Guinea pigs are extremely clean animals. But at home, a lot depends on the owner. You need to maintain hygiene, regularly clean the cage and clean the entire apartment. Otherwise, parasites may appear. These include lice eaters, which feed on skin flakes and gland secretions. They live in fur and cause serious discomfort. Lice eaters cause severe itching in guinea pigs and lead to shedding. At the first symptoms, you should immediately take the first measures and contact a veterinarian.
Existence and reproduction of lice eaters
The parasite has a flat body. The maximum size of an adult is 2 mm. On dark pig fur it appears white or yellowish, on white fur it appears grey.
When magnifying the lice eater under a microscope, it was discovered that its fur was covered with bristles. The head is large, angular in shape, with eyes, antennae and a rather large mouth. The lice eater's jaws are powerful and covered with teeth. It moves on 6 paws with claws at the end, which additionally causes irritation on the skin of the affected animal.
Static louse multiply quite quickly. The lice beetle can lay more than 100 eggs at a time. The parasite glues them to the fur with a sebaceous substance that it secretes from its gland. The larva grows within 3 weeks.
What not to treat
| A drug | Indications. Treatment regimen | Notes |
| Drops Lawyer | From endo- and exoparasites, including worms and different types of ticks. Dose - 0.1 ml/1 kg. Take the required amount from the tube with a syringe, remove the needle and drop it onto the skin. Hold the animal in your arms for 10-15 minutes to prevent it from scratching the area where the medicine was applied. Repeat after 14 days | Do not drip onto scratched areas of the skin. |
| Drops of Stronghold | If this is a 6% solution, then calculate the dosage, taking into account that it is 0.1 ml for 1 kg. If 12%, then 0.05 ml | |
| Otodectin injections | 0.2 ml/1 kg. The injection is made in the withers area under the skin. Repeat the procedure after 10 days | If the animal is severely affected, a 4-fold injection is possible |
The results of treatment appear gradually. Full recovery occurs after 3-4 weeks, when all adult ticks and laid larvae are destroyed or immunity is restored so much that the eggs have no opportunity to develop.
Important! Only one drug can be used. The combination threatens intoxication
A repeated cycle of digging and injections is needed in order to destroy those mites that hatched from the deposited larvae. 14 days is their ripening period. The drugs do not affect the larvae because they are protected by the shell.
Choose a remedy for lice for your guinea pig based on reviews or a recommendation from a veterinarian. The following drugs should not be used:
- Ethnomazan;
- Stomazan;
- Butox.
They are well advertised but are used exclusively for the cage and its contents. They can easily harm the animal and even lead to death.
Use only proven methods for treating your guinea pig. Keep it clean and try to prevent the appearance of lice or other parasites.
Signs of parasites
Symptoms in an animal do not appear immediately, but then they are expressed in several forms:
- Itching on the skin. The pig begins to constantly itch and bite itself, trying to gnaw out the lice-eaters, without regulating the strength of the bites on the skin. As a result, wounds and abrasions appear.
- Lack of sleep and appetite. The animal becomes restless and stops eating food in normal quantities. As a result, vitamin deficiency and anemia appear, and immunity decreases.
- Hair loss.
- The animal has a sloppy appearance - the fur does not shine and looks greasy.
- The presence of parasites on the fur. When examining the fur closely, worms 1 mm long are visible.
- The tired appearance of an animal at any time of the day, as the constant struggle exhausts him emotionally.
- An allergic reaction is redness of the skin.
Important! Lice eaters are parasites that carry dangerous diseases such as helminthiasis, fungus, viruses and bacteria.
What symptoms indicate the presence of fleas
For treatment use:
- Shampoo. When bathing, apply to wet fur and rub over the entire body so that it does not get into the eyes and ears. The product must be rinsed off well. When it enters the body, the digestion of animals is disrupted. You need to wash the cage and the area near it with the same shampoo, and change the bedding. The procedure is repeated after 10 days to destroy the larvae. When choosing this method of treatment, one must take into account that pigs are afraid of water and experience stress when bathing.
