Before delving into the topic, it is worth clarifying a few points so as not to mislead anyone, in particular, what a gadfly bite actually is. The fact is that gadflies do not bite. Adult flying individuals do not even eat, since their oral organs are atrophied, that is, they physically cannot bite you - they simply have nothing to do it with. What's the catch then?
People who are not interested in insects from a scientific point of view most often use the names “gadflies” and “horseflies” as synonyms, although in fact they are completely different insects.
- Horseflies are blood-sucking parasites and they do often bite people, livestock and smaller animals.
- Gadflies are insects that do not bite anyone, but lay eggs on the bodies of animals and people, from which larvae then hatch, capable of entering the body in different ways.
Horsefly bites are painful, so if you are bitten by one, you will be able to see it before brushing it off. It will look like a dark, large flying fly. Such bites are treated like most flying insect bites:
- Disinfect the bitten area.
- Apply a healing and soothing ointment.
- If you have allergies, take an antihistamine.
- If symptoms are severe, consult a doctor.
In the case of gadflies, a reasonable question may arise: if the larvae enter the body, can they do this through bites? Yes, they can, but in order to attach themselves to the body of a potential carrier and get inside it, they need time, sometimes up to several days, on average 4–5. In the case of people, such a development of events is unlikely, since the average person takes care of himself and washes at least once a day, which greatly complicates the larvae’s task of infiltration. However, there are exceptions to any pattern. Bodfly larvae can end up inside the human body if:
- The eggs were immediately laid in an open wound caused in some other circumstances, although this is also unlikely if you care for it, disinfect it and heal it.
- The eggs of the gadflies did not get under the skin, but into the gastrointestinal tract along with food.
- The eggs got on your mucous membranes, and you didn’t notice it, for example, you inhaled them.
- The eggs were laid on the head, in the beard, or any other place where a lot of hair grows, and you didn't notice it.
In any case, you will feel the larvae gnawing passages into your body from the outside. It is this process that, in the context of this article, will be considered gadfly bites and will be examined in detail from the perspective of what to do with it. If you find out that you were bitten by horse flies and not by gadflies, in a sense you can consider yourself lucky.
What kind of insect is a gadfly and what does it look like?
Another name for the gadfly is paut, which is what these flies used to be called in the northern regions.
The more common name is string, and the origin of all these words still remains a mystery to lexicographers. Botflies belong to the order of Diptera and the infraorder of round-stitched flies. Their closest relatives are blowflies and true flies. To date, entomologists have described about 150 species of gadflies, all of them are typical synanthropes, i.e., their habitats are closely related to human life.
Gadflies are distributed throughout the globe, they are not found only in Antarctica. The inhabitants of temperate latitudes resemble an ordinary fly in appearance, but slightly larger in size. The size of an adult gadfly is about 17-20 mm. The insect has a fuzzy abdomen and translucent wings with veins.
A distinctive feature is large eyes, but the horsefly, with which the gadfly is often confused, has even larger eyes and is larger. The differences between the insects are clearly visible in the photo of the gadfly and the photo of the horsefly.
Horsefly with sucker on nose; Gadflies do not have such a sucker.
Gadflies from the northern regions are painted in discreet tones: dark brown, lead-gray and grayish-blue specimens are found.
Southern and tropical species of gadflies, with their orange-striped color, are more reminiscent of medium-sized bumblebees.
These flies are not interested in cows, horses and humans as food objects; the adults do not eat at all, but use up the reserves accumulated in the larval stage. But the biology of parasites is such that they are able to develop normally only within certain species of animals.
One of the types of gadflies. One of the types of gadflies.
general characteristics
People often call all the large gray flies that attack a person, painfully biting the skin and sucking blood, as gadflies. Horseflies actually do this. The gadfly is not a bloodsucker. This insect lives off the nutrients it accumulated in the larval phase. Their mouthparts are not developed, and they do not feed during their lives. They are more like bumblebees.
