Elimination of insects is only part of the disinfestation process aimed at preventing the occurrence and destruction of pathogens of infectious diseases. The whole process consists of measures of chemical, biological and mechanical action of a destructive and preventive nature.
The effectiveness of these activities is determined by clear planning based on preliminary collection and analysis:
- data on places of concentration, reproduction and distribution of pests;
- information about the stages of development and population size at the site;
- level of interaction of the target insect species with humans;
- influence of external factors (environmental conditions and human actions);
- the impact of certain drugs on a specific pest colony and its possible resistance to individual components of the substances;
- risks and rate of relapse after treatment with one or another insecticide.
A more detailed list of conditions that the developed disinfestation plan must meet is compiled by specialists for each specific treatment object.
Arthropods in the epidemic process of infectious diseases
The need and effectiveness of disinfestation was substantiated in 1910 by Russian microbiologist Nikolai Gamaleya as part of the fight against a typhoid epidemic. In turn, of the entire order of invertebrates, arthropod insects have proven their direct involvement and greatest influence on the development of epidemic processes. Thus, they were the main object of disinsection, as measures to prevent epidemics of various diseases.
The numerous types of invertebrate insects determine the extreme polarity regarding their interaction with humans - from beneficial to harmful, and even dangerous species. Harm to crop yields and, in general, to the development of agriculture and forestry, turns into a direct danger to humans through the spread of infectious diseases, including in livestock farming.
Their negative impact in specific conditions depends on the characteristics of each arthropod species, which determines a differentiated approach to the use of methods to combat them. Therefore, disinsection can be medical, sanitary, veterinary, agricultural, etc. The level and conditions of interaction between synanthropic insects and humans determine the degree of harm caused, which consists not only of the transmission of infections, but also of disruption of the sanitary and hygienic environment, as well as interference with the normal functioning of people.
For synanthropic arthropods, humans are, first of all, a source of food, which they use in active and passive ways. Some attack directly, like mosquitoes, blood-sucking flies and horseflies, others lie in wait, like bedbugs or ticks. Still others settle either directly on the owner, like a louse or a flea, or in his home, like ants and cockroaches.
According to the method of spreading infections, pests are divided into:
- on specific ones - where pathogenic microorganisms develop or multiply inside the insect (malaria mosquitoes, plague fleas or encephalitis ticks);
- mechanical - the infection is located on the surface of body parts of flies, horse flies, ants or cockroaches.
Thus, mechanical vectors could be considered less dangerous, since the pathogen is viable for only a short period of time. However, some insects are both types of participants in the epidemic process, which eliminates the need for selective disinfestation.
Who organizes and carries out pest control activities in apartment buildings
Owners of premises in an apartment building can independently carry out pest control measures within their apartments.
In houses with a HOA (homeowners' association) form of management, residents at a general meeting decide on the issue of attracting a specialized company to service the common area or transferring the organization of the disinfestation process to a management organization.
As already mentioned, for effective control it is necessary to have certain knowledge and skills in working with harmful and dangerous substances. It is correct to involve a specialized organization.
The management specialist entrusted with the work of organizing pest control work must, before signing the contract, make sure that the company offering pest control services:
- approved drugs are used;
- laboratory control is carried out;
- there are trained personnel;
- developed and implemented organization standards for safety for people and the environment;
- storage and transportation of hazardous substances are organized according to established rules.
Information on licensing of disinsection and sanitary control services can be clarified at the territorial office of the state sanitary and epidemiological service.
Types and methods of disinfestation
Goal setting determines the preventive or destructive nature of the measures, which, accordingly, are called preventive or focal current and final disinfestation. All these types are applicable to medical, veterinary and agricultural fields of activity.
Focal current is the main type of disinsection, aimed at the complete destruction of the causes of the epidemic situation, that is, the pest insects themselves in all stages of development. It is regular and is carried out directly at the source of infection.
The focal final stage is a kind of consolidation of the results of the current processing. This is a one-time event that eliminates the risk of new infectious manifestations at the facility.
Preventive disinfestation is preventive measures that create conditions for the impossibility of the emergence of epidemic foci of the spread of infectious diseases.
The success of any of these types of treatment depends on many factors that are taken into account when developing an action plan, which includes choosing the most appropriate method.