- Spray. The jet is directed onto the skin against hair growth. Most drugs have an unpleasant odor, so it is better to carry out treatment on the balcony or on the street. The pig should be held in your hands until the spray dries to prevent it from licking the medicine.
- Drops. The dose is drawn into a syringe, the needle is removed, the fur is pulled apart and dripped onto the skin, but not onto the wounds. You need to hold the animal in your hands for about 10-15 minutes until the product is completely absorbed.
- Injections. Subcutaneously into the withers.
Basic rules of treatment:
- at the same time it is necessary to process the hair of all domestic animals;
- every 3 days, disinfect cages and bedding (they must always be dry);
- You cannot use several different drugs at the same time;
- the preparations Neostamazan, Ethnomazan, Stomazan, Butox are not used for pigs (they can only treat surfaces - cages, bedding and other equipment).
The cage must be cleaned every three days.
Used against fleas:
- drops – Advocate, Blokhnet, Stronghold, which can be combined with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs;
- shampoo “Nizoral” and others containing pyrethritol;
- sprays – 8 in 1, Frontline, Bolfo.
Do not exceed the dose - this can lead to poisoning of the pig. It is better to buy special preparations for rodents. When using medications intended for kittens, take 0.1 ml of Advocate or 6 ml of Stronghold per 1 kg of pig's weight.
Use flea drops in conjunction with antimicrobial drugs.
The above sprays and drops are used against ticks in the same way, as well as injection preparations:
- Ivermectin. Per kg of weight, 0.02 ml of the drug is combined with 0.2 ml of saline solution. The product is considered difficult to use, since it is difficult to calculate the dose and measure it, and exceeding it is dangerous for the pig’s brain.
- Otodectin (variation with 0.1% ivermectin) at the rate of 0.2 ml/kg.
Injections are given once every 10 days, 2-4 injections in total (depending on the degree of damage). Ivermectin is applied to inflamed areas of the skin 2-3 times a day. The cage needs to be washed with a solution containing chlorine and the bedding changed.
Often a tick infection is complicated by the appearance of a fungus. It primarily affects the scalp, neck and extremities. It is treated with Chlorhexidine, Lamizine, etc.
We make injections into the animal's withers.
Help against lice and lice:
- sprays Bars, Celandine, Bolfo, Dana, Akaramectin;
- Ivermectin injections (if there are a lot of parasites);
- Advantix drops, Frontline, Advocate.
The least toxic are pyrethrin-based preparations, such as 8 in 1 sprays and Beaphar. They can be used to treat pregnant and lactating females and cubs weighing up to 500 g.
Sprays against lice and fleas destroy only adult individuals, but not nits.
Seek help from a veterinarian
Not really
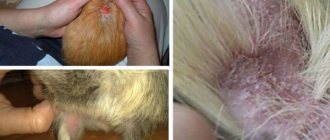
Symptoms in guinea pigs indicating the presence of lice eaters are as follows:
- Itching is the main sign of the presence of pests in your pet's fur. The animal is constantly itching, it constantly bites its fur, trying to gnaw out the parasite. Subsequently, abrasions, wounds and crusts appear on the surface of the skin.
- The rodent becomes very restless, it loses appetite and sleep, which can lead to a decrease in immunity, the development of anemia and vitamin deficiency.
- Swarming lice eaters and their eggs can be seen with the naked eye if you part the pet’s fur.
Lice eaters in guinea pigs
Reasons for appearance
Static lice are transmitted through direct animal contact. Parasites also settle in sawdust and hay, which are added to the cage when cleaning. They may also appear in food packaging that has not been hermetically sealed.
The maximum risk of infection occurs during the cold season (late autumn and winter), when the animal’s fur becomes thicker and the undercoat grows more actively.
To prevent infection, you need to clean the cage more often and use proven bedding materials.
