs. They can deliver about 4,000 eggs per host. fur.[2] Eggs go through four life cycle stages: embryo, larva, pupa, and adult (adult). The entire life cycle from egg to adult takes two to three weeks, although this depends on temperature. In cooler conditions this may take longer.[3]
What do fleas look like on dogs and how do they reproduce?
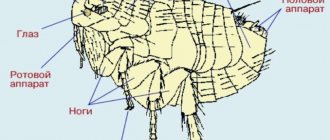
Dog fleas are small - their body length is about 2-4 mm. The chitinous cover, consisting of many bristles, allows the parasite to firmly adhere to the fur and move quickly. Fleas jump well - 3 times further than they can see.
This canine parasite is hardy, so it tolerates sudden temperature changes, high humidity, and even develops resistance to chemicals.
The flea's mouthparts are adapted to the dog's skin, but if there is a lack of food, the parasite can bite a person or other animal. If there is not enough food, the insect hibernates.
The flea has a complex reproductive system. Mating can last up to 10 hours. Almost all parasites begin copulation after drinking blood. After fertilization, the female immediately lays eggs. A flea can lay up to 10 eggs at a time.
Reproduction occurs in favorable conditions: in rags, dust, woolen products, a booth, on the floor, in clothes. The eggs are oblong in shape and resemble grains of rice.
Anatomy
The mouthparts of the dog flea are adapted for piercing skin and sucking blood. Fleas in dogs are external parasites that live hematophagically from the blood of dogs. The dog will often experience severe itching in all areas where fleas may be present.
Fleas do not have wings, and their hard bodies are laterally compressed and have hairs and spines, allowing them to move easily through hair. They have relatively long hind legs for jumping.[3]
The dog flea can be distinguished from the very similar cat flea by its head, which is rounded at the front rather than elongated, and the tibiae of the hind legs, which exhibit eight setae—notched instead of six.[4]
Reasons for appearance
The flea invasion occurs in the warm season and begins in spring and ends in October. Parasites choose their refuge in private houses or on the first floor of apartment buildings.
Fleas can be caused by contact with other dogs.
The main sources are:
- dirty entrances;
- neighboring apartments;
- infected pets;
- flea colonies in the basement or attic;
- presence of rats and mice;
- garbage dumps.
Fleas lay eggs in an animal's fur, so the owner can transmit parasites to his pet if he first pets an infected dog and then a healthy one.
Prevention
As a preventive measure, it is recommended to use drops on the withers (Frontline, Advantix or Charter) or an anti-flea collar (Foresto, Kiltix). These products last up to 8 months and effectively protect dogs from fleas and ticks. You can also use specialized shampoos.
These simple precautions will keep the animal healthy and save owners from having to remove fleas from the apartment. If infection occurs, treatment begins immediately. This will help prevent complications.
Can they transfer to people?
Fleas cannot live on humans, so they are not transmitted to people from sick animals. However, if your pet brings this insect back from a walk, immediate action should be taken. If there are too many fleas, they may bite people in search of food.
Fleas live on bedding or carpets, in garbage. If, for example, an animal left the house for some time, and parasites remained on its blanket, then they will begin to attack people in order to satisfy their hunger.
How they bite
The oral apparatus is designed in such a way that it is convenient to suck blood . Fleas' sense of smell allows them to identify humans by the smell of carbon dioxide. Once on the body, the insect bites through the skin and begins to suck blood. The parasite's proboscis is short, so it inserts both its head and part of its body into the wound, assuming a vertical position.
The flea does not mask the bite with an anesthetic, so it causes pain to the victim. During the puncture process, the insect injects saliva, which impairs blood clotting, and along with it harmful bacteria.
Having received a portion of blood from one wound, the parasite crawls a few centimeters and makes a new one. During one feeding, the insect makes 3-5 bites.
Flea bites.
Consequences of bites
The consequences of a bite can be:
- various skin lesions, ranging from severe itching to abscesses and dermatitis;
- high fever;
- development of brucellosis;
- transfer of worms, tapeworms from the previous “owner”;
- sleep disturbance.
When scratching the bite area, boils, abscesses and growths can form.
An allergic reaction is a common consequence.
Signs and symptoms
Fleas can not only be annoying to dogs, cats and people, but they are also very dangerous. Problems caused by fleas can range from mild to severe itching and discomfort, as well as skin problems and infections. Anemia can also result from flea bites in extreme circumstances. In addition, fleas can transmit tapeworms and diseases to pets.
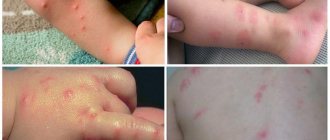
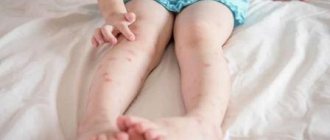
When fleas bite people, they may develop an itchy rash with small bumps that may bleed. This rash is usually located on the armpit or crease of a joint, such as the elbow, knee, or ankle. When you click on an area, it turns white.
