Wasps often build a nest under the roof of a house in a summer cottage, in a basement or on a balcony. This causes a lot of inconvenience and is dangerous to health, because a swarm can attack, sting and spoil food. It is difficult to cope with this scourge in the summer; the wasp brotherhood does not sleep and fights back anyone who tries to attack their home. And with the onset of cold weather, the nest becomes empty. To drive away dangerous insects once and for all, you need to figure out where wasps spend the winter and whether they will return to their home after winter. Should an empty nest be destroyed?
Description and features
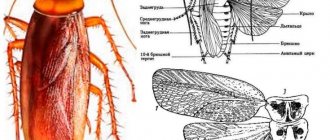
The wasp is brightly colored.
The pattern on her body is an alternation of black areas with yellow stripes on the body, as well as a pattern of the same color on the head and six legs. Usually the bright color of insects in nature often indicates that this creature is poisonous. Wasps are often the name given to all stinging flying insects belonging to the suborder Stalk-bellied insects, with the exception of bees.
All wasps in the photo look the same, just like in real life, but they may differ in size. They have four transparent wings arranged in pairs. In addition, they have a very powerful mouthparts and faceted eyes, which provide the insect with excellent vision.
Coarse hairs can be observed on their paws, allowing such creatures to grip and hold on to a variety of surfaces.
This insect has two ways of fighting against the enemies that the wasp has in nature: mammals, birds, lizards and others.
First of all, the bright colors themselves provide powerful protection. It frightens the enemy, and hunters of various stripes, hungry for prey, lose their appetite when they look at the wasps. It’s just that their color causes unpleasant associations in many living creatures.
But even if one of the predators foolishly attempts to feast on such an insect, after the first misfire, their desires completely disappear. It's just that the sensations are not very pleasant. Therefore, subsequently, enemies stop making attempts to hunt wasps, having developed a warning reflex in themselves.
But in addition to passive methods of protection, these insects also have active methods. And their poisonous sting helps them in this - an autonomous organ, similar to a dagger blade in appearance and principle of action.
It freely penetrates under the skin of the animal, and also comes out without difficulty, having previously injected its portion of poison. This organ is located at the end of the abdomen, like a bee, because it is an insect very similar to a wasp , also capable of stinging.
But the bites of these two poisonous creatures have a number of differences, primarily for themselves. Unlike bees, who die after using their sharp weapon at least once and leaving it in the enemy’s body, wasps remain alive.
When a wasp stings, it does not leave a sting, unlike a bee.
Moreover, they feel great after a bite and are quite capable of making a new attack. In addition, wasps are endowed with the ability to use not only stings, but powerful jaws when attacking. But, like bees, these insects, sensing the smell of poison released by a fellow insect into the enemy’s body, will certainly enter into battle, collectively attacking the object that caused the alarm.
Externally, these insects are certainly similar, but it is not very difficult to distinguish them even by color. If the wasp is yellow and black, then the stripes on the bee’s body have a slightly different hue, with the addition of orange tones.
Pictured is a wasp and a bee
What to do if bitten by a wasp?
The greatest chance of getting bitten is in mid-summer. Mature individuals feed on sweet fruits and berries, so you can most often encounter a dangerous insect in the garden. Only females inflict painful bites: the sting is an ovipositor modified in the process of evolution. The smooth weapon quickly moves out of the body, having delivered a blow, and just as quickly retracts back. Sometimes she is able to make several attacks until her poison supply is depleted.
Having removed the stinging weapon, the undamaged wasp flies away, unlike a bee, which has serrations on the sting that prevent it from being removed from the victim’s body, which leads to the death of the beneficial insect.
Wasp venom
Paper wasp venom contains:
- neurotoxins that can lead to suffocation, paralysis, and compromise blood pressure;
- hyaluronidase ─ destroys cell membranes, causing redness and itching at the bite site;
- histamine, which provokes an allergic reaction;
- acetylchonine, which affects the manifestation of nerve impulses, causes pain after a bite;
- Phospholipases ─ destroy the walls of blood cells and tissues.