Disinsection methods
The choice of treatment method is based on the characteristics of the pests and the object of invasion. The variety of these features dictates the need to divide into 3 main methods of disinfestation:
- Physical
- Chemical
- Biological.
Method of physical treatment against insects
The concept of physical disinsection includes the use of mechanical devices and heat treatment. Mechanical means include:
- all cleaning options;
- specialized traps;
- window and door screens.
As a rule, pest control by mechanical means is of a preventive nature or as additional measures to total extermination methods.
Heat treatment takes advantage of the biological characteristics of arthropods. The weak resistance of insects to temperature fluctuations allows this parameter to be used to have a negative effect on their body. An increase in temperature to a value beyond the optimum for a particular arthropod species leads to their death.
Temperature effects include:
- open fire - in strictly defined and rather rare cases;
- boiling water – treatment of infested items by boiling;
- heated air – destroys pests in clothes and things placed in a special chamber;
- water vapor - exceeding a temperature of 100 °C ensures the reliable elimination of nits, lice, bedbugs, fleas and other insects in contaminated things.
Chemical disinfestation method
Preparations used for chemical treatment of arthropods contain the main component – an insecticide. Depending on the biological specificity of certain types of insects, the drug contains other substances, for example, acaricides that destroy ticks or repellents that have a repellent effect on insects.
For pests, these are poisons that cause negative processes in the body and, depending on the dosage and some other factors, kill or do not kill. These "other" factors are:
- The correspondence of the chemical composition of the product to the insect body, which determines its complete absorption. For complete dissolution, the poison must correspond to the metabolism, tissue structure and functioning of certain organs of a particular type of arthropod pest.
- The method of administration of the drug, determined by its physical state - solid, liquid or gaseous. These can be granules, bulk fertilizers, gels, water-soluble powders, aerosols and sprays. In professional disinsection, the most effective methods of liquid treatment with finely dispersed irrigation and gaseous disinfestation with hot fog are used.
- Compliance with the time parameters required to ensure the full effect of the toxic effect of the substance. Properly selected components of the drug will interact with the tissues of the insect’s body as quickly as possible.
- Acceptable temperature conditions for the use of drugs. An important detail that affects the action of the drugs themselves and the reaction of certain types of insects to them.
An important feature of most modern chemicals is their prolonged properties, that is, a long residual effect after treatment. Covering surfaces with a continuous film of insecticide has a detrimental effect on the individuals that survived during treatment or the larvae that subsequently hatched.
Contact, intestinal and respiratory are categories of drugs according to the method of their penetration into the insect’s body. Long-acting preparations, as a rule, have a combination of contact and fumigation properties.
Biological disinsection
A relatively new direction in pest control involves the use of biochemical and bacterial substances, the advantages of which are:
- high efficiency in small dosages;
- narrowly targeted action;
- safety for people and animals;
- lack of resistance to drugs in insects.
Exposure to synthetic hormones disrupts important processes in embryonic development, which prevents the appearance of offspring of pests. Biological preparations are most effective when combined with chemical disinfestation.
The implementation of disinfestation activities is regulated by the requirements of SanPiN, approved in 2003, and is controlled by the relevant departments of the Main Sanitary and Epidemiological Service and Rospotrebnadzor.
Preparations for pest control in the apartment
The most popular means, which have repeatedly proven their effectiveness, remain chemical poisons. Modern chemistry does not stop at the achieved results, improving poisons, making them less toxic to humans and more dangerous to pests. Professional parasite control services purchase expensive, potent substances and dilute them in the required proportions. The average person can go to the store and, without prior preparation, choose the appropriate chemical product for themselves, focusing on the labels and names.
Many pest control products are universal and have a detrimental effect on different types of insects. For example, pest control of bedbugs in an apartment can also help get rid of fleas, cockroaches, and body lice. The main drugs that help in the fight against arthropods are described in the table.