Preventive actions
To prevent infection with ectoparasites, pigs need proper care and maintenance, the nature and characteristics of which are as follows:
- periodic examination of all pets;
- treating all items they use with insecticides;
- disinfection of feed purchased in bulk (it is kept in the freezer for 1 day);
- maintaining personal hygiene before interacting with a rodent.
Pets that are taken for walks should wear tick collars in the spring and summer. During this period, parasites are especially active. Some of them are carriers of the meningoencephalitis virus, which is dangerous for animals and people.
The weakened immunity of the pig can become the basis for the appearance of subcutaneous mites and fungal diseases. An unhealthy animal with poor appetite becomes depleted quickly when attacked by parasites.
To improve health, vitamin complexes (C, B1, B2, A, E, folic acid), drugs with anti-inflammatory, antitoxic and immunostimulating effects are prescribed - Sporovit, Katozal, Gamavit, etc.
If your pig develops itching and anxiety, it is best to contact a veterinarian or rodentologist (a specialist in small exotic mammals) and undergo treatment under medical supervision.
Infection with lice beetles in humans
Experts' opinions on this matter are divided. Some scientists, as a result of research, have found that the parasite can settle on any hair surface of animals and humans.
When parasites appear, a person experiences irritation, itching, and bald areas of the scalp appear. Treatment method: anti-lice medications.
Other scientists are confident that the owner of the pig cannot become infected for the following reasons:
- Insufficient hair thickness.
- Body temperature is too low. To exist and reproduce, lice eaters need a body temperature, like that of animals, not lower than 37.4-39.3.
- If it gets on the skin, the parasite will bite, but will not be able to live long and will die after 7 days, leaving no offspring. However, an infected animal should not come into contact with children and the elderly. Their immunity is weak and interaction can lead to dermatitis.
Group of ectoparasites
This type includes skin types of parasites. The most common are skin lice, fleas and lice. The first symptoms of a pet infection include redness and itching of the skin, as well as hair loss in areas where microorganisms accumulate. It is this type of parasite that causes diseases that cause exhaustion, purulent ulcers, and in advanced cases, death. Moreover, the latter scenario can occur not only due to the animal’s lack of appetite, but also due to less obvious signs such as general blood poisoning. The fact is that toxic substances enter the blood through abrasions and microcracks formed by scratching the affected areas by the animal itself.
Methods of treatment and prevention of diseases
Today, means of treatment and protection against lice eaters are presented in a wide range. For ease of use, they are available in several forms:
- spray;
- drops;
- emulsion;
- shampoo;
- powder;
- collar.
Sprays are prepared based on biocidal elements. The simplest method of application is to spray the skin of the pig and spread it over the hair using massaging movements. At the initial stage of the disease, one application is sufficient. The drugs Blokhnet, Dana, Bars, and Inspector have proven themselves well.
The drops have the same base as sprays and are designed to get rid of ticks and lice. It is enough to apply a few drops on the spine in the area of the animal’s withers, where it cannot reach. Today, the effectiveness of this form is recognized as the simplest and most effective, because it provides a long-term preventive effect.
Emulsions are diluted with water or injection solution, since they are produced in concentrated form. The solution is used to treat wool. Recommended: Stop Itching, Atop 7+.
Shampoo is the safest way. A properly selected shampoo can prevent the appearance of lice by creating a protective barrier on the animal's fur. A sick animal cannot be cured by washing it with shampoo the first time. Use Phytoelite, Dana, Frontline and Bars. Their action, consistency and consumption are identical.
Collars quickly get rid of lice and protect your pet for a long time. The disadvantage of this form is a possible allergy of the pig to the components, which will be expressed in the form of skin irritation.
The powder is very fine and has a powder-like consistency. Advantages: relief from itching and irritation of the skin in a short period of time. It is enough to rub it into the skin once to maintain the effect for 1.5 weeks.
After treating the animal, you need to treat its cage or enclosure, as well as all the objects it uses. This is done with a solution of special preparations.