But then why do gadflies bite people is a question to which not everyone can find an answer. Males consume only flower nectar, but the fertilized female seeks a warm-blooded incubator. Therefore, the bite of a gadfly has another purpose: to lay eggs under the skin of the victim. Typically, the main hosts for the offspring of these insects are cattle, horses, camels, and deer. The larvae live and develop in the body of their host until they develop into adults. And the life cycle repeats again. Parasitism in the human body is very rare.
Interesting!
There are about 150 species of these insects in the world, but only one attacks humans - the human skin gadfly. Luckily, it is only found in Central America.
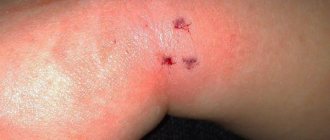
Gadfly bite: photo
If you have been bitten by a gadfly, this means that there are already or have begun to appear holes in your body through which the insect penetrates into the body. Externally, such bites may look like this:
- A large tumor appears at the site of the bite.
- Severe redness is observed, and the tissues may gradually turn blue.
- A dark dot is visible in the center of the bite, which is the passage through which the insect enters the body.
- Many such bites can appear simultaneously.
Skin damage by larvae looks extremely specific, but if you still have doubts, you can additionally look at what a gadfly bite looks like in the photo.
Manifestation of a parasite bite
Consequences of a gadfly bite
If you look at the photo of the symptoms of a gadfly bite in a person, you can note that they are very similar to a wasp sting, namely:
- pain;
- burning;
- edema;
- skin redness;
- itching;
- poor blood clotting;
- the bite site on the skin acquires a certain character, a tumor similar to a neoplasm appears.
On a note!
The consequences of a gadfly bite, including an allergic reaction, may go away in a couple of days if the wound does not get infected and purulent inflammation does not develop as a result.
General information about horseflies
Horsefly
A simple person who does not have serious knowledge of biology cannot distinguish a gadfly from a horsefly, which belongs to the order Diptera, but knows that the bite of a gadfly can be painful, so he is afraid of such an insect. The horsefly is a blood-sucking parasite. It lives in forest, taiga, forest-steppe zones. In arid areas, the insect can be found mainly near rivers and lakes; in the mountains it spreads to the borders with eternal snow.
Horseflies are popularly called gadflies. Only fertilized females, who need blood for the development of eggs, bite humans and animals. Males are smaller in size and feed on plant nectar. Females have a proboscis in their mouthparts, with which they cut the skin of the victim and inject substances into the wound that prevent blood clotting.
The length of the insect ranges from 6 to 30 mm. The color of the wings is gray, marbled, or it can be variegated. Bloodsuckers fly in good weather without rain or wind. The air temperature should not be lower than +15, but not higher than +32 degrees. Outside these temperature limits, bloodsuckers are inactive.
On a note!
The most common representatives in our country are rainflies, lacewings and horseflies. They show noticeable activity before the rain, but in wet weather you will not see them. Only rainflies can attack humans even during light precipitation.
Why do insects bite?
Insects bite for 2 reasons:
- show aggression in self-defense;
- human blood is their food.
In their understanding, a person represents a potential danger. Insects protect their habitat and offspring, and therefore behave aggressively. Bees and wasps are kept away from the hives, protecting the colonies and the honey.
Blood-sucking insects are hungry. Many people know that only female mosquitoes bite people - they need human blood as an additional source of protein to reproduce. Male mosquitoes feed on nectar and plant sap.
The compositions are low toxic to humans and have a repellent or exterminating effect on insects.
What you need to know
The overwhelming majority of people cannot accurately distinguish a horsefly (large, often with multi-colored eyes playing with colors) from a gadfly (smaller, less bright), and the assistance that should be provided to the victim depends on this. There are more than 3.5 thousand varieties of large flies that attack humans and mammals.
Most are classified as horseflies (3000 species) and gadflies (50 species). They are quite similar, so at first glance it can be difficult to determine exactly which particular insect this is, even for an experienced biologist.
Subcutaneous botfly - more often causes invasion in humans than other species
Important. The fundamental difference between horseflies and gadflies is that the former feed on blood, while the latter lay eggs under the skin of warm-blooded animals.