The danger of poison is possible Quincke's edema, which is accompanied by difficulty breathing. Anaphylactic shock caused by a bite, without urgent medical intervention, can be fatal.
Immediately after being bitten you should:
- Rinse the wound thoroughly.
- Disinfect the bite site with peroxide, alcohol, soap or furatsilin.
- Apply a cold compress.
- Take an antihistamine. The product will help relieve swelling, itching, and burning after a bite.
- Lie down and drink plenty of fluids.
Hot tea and sweetened water will help restore strength and neutralize the effect of poison on the body. Swelling from a bite can last from several hours to several days, accompanied by an increase in temperature. The victim must be monitored constantly. At the slightest sign of an allergic reaction, provide emergency medical care. You can neutralize the effect of wasp poison with the juice of parsley, lemon, or dandelion milk.
The victim of such insects needs to promptly cool the bite site with ice or a wet towel. Plantain helps a lot in such cases. Its leaves are first washed, then crumpled and applied to the affected area. Such compresses should be changed from time to time, and then painful redness and swelling usually disappear quickly.
Lifestyle and habitat
Wasps can be found almost everywhere, in almost every corner of the planet, with the exception of areas that are particularly unsuitable for life. They prefer to settle close to humans, because in the immediate vicinity of people and their homes there is always something to eat.
Now it's time to talk more about the social structure inherent in paper wasps. It is these representatives of the diversity of species already described that should be given special attention, because when they talk about wasps, they usually mean wild social wasps. Although this is not entirely correct.
The groups in which these insects gather to live together are close-knit families called colonies. They can have up to 20 thousand members. In such families there is a clearly established social structure and division into castes with a certain range of responsibilities.
The uterus is engaged in breeding offspring. Worker wasps look after the larvae, feed the rest of the family and guard the common home. The queen builds a nest out of a paper-like material.
It is produced naturally by wasps themselves, by grinding wood and mixing the material with their own saliva. Powerful jaws help these creatures build nests.
With these, the queen is capable of finely grinding hard wood. Worker wasps and drones are on average about 18 mm in size, but the queen of these insects is slightly larger. Males and females are approximately the same color, but females have a slightly larger abdomen. Single wasps may not build nests, but use burrows made by other insects and small rodents.
Meaning in nature
Why are wasps needed in nature, what significance do they have in human life? There is a preconception that they cause great harm. It is assumed that the main purpose of this aggressor is to sting a person. If we compare wasps and bees, no one will dispute that the benefits of the latter are invaluable. Their healthy honey is a storehouse of health. Its value outweighs the harm caused by bee stings. Bee venom is known to be beneficial in moderate doses. For example, it is used in the treatment of joint diseases. In all respects, these are very necessary insects.
Wasps are treated very differently. Their presence in the garden causes concern. They irritate with their desire to sit down on drinks and dishes during summer feasts.
In nature, there are two categories of wasps: social and solitary. They are very different in their way of life. Solitary wasps do not build nests and live solitary lives. All adults are capable of producing offspring. Social wasps form families in which only the queen and males reproduce. The rest are infertile female workers. Families can have up to several thousand members. A swarm of wasps lives only for one season. They build their nests in houses, various buildings, on tree trunks and strictly guard them.
In nature, being predators, wasps help regulate the number of other insects. Their main food is flower nectar. To feed the offspring, protein is required, obtained from ripe fruits, honey, meat, and available insects. Therefore, their larvae are fed with flies or pre-chewed caterpillars. Thanks to wasps, you can get rid of pests that cause damage to agriculture. They reduce the number of flies that spread bacterial diseases in the garden with their paws. Not only flies, but also garden aphids, mosquitoes and other insects become the object of hunting. They are able to carry away a bee and feed it to their larvae.
Like bees, wasps pollinate plants, although they do so randomly. Their structure is not designed to collect pollen. They collect food from flowers rather than pollinate. Having gotten dirty with pollen, they involuntarily transfer it to another flower.