Rules for caring for a pig
When cleaning the cage and bathing the animal, periodically wipe toys and care products with a special solution:
- combs;
- bowls;
- the bottom and walls of the habitat;
- hairpins
Do not give your pig objects that have been used by other animals.
Conduct a visual inspection of the animal constantly, at least once a week.
Under no circumstances should you place untested animals in the cage, which could become carriers of parasites. When buying a new pet, do not immediately put it in a cage with a “keeper”, but after pre-treating it, keep it in quarantine for 7 days.
Insignificant savings and failure to comply with basic hygiene will entail large costs for the treatment and suffering of the animal. Simple rules will make the animal happy and healthy.
Try to change your pet's living conditions and diet. His house should be free and clean. Remember to regularly clean your pet's cage. Even the most comfortable house gets boring over time, so you need to periodically let the animal out to walk around the room and play with it.
Guinea pigs do not like sharp and loud sounds, so it is better to place their home in a quiet corner. There should always be food, useful elements and clean water inside. Make sure that water can flow from the waterer before placing it in the cage.
If a pet is infected with parasites, then this ultimately leads to sad consequences. If you notice that the animal is itching and is acting restless, then you need to start treating it immediately. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a veterinarian. Remember that by providing your pet with favorable living conditions, you reduce the risk of parasite infection.
Infections
Guinea pigs can become infected with fungal, viral, and bacterial infections, such as:
- Plague is a dangerous disease of viral etiology. It is highly contagious and often ends in the death of the rodent. Once initiated, the latency period in most animals is typically a maximum of 21 days. After which symptoms of the disease are observed. The animal becomes lethargic, indifferent to what is happening. He may experience seizures, problems with coordination, and paralysis of his hind legs. Unfortunately, there is no cure for this disease and, if the diagnosis is confirmed, the infected scree is euthanized.
- Pseudotuberculosis is an infectious disease of a bacterial nature that is often diagnosed in guinea pigs. Infection is possible through contaminated food.
The infection often results in the death of the pet, as it occurs in a lightning-fast form
Therefore, it is important to know the symptoms of the disease in order to begin treatment in a timely manner. The main symptom of infection is stomach upset. Mucus and blood can be found in the stool. In addition, the owner may notice loss of appetite in the animal, inflammation of the conjunctiva, enlargement of the mesenteric lymph nodes, and convulsions.
What to do when it appears? It is necessary to show the rodent to a veterinarian as soon as possible. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then antibiotics and sulfonamides are prescribed. Tetracycline can be prescribed for treatment in loading dosage.
Paratyphoid fever is an intestinal infection caused by bacteria and accompanied by signs of gastrointestinal damage, such as persistent diarrhea and bloating. The pig's stool is greenish and has an unpleasant odor. The animal refuses to eat, moves little, and is disheveled. If infection is confirmed, tetracycline and sulfadimizine are prescribed, and anti-typhoid serum is administered. In addition, to reduce the likelihood of re-infection, you should clean up after the rodent more often. Your pet's diet should consist of foods that are quickly digestible. The animal must have constant access to water. Pasteurellosis is a bacterial zoonotic disease that is dangerous to humans. If a guinea pig is sick, it will experience symptoms of respiratory damage: purulent nasal discharge, sneezing, shortness of breath, wheezing. As the infection progresses, indigestion, pustules, redness of the skin, and convulsions occur. The disease often causes the death of a rodent. Young individuals die especially often. If the infection is severe, the animal is destroyed. Treat a sick rodent with antibiotics. When pets have multiple antibiotics, antibiotic therapy is prescribed for all pets, regardless of whether they have symptoms of infection or not. Medicines are given within 7 days from the moment the disease is detected
It is also important to disinfect the room where the rodent is kept. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis is a dangerous viral disease not only for the animal, but also for its owners, which usually ends in the death of the pet. An infected individual exhibits elevated temperature and asthenia. The disease is incurable, so the infected individual is destroyed. Bordetellosis is a disease that affects not only guinea pigs, but also cats, dogs and other rodents. The main measure to prevent infection is vaccination of cats and dogs.