Table - Examples of different types of disinfestation agents
| View | Example | Purpose | Application |
| Aerosol | — “Raptor”; — “Combat”; — “Dichlorvos”; - "Clean house"; - "Armol" | Universal | — Sprayed in places where parasites live; - kept for several hours in a completely enclosed room |
| Con; — “Delta Zone”; —Get; — “Xulat Micro”; — “Effective Ultra” | Universal | — Depending on the pest, it is diluted with water to a certain concentration; - pour into a spray bottle and spray around the room; — washed off with water after 7-8 hours | |
| Insecticidal gels and crayons | - "A great warrior"; — “Absolute gel”; — “Adamant”; — “Insectogel”; — “Dohloks”; — “Trap”; - "Titanic"; - "Brownie" | Against crawling insects (disinfestation of cockroaches, ants) | — Applied in lines near the habitat of parasites; - does not wash off for a long time (about 2 months) |
| Powders or dusts | — Tornado; - "Clean house"; - "Phenaxin" | Against crawling and jumping insects | Scattered around the house in different corners |
| Fumigators | — “Raid”; — “Mosquitoll”; — “Fumitox”; — Picnic Family; — "Raptor" | Against flying insects (fighting moths, mosquitoes); | Fumigation is carried out in a closed space due to electrical connection, heating and evaporation of the product |
Even the most expensive and effective remedy has its drawbacks. Most often, the big disadvantage is the strong unpleasant odor of the toxic substance. Some manufacturers try to disguise the product with fragrances, which does not always work. Due to the strong “aroma”, it is recommended to leave the apartment during treatment.
Areas of application of sanitary rules
Disinsection is carried out in accordance with SanPin requirements for these works. These documents are a guide to the preparation and implementation of operations to protect all types of premises, as well as transport, open areas, settlements and adjacent natural areas from all types of harmful insects that threaten the sanitary and epidemiological situation.
The rules are mandatory for legal entities and individuals, as well as organizations of any type of property, whose professional activities are related to pest control operations. Extermination-type procedures involve the destruction of harmful insects, whose biological characteristics allow them to be carriers of infections dangerous to human health. Preparatory, sanitary-technical and hygienic disinsection operations are carried out with the aim of preventing and creating conditions that exclude the appearance of insects that are a threat to sanitary and epidemiological well-being.
Objects of some categories have their own methods of performing operations.
Railway transport - work is carried out in full compliance with the standards and methodological documents defining the requirements of passenger transportation.
Sea and river vessels - disinfestation operations in this category are carried out taking into account these SanPin rules and standards for river or sea types of vessels. For some types, the methodological documentation may be the International Code regulating the transportation of dangerous goods.
The most favorable and acceptable period for carrying out disinsection on seagoing vessels and those intended for inland navigation is when they are parked in ports or docks, due to the absence of people at the facility. Surfaces in the hold are treated with both chemical and physical methods, while cockpits, cabins, catering units or fish processing plants are treated with disinfestation substances acceptable for the treatment of food processing plants and residential areas.
If necessary, in disinsection operations on ships during navigation, preparations and methods are used that are intended for use in household and preventive areas, as well as those used in food industry enterprises. Fumigation methods for disinsection of sea vessels are permissible in compliance with all safety standards, and only in premises where complete sealing can be ensured.
After disinfestation, operation of any type of passenger transport, including automobile, rail or water transport, can be continued only after general cleaning using soap and soda solutions.
Air transport - aircraft disinfestation is carried out either by an airline service that has the appropriate licensing and provides maintenance for the aircraft, or by a separate organization specializing in air transport pest control operations. Activities are carried out during the preparation of the board for flight and during general cleaning. Long-acting drugs are used.
For transit aircraft, disinfestation operations can be carried out if there are pests on board or at the request of a special airport service:
- 20 minutes before passengers are seated in the cabin;
- in the period before taxiing;
- 20 minutes before the plane descends for landing.
Disinsection in such cases is carried out by the crew, using aerosol-type insecticidal substances.
Also, individual organizations can carry out disinsection of aircraft while parked at the airport between flights as part of standard processing. Such operations are carried out in the absence of strangers, in the presence of harmful insects and flies in the aircraft cabin, or at the request of the airport sanitary service.
Preventative treatment
The consequences of the emergence and proliferation of infection carriers are easier to prevent than to waste time and effort on the fight. The primary measure is compliance with sanitary rules and cleaning using special detergents. Preventive work consists of the following:
- places of possible occurrence and spread are identified;
- the most effective method is determined;
- actions are carried out as a result of which a repellent environment is created or factors leading to the appearance of harmful insects are eliminated.
Timely preventive measures significantly reduce the risk of fleas, bedbugs, cockroaches and ticks. If time is lost, measures will have to be taken to destroy them.