Only females always bite. If she manages to lay a clutch, then after a short period of time the larvae begin to hatch under the epidermis.
The duration of the infestation may vary, depending on the type of insect. For humans, the danger is posed by the subcutaneous gadfly (see photo), in this case it lasts about two months - all this time the larvae will parasitize and cause severe discomfort.
Most often, laying does not occur due to noticeable pain at the time of piercing the skin, but in certain cases (deep sleep, intoxication, the inability of a person (for various reasons) to drive away an insect, etc.) the eggs still end up under the skin.
All other types of gadflies are not so dangerous for humans, except in cases where the larvae end up in the eyes, which can cause the development of conjunctivitis and deterioration of the visual analyzer; in special situations, treatment even requires surgical intervention. Most of all, insects bother large warm-blooded animals, but sometimes small rodents also suffer. The larvae infect various organs, and when they accumulate in large numbers in the body, they cause the death of the infected individual.
Life cycle
Eggs
Females of Dermatobia hominis lay mature eggs on arthropods that feed on blood, usually mosquitoes and ticks. This behavior is known as phoresia. Because mosquitoes feed on blood, the eggs react to changes in temperature and hatch.
Larvae
The larvae enter the skin through a bite wound or hair follicles, where they penetrate inside. It protects itself with two anal hooks, secreting an antibiotic into its burrow, which prevent the appearance of bacteria and fungi.
It protrudes from a tiny hole to breathe, and a small mound forms that will grow to the size of a goose egg. They breathe through two posterior spiracles, which are flush with the host's skin. After the seventh day of infection, they molt to the second, then to the third instar after eighteen days.
After about thirty days, the third instar larvae, which can grow to a relatively large size, crawl out of the host to pupate in the soil. Life inside the host is from 5 to 12 weeks. The botfly larva feeds on tissue exudate. It develops at the site of penetration and does not migrate throughout the body, although it moves under the skin.
Find out more Midge bites - treatment methods, methods of protection
Doll
Pupation occurs in the ground. The pupae do not feed. Adults will emerge in two to three weeks.
Adults
Individual flies emerge from the pupae. Extremely sensitive antennae (compensating for poor eyesight) allow males and females to quickly find each other. During the adult stage, the gadfly does not feed.
The gadfly is a dangerous insect: what does a bite feel like for a person?
If a gadfly bites you, it means the insect is at the larval stage; the bite for a person in this case will be felt very strongly, since the process of gnawing your body by a foreign creature occurs, which cannot be ignored or not felt.
The following symptoms may appear:
- Swelling, redness and swelling in the affected area
- Severe itching
- Feeling the physical movement of larvae under the skin
- Acute pain due to torn and chewed tissues
- Cramps and spasms in the affected areas
- Increased blood pressure due to pain and nervous tension
- Increase in body temperature
Bites can additionally cause an allergy, then its symptoms will be added to the symptoms described above.
What happens if a gadfly bites
Gadfly bite
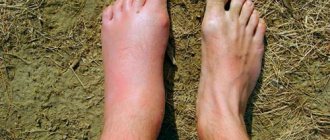
If a gadfly has bitten a person, it is impossible not to notice, since a strong burning sensation and pain are immediately felt, redness appears on the skin, and allergic reactions may occur. A photo of a gadfly bite clearly demonstrates the consequences of an insect attack. Blood in a wound does not clot for a long time, so you need to try to get rid of all the insects so as not to be attacked again. Gadflies find their prey with their eyes, which means they can escape from the bloodsucker.
Induration, swelling and redness immediately appear after a gadfly bite. The skin begins to itch and itch. A person with allergies may experience dizziness, fever, enlarged lymph nodes, swelling and severe redness in the bite area. If no complications occur in the form of allergic reactions (insect saliva is an allergen), then all these unpleasant phenomena disappear after a few days.
The gadfly's bite is very itchy. A person scratching the skin around a wound can introduce an additional infection that will require further treatment. But an allergy to a gadfly sting is quite rare. There are practically no cases of poisoning of the human body due to a horsefly bite Photo of a gadfly bite or severe allergic reactions in real life. But sometimes Quincke's edema can even occur.