There is also a vaccination against bordetellosis for guinea pigs, but, unfortunately, it is ineffective and only alleviates the course of the disease.
An infected pig may sneeze and have difficulty breathing. She may have a fever, nasal discharge, conjunctivitis, ear inflammation, loss of appetite, and impotence. Often, with such an infection, the pet's head is turned to the side. When a disease is detected, the pet must be treated comprehensively; the animal is prescribed antibiotics and sulfonamides.
Prescribe either Baytril (s.c.) at a dose of 5 mg per kg of body weight for 5 days or gentamicin (i.m.) at a dose of 4-5 mg per kg of body weight. In addition, sulfadimethoxine (25 mg/kg) or sulfatone (15 mg/kg) is given with food. The course of therapy is 5 days. Expectorants are also prescribed and added to the food. You can give your animal cough tablets with thermopsis or pectusin. To normalize breathing, prescribe sulfocamphocaine or caffeine in ampoules. Atropine is prescribed to relieve spasms. For a speedy recovery, it is recommended to give the animal multivitamins.
How to withdraw
To treat parasitic infections external preparations are used ; they are sold in a veterinary pharmacy. When purchasing, pay attention to the label; it should indicate that the product is intended specifically for rodents. Drops and sprays for cats contain a higher concentration of the insecticidal substance and can cause poisoning in guinea pigs.
For treatment the following are used:
- Shampoos;
- Sprays;
- Powders;
- Drops.
Are there allergies to guinea pigs?
Preparations containing pyrethrin are considered the least harmful. These include:
- Spray 8 in 1;
- Flea&Tick;
- Spray Beaphar.
Products based on synthetic pyrethrin analogues are more potent. This:
- Frontline;
- Spray "Bars" for rodents;
- Bolfo.
It is better to treat the rodent outdoors or near an open window, since many preparations have an unpleasant chemical odor.
What exactly should I do? The rules for using insecticides are as follows:
- The medicine should not get on the pet’s face or eyes;
- The skin is treated with a jet of liquid against the growth of the fur;
- After the procedure, the animal should be held in your arms until the hair is completely dry.;
- At the same time, the wool of all animals living in the house is processed;
- In some cases, disinfection should be repeated after a week to destroy insects hatched from eggs.
Veterinary clinics use injections of the drug Ivermectin. However, the active substance is quite toxic, so it is used only in extreme cases.
Redness of the skin, itching, hair loss may indicate other diseases: allergic dermatosis, neurodermatitis, streptococcal infection, metabolic disorders. Be sure to show your pet to the veterinarian so as not to miss a dangerous pathology.
Ticks
There are two types of mites on guinea pigs - subcutaneous and scabies. Each has characteristic features both in manifestation and in treatment.
The difference between this type of mites lies in the fact that they can cause severe itching of the animal’s skin. The danger for the animal lies in the fact that not only the blood will be infected, but the animal may also die due to stress. The main symptoms of subcutaneous mite infestation include the following:
- skin itching;
- severe hair loss;
- redness and dryness of the skin;
- high temperature, chills;
- refusal to eat completely or partially.
Primary lesions in guinea pigs include the head, back, sides and shoulders. But if you do not pay attention to the problem in time, they can spread throughout the animal’s body, causing even more discomfort. It’s even worse if a pregnant female is infected with parasites. In this case, there is a risk of miscarriages and complications during pregnancy.
Fur type mite
The difference from the previous species is that it settles, as a rule, on the surface of the skin. Symptoms of infection with the disease in an animal are similar to previous species. Only peeling of the skin is also observed. Refusal of water and restlessness of the animal are typical symptoms of a tick. If the infection is severe, painful ulcers may appear on the skin, and fur will begin to fall out at an increased rate.