Where does the wasp live?
Representatives of wasps are widespread throughout the world. They can easily be found in Belarus, Russia, Ukraine, Europe, Africa, Argentina, Canada, Mexico, Australia, China, Japan. Such animals do not live only in the hot Sahara, the Arctic and the Arabian Peninsula. Wasps prefer a temperate climate and cannot exist in regions that are too hot or too frosty.
Interesting fact: A very dangerous species of wasp lives in Japan and China - the Asian hornet. Its size can reach six centimeters. One bite of such an insect is quite enough to kill a person, especially if he is allergic. According to statistics, up to fifty people die every year from the sting of the Asian hornet in these countries.
Most representatives of wasps live in the Northern Hemisphere. Only a small population can be found in Brazil. These insects choose their habitat according to several criteria: temperate climate, presence of trees, humans. The thing is that the human habitat makes it easier for wasps to get their food. The tree is used for building nests and raising larvae. Some individuals build homes from clay and pebbles. Their nests look very much like small castles.
What kind of homes do wasps have?
An example of a social wasp's nest is the home of hornets, the largest stinging insects of the suborder Stem-bellied. The whole process begins with one uterus. Its task is to create a small ball where nests could be made for several working individuals.
First, the uterus creates one layer, moving from the center to the periphery. Under this layer she makes a leg to which several cells are attached. Eggs are laid in each of them. After this, the queen builds several tiers until new workers appear from previously laid eggs. The more workers appear, the more extensive the wasp’s jaws create a paper ball, and the queen, meanwhile, is engaged in her direct function - reproduction.
In biology, this group includes all insects belonging to the order Hymenoptera and the suborder Stalk-bellied.
The nests of the solitary wasp are very diverse. Thanks to the research of the famous insect behaviorist Jean Henri Fabre, the life of the burrowing ground wasp became known not only to scientists. These predatory wasps inject a paralyzing injection into the nerve center of a large spider, drag the poor thing into a hole, and then lay eggs on it. Soon the larvae emerge from the eggs and begin to eat the spider alive.
The flower wasp builds its cells somewhere in secluded places. Pill wasps (aka pottery wasps) make nests from earth and clay. It looks like a bandoleer for 3-4 rounds, which is hidden in the forest canopy. However, pottery wasps get along well with humans, disguising their cartridge belt on the walls of houses and even inside a person’s home.
Some wasps dig small shelters in plant stems. Finally, there are species that do not burden themselves with any construction work at all. They simply use natural depressions as their humble home.
Can wasp venom be used as a treatment against cancer?
Spain really took the beneficial properties of wasp venom seriously. Just recently, a group of scientists from the Barcelona Institute of Biomedical Research published the results of experiments in which components of wasp venom were used to kill cancer cells.
The idea of using wasp venom in this way is well understood: if its components successfully destroy the walls of ordinary cells, as well as blood cells, then they can also destroy cancer cells. The task was only to force the toxins to selectively act on cells - to destroy cancerous ones, but not to touch healthy ones.
In test tube experiments, scientists were able to “glue” the molecules of the individual components of wasp venom with a special protein that could only connect to the surface of the cancer cell. As a result, such a tandem safely passed by all the healthy cells in the culture and immediately stuck to the cancer cell that came across its path. This was followed by the destruction of the cancer cell membrane and its death.
All these encouraging results are just the beginning of a long journey. The next step is to test a drug made from bee toxin and a special transport protein on mice.
Of course, pure wasp venom cannot be considered a useful cure for cancer. And it would be even more stupid to use wasp stings for this in everyday life: the poison will equally affect both healthy and diseased tissues.
How social wasps overwinter
The usual wasp nest is a summer house, which becomes empty with the onset of cold weather. Where wasps hibernate in winter and how they do it depends on the type of insect. The most common and well-known are social wasps, or as they are also called, paper wasps. Their family practices division into castes, with the fertile female at the head.