Requirements for measures to protect objects from arthropods
To prevent the occurrence of breeding grounds and the spread of harmful insects in buildings, during their design and construction, special measures of engineering, construction, technical and sanitary-hygienic nature are applied. They are designed to provide buildings with standard features of protection against insects.
- autonomous ventilation;
- sealed seams and joints of building structures;
- sealed areas for entry and distribution of electrical wiring and other communication systems;
- non-buried waste collection chambers;
- garbage chutes made of materials that can withstand regular mechanical cleaning.
The following measures are taken to prevent the emergence of foci for the spread of arthropods during the operation of construction sites and transport:
- timely work to restore the tightness of all areas of possible penetration of arthropods;
- regular cleaning and disinfestation in compliance with all requirements and standards;
- lighting in basements, attics and non-residential areas;
- protecting doors, ventilation ducts and windows with appropriate methods - sealing, grilles and nets;
- reliable floor protection;
- maintenance of drainage channels and blind areas;
- maintaining basement underground areas in proper condition.
To prevent the spread of insects throughout the building, you must adhere to the following rules:
- prevent the emergence and expansion of garbage dumps in residential courtyards, in open areas within the boundaries of populated areas, as well as in open natural and park areas directly adjacent to these boundaries;
- formation of water in pits (leads to the emergence of breeding grounds for mosquitoes);
- pollution of economic and landscape reservoirs, swimming pools, fountains;
- accumulation of food waste in underground structures;
- overflow of sewage trucks in underground mines.
Extermination activities
To get rid of insects, regardless of their number, you will have to carry out intensive treatment of an expanded area. This will have to be done to prevent pests from moving to the neighboring area. For destructive purposes they use:
- chemicals - insecticides and poisons that effectively act on a certain type of insect;
- traps - more often used in small rooms;
- installations spraying hot or cold fog, with a temperature level unviable for insects;
- microbiological fumigants that affect the respiratory tract and intestinal insecticides.
Sometimes, complete eradication requires complex measures and repeated processing. It is especially difficult to get rid of insects in large buildings with many rooms.
Production control in organizations specializing in pest control operations
Responsibilities for production control are assigned to an authorized employee of an institution specializing in pest control operations, which requires the following documentation:
- current sanitary rules regulating professional activities;
- certificates and other documentation confirming the compliance of the drugs and methods used by the organization with current legislation, regulations and rules;
- sanitary records for each employee directly working with disinfestation substances;
- completed safety instructions when performing pest control operations must be stored in an accessible place.
Maintaining an acceptable level of concentration of disinfestation substances in the airspace of places that are intended for storage, warehousing and production and are owned by an organization specializing in disinfestation is carried out using laboratory research and tests. This event is held immediately at the beginning of professional activity and annually thereafter. The measures also apply to surrounding areas.
Production control also requires immediate notification of all necessary institutions and authorities in cases of contamination by the organization conducting chemical disinfestation:
- natural environment on the territory;
- soil;
- indoor air in the treated premises;
- in case of poisoning of employees.
Where to complain if no measures are taken to eliminate insects in the house
Often, pest control in an apartment does not bring results due to favorable conditions for their reproduction in basements or non-residential premises of apartment buildings.
In this case, first of all, you need to find out which organization maintains the building and apply there. If measures are not taken, you should contact the territorial Rospotrebnadzor. The Sanitary and Epidemiological Service will definitely look into it and identify those responsible for allowing the spread of infections. The violator will receive an order to eliminate and an unscheduled inspection at the end of the deadline for fulfilling the order.
Another effective way to organize pest control in common areas is to contact the State Housing Inspectorate. Currently, filing a complaint with the Civil Housing Inspectorate is possible using the State Services portal.
One of the indicators of the sanitary condition of an apartment building is the absence of harmful and dangerous insects. Timely and effective pest control measures can increase this indicator to the highest level. A house is considered safe from the point of view of the sanitary and epidemiological situation if there are no insects or prerequisites for their appearance in its premises.
Preparing for disinfestation
Carrying out pest control operations at a facility or on transport can be carried out in two ways:
- By the administration, owner or tenant
- Specialized organizations.
In the first case, all necessary conditions must be present; in the second, an agreement defining the relationship between the organization carrying out pest control and the customer.