When dogs are bothered by fleas, they itch and bite, especially in areas such as the head, neck, and around the tail. Fleas usually concentrate in such places. Continuous scratching and biting can cause your dog's skin to become red and inflamed. This is easily noticeable when the dog's fur is parted and the dog's skin is exposed.[5]
Flea allergy dermatitis develops in dogs that are allergic to flea saliva. In this case, the above symptoms are more pronounced. Due to obsessive scratching and biting, a dog can lose hair, develop bald spots, develop hot spots due to severe irritation and develop infections that cause the skin to develop an unpleasant odor.
How to fight
If parasites are found, disinsection must be carried out. To treat the room you will need a soda or saline solution (you can also add insecticidal shampoo).
The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Thoroughly vacuum the entire apartment, including upholstered furniture.
- Send for cleaning things that could harbor pests.
- Throw out the animal's bedding (it is recommended to change it more often), and treat all items belonging to the dog.
- Carry out wet cleaning with a solution.
- Close doors and windows hermetically.
- Move furniture away from the wall, treat all cracks, corners, carpets and other surfaces with insecticide.
- Leave the apartment for a few hours.
- Upon return, ventilate well.
- Do the cleaning again.
An option for flea control is a collar.
This treatment must be repeated after a week to ensure that both larvae and eggs are destroyed.
In a private house, it is necessary to treat not only the interior, but also the basement, cellar, attic and all outbuildings and the surrounding area.
Dog house treatment
The booth is disinfected after it is cleaned. To avoid “flooding”, you first need to dig drainage ditches at an angle. The entire house needs to be treated, both inside and outside.
The procedure can be carried out using an aqueous solution of formalin, creolin or Lysol. Creolin is used more often because it is easier to buy and easier to dilute with water.
Regular scheduled treatments are carried out in winter, spring and autumn. In summer, disinfection is carried out every month. The kennel is washed out unscheduled with a solution if a flea infestation has been detected, or before moving a new pet into it.
Whatever solution is used for treatment, the animal should not be allowed near the booth until it is completely dry. Otherwise, there is a risk of harming your pet's health.
Animal handling
It is possible to remove these parasites yourself at home if a severe infection has not yet occurred.
The fastest way to get rid of parasites is to use a spray. After treatment, the drug begins to act instantly, the protective effect lasts about a month. Before spraying, you need to straighten the animal's fur so that the liquid gets on the skin. Everything is treated except the head. The pet needs to be occupied with playing for a while so that the drug has time to dry.
Drops are considered a more effective remedy, but they begin to act only on the 2nd day. During this period, the animal should not be bathed so as not to wash off the medicine. The drug is applied directly to the skin from the back of the head to the withers.
A special flea collar is the safest remedy. A plastic headband with insect repellent is more suitable for prevention. You need to wear it constantly, it begins to act gradually. The duration of the collar is indicated on the packaging.
How to detect the presence of fleas in the house?
If you begin to notice itching on your legs, especially at night, then there is a high probability of fleas in your apartment. Detecting them is quite difficult, but there is a special detection method:
- determine which room the fleas have settled in;
- lay several sheets of white paper or a white sheet on the floor;
- leave the room for a few minutes, then check the white canvas - if black dots appear on it, which disappear when approached, these are fleas.
Description of insects
The insects' body is smooth and equipped with spines that help them cling to their prey. Fleas have 3 pairs of legs; the rear ones are longer and provide jumping ability. Insects are good jumpers, so they fly to the victim without direct contact.
Body length – 3 millimeters, color – brown. The compressed sides allow for easy movement between hairs. They usually live outside the human body, visiting for food. They jump quickly, up to 50 centimeters. It is difficult to catch and crush an insect.
The eggs are thrown in small batches in different places, sometimes on the host. Larvae hatch, similar to worms, which actively move, live in garbage and dust, and feed on organic debris there.
Physiology
They feed on the blood of warm-blooded creatures, including humans. They can live near people or animals, hiding almost all the time when they are not looking for food.
They live up to 500 days, but usually much less. If they don't find people, they terrorize domestic animals.
Why are they dangerous?
The main threat lies in the diseases that fleas spread. Among the most significant and likely:
- salmonellosis;
- hepatitis;
- helminthiases;
- tick-borne encephalitis.
Even if infection does not occur, many people suffer from skin irritation, peeling, and loss of appearance. Often, especially in children, allergic reactions are added. Unpleasant neighbors can seriously ruin your life, leading to neurosis.
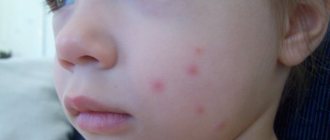
What does a bite look like?
The bite site is a small red bump that rises slightly above the skin. With a large number of wounds, they resemble a large rash. If scratched - swelling of the skin, abraded areas of the epidermis, redness.
Distribution routes
The human flea takes a liking to empty rooms near humans. They live in close proximity and are brought in mainly by the person himself on clothes, shoes, things from the attic or closet.
Fleas move well on their own, they sense where they can feed, so they try to live nearby. They easily migrate from the extreme floors of houses to apartments.