The gadfly can be dangerous because it is a carrier of diseases such as:
- tularemia;
- anthrax;
- filariasis.
These diseases are transmitted through blood, which the insect can receive from sick people or animals.
Important!
It is difficult to treat such diseases, so when going into nature, you should think about protective equipment in advance. If possible, it is advisable to take the insect to a laboratory, where it will be determined whether it is the causative agent of the infection.
A bite can cause serious illness, so do not delay visiting a doctor.
What diseases do gadflies carry?
A flying parasite can carry diseases dangerous to humans and infect them through a bite. Cases of infection with anthrax, filariasis, and tularemia have been recorded. Also, when scratching the tumor site, the victim independently introduces bacteria, which results in prolonged inflammation and abscesses. If a female gadfly lays larvae, severe compaction, itching, irritation appears under the skin, and blood and pus ooze from the wound. Diseases will require medical treatment using glucocorticoid drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antibiotics.
A gadfly bite is always very painful. The skin instantly swells, turns red, and begins to itch very much, and in young children the temperature may rise, sleep may be disturbed, and appetite may disappear. Therefore, when going outdoors or fishing, you need to stock up on insect repellent and take a first aid kit with you. To provide first aid, it is enough to use an alcohol compress and antihistamines. If an allergic reaction develops, you will need the help of a doctor.
Signs of infestation with gadfly larva
When the parasite gets into the eye, there is a strong burning sensation, lacrimation, and conjunctivitis quickly develops. If you do not see a doctor, you may lose your vision.
The larvae of the esophagus and subcutaneous gadfly reveal their presence with typical symptoms:
- the place where the larvae penetrate the skin turns red, swells, and in people prone to allergies itches unbearably;
- after 7-14 days, a bluish swelling remains with a focus of suppuration and a small rod in the center;
- general health worsens: temperature rises, weakness, nausea are noted - classic signs of intoxication of the body;
- When the larva gets into the nasal sinuses, pain and swelling appear.
The consequences of parasitism can be dire. The migration routes of the larvae are not fully understood, and once they enter the brain or heart, tissue degradation becomes irreversible.
As a result of the vital activity of subcutaneous, gastric and cavity larvae, parasitic diseases develop - skin, intestinal, and genitourinary myiases. The so-called “wandering larva syndrome” causes hypodermatosis - periodically appearing and disappearing skin seals. And this is not a complete list of health problems that may arise after meeting a gadfly, so medical assistance is necessary in any case.
Bodfly bite. Consequences of a gadfly bite.
Where is it found?
This species lives in North and South America, Costa Rica, southeastern Mexico, northern Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay. Some cases of the botfly bite have been reported in Europe.
Since the maggots take 8 weeks to develop, unless the wound becomes infected, patients rarely experience infections unless they kill the maggot and remove it completely.
| Diptera species | Country of origin | Incubation period | Appearance of a mature larva |
| Cochliomyia hominivorax | Central and South America | 4-8 days | Typical larval shape, 15-17 mm long, bands of spines surround the anterior edge of each body segment. |
| Cordylobia anthropophaga | Central and Tropical Africa | 10-12 days | Oval, 11-15 mm, 3 curved slits in spiracles, numerous small black spines. |
| Cordylobia rhodhaini | Tropical, Central Africa | 10-12 days | Scattered spines up to 23 mm long, 3 sinuous cuts in each posterior spiracle. |
| Dermatobia hominis | Central and South America | 5-12 weeks | Length 18-25 mm, pair of flower-like anterior spiracles, spines in rows. |
Treatment of parasitic infection caused by gadfly
An infectious disease specialist is responsible for ridding a person of parasites. A visual examination and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent blood test can confirm or refute infection with a gadfly larva.
If the test is positive, a gastroenterologist, ENT specialist, ophthalmologist and other specialists are involved in treatment, depending on the location of the parasites.
The patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics and antiparasitic drugs. Subcutaneous larvae are removed medically or surgically.
Everyone is at risk of infection by the parasitic fly, which is widespread everywhere, but especially those living or staying in areas where livestock farming is developed. Therefore, you should not ignore basic protective measures.
What to do if you are bitten at home?
Unpleasant symptoms and consequences of a gadfly attack on a person are treated symptomatically or go away on their own. To prevent infection from developing, swelling to subside, itching to decrease, you can treat the bite site at home.
If complications develop, you will need the help of a doctor. Surgical intervention is recommended if the wound becomes suppurated, subcutaneous lumps form, or larvae are identified.
First aid
Gadflies are subjected to painful bites in nature, fishing or during agricultural work. Even the use of insect repellent sprays or creams will not protect you. Therefore, you should know a simple algorithm of actions that will minimize the consequences and eliminate severe pain and itching.
- The bite site must be pressed with any hard object or finger. These actions will relieve pain and burning and prevent intoxication with harmful substances.
- To prevent the appearance of redness, rash, and swelling, it is necessary to apply something cold to the wound.
- To disinfect the bite site, wash it generously with running water and soap. Next, the wound is treated with an antiseptic (iodine, chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, alcohol) and lubricated with antiallergic ointment.
- To avoid an allergic reaction, be sure to take an antihistamine orally.
In field conditions, the use of soap, antiseptics, and antihistamines is impossible. Therefore, it is proposed to use traditional medicine recipes. To disinfect the wound, squeeze onion juice onto it or make a salt compress (1 teaspoon of salt is diluted in 100 ml of water). Seed and plantain juice are good for relieving swelling and itching. Crushed dandelion leaf helps against inflammation and allergic reactions.
Pain relief
To relieve pain, you can apply cold water to the wound, apply a compress with cooling ointment, and take an analgesic orally. Local anesthesia reduces discomfort. If the tumor grows, it is recommended to use Fenistil or Soventol. These drugs heal the wound, reduce inflammation, and prevent the development of an allergic reaction.
If discomfort is accompanied by chills, nausea, vomiting, it is recommended to drink Nise or Nimesulide. For children, you can use syrup or tablets Ibuprofen, Nurofen.
Relieving swelling, swelling and redness
At home, you can relieve tissue swelling and redness using dandelion or yarrow juice. For a child, hyperemia is treated with a compress of Vishnevsky ointment, Sinaflan or an iodine mesh. Baths with the addition of a decoction of oak, willow, birch or poplar buds are useful.
Until complete recovery, essential oils of lemon balm, cloves, lemon, and pine are applied to the wound several times a day. Severe swelling and rash are removed with anti-inflammatory and regenerating agents (Levomekol, Gistan, Fenistil).
Allergic reaction
If urticaria (an itchy rash) is observed on the skin, shortness of breath appears, swelling spreads to adjacent tissues, and the person has an allergic reaction. First of all, you will need to take a fast-acting antihistamine: Suprastin, Loratadine, Zodak, Tavegil or Diazolin. An alcohol compress is applied to the wound.
Note! In medical practice, several cases of death after a gadfly bite have been recorded. Death occurred due to the development of anaphylactic shock. Therefore, if there is difficulty breathing, loss of coordination and loss of consciousness, the victim must be urgently taken to the hospital.
What ointments should I use?
Local treatment with ointments will help relieve all symptoms of a gadfly bite. For severe allergic edema, glucocorticoid drugs are prescribed: Cortisol, Celiderm, Prednisolone. The pain calms down after applying Advantan, Sinaflan, Baneocin. For children, healing agents are used: Bepanten or Fenistil. Redness, irritation and itching are treated with Psilobalm, Rescuer.
When should you go to the doctor?
Young children, people with insect allergies, and those who have been attacked multiple times will need medical attention. A particularly dangerous condition is when generalized edema begins, hyperemia of the eyelids, lips, and scalp appears. Also, if possible, it is worth taking the gadfly to the laboratory, where they will determine whether it is a carrier of a serious infection. If the result is positive, antibacterial or antiviral therapy should be started immediately.