The largest number of insects of this species appears in mid-summer, when vegetables and fruits ripen, a stable warm temperature is maintained outside, and there is an abundance of food. However, with the onset of cold weather, around mid-autumn, wasps disappear from their nests and are not active in the wild.
The main question is whether these insects fall asleep or die, where they can go.
Wintering of wasps requires females to search for suitable places and does not provide for the storage of food supplies or the construction of special shelters. Wasps overwinter in nature under rotten stumps, in abandoned hollows, and under the bark of trees. Domestic inhabitants who set up nests under the roof of outbuildings, in attics, on balconies, hide in cracks for the winter.
Will wasps return to a hive under a roof in the spring?
Regardless of where wasps spend the winter, with the onset of warm weather they need a home where they will live, where a new generation will be born and grow. Singles find a suitable place and arrange their home themselves. The queen begins to build a house for the future colony. At first, the nest consists of only a few cells where the queen lays her eggs. But gradually the nest grows, and when the first generation of worker bees grows up, the construction process accelerates significantly.
There is an opinion that wasps never return to old nests, but most often build new ones in familiar and familiar territory - in the same barn, on the veranda or under the roof of the house. However, many of those who live outside the city are ready to argue with this statement, claiming that they have more than once noticed how insects return to their former homes in the spring.
Variety of species
The wasps that are familiar to most of us and have yellow and black stripes on their bodies are called paper wasps. This species name is due to the fact that the material from which insects build their homes is very similar to paper. It is made from wood fibers chewed by arthropods, which are glued together with saliva.
Other types of wasps have different colors. The size of the insect depends on its species. They range from 1.5 cm to 10 cm. What do wasps eat? The adult eats mainly liquid food - nectar, fruit juice. For their larvae, wasps get: flies and other insects. Predatory wasps themselves eat insects, and can also feed on other types of food.
The wasp catches its prey and injects its poison into it through its sting, which does not kill, but only paralyzes. Thus, the meat of the prey is kept fresh until the time of the meal.
Different types of wasps live almost everywhere. For example, ground wasps choose soil to build their “homes”. Paper wasps build their “family nest” under a tree branch or on any structure. It should be noted that wasps are very willing to settle near people. This proximity makes it much easier for them to find food. The wasp eats sweets and other foods left in a visible place in a person’s home. But also, it catches pests there such as flies, which carry various infections and thereby brings benefits. In the garden, wasps can find not only flies and ants, but also a huge number of insects that are pests. Wasps love honey very much and therefore pose a threat to bees.
The queen is the largest individual of the paper wasp family. The length of its body is approximately 20 millimeters, while the body length of a working wasp or drone is about 18 millimeters. Females have a larger abdomen than males. Insects do not differ in body color by gender. Males and females have the same yellow and black striped color.
Reproduction
The future queen builds a honeycomb, in the cells of which she lays eggs. After a few days, carnivorous larvae appear, demanding meat food. During this period, the female is actively engaged in the destruction of tree pests; they serve as food for the growing larvae. The first wasps are sterile females and will assist the queen in caring for the next generation and building the nest.
In August and September, young queens and males will appear ready to mate for reproduction. After fertilization of females, most males die. Old queens that have lost the ability to lay eggs will not survive the second winter. They will die along with the workers. Among the many species of paper wasps, there are females whose life cycle is 2-4 years. They enter a state of winter sleep several times.
Information. What do wasps eat in winter? Before the onset of cold weather, females try to accumulate more nutrients in the body. After entering diapause, they become so passive that they survive the winter due to accumulated substances.
Birth and nest construction
Wasps are not noticeable in winter and early spring, but with the onset of stable warmth, the first scouts fly out. These are future queens who, since last autumn, have been storing in their bodies the sperm of the males who fertilized them. Insects look for the first flowers to feed on nectar. The young female will have to fulfill the main function of her life - to give birth to a new family. She finds a suitable place and begins building a nest. The material is chewed tree bark, generously moistened with saliva. After drying, the substance becomes like thick paper.