Signs of the presence of a parasite
If fleas have settled down to live in an apartment, it is impossible not to detect their traces. Household members are covered with red spots and itch. Small eggs are easy to spot in different places. Although the tracks resemble those of mosquitoes, flying squeakers are usually detected immediately.
Is it easy for a person to get fleas?
There is no need to think that fleas appear in people only where there is dirt, garbage and chaos. Of course, without proper sanitation, the risk of flea infestation increases significantly. But fleas can also appear even where hygiene is taken care of. Fleas live wherever there are animals. You can pick them up at the zoo, on a farm, hunting, or while walking in the forest or park. You can bring them from any public place, transport, or work. Even on the playground there can be fleas, because not only children can walk there, but also cats or dogs on their own.
In older homes, fleas can live for decades in basements and attics. There they feed not on the blood of domestic animals, but on rats or mice, which is even more dangerous, since rodents are carriers of the most dangerous diseases, and fleas, by biting them, spread these diseases further. In such houses, residents constantly suffer from infestations of fleas that come from common areas, utility rooms into apartments.
Symptoms of bites in humans
A person’s reaction to a flea bite depends on the characteristics of the body. Some feel a stabbing sensation at the moment of biting the skin, others experience an unpleasant burning and itching a little later or after finishing sucking.
A flea bite is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- red spots with swelling of the skin at the site of the bite, similar to traces of mosquito bites (up to 5 millimeters);
- swelling surrounding the spot usually goes away after a few hours;
- severe itching, burning, desire to scratch the affected area of the skin.
The spots and itching persist for up to two days. Other reactions largely depend on the individual characteristics of a person. Some develop blisters, noticeable swelling, and hives caused by the enzymes introduced by the flea.
How to recognize fleas
Insects move by jumping; they do not live on the human body, but only feed. Bite sites are most often localized on the ankles, where they are able to jump. If an apartment is infested with fleas, then when a person is sleeping, they can bite him anywhere.
You can detect fleas:
- by the characteristic bite spots that will appear regularly, because individuals need to eat;
- according to the appearance of the discovered insects, the color is brown, size is 2-3 millimeters, the hind legs are longer than the others, there are 6 legs in total;
- scattered eggs of small size and white-transparent appearance - in the folds of furniture and bedspreads, rugs, where pets lie.
There is no doubt that if fleas live in the house, they will reveal themselves. Animals and people will itch constantly. Note that bites usually do not appear under hair; this localization is typical for lice.
Routes of transmission to humans
One should not blame only domestic animals for the appearance of fleas in people, although pets are most often their source. Fluffy fur and corners of sofas favored by pets are the main places where insects get onto humans.
Other sources of bloodsucking:
- livestock and their habitats;
- courtyard buildings;
- non-residential parts of premises - attics, basements, stairs;
- small pets – rats, birds, their cages.
Dirty basements, habitats of street animals and homeless people are usually heavily infested with fleas of various species. Fleas live where warm-blooded creatures live or frequent, giving them food. These can be nurseries for domestic or wild animals, dovecotes, chicken coops.
Habitats
Fleas are almost elusive; swatting them down requires a fair amount of dexterity. A person is a source of food, not a place of permanent residence. At the same time, insects have convenient means on their bodies for attaching to hair and tissues, so they can live in the fur and not leave the animals. People leave after satiation.
Fleas live in close proximity to humans:
- in secluded crevices of furniture and walls;
- in the folds of fabrics, covers, bedspreads;
- close to the habitats of animals and birds.
They love places where people rarely go to clean or ventilate, or move things. They often live in neighboring non-residential premises - closets, utility rooms, sheds.
Preventive measures to prevent fleas
It is much easier for a person to prevent the appearance of blood-sucking insects in the house than to get rid of them. Considering how fleas are transmitted, you can avoid their appearance. The most likely reason for the appearance of parasites in the house is unprotected animals that transport dangerous insects on themselves. A dog can pick up bloodsuckers while walking, playing with other infected animals, or at the entrance.
After every walk, you need to check your pet's fur. If a jumping insect is detected, the dog should be immediately bathed using appropriate shampoo. You should periodically check dog accessories: bedding, rugs, toys. Parasites do not use the body of their host for permanent residence. Once fed, they mate and lay eggs close to their prey. As a safe preventative measure, you can fill animal bedding with pine sawdust.
Preventive measures
The most optimal preventive measure is to purchase a special collar that will protect the dog not only from fleas, but also from many other insects. The Celandine collar has proven its effectiveness. Drops that are applied to the dog’s withers have proven themselves to be effective. They contain insecticidal agents, thanks to which not a single parasite will come close to your four-legged friend. There is a large selection of such products on sale. The best drops are:
- Frontline;
- Bars Forte;
- Barrier;
- Blokhnet;
- Advocate;
- Celandine;
- Advantix;
- Practitioner.
If you pet your dog on the street and suspect that it is infected with blood-sucking harmful insects, immediately take a shower and wash your hair when you arrive home.
In cases where a pet is infected with fleas, it is necessary to carry out a set of measures, which includes removing dangerous insects from the pet and treating the entire room or apartment in which the dog lives.