Gadfly bite marks
You can recognize a gadfly bite by the characteristic mark that it leaves. This is a small dot, a puncture of the skin. Around it there is almost always redness, slight swelling of the skin, swelling, and severe itching. However, there are cases when swelling does not develop.
Usually, after treatment has been carried out, the mark disappears completely and no scars remain. In any case, you need to visit a doctor who will examine the bite and make a diagnosis. In this case, differential diagnosis can play an important role, which is based on the need to differentiate the signs of different bites that have approximately the same external manifestations. In addition to a visual inspection, additional laboratory and instrumental studies may be required.
Complex therapy is mainly used, which includes both systemic drugs and local ointments and creams against itching, swelling, and inflammation. Apply special creams, ointments, gels, which can be bought ready-made at the pharmacy, or prepared at home yourself, using an available recipe. In order to quickly relieve swelling, diphenhydramine is used (0.025 - 0.05 mg orally). There are also a large number of combination drugs, which include various non-steroidal drugs, such as aspirin.
Skin rashes in the area of the gadfly bite
A characteristic feature of a gadfly bite is redness and swelling. Skin rashes can develop in a person who is prone to dermatological diseases. But this is rarely observed and usually occurs some time after the bite, about 5-10 days. A gadfly bite can provoke an exacerbation of existing skin diseases.
Swelling and redness after a gadfly bite
Redness develops immediately after a gadfly bite. But a tumor can develop after 5-14 days, and this is usually an unfavorable sign. This may indicate that the bite site has become infected and an inflammatory process is developing,[5] or that larvae have entered the body.[6] In both cases, immediate qualified assistance is required. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. You need to see a doctor as soon as possible. If possible, see an infectious disease specialist, parasitologist or bacteriologist. If there are no such doctors in the clinic, a therapist will be enough, he will give the necessary referral to the necessary specialist. Perhaps a surgeon will help, or a consultation at a specialized infectious diseases hospital will be required.
Itching at the site of the gadfly bite
There is nothing surprising or unnatural about the fact that a gadfly's bite itches. This is a completely natural reaction, since an allergic reaction develops after a bite. A large number of antibodies, histamine, can cause itching and other symptoms that develop mainly locally.
Treatment is to prevent the development of an inflammatory, infectious process and severe allergies. If the bites itch, then first of all, you need to drink an antiallergic drug, and also anoint them with a special anti-itch agent.
The main antiallergic agent is suprastin. It is taken 1 tablet 2-3 times a day. Suprastin has one significant drawback - it can cause drowsiness and a slow reaction. Anti-inflammatory ointments, as well as ointments against itching and allergies, also help well against bites. Steroid and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. The following ointments work well: diclofenac, ibuprofen, indomethacin, naproxen.
Swelling from a gadfly bite
A botfly bite can cause swelling, and this happens in most cases. Most often, complex treatment is prescribed, which includes both drug treatment and local remedies. The bite site is treated with an antiallergic and anti-inflammatory agent, or a special antiseptic. An excellent addition to standard therapy are compresses, lotions, baths and complex therapeutic baths, and ingestion of stimulating balms.
Bruise from a gadfly bite
Bruising is a fairly rare occurrence. A gadfly bite often causes swelling, redness, pain, and burning. A bruise (hematoma) may be the result of pinching or damage to a small blood vessel, a capillary, in which hemorrhage occurs under the skin. Also, a similar reaction occurs with severe swelling from which the vessel suffers. It is necessary to take measures aimed at eliminating the swelling and removing the hematoma. Usually bruises appear 3-4 days after the bite, not earlier. Baths, compresses, lotions using various medicinal decoctions and infusions help well. You can take immunostimulating agents orally.
Temperature from a gadfly bite
An increase in temperature from a gadfly bite indicates that a systemic reaction is developing in the body, in which the inflammatory and infectious process affects not only the site of the bite. There is a generalization of the reaction throughout the entire body. Complex treatment and mandatory consultation with a specialist are required. The danger also lies in the fact that infection may occur, or the development of a parasitic disease (larvae have gotten under the skin)
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the location of the gadfly larva on the body. Usually found on the arms, legs, back, scalp. Other areas reported are:
- brain;
- eyelids;
- language;
- nose;
- genitals;
- buttocks.