What do they eat in summer
The diet and feeding habits of larvae and adults differ significantly. Thinking about what wasps eat, you might think that they are omnivores, but this is a mistaken opinion. There are quite a lot of things that wasps eat and will never touch. Moreover, they are quite picky when it comes to nutrition.
The most constant food for insects is fruit and berry juice, which ripens during the period of their activity. Such nutrition is the main source of energy. In addition, wasps love the insides of berries and are able to leave behind only the skin. This applies to plums, raspberries, strawberries, blackberries and grapes.
Representatives’ favorite products are also:
- Sugar;
- Honey products;
- Fruit varieties of jam;
- Sweet syrups.
In turn, the larvae feed exclusively on protein tissues, that is, other insects. Suitable for feeding and development of future offspring:
- Slug;
- Butterfly;
- Spider;
- Caterpillar;
- Cockroach;
- Bedbugs and other insects.
Important! If there are hives with bee families nearby, there is a danger of the striped workers being destroyed by predators.
Main distinguishing feature
The life of a wasp depends on whether it is a social or solitary individual. Already from the name it becomes clear that the former live in families, and the latter – separately. This division exists in all numerous insect species. Each single individual has the opportunity to reproduce. In the family, only the uterus continues the family line.
Solitary wasps prefer not to live in large groups. They mate and then lead a solitary life. Paper single females build their nest. In each cell, in addition to the laid egg, the female places a supply of food for the impoverished larva. These are small insects and spiders paralyzed by poison. Having filled the cell, the female seals it.
The larva eats the supplies prepared by the caring mother and develops inside the cell. When it reaches maturity, it gets out of the nest on its own. Young insects fly away in search of a place to build their own “home”.
Summer-autumn period
Experts say that it is the food that the larva eats that determines who will emerge from it - a working disembodied individual, either a female or a male. The queen lays eggs only at the end of summer, from which insects capable of reproduction will hatch. They are fed food that promotes the development of reproductive organs.
What does it consist of? This can be chewed pieces of leaves and other plant foods, as well as “meat” in the form of various insects. In particular, flies, beetles, spiders, etc. The wasp larva does not leave the cell until it becomes an adult. Having reached maturity, the insects swarm and mate with each other. Thus, the life cycle begins anew.
Aggressive insect
The peculiarity of the structure of the ridge allows the head to move very well. The mouthparts of an insect are of the gnawing type. It is designed to grind food and wood fibers used in the construction of honeycombs. Stripes have a serrated sting, which does not have a knot at the end, but the serrations are smaller than those of a bee.
Only females have a sting. After all, in essence, it is an ovipositor, through which, if danger arises, the “minke whale” can also spray poison. But wasps are quite aggressive and prefer to attack first. Females quite often use the sting for purposes other than its intended purpose.
Nature dictates that the bright yellow-black color makes the insect very noticeable and thereby warns other animals that its owner is poisonous. The minke whale stings and bites its opponent. Although the bites are less painful than the venom released by the stinger.
It should be borne in mind that minke whales attack at the slightest disturbance - this demonstrates how dangerous they are to their enemies. When biting, it does not leave a sting in the body of its “victim”, as bees do. Therefore, insects do not die after being stung. They may repeat the attack again.
It is very important to know that the venom of the striped insect has a smell. If one wasp stung and another was nearby, it will smell the poison and fly to the aid of its “relative.”
It is especially dangerous to disturb a formidable arthropod near its home. Then the whole family can attack. It’s not for nothing that there is a saying “to stir up a hornet’s nest,” which implies major troubles.
Wasp eye model
Scientists have managed to construct an optical device that replicates the abilities of a wasp's eye. This is a 280 degree viewing system. Experts plan to install the unique device on aircraft, military equipment, and robots for various purposes.
The design is at the stage of improvement. Experts plan to replicate the exact model of a wasp's eye. Insects have 3 photoreceptors - near ultraviolet, blue, green, allowing them to see at relatively long distances. The wasp quickly detects movement thanks to the flickering light.