Individual disinfestation is permitted in cases where citizens use disinfestation substances and treatment methods approved for domestic use for the treatment of individual residential premises, structures, houses and adjacent areas.
Objects that are infested with foci of infectious diseases or have suitable conditions for their occurrence are subject to mandatory disinsection. Natural habitats of synanthropic arthropods are also treated to prevent the spread of various types of infections.
Before starting disinfestation activities, the owner or administration of the facility must fulfill a number of conditions to ensure the safety of employees and the necessary conditions for the complete and effective implementation of the process. These include:
- appointment of a responsible person from the personnel of the facility being processed;
- troubleshooting floors, staircases, ventilation shafts and lighting systems;
- ensure electrical and vapor safety for workers carrying out pest control;
- eliminate the presence of stray animals and pets at the operation site;
- take measures to prevent cases of domestic or work-related injuries.
The facility must be fully accessible to employees carrying out disinfestation, for which measures are taken to clear cluttered passages, walls, and territory. Passages along walls or between loads must have a width of at least 70 cm. If this is not possible at the appointed time, the period for which this will be done is determined, but not more than 2 months.
Necessary procedures that must be carried out before starting pest control operations:
- wet cleaning of surfaces in all rooms where treatment will be carried out;
- remove food products from the premises;
- Pack dishes and kitchen utensils or cover them with waterproof film;
- ensure the absence of anyone not directly related to the work in the treatment areas during disinfestation operations.
Indoor cleaning in areas after completion of treatment is carried out 12 hours later. Before this, the premises cannot be used for their intended purpose. At the same time, surfaces coated with preparations that have volatile properties can be wiped down 4 hours after completion. Cleaning should be done with intensive ventilation - artificial or natural. The duration of room ventilation is determined by the drugs used.
Cleaning should be done with damp sponges or rags. They also use a vacuum cleaner to remove traces from the floor and other surfaces that will inevitably come into contact - tables, chairs, equipment. Priority is given to places where the drug used can get on food products; these places are washed with a soda-soap solution.
Places where a long-acting chemical, by definition, will not reach food, are removed after the extension period ends. Mattresses, blankets and carpets are cleaned 3 hours after disinfestation with a vacuum cleaner. It is advisable to thoroughly ventilate these accessories outdoors.
Ways to get rid of insects in apartment buildings
The difficulty of combating the spread of insects in apartment buildings is that the size of the pests allows them to migrate from room to room. In addition, there are restrictions on the use of chemicals directly in apartments. It is safer to use them in basements and attics.
In apartments, toxic substances are placed in places inaccessible to pets and without the risk of getting on food. Recently, you can often come across offers to purchase devices for exterminating insects. To avoid wasting money on a useless item, you should first get advice from a pest control specialist.
Carrying out disinfestation
All operations related to the disinfestation of an object consist of several points, including the following procedures:
- preliminary audit to study the sanitary and epidemiological condition of the facility, establishing the presence of pests, determining their type and areas of concentration;
- control studies to record the appearance, presence, development, and recession of the arthropod population at the site;
- choosing a disinfestation technique;
- development of a procedure plan;
- implementation of the plan.
Control studies are carried out 4 times a month for trade and food enterprises, as well as public catering establishments in which outbreaks of pests have been detected. The same control registration activities are carried out 2 times a month for institutions with a special status according to sanitary requirements. These include:
- treatment and prophylactic complexes;
- schools, kindergartens and preschool institutions;
- children's entertainment and recreation areas;
- communal and household institutions;
- zones of trade, food industry, public catering - in which infestation by arthropod pests has not been detected.
The entire range of disinfestation operations should be carried out only by specially trained and trained employees of an enterprise or organization, or by a service specializing in disinfestation. Information about the date and time of the start of disinfestation is communicated in advance to the administration of the facilities where the treatment will be carried out. Facility employees must be notified of safety measures and instructed on the rules for preparing the facility for disinfestation.
When processing in enclosed spaces, air circulation should not be allowed, therefore all natural methods of ventilation should be excluded (windows, doors and other possible sources of air access are closed), and artificial ventilation should be turned off. On the contrary, after maintaining the required time for the method and preparation used after treatment, ventilation should be activated - open all windows and doors for intensive ventilation of the treated area.