Approximately 24 hours after infection, a small (2-3 mm) papule forms, resembling an insect bite. It will gradually increase to 10-35 mm and will be approximately 5-10 mm in height, surrounded by an area of compaction. A breathing hole is visible in the center of the lesion.
As the larva develops, the wound becomes itchy and causes discharge that can be serous, serous-bloody, or purulent. Secondary bacterial infection is rare.
Often a person feels pain (acute feeling). This is the result of the larva tearing off tissue as it feeds and the spine irritating the tissue as it moves. Usually there are no systemic signs and symptoms, but sometimes there is malaise, lethargy, and insomnia.
In some cases, people feel the parasites moving when they shower or cover a wound. The human body reacts with an increased number of white cells, and a large number of macrophages are found around the wound. For this reason, pus often comes out of the wound.
Most injuries occur when the larvae exit a person through the skin.
The most dangerous are some of the nose flies. The adults deposit live larvae in the nostrils of the host (usually a sheep). These nasal parasites eat through the tissue in the sinuses, and the associated infections can be fatal. This is an extremely rare occurrence in humans. (Handbook of Medical Entomology, Entomology and Human Health 1979).
Treatment
After being bitten by a parasitic fly, the victim should be given first aid. If there is no car with a first aid kit nearby, you will have to do without disinfectant solutions and antispasmodics. If there is free access to pharmacological drugs, recovery can be significantly accelerated.
Recipes from traditional healers
Many folk remedies for gadfly bites are right under your feet. Medicinal herbs have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiseptic properties. This is exactly what is necessary to provide first aid for any insect bites. The most effective ways to prevent infection include the following folk remedies:
- Plantain leaves. The young plant must be crushed to a thick paste and applied to the bite site, and after the product has dried, the procedure should be repeated. Plantain contains biologically active substances that reduce the severity of pain and prevent the development of edema;
- Dandelion leaves. Fresh leaves need to be mashed a little, applied to the bite site and secured with a bandage. Dandelion exhibits antiseptic and anti-inflammatory activity and is able to stop the spread of infection.
You can do without medicinal plants. What to do if you are bitten by a gadfly and there is no medicine at hand:
- dilute a teaspoon of soda in a glass of water, soak a bandage in the solution and apply to the site of the gadfly bite;
- treat the damaged area of skin with sour cream or freshly squeezed tomato juice;
- place ice in a plastic bag, wrap it in a thick cloth and apply to the bite area for 10 minutes.
A compress of grated fresh potatoes effectively eliminates swelling of all layers of the epidermis. You can lubricate the bite site with low-fat sour cream, kefir, and valerian tincture.
“Warning: It is inappropriate and even dangerous to try to squeeze out insect saliva. The fly makes such a thin puncture that at best a small drop of blood will appear from the hole. Strong pressure will only accelerate the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into soft tissues.”
Pharmacological drugs
If an insect attacks a person while hiking or gardening, you need to use disinfectant or antiseptic solutions that are in any first aid kit. How to anoint a gadfly or horsefly bite:
- 3% hydrogen peroxide;
- alcohol solution of chlorhexidine bigluconate;
- brilliant green solution;
- alcohol solution of iodine;
- a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Ethyl alcohol, and even regular vodka without additives, will help prevent the spread of infection and reduce the severity of swelling. The victim should definitely be given a tablet of any antihistamine:
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Loratadine;
- Cetrin;
- Zyrtec.
To quickly eliminate the symptoms of general intoxication (chills, fever, pain), you can use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. How to treat a gadfly bite with NSAIDs:
- for adults, take a tablet or capsule of Ibuprofen, Nise, Nimesulide;
- Give the child a teaspoon of syrup or suspension of Ibufen, Nurofen.