Causes of wasps
Wasps in the house can appear for various reasons, among which it is worth highlighting the most important:
- They can be lured by various foods - meat, fish, fruits, sweet foods;
- A warm and comfortable place to locate your nest;
- Nesting for the purpose of overwintering. These insects often fly to private homes in the fall to spend the winter. Everyone knows that insects die in severe frosts;
- They can get into the house by accident. Often these creatures enter the house accidentally, for example, in search of food or water. If one wasp flies into it, then soon a whole swarm will live there.
Knowing these reasons will help make the process of controlling these insects easier. It is enough to simply create conditions in which these creatures will not be able to live.
Do wasps die in winter?
In autumn, when the air temperature steadily drops, wasps gradually begin to disappear. They no longer circle over sweet fruits hanging on trees or fly into houses. The thing is that most of the adult individuals die with the onset of cold weather, and the remaining ones hide in secluded corners until spring.
To understand why this happens, we need to take a closer look at the process of wasp reproduction. All summer the queen reproduces sterile worker wasps. And only at the end of summer do males and females capable of fertilization begin to appear. They actively mate, after which the males, whose main task is completed, die.
The same fate awaits worker wasps, who live for about 1.5–2 months and fall asleep when the temperature drops below the critical mark of +10⁰С, and die with the arrival of real cold weather. The queen leaves the nest in the fall, like other insects, and also dies with the onset of cold weather.
As a result, only fertilized females remain for the winter. They hide in secluded places, fall into suspended animation and sleep until spring.
When do wasps wake up?
Wasps hibernate for quite a long time. They are not awakened by the thaw and the rays of the spring sun. In order to wake up, insects require certain environmental conditions. First of all, it is the air temperature. Wasps begin to wake up only after the thermometer rises above +10…+12⁰С. When the air warms up to +15⁰C, insects begin to live in their normal rhythm.
So the exact timing of when wasps will emerge from their winter hiding places varies depending on their region and weather conditions. But it’s not immediately possible to see wasps in the spring, because at first there are very few of them and everyone is very busy building a house for the new season.
Preparing for winter
In the fall, they scatter around the surrounding area and after that they no longer show their former activity and become much more vulnerable, sleepy and inactive. The fate of each individual individual develops differently. Some of them simply live out their lives as summer ends. After that they freeze.
If we are talking about fertile and fairly young females, then they usually mate at the very end of August, and then simply sleep in a secluded corner. This is necessary in order to continue life after the onset of spring (with the onset of heat). At the end of the season, the males die, as well as the working females and the old queen. It also happens that fertile females are born only at the very end of the season.
Another circumstance that has a strong impact on the situation with these insects is the slowdown of metabolic processes in the body of the uterus. After this, preparations for wintering begin. The body temperature of these insects begins to drop to a minimum level, which will help cope with freezing on too cold winter days. Wasps in winter are able to withstand even the harshest conditions if they manage to find a secluded place.
Lifestyle
The rules for the existence of hornets in nature are very similar to those of bees and ants.
In order to survive during the cold winter and give birth to offspring every year, insects have to sacrifice someone and something. They sacrifice males, who die soon after mating. This way resources are not wasted on already “useless” individuals. After all, in the hornet family, the females are the main ones. Therefore, they must prepare well for hibernation, survive it, and in the spring become the founder of a new colony. The uterus needs a large amount of protein to produce eggs and develop ovaries. In order to successfully overwinter, it eats very richly and accumulates a fat body.
Mating Features
The greatest activity in the hornet family is observed at the end of the warm period of the year, namely the end of August and the beginning of September. By this period, individuals of both sexes become adults. They all leave their home, swarm and mate. Thus, mating occurs before the onset of cold weather. Female hornets spend the winter pregnant.