Disinfestation in industrial areas must be preceded by the removal of all products from them in order to prevent possible contact with chemicals. Each specific method and drug requires strict adherence to its instructions for use. The difference between professional pest control is qualified employees who are well aware of all the features and specifics of using any drugs and methods.
Classification of drugs by hazard category:
- Hazard group I – individual use by a resident is not allowed, and treatment of residential and domestic areas is also prohibited;
- Hazard group II – not used in treatment and prophylactic complexes, preschool and educational, health and entertainment children's institutions, as well as in public catering establishments;
- III hazard group - there are no clear restrictions on use, in addition to the mandatory precautions that are indicated in the instructions in relation to a specific substance.
Disinsection operations in all children's and educational institutions are organized exclusively on days when there are no children or employees there. The necessary safety measures are identical to those used in the food industry, with one difference - the drug should not get on things that children are in direct contact with, that is, toys, so they should be completely removed from the operation area during processing. Before opening the institution for a full resumption of activity, it is ventilated, surfaces are wet cleaned and traces of substances are wiped off from places of direct contact - tables, door handles, switches, etc.
Fleas, gamas ticks and other similar insects, whose habitat is wild animals, have a special epidemic danger for people. Therefore, disinsection against these pests is carried out at those facilities where they can infect people, as well as in the habitats of their carriers; treatment of basements and attics is especially important. It is better if pest control operations are carried out together with deratization of the places where these animals live.
Mosquitoes are destroyed where they breed and spread - in bodies of water with standing water, areas of populated areas with dense vegetation and in buildings.
The number of synanthropic insects is constantly studied through control testing. Those disinfestation operations will be considered effective after which control testing of the treatment area, building or territory shows a zero percentage.
Unpleasant “neighbors”: who are they and why are they dangerous to humans?
Despite the fact that people moved away from wildlife and moved to cities, they failed to get rid of arthropods. On the contrary, human habitations made it possible for a variety of species to spread and improve. Many insects even received the prefix “home”, since their main habitat is apartments and private houses. Some arthropods can be tolerated by humans, while others must be urgently disposed of.
The destruction of insects is associated not only with people’s personal disgust and painful bites. Many parasites are a source of infections and unsanitary conditions. The table describes in detail what pests can “bring” into a person’s home, and where they like to settle.
Table - Description of harmful arthropods
| Pests | Where do they live? | What are they threatening? |
| flies | — Places with fresh food and food scraps (landfills, compost); — waste places; - sheds, stalls, stables | — They spread intestinal diseases; — are carriers of pathogens of tuberculosis, cholera, anthrax; - some species bite animals and humans |
| Dust mites | — Furniture upholstery; - books; - fleecy surfaces; - bed | — Cause inflammation of the nasal mucosa, allergic reactions; - are one of the causes of bronchitis and asthma; - contribute to the development of dermatitis |
| Cockroaches | — Sewerage and bathroom; — places of food waste; - garbage chute; - basement; - attic | — Carries pathogens of intestinal diseases; — are carriers of helminth eggs; - bite adults and children; - cause allergic reactions |
| Lice | - Closet; - human hair | - They are the cause of pediculosis; - cause itching and allergies |
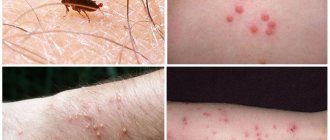
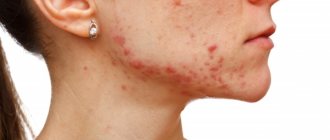
| Fleas | - Skirting board; - furniture upholstery; - carpet; - fur and feathers of domestic animals; - mattress | — Leave painful bites on animals and people; - cause allergies; - when bitten, they transmit pathogens that are fatal to humans; - are carriers of helminth eggs |
| Pharaoh ants | - Basement; - ground floor; - baseboard; - ventilation (they move and penetrate into the apartment) | — Carries pathogenic microorganisms; - spoil food; - create waste places in different corners of the apartment |
| Bedbugs | — Bed; - baseboard; - cracks in the walls | — They bite animals and people painfully; - cause allergic rashes, in rare cases accompanied by headaches, nausea, and fever; - contribute to sleep disorders |
There is no need to panic and pack your bags when you discover harmful arthropods at home. Properly carried out disinfestation will eliminate the problem in an apartment in an average of two weeks. You should start immediately, before the colonies grow to several thousand individuals.