If there are no such products in the medicine cabinet, then regular Paracetamol in tablets or syrup will help reduce the temperature and relieve pain.
“Recommendation: If the bite site has festered, is very swollen and red, then you should immediately consult a doctor. He will prescribe drugs with antibacterial activity to destroy pathogenic microorganisms.”
Severe consequences
An attack by a large fly is dangerous not only due to unpleasant sensations, skin damage, allergic reactions, but also terrible diseases. Insects are carriers of many diseases. Animals and humans can become infected with tularemia, filariasis, anthrax, and trypanosomiasis. You can get rid of horse flies using various means and traps.
If, in addition to the symptoms described above, there is a significant deterioration in health, body temperature rises, and the bite site swells, you must seek help from specialists, undergo an examination, and do not self-medicate.
Important!
In most cases, a horsefly bite goes away within a week, and the itching disappears within a few days. What to do if bitten by a horsefly, do not panic. Try to quickly treat the wound with an antiseptic, wipe with any alcohol tincture. Further actions depend on the condition of the skin and the body’s reaction.
Preventive measures
There are a number of precautions you can take to avoid insect bites.
It is especially important to follow these tips if you are allergic to stings:
- Move slowly and don't panic if you encounter wasps, hornets or bees. Don't wave your arms.
- If you are going outside when insects are most active, such as sunrise or sunset, wear long sleeves and pants.
- Avoid walking without shoes outdoors.
- Apply insect repellent to exposed skin.
- Avoid using items with strong odors such as soaps, shampoos and deodorants as they may attract insects.
- Avoid flowering plants, places where food is served or where garbage is stored.
- Avoid resting near ponds and swamps. Dangerous insects are most often found near water.
- Keep doors and windows closed or install fine mesh to prevent insects from entering your home. Also keep your car windows closed.
- Don't break bee evidence. Find a professional to get rid of them.
Prevention of infection by gadfly larva
Mosquito nets on windows are an effective way to keep parasites out of your home. When going for a walk, it is recommended to treat your clothes with one of the following preparations:
- Argus: repellent in spray and spiral form. When treating clothing, the protective effect against gadflies, midges, horse flies and other insects lasts up to 20 days;
- “Picnic”: repellent against gadflies and horse flies; when sprayed on the skin, repels insects for 2-3 hours;
- OZZ: creams, lotions and aerosols with a wide spectrum of action.
Chemical products are good for one-time use, on a picnic, fishing or on a hike. In your summer cottage against the gadfly, it is better to use traditional methods:
- the smell of spruce needles, bird cherry, mint, cloves, basil and tomatoes repels parasitic insects;
- the site area is periodically treated with a solution prepared from ammonia, lemon juice and mint mouthwash;
- You can spray an infusion of herbs on your clothes: mint, wormwood or tansy.
Maintaining personal hygiene, especially after visiting stud farms and farms, significantly reduces the risk of becoming the host of a parasitic fly larva.
Parasitic and blood-sucking flies:
- Tsetse fly: photo.
- Photo of horsefly. common pied
- photo of bullfly
Prevention of attacks
Treatment for a bite lasts about 5-6 days, while the victim suffers from severe itching and pain. Young children, the elderly, or those with allergies are especially sensitive to toxins. Therefore, it is easier to prevent a gadfly attack before going outside. Attack prevention includes:
- You must wear long sleeves;
- It is better to place the picnic away from water, tall grass and thickets;
- the skin should be treated with repellents;
- essential oils of clove, fir, and lavender are applied to the hands and face;
- After swimming in reservoirs, you should thoroughly dry your body and immediately put on clothes.
Note! To protect their home from gadfly attacks, owners of private houses must take all security measures. It is required to regularly mow the grass on the site, install mosquito nets on the windows and pump out the cesspools in a timely manner.
When going outdoors, you need to take a first aid kit with you, which should contain alcohol, cotton wool, a bandage, antihistamines, and Chlorhexidine. Pet owners treat their fur with special sprays that repel insects. On farms and barns where cattle live, it is necessary to lay out brooms of chamomile, tansy, wormwood, and mint.