Males die soon after mating. Females lead a solitary lifestyle. They feed heavily, and between meals they fly around the nearby territory in search of a safe place for winter shelter. Overwintering of a pregnant female hornet, which falls into suspended animation, is possible only in a secluded place where enemies and cold winds will not find her.
Wintering conditions
Crevices in rocks, tree hollows, shelters under stones and fallen trunks, and small cavities on the outside of unheated buildings or houses are well suited for this. There is no need to be afraid that the female will hide inside a human house. There's a good reason for this. When cold weather sets in, when the air temperature drops below 0C, all water freezes.
But the water in the hornets does not freeze. This is due to the fact that in the body of insects, water is replaced by glycerol. It does not freeze, but it slows down all life processes. This way, the glycerin cannot turn into ice and rupture the insect cells. If the hornet warms up prematurely, it will die during the next cold snap.
When the female hides for the winter in a heated human house, the warm air temperature will contribute to her premature awakening and the natural need to build a nest. If she manages to hide in a house from human eyes, then it will be very difficult for her to look for material to build the honeycomb of her “house”.
When she manages to build a nest, she will not be able to find enough food in the house to feed her offspring. Thus, she will doom him to certain death. Therefore, female hornets do not choose heated human houses for wintering.
A lot of female hornets die during harsh winters with little snow, as well as in the presence of winter thaws. If the female does not manage to hide well, she will become prey to various birds or small predators. Therefore, a significant number of hornets do not survive until spring.
Spring chores
The female hornet wakes up when the air temperature warms up to +15C. Young pregnant insects that wake up begin to actively hunt so that the embryos can develop into full-fledged eggs. In addition, the young female is looking for a suitable place to build her nest.
Help with a bite.
Old females also wake up, but they do not look for a place to build a nest. They scatter around the surrounding area. When the first cold days arrive, they stop their activity and freeze. As a rule, they die before they reach their second wintering. After a nest site has been found, the young female builds the first comb and lays her eggs there.
Only worker hornets emerge from the first eggs. The female must raise them. Then they take the baton into their own hands. Working individuals independently complete the nest and feed the larvae from later eggs. Already from these larvae males and females will grow. They will begin a new cycle in August. The lifespan of worker insects is only three to four weeks.
If you meet a hornet in early spring, it is most likely a pregnant female busy with procreation. She doesn't specifically touch people, but she's not afraid of them either. The female is not dangerous to you. She has no time to threaten anyone, because she has many more important things to do. Don't touch her. Let her reproduce her offspring.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
To get rid of insects, our readers recommend the Pest-Reject repeller
. The operation of the device is based on the technology of electromagnetic pulses and ultrasonic waves! Absolutely safe, environmentally friendly product for humans and pets. Read more here...
Where do they winter?
The most common version is that after the wasps leave the nest with the onset of cold weather, they look for a place where they can overwinter. But there is another one - insects are looking for a place to winter not in the fall, but starting from the end of summer. In any case, the shelter in which the wasp will spend the winter must maintain a constant temperature and be as closed as possible from wind and frost. That is why in the fall, wasps sometimes actively climb into a house, barn, or bathhouse, hiding in cracks and crevices.
Most often in nature, wasps spend the winter in places such as:
- tree bark (insects gnaw holes in it or get into existing cracks);
- in old rotten stumps;
- in rotten fallen trees;
- in a heap of fallen leaves.
Wasps moisten the walls of their winter shelter with saliva. Thanks to the enzymes it contains, the wood becomes denser and better protects the female until the weather warms up and she can fly again.
Wintering process
Wasps live in winter in places hidden from human eyes. In most cases, in wood. They can hide and sleep under the bark, in old stumps, abandoned hollows, and crevices. Snowy winters contribute to successful wintering. The thaw has an unfavorable effect when the ice cover melts, the cracks become open to wind and frost. Unfavorable weather conditions, as well as natural enemies, prevent insects from overwintering.