Storage, use and transportation of substances for pest control operations
A separate, specially equipped place should be used for storing disinfestation substances. It excludes the presence of food products and drinking water. In the storage room for disinfestation substances, you must not eat food, drink water, or be present to people not directly involved in the use of these drugs. The place must be equipped with an alarm system and fire safety items.
Particular attention is paid to ventilation of such areas. Only supply and exhaust systems are installed in them. To store small containers, you need to install racks made of metal, and for glass ones, wooden racks. The finishing of walls and floors should be made from materials that do not absorb substances from the air (ceramics, paint, linoleum) and can be easily cleaned with wet cleaning using detergents. Temperature range – from 17 to 20°C.
Household disinfectants should be located in places separate from the storage of food and drinking water, and also be inaccessible to children and pets. It is necessary to transport drugs (except for household ones) in separate vehicles that are specialized for performing such operations.
What is the deratization procedure
Deratization is the process of exterminating rodent pests.
There are two types of deratization:
- preventive – creating unfavorable living and reproduction conditions;
- implying total extermination - the destruction of the entire colony of animals.
Deratization is carried out using one of the following methods:
- biological (hunting by domesticated small predators);
- mechanical (using special traps);
- chemical (using poisons);
- gas (gas spraying in the room);
- ultrasonic (using ultrasonic devices);
Safety precautions for disinfestation
For persons working with pest control products, the law provides for special requirements that all employees of the relevant positions must meet. They must have the necessary qualifications, undergo training and meet regulatory and medical requirements.
Packaging, preparation of working fluids of any consistency, treatment with drugs must be carried out exclusively in a special protective form and using individual protective equipment.
Please note: the duration of direct work with disinfestation substances is no more than 4 hours a day with a 10-minute break every 45-50 minutes in the fresh air without a respirator. After a day, the duration of work can be increased to 6 hours.
Procedure for removing protective clothing:
- before removing protective gloves, they are cleaned in a 5% soda solution and washed in clean running water;
- remove eye protection (mask, visor, goggles);
- removal of protection of respiratory organs and tracts;
- removing foot protection;
- overalls;
- Protective equipment for the eyes and respiratory tract is washed in the same way as gloves.
After finishing working with chemicals, it is better to take a hot shower and rinse your mouth with water.
First aid for insecticide poisoning
The procedure for necessary measures in case of poisoning with disinfestation preparations before medical assistance is provided:
- move the victim from a closed room to an open area or outside;
- remove dirty clothes;
- remove traces of the substance from the skin without rubbing (it is better to use cotton wool);
- treat the affected area with 10% ammonia or soda solution (for organophosphorus preparations it is better to use 5% chloramine B).
If the necessary preparations for treatment are not available, soapy water can be used. If the substance gets into your eyes, you must immediately neutralize their negative effects by rinsing with plenty of running water for 8-10 minutes. If the negative reaction does not go away, you need to drop albucid into your eyes, and novocaine if you experience pain. If the pupils are constricted from an organophosphorus drug or vision impairment is observed, atropine sulfate should be used.
Accidental ingestion of chemicals into the esophagus
If a chemical enters the human digestive system, an intestinal lavage should be performed immediately. Inducing the urge to vomit also helps; for this, the victim is given several cups of warm water or a low-concentrated solution of potassium permanganate (until pinkish) to drink in a row. Repeat several times. All this cannot be done if the victim is unconscious or has convulsive symptoms.
After the drug is removed, rinsing with soda solution should be repeated again. It is also effective to use activated carbon, saline laxative and magnesium.
Cold fog
A special generator under pressure sprays a reagent liquid at a temperature corresponding to the ambient temperature. Due to the relatively large mass of droplets, the vapor remains in the air for about 4 hours, which is slightly less than when it is hot.
The main areas of use are a comprehensive method of disinfestation, small populations of parasites or the prevention of their appearance. The advantages of this option include:
- duration of exposure;
- the ability to process large-scale objects and premises;
- low cost.
The disadvantages of this procedure include the need for preparation (move furniture away from the walls), the penetration of poison only into open areas, and the inability to kill pathogenic organisms in the form of microbes and viruses. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of this procedure has long been proven and is very popular, especially among entrepreneurs who need to efficiently process large areas.