In the wild, insects become victims of birds and animals. Bears deliberately tear open old hollows and eat prey before the insects can get out in the spring. Whether or not wasps sleep in winter is a controversial issue. This is a unique condition, as a result of which activity is lost, metabolic processes slow down, and nutrition as such stops. Wasps become inactive during the winter and save energy. With the onset of warmth, they awaken and continue normal life activities.
Wintering places
In the summer, wasps can be found almost everywhere in nature. Before the fruits ripen, these insects actively eat pests. Their numbers are usually small. However, as the fruits ripen, the number of insects increases.
The first young wasps are sterile females. They help the queen care for the new generation and build a nest. At the end of summer - beginning of autumn, young queens and males mate. With the arrival of cold weather, the nests quickly become empty: most of the male and working individuals die.
And young females choose places that are completely hidden from human eyes as their winter “dwelling.” In most cases, this is the thickness of wood, old stumps and cracks in outbuildings or houses.
Enemies
Wasps are killed ahead of time by insecticides used by humans to combat various agricultural and forest pests, directly against wasp families. Among the main enemies of common wasps are hornets, as well as some species of birds. In autumn, inactive insects are eaten by animals, spiders, and large beetles.
The lifespan of the wasp family also depends on weather conditions. Nests and hives are destroyed by floods, forest fires, and premature frosts. A wasp can live genetically for a long time, but in practice the lifespan is shortened several times.
There are a huge number of wasp species in the world, which differ in lifestyle, behavior and appearance. They can be divided into two groups, which determine the main characteristics - social and solitary wasps. These insects have become a familiar environment during the warm season. They can be annoying and often aggressive, which is why people find such a neighborhood unpleasant. How long wasps live depends on their position in the family hierarchy. Working individuals die quickly, but queens live longer.
Fighting wasps in the autumn-winter period
Prepare your sleigh in the summer, and start fighting wasps in the winter. Just because wasps have left their nests for the winter doesn't mean they won't return in the spring. Therefore, certain work must be carried out while there is no one in the nests, or rather, as soon as the temperature outside the window drops to 9 - 10 degrees. This makes the task much easier.
First of all, it is necessary to carefully examine their possible wintering places - attics, sheds, all dark and dry corners. Look into every crevice where wasps could possibly live. If boards and other things are piled up on the site “just in case,” they should be moved to another place or rearranged. If wasps were hiding there, then if they were left without a roof over their heads, they would quickly die.
If you find a nest or something similar to it, remove it carefully and destroy it. The place where you found the remains of a wasp nest must be watered with something with a strong and pungent odor. Kerosene, for example, or dichlorvos. These measures will lead to the fact that next year the wasps will look for other nesting places. In addition, before snow falls, it is necessary to collect and burn fallen leaves, if possible, remove dry branches and trees from the area, or peel off the bark from them. Thus, we will significantly reduce the number of places where wasps can hide for the winter. The right owner will not forget to replenish supplies of insecticides. In winter, they are needed much less and, accordingly, their price is lower. Whether to collect plastic bottles for traps or not is something everyone will decide for themselves. Considering that almost all liquids are sold in such bottles, it is not advisable to collect and store them all winter.
Sources
- https://givnost.ru/osa-nasekomoe-opisanie-osobennosti-obraz-zhizni-i-sreda-obitaniya-osy/
- https://klopkan.ru/osy/kak-razmnozhayutsya-osy-zhiznennyy-tsikl-skolko-zhivut/
- https://dr-dez.ru/muhi/gde-zimuyut-osy-zhivushchie-pod-kryshej.html
- https://klopkan.ru/osy/gde-zimuyut-osy-esli-osenyu-ih-gnezda-pusteyut/
- https://WikiParazit.ru/osy-i-pchely/kak-zimuyut-i-chem-pitayutsya-osy.html
- https://queenbee.ru/osy-shershni-i-shmeli/gde-zimuyut-osy
- https://apest.ru/osy/ob-osah/zimuyut-osy/
- https://DomPchel.ru/pchelovodstvo/poleznoe/kak-zimuyut-osy/
[collapse]